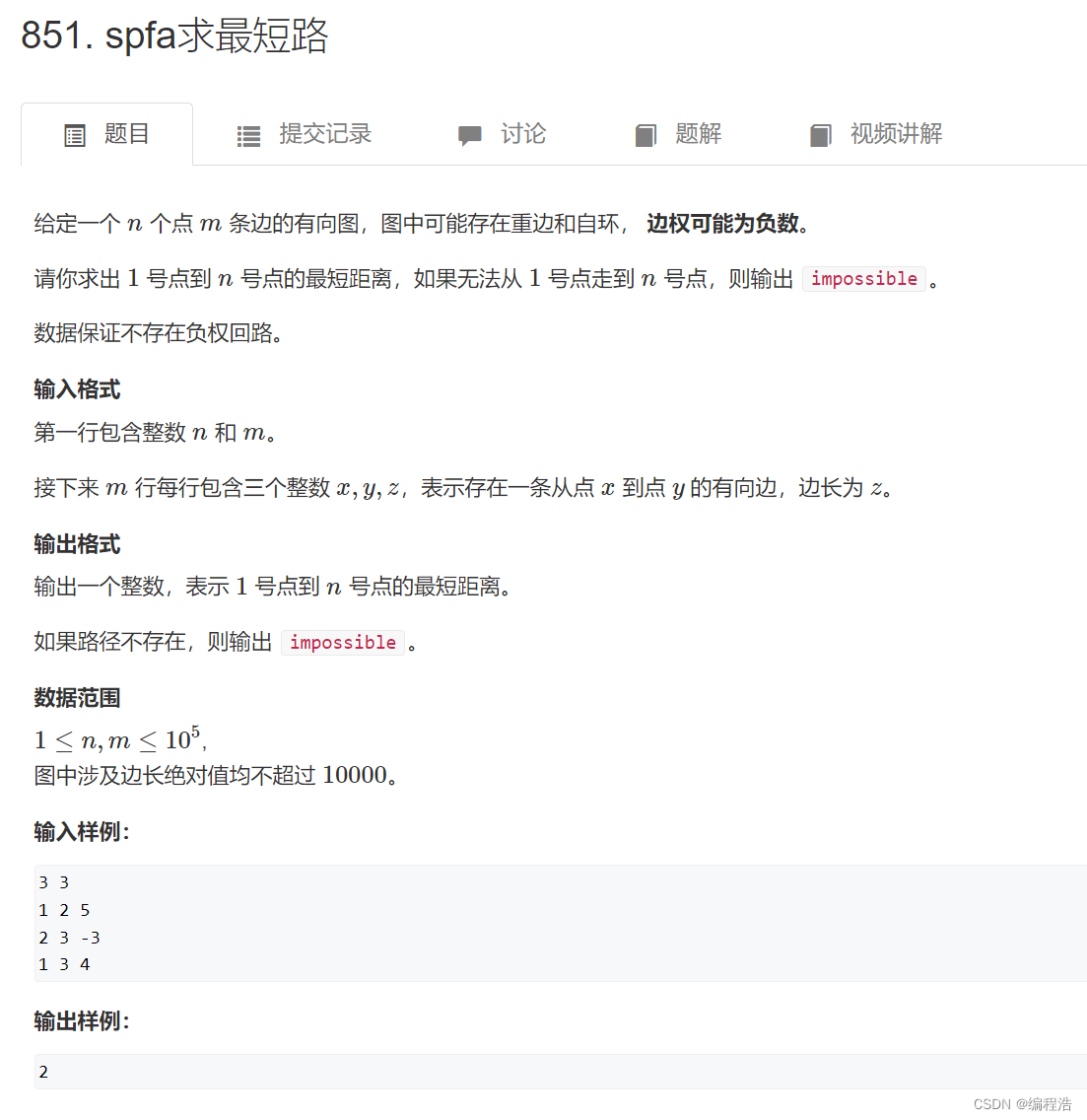
“Hello world”程序
函数原型
1. pthread_create
函数原型:int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
功能说明:创建一个线程。
参数说明
thread:线程句柄,需要先定义一个 pthread_t 类型变量 thread,将该变量的地址 &thread 传递到该参数中去。这是一个传出参数,传递进去的 thread 会得到系统为我们创建好的线程句柄。
attr:attr可以是一个struct的指针,里面包含有所有你需要赋给这个线程的参数,如果attr为NULL,那么使用默认值如果创建成功,函数返回0,否则返回-1,并且返回报错类型
start_routine:线程函数,它是一个函数指针类型,返回类型为 void *,参数为一个 void * 类型变量,创建好这样类型的一个函数,将函数名传递进去即可。
arg:线程参数,代表需要在主线程传递给子线程的参数,给 arg 赋值后可以在线程函数的参数中取到。
返回值说明
成功情况下返回 0,失败情况下返回错误码,并且 tid 的值是不确定的。Linux 环境下所有线程函数调用失败时均是返回错误码,除了部分返回值为 void 的函数。
2.pthread_join
函数原型:int pthread_join(pthread_t thread,void **retval);
功能说明:阻塞等待线程退出,获取线程退出状态,相当于进程中的 waitpid 函数,如果线程退出,pthread_join 立刻返回。
参数说明
thread:代表要等待线程的线程 ID
retval:获取该线程的退出状态
返回值说明
成功情况下返回 0,失败则返回错误码。
如果主线程创建了多个子线程,并希望在所有子线程完成后再继续执行,可以使用pthread_join来等待每个子线程的结束。
编译链接执行
gcc -g -Wall -o pth_hello hello.c -lpthread
./pth_hello 4
./pth_hello 10
4个进程情况
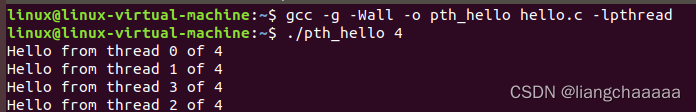
10个进程情况
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int thread_count;
void* Hello(void* rank)
{
long my_rank;
my_rank = (long)rank;
printf("Hello from thread %ld of %d\n",my_rank,thread_count);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
long thread;
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10); //argv[1]为字符串,10位进制数
pthread_t* thread_handles;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count * sizeof(pthread_t));
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Hello,(void*)thread);
//对象地址 对象属性 函数指针 主进程传给子进程的参数
}
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}矩阵向量乘法
上课时提到了pthread_create函数可以传入多个参数,打包成一个结构体指针的写法。尝试了一整天,不把矩阵数值放在global区实现,始终无法得到预期结果,Pthread使用还是不够娴熟,最终只得将共享数据放到全局区实现并行程序。
调了很久没成功的想法如下
struct thread_args{
int rank;//线程号
int n;//列数
int m;//行数
double* A;
double* x;
double* y;
};
pthread_create(&thread_handles[i],NULL,Pth_vect_mult,&arg);实现代码
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int thread_count;//线程数量
int m,n;
double *A ;
double *x ;
double *y ;
void Get_dims();
void Read_matrix(char* prompt);
void Read_vector(char* prompt);
void Print_matrix(char* title);
void Print_vector(char* title);
void *Pth_vect_mult(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
Get_dims();
A = malloc(m*n*sizeof(double));
x = malloc(n*sizeof(double));
y = malloc(m*sizeof(double));
Read_matrix("A");//读入A矩阵
Read_vector("x");//读入x向量
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[i],NULL,Pth_vect_mult,(void*)i);
}
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[i],NULL);
}
Print_vector("y");
free(thread_handles);
free(A);
free(x);
free(y);
return 0;
}
void Get_dims()
{
printf("Please enter the number of rows:\n");
scanf("%d",&m);
printf("Please enter the number of columns:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n<=0 || m<=0){
fprintf(stderr,"m and n must be positive interger\n");
