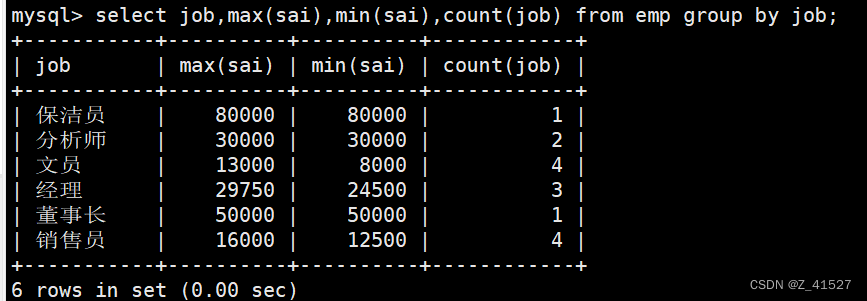
Android中的Handler是一个用于处理消息和线程间通信的机制。它可以将Runnable对象或Message对象发送到特定的线程中进行处理。
使用Handler的主要目的是在不同的线程之间进行通信,特别是在后台线程中执行一些任务后,将结果发送到UI线程进行更新。
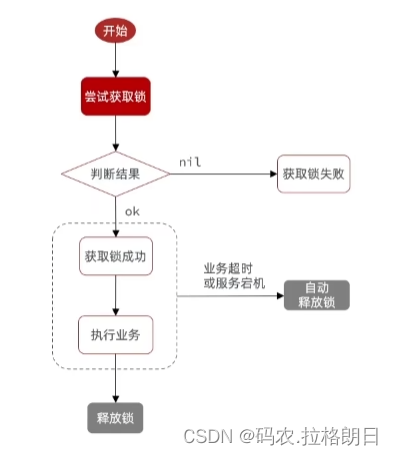
流程图:
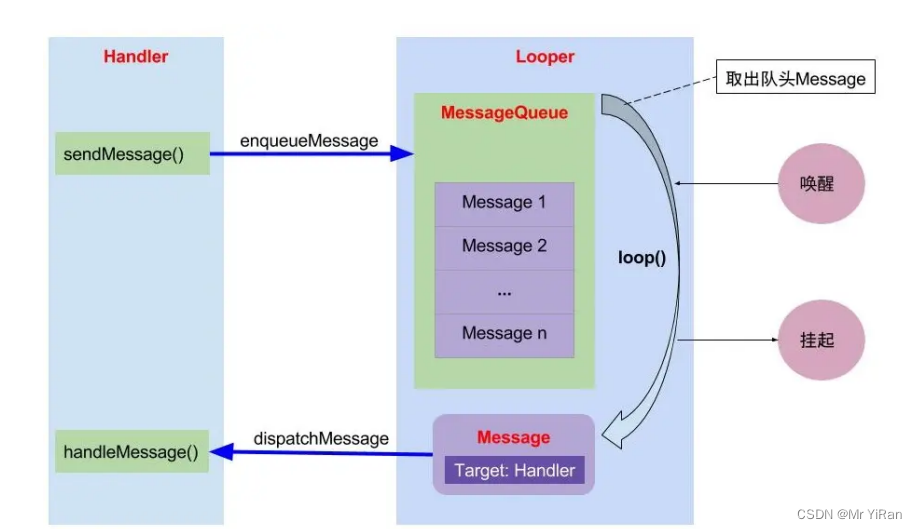
下面是一个示例代码,演示如何创建Message对象并发送给Handler:
// 创建一个Handler对象
Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// 在UI线程中处理接收到的消息
switch (msg.what) {
case 1:
// 处理消息类型为1的情况
String messageText = (String) msg.obj;
// 执行相应的操作
break;
case 2:
// 处理消息类型为2的情况
// 执行相应的操作
break;
// 可以根据需要处理其他消息类型
}
}
};
// 在其他线程中创建并发送Message对象
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 创建一个Message对象
Message message = handler.obtainMessage();
// 设置消息类型
message.what = 1;
// 设置消息内容
message.obj = "Hello, Handler!";
// 发送消息给Handler所关联的线程
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
});
// 启动线程
thread.start();
Handler源码分析
第一条主线:入队(谁入的队?怎么入的?入的什么队?)
首先进入handler.sendMessage(msg);
/**
* Pushes a message onto the end of the message queue after all pending messages
* before the current time. It will be received in {@link #handleMessage},
* in the thread attached to this handler.
*
* @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting.
