专注 效率 记忆
预习 笔记 复习 做题
欢迎观看我的博客,如有问题交流,欢迎评论区留言,一定尽快回复!(大家可以去看我的专栏,是所有文章的目录)
文章字体风格:
红色文字表示:重难点★✔
蓝色文字表示:思路以及想法★✔
如果大家觉得有帮助的话,感谢大家帮忙
点赞!收藏!转发!
本博客带大家一起学习,我们不图快,只求稳扎稳打。
由于我高三是在家自学的,经验教训告诉我,学习一定要长期积累,并且复习,所以我推出此系列。
只求每天坚持40分钟,一周学5天,复习2天
也就是一周学10道题
50天后我们就可以学完76道题,相信50天后,我们一定可以有扎实的代码基础!我们每天就40分钟,和我一起坚持下去吧!
qq群:866984458
本题出自 acwing网站
这个系列是免费的
打卡即刻退回费用。
第二十一天【剑指Offer例题代码 系列】
- 30. 栈的压入、弹出序列
- 31. 不分行从上往下打印二叉树( 层序遍历二叉树bfs )
- 32. 分行从上往下打印二叉树( 利用两个队列遍历 )
- 33. 之字形打印二叉树
- 34. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 考点:根据二叉搜索树的后序遍历的特点
- 35. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径( dfs回溯 )
- 注意:只能是根节点到叶子节点
30. 栈的压入、弹出序列
原题链接

class Solution {
public:
bool isPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
if(popV.size() != pushV.size())
{
return false;
}
if(pushV.size()==0 && popV.size()==0)
return true;
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 0,j = 0; i < popV.size(); i++)
{
if(popV[j]!=pushV[i])
{
st.push(pushV[i]);
}
else
{
st.push(pushV[i]);
while(st.size() && j < popV.size() && st.top() == popV[j])
{
st.pop();
j++;
}
}
}
if(st.size()==0)
return true;
return false;
}
};
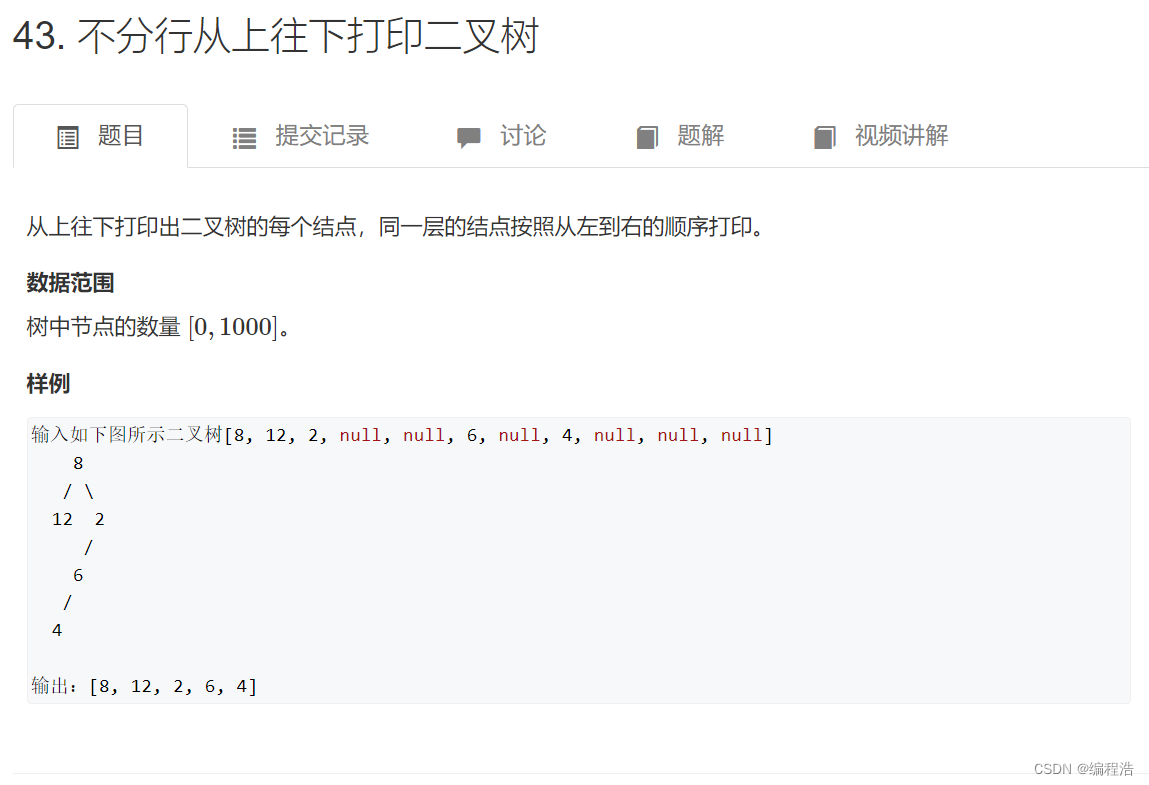
31. 不分行从上往下打印二叉树( 层序遍历二叉树bfs )
原题链接
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
if(root==NULL)
return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left != NULL)
q.push(t->left);
if(t->right != NULL)
q.push(t->right);
}
return ans;
}
};
32. 分行从上往下打印二叉树( 利用两个队列遍历 )
原题链接