exit(-1);
}
}
void Read_matrix(char* prompt)
{
printf("Please enter matrix %s\n",prompt);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
scanf("%lf",&A[i*n+j]);
}
}
}
void Read_vector(char* prompt)
{
printf("Please enter vector %s\n",prompt);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf",&x[i]);
}
void Print_matrix(char* title)
{
printf("\nThe matrix %s\n",title);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
printf("%lf ",A[i*n+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void Print_vector(char* title)
{
printf("\nThe vector %s\n",title);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
printf("%lf ",y[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void *Pth_vect_mult(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
int i,j;
int local_m = m/thread_count;//按行分配任务
int my_first_row = my_rank*local_m;
int my_last_row = (my_rank+1)*local_m-1;
for(i = my_first_row;i<=my_last_row;i++){
y[i] = 0.0;
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
y[i]+=(A[i*n+j])*(x[j]);
}
}
return NULL;
}
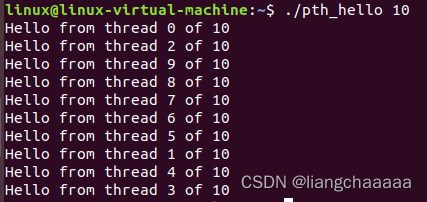
Linux系统下的运行结果
计算π值
原始并行
void *Thread_sum(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
double factor,my_sum = 0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n = n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i = my_rank * my_n;
long long my_last_i = my_first_i + my_n;
if(my_first_i%2==0) factor = 1.0;
else factor = -1.0;
for(i = my_first_i;i<my_last_i;i++,factor=-factor)
sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
return NULL;
}未让临界区互斥访问造成结果误差
忙等待并行
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int thread_count;//线程数量
double sum;
double n;//迭代次数
int flag;
void *Thread_sum(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
printf("输入迭代次数N:\n");
scanf("%lf",&n);
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[i],NULL,Thread_sum,(void*)i);
}
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[i],NULL);
}
printf("pi值为:%lf\n",4.0*sum);
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}
void *Thread_sum(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
double factor,my_sum = 0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n = n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i = my_rank * my_n;
long long my_last_i = my_first_i + my_n;
if(my_first_i%2==0) factor = 1.0;
else factor = -1.0;
for(i = my_first_i;i<my_last_i;i++,factor=-factor)
my_sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
while(flag!=my_rank);
sum += my_sum;
flag = (flag+1)%thread_count;
return NULL;
}
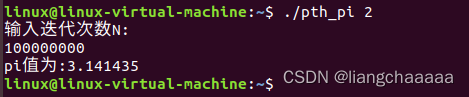
忙等待运行结果,可以明显感觉有一丝停顿,不是立即出结果(没有用严谨的计时函数计算)

互斥锁并行
- 同一线程不应对同一互斥量加锁两次。
- 线程不应对不为自己所拥有的互斥量解锁(亦即,尚未锁定互斥量)。
- 线程不应对一尚未锁定的互斥量做解锁动作。
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int thread_count;//线程数量
double sum;
double n;//迭代次数
