目录
- 前言
- 1. warpAffine
- 2. warpAffine案例
- 2.1 导言
- 2.2 main函数
- 2.3 warpaffine_to_center_align函数
- 2.4 warp_affine_bilinear函数
- 2.5 warp_affine_bilinear_kernel核函数
- 2.6 AffineMatrix结构体
- 3. 补充知识
- 总结
前言
杜老师推出的 tensorRT从零起步高性能部署 课程,之前有看过一遍,但是没有做笔记,很多东西也忘了。这次重新撸一遍,顺便记记笔记。
本次课程学习精简 CUDA 教程-使用 cuda 核函数加速 warpAffine
课程大纲可看下面的思维导图

1. warpAffine
warpAffine 主要解决图像的缩放和平移,它用来处理目标检测中常见的预处理行为
关于 warpAfiine 你需要知道:
- warpAffine 是对图像做平移缩放旋转变换进行综合统一描述的方法
- 同时也是一个很容易实现的 cuda 并行加速算法
- 在深度学习领域通常需要做预处理,比如 CopyMakeBorder,RGB->BGR,减去均值除以标准差,BGRBGRBGR->BBBGGGRRR
# 正常预处理流程 img = cv2.resize(img) img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img) img = cv2.cvtColor(img, BGR2RGB) img = (img - mean) / std img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1)[None] # 一个warpAffine完成整个预处理 img = warpAffine(img)
- 如果使用 cuda 进行并行加速实现,那么可以对整个预处理都进行统一,并且性能贼好
- 由于 warpAffine 是标准的矩阵映射坐标,并且可逆,所以逆变换就是其变换矩阵的逆矩阵
- 对于缩放和平移的变换矩阵,其有效自由度为 3
2. warpAffine案例
关于 warpAffine 原理和更多细节请查看 YOLOv5推理详解及预处理高性能实现
2.1 导言
神经网络模型的输入一般是固定大小的,比如 640x640,但是我们都知道图片尺寸有大有小,怎么将图片大小转换成网络模型输入的大小呢?在这里可以通过 warpaffine 来实现,warpaffine 的本质是对源图上的每一个像素点进行坐标变换,将源图上的像素点填充到目标图像上即可,而当目标图像通过坐标变换的逆变换即 M − 1 M^{-1} M−1 去源图取值时,可能得出的坐标是非整数,无法进行取值,需要使用插值算法,整个预处理过程如下

2.2 main函数
首先写一个 main 函数,用于实现总体框架,主要通过读取一张图像,经过预处理之后,保存下来,其代码如下
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
#define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b))
#define checkRuntime(op) __check_cuda_runtime((op), #op, __FILE__, __LINE__)
bool __check_cuda_runtime(cudaError_t code, const char* op, const char* file, int line){
if(code != cudaSuccess){
const char* err_name = cudaGetErrorName(code);
const char* err_message = cudaGetErrorString(code);
printf("runtime error %s:%d %s failed. \n code = %s, message = %s\n", file, line, op, err_name, err_message);
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
Mat image = imread("cat.png");
Mat output = warpaffine_to_center_align(image, Size(640, 640));
imwrite("output.png", output);
printf("Done");
return 0;
}
2.3 warpaffine_to_center_align函数
该函数为 host 函数,用于分配内存,调用预处理函数等功能,首先来看该函数要实现的具体功能
-
- 在 CPU 上开辟空间,用于保存预处理完成后的图像
-
- 在 GPU 上开辟空间,将读取的图像数据拷贝到 GPU 上
-
- 调用预处理函数
-
- 将预处理后的图片重新拷贝到 CPU 上进行保存
-
- 释放 CPU 和 GPU 上分配的内存

了解完 warpaffine_to_center_align 函数需要实现的功能之后,其代码就相对容易实现了,代码如下
void warp_affine_bilinear(// 声明
uint8_t* src, int src_line_size, int src_width, int src_height,
uint8_t* dst, int dst_line_size, int dst_width, int dst_height,