*/
public final boolean sendMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
}
再点进来sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
/**
* Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages
* before (current time + delayMillis). You will receive it in
* {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached to this handler.
*
* @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a
* result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if
* the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message
* occurs then the message will be dropped.
*/
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
}
再进来sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis)
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
进入enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis)
private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,
long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis)其实执行的是Message的enqueueMessage方法
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
//对msg进入标记
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
//如果队列中没有数据,将消息放入头部
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake
// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue
// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
说明了入队的过程是:Handler.sendMessage()->sendMessageDelayed()->sendMessageAtTime()->enqueueMessage()->MessageQueue类的enqueueMessage()
Handler发送消息(message)进行入队(MessageQueue)
入队时,如果队列中没有数据,直接将msg放到头部;如果有,则需要遍历队列中的数据,进入插入操作;
第二条主线出队(消费)
app启动的时候会调用ActivityThread这个类
会调用ActivityThread类中的main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// Install selective syscall interception
AndroidOs.install();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
// Call per-process mainline module initialization.
initializeMainlineModules();
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Find the value for {@link #PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT} if provided on the command line.
// It will be in the format "seq=114"
long startSeq = 0;
if (args != null) {
for (int i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (args[i] != null && args[i].startsWith(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT)) {
startSeq = Long.parseLong(
args[i].substring(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT.length()));
}
}
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
点进去看Looper.loop();
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
if (me.mInLoop) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"
+ " before this one completed.");
}
me.mInLoop = true;
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
// Allow overriding a threshold with a system prop. e.g.
// adb shell 'setprop log.looper.1000.main.slow 1 && stop && start'
final int thresholdOverride =
SystemProperties.getInt("log.looper."
+ Process.myUid() + "."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ".slow", 0);
boolean slowDeliveryDetected = false;
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
// Make sure the observer won't change while processing a transaction.
final Observer observer = sObserver;
final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;
long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;
long slowDeliveryThresholdMs = me.mSlowDeliveryThresholdMs;
if (thresholdOverride > 0) {
slowDispatchThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;
slowDeliveryThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;
}
final boolean logSlowDelivery = (slowDeliveryThresholdMs > 0) && (msg.when > 0);
final boolean logSlowDispatch = (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0);
final boolean needStartTime = logSlowDelivery || logSlowDispatch;
final boolean needEndTime = logSlowDispatch;
if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {
Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));
}
final long dispatchStart = needStartTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
final long dispatchEnd;
Object token = null;
if (observer != null) {
token = observer.messageDispatchStarting();
}
long origWorkSource = ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(msg.workSourceUid);
try {
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (observer != null) {
observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);
}
dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
} catch (Exception exception) {
if (observer != null) {
observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);
}
throw exception;
} finally {
ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
if (logSlowDelivery) {
if (slowDeliveryDetected) {
if ((dispatchStart - msg.when) <= 10) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Drained");
slowDeliveryDetected = false;
}
} else {
if (showSlowLog(slowDeliveryThresholdMs, msg.when, dispatchStart, "delivery",
msg)) {
// Once we write a slow delivery log, suppress until the queue drains.
slowDeliveryDetected = true;
}
}
}
if (logSlowDispatch) {
showSlowLog(slowDispatchThresholdMs, dispatchStart, dispatchEnd, "dispatch", msg);
}
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
在for循环中有Message msg = queue.next();在MessageQueue的next()可以发现
@UnsupportedAppUsage
Message next() {
// Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.
// This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit
// which is not supported.
final long ptr = mPtr;
if (ptr == 0) {
return null;
}
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
}
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
synchronized (this) {
// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
// Got a message.
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
// No more messages.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.
if (mQuitting) {
dispose();
return null;
}
// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.
// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message
// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
}
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
mBlocked = true;
continue;
}
if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
}
mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
}
// Run the idle handlers.
// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
boolean keep = false;
try {
keep = idler.queueIdle();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
}
if (!keep) {
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
}
}
}
// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
}
}
MessageQueue中for循环取对象,将对象找到返回,此时Looper方法里的msg 就是返回的对象。
并利用msg去调用loop()方法中的dispatchMessage方法
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
说明了第二条主线的流程是:ActivityThread类的main()->looper.loop()->queue.next()
通过next()找到msg对象,然后通过msg绑定target,也就是handler,调用dispatchMessage回调handleMessage方法
/**
* Handle system messages here.
*/
public void dispatchMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
第三条主线:Handler,MessageQueue,Message,Looper四个类是什么关系,怎么串联?