/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> get_val(vector<TreeNode*> level)
{
vector<int> res;
for (auto &u : level)
res.push_back(u->val);
return res;
}
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>>res;
if (!root) return res;
vector<TreeNode*>level;
level.push_back(root);
res.push_back(get_val(level));
while (true)
{
vector<TreeNode*> newLevel;
for (auto &u : level)
{
if (u->left) newLevel.push_back(u->left);
if (u->right) newLevel.push_back(u->right);
}
if (newLevel.size())
{
res.push_back(get_val(newLevel));
level = newLevel;
}
else break;
}
return res;
}
};
33. 之字形打印二叉树
原题链接

本题和上一道题差不多
就是需要定义一个变量
判断是否需要翻转
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> get_val(vector<TreeNode*> level)
{
vector<int> res;
for (auto &u : level)
res.push_back(u->val);
return res;
}
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>>res;
if (!root) return res;
vector<TreeNode*>level;
level.push_back(root);
res.push_back(get_val(level));
bool zigzag = true;
while (true)
{
vector<TreeNode*> newLevel;
for (auto &u : level)
{
if (u->left) newLevel.push_back(u->left);
if (u->right) newLevel.push_back(u->right);
}
if (newLevel.size())
{
vector<int>temp = get_val(newLevel);
if (zigzag)
reverse(temp.begin(), temp.end());
res.push_back(temp);
level = newLevel;
}
else break;
zigzag = !zigzag;
}
return res;
}
};
34. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
原题链接

