文章目录
- Q1:6913. 最长交替子序列
- 思路
- 竞赛时代码
- 代码优化
- Q2:6469. 重新放置石块
- 思路
- 竞赛时代码
- Q3:6923. 将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串
- 解法1—— dfs回溯 + 剪枝 + 判断
- 解法2——动态规划
- Q4:6928. 黑格子的数目
- 代码优化
- 成绩记录
https://leetcode.cn/contest/biweekly-contest-108/
Q1:6913. 最长交替子序列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-alternating-subarray/

思路
数据范围很小,只有 100。
可以枚举每个子数组。
实际操作时,可以枚举左边界,判断条件扩展右边界。
竞赛时代码
class Solution {
public int alternatingSubarray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, ans = -1;
// 枚举左端点,尝试扩展右端点
for (int l = 0; l < n; ++l) {
int r = l, t = 1;
while (r + 1 < n && nums[r + 1] - nums[r] == t) {
t *= -1;
r++;
}
// 答案要求长度 > 1
if (r - l + 1 >= 2) ans = Math.max(ans, r - l + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
代码优化
class Solution {
public int alternatingSubarray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, ans = -1;
// 枚举左端点,尝试扩展右端点
for (int l = 0; l < n; ++l) {
int r = l, t = 1;
while (r + 1 < n && nums[r + 1] - nums[r] == t) {
t *= -1;
r++;
}
// 答案要求长度 > 1
if (r - l + 1 >= 2) ans = Math.max(ans, r - l + 1);
l = Math.max(l, r - 1); // 小优化
}
return ans;
}
}
每次更新 l 不一定需要 l = l + 1,而是根据 r 扩展到的位置来更新 l。
即
l
=
M
a
t
h
.
m
a
x
(
l
,
r
−
1
)
;
l = Math.max(l, r - 1);
l=Math.max(l,r−1);