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *Thread_sum(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
printf("输入迭代次数N:\n");
scanf("%lf",&n);
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[i],NULL,Thread_sum,(void*)i);
}
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[i],NULL);
}
printf("pi值为:%.15lf\n",4.0*sum);
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}
void *Thread_sum(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
double factor,my_sum = 0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n = n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i = my_rank * my_n;
long long my_last_i = my_first_i + my_n;
if(my_first_i%2==0) factor = 1.0;
else factor = -1.0;
for(i = my_first_i;i<my_last_i;i++,factor=-factor)
my_sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
sum += my_sum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
生产者消费者同步

#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
int thread_count;//线程数量
char **message;
sem_t* semaphores;//信号量集
const int MSG_MAX = 100;//消息最大长度
void *Send_msg(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
long thread;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
semaphores = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(sem_t));
message = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(char*));
// extern int sem_init __P ((sem_t *__sem, int __pshared, unsigned int __value));
// sem为指向信号量结构的一个指针;
// pshared不为0时此信号量在进程间共享,否则只能为当前进程的所有线程共享;
// value给出了信号量的初始值。
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
sem_init(&semaphores[thread],0,0);
//value设为0表示locked
}
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Send_msg,(void*)thread);
}
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
free(message[thread]);
sem_destroy(&semaphores[thread]);
}
free(message);
free(semaphores);
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}
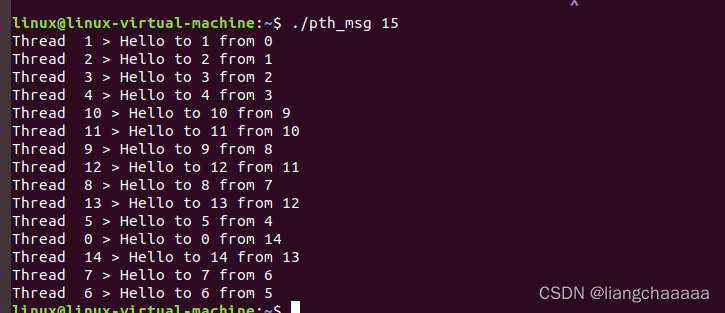
void *Send_msg(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
long dest = (my_rank+1)%thread_count;//当前进程要给dest发送消息
char* my_msg = (char*)malloc(MSG_MAX*sizeof(char));
sprintf(my_msg,"Hello to %ld from %ld",dest,my_rank);//格式化字符串
message[dest] = my_msg;
sem_post(&semaphores[dest]);//给进程dest传输完消息,dest解锁
sem_wait(&semaphores[my_rank]);//阻塞自己,等待消息传输
printf("Thread %ld > %s\n",my_rank,message[my_rank]);//展示收到的消息
return NULL;
}
路障和条件变量
路障:使所有线程到达程序中同一个位置后,再继续执行。
timer.h
/* File: timer.h
*
* Purpose: Define a macro that returns the number of seconds that
* have elapsed since some point in the past. The timer
* should return times with microsecond accuracy.
*
* Note: The argument passed to the GET_TIME macro should be
* a double, *not* a pointer to a double.
*
* Example:
* #include "timer.h"
* . . .
* double start, finish, elapsed;
* . . .
* GET_TIME(start);
* . . .
* Code to be timed
* . . .