考点:根据二叉搜索树的后序遍历的特点
由于是后序遍历,所以最后一个结点就是根节点,又因为是二叉搜索树,所以从第一个结点开始所有比它小的结点就是它的左子树,其他就是它的右子树。如果右子树有点不大于根节点的话就说明不是一棵二叉搜索树,返回false。最后递归处理左右子树。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> seq;//设成全局变量方便操作
bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
seq = sequence;
return dfs(0, seq.size() - 1);
}
bool dfs(int l, int r)
{
//如果区间内啥也没有就说明把所有的结点都判断完了,却没有一个是有问题的,所以返回true
if (l >= r)
return true;
//取出根节点
int root = seq[r];
//找出所有从l开始连续的比根节点小的结点
int k = l;
while (k < r && seq[k] < root)
k ++;
//这时k就是右子树后序遍历中的第一个结点
//如果不满足二叉搜索树的性质就返回false
for (int i = k; i < r; i ++)
if (seq[i] < root)
return false;
//递归处理左右子树
//y总的视频里的代码是错的
//他写的是return dfs(l, k - 1) && dfs(k + 1, r);
//这样会WA
return dfs(l, k - 1) && dfs(k, r - 1);
}
};
35. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径( dfs回溯 )
注意:只能是根节点到叶子节点
原题链接
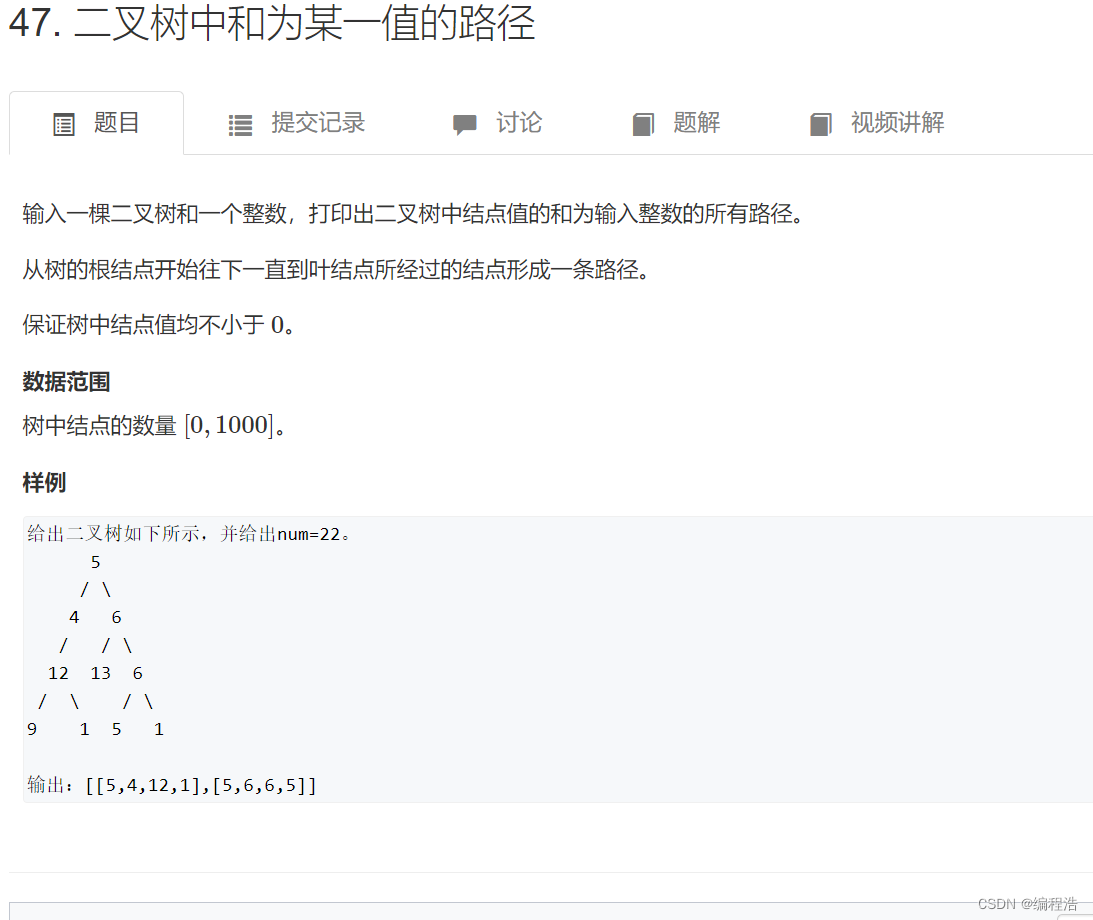
首先补充题意:本题要求的路径是根节点到叶子节点
本题就是一个dfs回溯问题
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<int> sup;
dfs(root,sum,sup);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int sum,vector<int>& sup)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
sum -= root->val;
sup.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && sum == 0)
ans.push_back(sup);
dfs(root->left,sum,sup);
dfs(root->right,sum,sup);
sum += root->val;
sup.pop_back();
}
};

![常用数据聚类算法总结记录与代码实现[K-means/层次聚类/DBSACN/高斯混合模型(GMM)/密度峰值聚类/均值漂移聚类/谱聚类等]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1e5eea9aa6d84f91ba12b4223d5161fc.png)