uint8_t fill_value
);
Mat warpaffine_to_center_align(Mat image, const Size& size){
// 步骤1 在CPU上开辟空间,用于保存预处理完成后的图像
Mat output(size, CV_8UC3);
// 步骤2 在GPU上开辟空间,将读取的图像数据拷贝到GPU上
uint8_t* psrc_device = nullptr;
uint8_t* pdst_device = nullptr;
size_t src_size = image.cols * image.rows * 3;
size_t dst_size = size.width * size.height * 3;
checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&psrc_device, src_size));
checkRuntime(cudaMalloc(&pdst_device, dst_size));
checkRuntime(cudaMemcpy(psrc_device, image.data, src_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
// 步骤3 调用预处理函数
warp_affine_bilinear(// 调用
psrc_device, image.cols * 3, image.cols, image.rows,
pdst_device, size.width * 3, size.width, size.height,
114
);
// 步骤4 将预处理后的图片重新拷贝到CPU上进行保存
checkRuntime(cudaPeekAtLastError()); // 检查核函数执行是否存在错误
checkRuntime(cudaMemcpy(output.data, pdst_device, dst_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
// 步骤5 释放CPU和GPU上分配的内存
checkRuntime(cudaFree(pdst_device));
checkRuntime(cudaFree(psrc_device));
return output;
}
2.4 warp_affine_bilinear函数
该函数为 host 函数,用于调用核函数,主要有以下几点说明
-
- 首先确定 grid_size 和 block_size 的大小。我们启动的线程数为图像宽*图像高,每个线程处理一个像素(3通道),又由于之前提到过核函数启动时 gird 只是逻辑层,而 SM 才是执行的物理层,且 SM 的基本执行单元是包含 32 个线程的线程束,所以 block 一般设置为 32 的倍数,在这里 block_size 设置为 2-dim 的 block(32, 32),grid_size 可通过 block_size 的大小计算得到。
-
- 定义仿射变化矩阵 M \scriptsize M M
-
- 调用 warp_affine_bilinear_kernel 核函数
代码如下
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <iostream>
void warp_affine_bilinear(// 实现
uint8_t* src, int src_line_size, int src_width, int src_height, // 像素0~255 uint8
uint8_t* dst, int dst_line_size, int dst_width, int dst_height,
uint8_t fill_value
){
// 需要多少threads
dim3 block_size(32, 32);
dim3 grid_size((dst_width + 31) / 32, (dst_height + 31) / 32);
AffineMatrix affine;
affine.compute(Size(src_width, src_height), Size(dst_width, dst_height));
warp_affine_bilinear_kernel<<<grid_size, block_size, 0, nullptr>>>(
src, src_line_size, src_width, src_height,
dst, dst_line_size, dst_width, dst_height,
fill_value, affine
);
}
2.5 warp_affine_bilinear_kernel核函数
核函数的功能主要是实现 warpAffine 和双线性插值即预处理,主要有以下几点说明
-
- 一个 thread 负责一个像素(3通道),所以有全局 Idx 的计算
-
- 已知源图像求目标图像的像素,通过仿射变换逆矩阵
M
−
1
M^{-1}
M−1 可得,即代码中的
affine_project()
- 已知源图像求目标图像的像素,通过仿射变换逆矩阵
M
−
1
M^{-1}
M−1 可得,即代码中的
-
- 之前讨论过,目标图像通过 M − 1 M^{-1} M−1 去取源图像时可能存在超出边界问题,此时填充常量值即可
-
- 对于能取到值的像素,其映射回源图坐标可能是非整数,此时需要插值算法(双线性插值),计算距离最近的四个像素点的加权值作为最终的像素值