Q2:6469. 重新放置石块
https://leetcode.cn/problems/relocate-marbles/
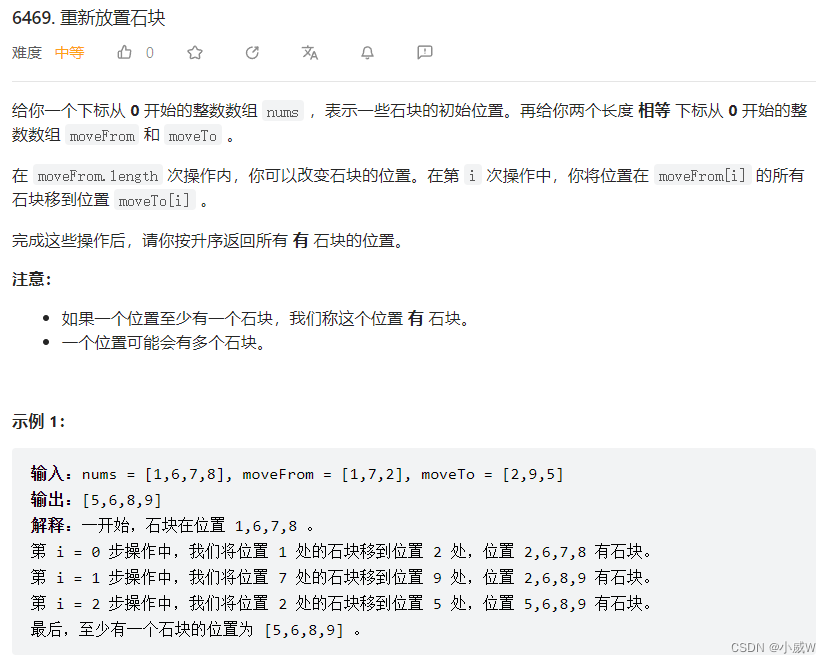
思路
每个位置的石头每次移动会被全部移走,因此每个位置石头的数量无所谓。
使用哈希集合存储石头位置即可。
竞赛时代码
class Solution {
public List<Integer> relocateMarbles(int[] nums, int[] moveFrom, int[] moveTo) {
Set<Integer> s = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toSet());
for (int i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; ++i) { // 移动石头
s.remove(moveFrom[i]);
s.add(moveTo[i]);
}
return s.stream().sorted().toList(); // 返回答案
}
}
Q3:6923. 将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-string-into-minimum-beautiful-substrings/
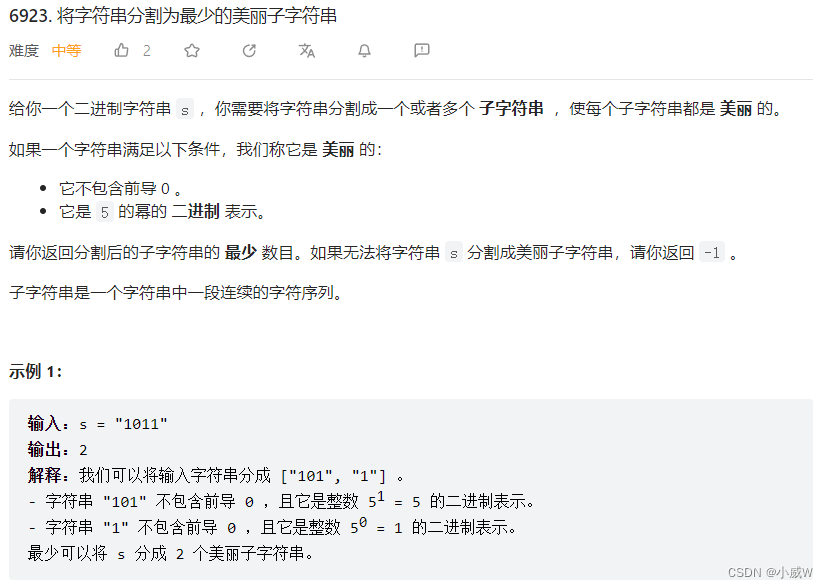
解法1—— dfs回溯 + 剪枝 + 判断
爆搜出每一种分割方式(中间加了剪枝)
检查是否合理并更新答案。
class Solution {
static int ans = 20;
static Set<Long> set = new HashSet(); // 处理出所有5的幂
static {
long v = 1;
while (v < Long.MAX_VALUE / 5) {
set.add(v);
v *= 5;
}
}
public int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(String s) {
ans = 20;
dfs(0, s, 0, 0);
return ans == 20? -1: ans;
}
public static void dfs(int i, String s, int last, int cnt) {
if (last == s.length()) {
ans = Math.min(ans, cnt);
return;
}
if (i >= s.length()) return;
if (s.charAt(last) == '0') return;
// 不选i
dfs(i + 1, s, last, cnt);
String ss = s.substring(last, i + 1);
long v = Long.parseLong(ss, 2);
// 检查能不能选
if (!set.contains(v)) return;
// 选i
dfs(i + 1, s, i + 1, cnt + 1);
}
}
解法2——动态规划
https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-string-into-minimum-beautiful-substrings/solution/on2-ji-yi-hua-sou-suo-dao-di-tui-by-endl-99lb/
在这里插入代码片
Q4:6928. 黑格子的数目
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-black-blocks/
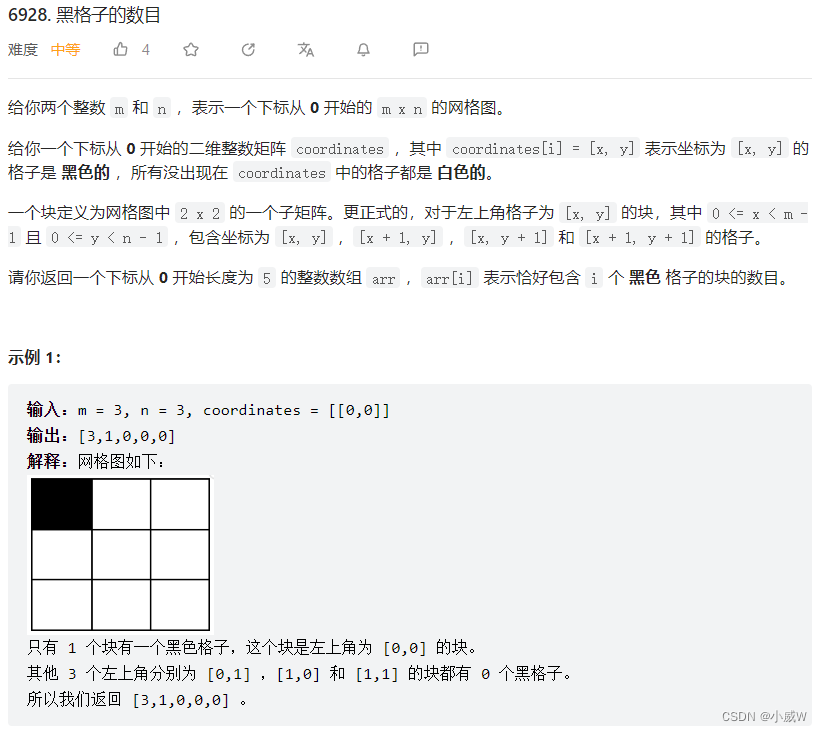
由于数据范围的原因
枚举coordinates,每次会影响周围最多4个2*2区域的内容
因此时间复杂度可以控制在
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
用哈希表存储已有黑点的情况防止空间不够。
class Solution {
int[] dx = {1, 1, -1, -1}, dy = {1, -1, 1, -1};
public long[] countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, int[][] coordinates) {
long[] ans = new long[5];
ans[0] = (long)(m - 1) * (n - 1); // 初始值
Set<String> s = new HashSet();
for (int[] c: coordinates) {
int x = c[0], y = c[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { // 枚举被影响的四个2*2区域
int cnt = 1;
int nx = x + dx[k], ny = y + dy[k];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
if (s.contains(nx + " " + y)) cnt++;
if (s.contains(nx + " " + ny)) cnt++;
if (s.contains(x + " " + ny)) cnt++;
ans[cnt]++;
ans[cnt - 1]--;
}
s.add(x + " " + y);
}
return ans;
}
}
代码优化
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-black-blocks/solution/mei-ju-by-endlesscheng-0mnx/
在这里插入代码片
成绩记录

AK 了就是胜利!(只可惜写错了3次!)
https://lccn.lbao.site/