* GET_TIME(finish);
* elapsed = finish - start;
* printf("The code to be timed took %e seconds\n", elapsed);
*
* IPP: Section 3.6.1 (pp. 121 and ff.) and Section 6.1.2 (pp. 273 and ff.)
*/
#ifndef _TIMER_H_
#define _TIMER_H_
#include <sys/time.h>
/* The argument now should be a double (not a pointer to a double) */
#define GET_TIME(now) { \
struct timeval t; \
gettimeofday(&t, NULL); \
now = t.tv_sec + t.tv_usec/1000000.0; \
}
#endif
time.c
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
#include "timer.h"
int thread_count;//线程数量
int barrier_count;//障碍数量
int counter;//计算运行完的线程数
sem_t counter_sem;//专门维护counter
sem_t *barrier_sems;//每个路障需要一个共享变量,不能重复使用
void *Thread_work(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
barrier_count = strtol(argv[2],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
double start,finish;//开始结束时间
long thread;
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
barrier_sems = malloc(barrier_count*sizeof(sem_t));
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
sem_init(&barrier_sems[thread],0,0);
//默认所有线程刚开始还没到障碍点,初始化为0
}
sem_init(&counter_sem,0,1);//默认有一个资源可以给线程申请使用
GET_TIME(start);
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Thread_work,(void*)thread);
}
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
GET_TIME(finish);
printf("Elapsed time = %e seconds\n", finish - start);
for(thread = 0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
sem_destroy(&barrier_sems[thread]);
}
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}
/*有多少个路障就有多少个“对齐”点
*每到一个“对齐”点必须等所有线程
*到达才可接着运行程序*/
void *Thread_work(void* rank)
{
long my_rank = (long)rank;
int i,j;
for(int i=0;i<barrier_count;i++){
sem_wait(&counter_sem);
if(counter == thread_count-1){
counter = 0;
for(j=0;j<barrier_count;j++)
sem_post(&barrier_sems[j]);
sem_post(&counter_sem);
}else{
counter++;
sem_post(&counter_sem);
sem_post(&barrier_sems[i]);
}
}
return NULL;
}
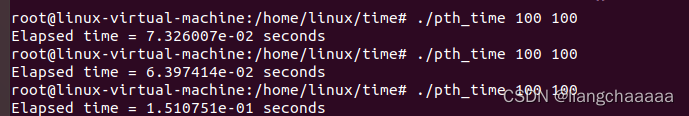
1000个线程 1000个障碍运行结果
gcc -g -Wall -o pth_time time.c -\pthread
./pth_time 1000 1000

条件变量
条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:
一个线程等待"条件变量的条件成立"而挂起(不用忙等待空转);
另一线程使"条件成立"(给出条件成立信号)。
为了防止竞争,条件变量的使用总是和一个互斥锁结合在一起。
1.条件变量类型:pthread_cond_t
2.解锁一个阻塞线程:int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t * cond_var_p /*in/out*/);
3.解锁所有阻塞线程:int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t * cond_var_p /*in/out*/);
4.阻塞线程线程在满足特定条件之前进入等待状态,并在条件满足后被唤醒继续执行
cond:指向条件变量的指针。mutex:指向互斥锁的指针,用于保护对条件变量的访问。int pthread_cond_wait(
pthread_cond_t * cond_var_p /* in/out */,
pthread_mutex_t * mutex_p /* in/out */);5条件变量实际做的:加锁--等待条件成立--解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_p);
wait_on_signal(&cond_var_p);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_p);
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
#include "timer.h"
int thread_count;//线程数量
int barrier_count;//障碍数量
int counter;//计算运行完的线程数
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond_var;
void *Thread_work(void* rank);
int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
{
thread_count = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
barrier_count = strtol(argv[2],NULL,10);
pthread_t* thread_handles;
double start,finish;//开始结束时间
thread_handles = malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond_var,NULL);
GET_TIME(start);
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Thread_work,(void*)thread);
}
for(int thread=0;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
GET_TIME(finish);
printf("Elapsed time = %e seconds\n", finish - start);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_var);
free(thread_handles);
return 0;
}
/*有多少个路障就有多少个“对齐”点
*每到一个“对齐”点必须等所有线程
*到达才可接着运行程序*/
void *Thread_work(void* rank)
{
for(int i=0;i<barrier_count;i++){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
counter++;
if(counter == thread_count){
counter = 0;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_var);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}else{
while(pthread_cond_wait(&cond_var,&mutex)!=0);
//cond_var条件变量 mutex保护条件变量的锁
//这里的条件指所有线程都到达了障碍
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
return NULL;
}
100个线程+100障碍三次结果

![火车头小发猫AI伪原创[php源码]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6b0790b51d7f4bf192da2d3e2ff6f57a.png)