-
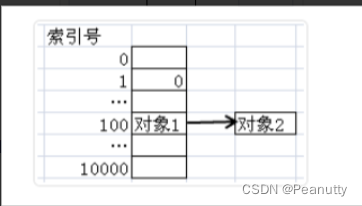
- 已知全局 Idx 索引 (dx,dy),如何确定像素填充的具体位置呢?可看 图2-3,图中是一个 4x4 大小的图片,如果我想要填充 Idx=(1,2) 的像素值,我如何获得其内存地址呢?假设图片起始地址为 src,则有 p s r c = s r c + d y ∗ s r c _ l i n e _ s i z e + d x ∗ 3 psrc = src + dy * src\_line\_size + dx * 3 psrc=src+dy∗src_line_size+dx∗3

代码如下
__device__ void affine_project(float* matrix, int x, int y, float* proj_x, float* proj_y){
// matrix
// m0, m1, m2
// m3, m4, m5
*proj_x = matrix[0] * x + matrix[1] * y + matrix[2];
*proj_y = matrix[3] * x + matrix[4] * y + matrix[5];
}
__global__ void warp_affine_bilinear_kernel(
uint8_t* src, int src_line_size, int src_width, int src_height,
uint8_t* dst, int dst_line_size, int dst_width, int dst_height,
uint8_t fill_value, AffineMatrix matrix
){
// 全局idx的计算,一个thread负责一个像素(3通道)
int dx = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;
int dy = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y;
if(dx >= dst_width || dy >= dst_height) return;
float c0 = fill_value, c1 = fill_value, c2 = fill_value;
float src_x = 0; float src_y = 0;
affine_project(matrix.d2i, dx, dy, &src_x, &src_y); // 由目标图像dx,dy以及M^-1计算源图像坐标src_x,src_y
// 已知src_x,src_y
if(src_x < -1 || src_x >= src_width || src_y < -1 || src_y >= src_height){
// out of range
// src_x < -1时,其高位high_x < 0,超出范围
// src_x >= -1时,其高位high_x >= 0,存在取值
}else{
int y_low = floorf(src_y);
int x_low = floorf(src_x);
int y_high = y_low + 1;
int x_high = x_low + 1;
uint8_t const_values[] = {fill_value, fill_value, fill_value};
float ly = src_y - y_low;
float lx = src_x - x_low;
float hy = 1 - ly;
float hx = 1 - lx;
float w1 = hy * hx, w2 = hy * lx, w3 = ly * hx, w4 = ly * lx;
uint8_t* v1 = const_values;
uint8_t* v2 = const_values;
uint8_t* v3 = const_values;
uint8_t* v4 = const_values;
if(y_low >= 0){
if(x_low >= 0)
v1 = src + y_low * src_line_size + x_low * 3;
if(x_high < src_width)
v2 = src + y_low * src_line_size + x_high * 3;
}
if(y_high < src_height){
if(x_low >= 0)
v3 = src + y_high * src_line_size + x_low * 3;
if(x_high < src_width)
v4 = src + y_high * src_line_size + x_high * 3;
}
c0 = floorf(w1 * v1[0] + w2 * v2[0] + w3 * v3[0] + w4 * v4[0] + 0.5f);
c1 = floorf(w1 * v1[1] + w2 * v2[1] + w3 * v3[1] + w4 * v4[1] + 0.5f);
c2 = floorf(w1 * v1[2] + w2 * v2[2] + w3 * v3[2] + w4 * v4[2] + 0.5f);
}
uint8_t* pdst = dst + dy * dst_line_size + dx * 3;
pdst[0] = c0; pdst[1] = c1; pdst[2] = c2;
}
2.6 AffineMatrix结构体
结构体主要是为了计算仿射变换矩阵 M M M 以及逆矩阵 M − 1 M^{-1} M−1
代码如下
struct Size{
int width = 0, height = 0;
Size() = default;
Size(int w, int h)
:width(w), height(h){}
};
struct AffineMatrix{
float i2d[6]; // image to dst(network), 2x3 matrix ==> M
float d2i[6]; // dst to image, 2x3 matrix ==> M^-1
// 求解M的逆矩阵,由于这个3x3矩阵的第三行是确定的0, 0, 1,因此可以简写如下
void invertAffineTransform(float imat[6], float omat[6]){
float i00 = imat[0]; float i01 = imat[1]; float i02 = imat[2];
float i10 = imat[3]; float i11 = imat[4]; float i12 = imat[5];
// 计算行列式
float D = i00 * i11 - i01 * i10;
D = D != 0 ? 1.0 / D : 0;
// 计算剩余的伴随矩阵除以行列式
float A11 = i11 * D;
float A22 = i00 * D;
float A12 = -i01 * D;
float A21 = -i10 * D;
float b1 = -A11 * i02 - A12 * i12;
float b2 = -A21 * i02 - A22 * i12;
omat[0] = A11; omat[1] = A12; omat[2] = b1;
omat[3] = A21; omat[4] = A22; omat[5] = b2;
}
// 求解M矩阵
void compute(const Size& from, const Size& to){
float scale_x = to.width / (float)from.width;
float scale_y = to.height / (float)from.height;
float scale = min(scale_x, scale_y);
/*
M = [
scale, 0, -scale * from.width * 0.5 + to.width * 0.5
0, scale, -scale * from.height * 0.5 + to.height * 0.5
0, 0, 1
]
*/
/*
- 0.5 的主要原因是使得中心更加对齐,下采样不明显,但是上采样时就比较明显
参考:https://www.iteye.com/blog/handspeaker-1545126
*/
i2d[0] = scale; i2d[1] = 0; i2d[2] =
-scale * from.width * 0.5 + to.width * 0.5 + scale * 0.5 - 0.5;
i2d[3] = 0; i2d[4] = scale; i2d[5] =
-scale * from.height * 0.5 + to.height * 0.5 + scale * 0.5 - 0.5;
invertAffineTransform(i2d, d2i);
}
};
OK!至此 warpAffine 案例代码已完成了简单分析,运行效果如下:


3. 补充知识
关于 warpAffine 的知识点:(from 杜老师)
- 抖音辅助讲解视频合集
- 仿射变换+双线性插值,在 CV 场景下,解决图像预处理是非常合适的
- 例如 Yolo 的 letterbox,实则是边缘填充
- 例如 CenterNet 的居中对齐
- 该代码仿射变换对象是 CV8UC3 的图像,经过简单修改后,可以做到端到端,把结果输入到 tensorRT 中
- 可以直接实现 warpAffine + Normalize + SwapRB
- 参考:https://github.com/shouxieai/tensorRT_Pro/blob/main/src/tensorRT/common/preprocess_kernel.cu
- 这样的话性能会非常好
- 在仿射变换函数里面,我们循环的次数,是 dst.width * dst.height,以 dst 为参照集
- 因此无论 src 多大,dst 固定的话,计算量也是固定的
- 另外核函数里面得到的是 dst.x,dst.y,我们需要获取对应在 src 上的坐标
- 所以需要 src.x,src.y = project(matrix, dst.x, dst.y)
- 因此这里的 project 是 dst-> src 的变换
- AffineMatrix 的 compute 函数计算的是 src->dst 的变换矩阵 i2d
- 所以才需要 invertAffineTransform 得到逆矩阵,即 dst->src,d2i
总结
本次课程学习了使用 cuda 核函数加速 warpAffine,相比上次课难度跨度有点大呀😂。在这次课程可能你需要对目标检测中的预处理有一定了解,同时还需要掌握双线性插值、仿射变换的推导,具体可参考 YOLOv5推理详解及预处理高性能实现
利用 cuda 核函数对 warpAffine 进行加速处理可以实现高性能预处理,同时一些常见的预处理操作比如 BGR->RGB,减均值除标准差都可以一并处理,性能非常好