- 在mHandler.obtainMessage()中Handler创建Message对象
- 在MessageQueue中的enqueueMessage方法中Handler将创建的对象放入MessageQueue中
- Looper是通过ActivityThread的main()方法进行创建,MessageQueue在创建Looper的时会同时创建
ActivityThread类中
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
prepareMainLooper()点进来
@Deprecated
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false);
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
进来 prepare(false);
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
sThreadLocal.set方法中创建了Looper对象
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
在创建Looper对象的同时,构造方法里也创建了MessageQueue对象
- 在Handler的enqueueMessage方法中,通过msg.target=this将Handler赋值给msg.target对象
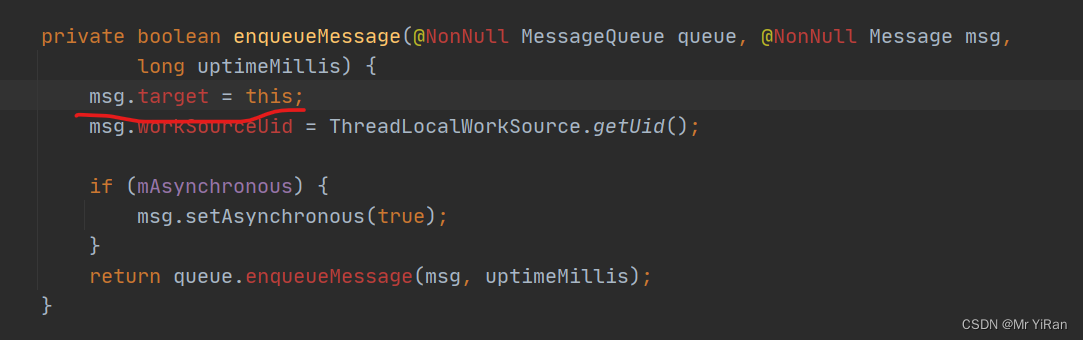
而我们在调用mHandler.obtainMessage()中
Message msg= mHandler.obtainMessage();
点进去obtainMessage
/**
* Returns a new {@link android.os.Message Message} from the global message pool. More efficient than
* creating and allocating new instances. The retrieved message has its handler set to this instance (Message.target == this).
* If you don't want that facility, just call Message.obtain() instead.
*/
@NonNull
public final Message obtainMessage()
{
return Message.obtain(this);
}
进来 Message.obtain(this)
/**
* Same as {@link #obtain()}, but sets the value for the <em>target</em> member on the Message returned.
* @param h Handler to assign to the returned Message object's <em>target</em> member.
* @return A Message object from the global pool.
*/
public static Message obtain(Handler h) {
Message m = obtain();
m.target = h;
return m;
}
进行obtain()方法
/**
* Return a new Message instance from the global pool. Allows us to
* avoid allocating new objects in many cases.
*/
public static Message obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
Message m = sPool;
sPool = m.next;
m.next = null;
m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
sPoolSize--;
return m;
}
}
return new Message();
}
可以看到在Message.obtain()中message对象采用了复用池,避免资源的浪费;
常见问题解答?如果有错误欢迎指正!
1. 为什么Message需要使用复用机制?每次直接new一个不好么?
当我需要主线程和子线程直接进行沟通的时候一般都使用handler,发送Message对象一般都比较多,如果每发送一次就创建一次的话,会造成资源的浪费,在每次创建Message对象时,都需要分配内存和进行垃圾回收。而使用复用池可以避免频繁地创建和销毁Message对象,从而减少内存的分配和垃圾回收的开销。
Message:单链表结果,链表是非线性,非顺序的物理结构,由N个节点组成;
2. message为什么使用单链表?为啥不使用其他类型:arrayList
- arrayList每次创建的时候会创建一个默认大小的空间,如果超过默认大小的空间就需要进行扩容,就需要对这个ArrayList的内存空间重新进行计算和排列,这可能会导致频繁的内存拷贝和垃圾回收。
- 由于arrayList需要连续的内存块来存储元素,当我们一个arrayList的内存块不够用的时候,重新去创建一个的话又需要开辟一个内存块,当我们这个内存不够用的时候,我们就会去进行gc操作,而且内存中容易出现内存碎片,如果再存放内存容易奔溃。而单链表只需要分配新的节点,不需要进行大规模的数据迁移,而当我们存放的是一个对象的时候,对内存要求不高,只要有合适的空间都可以存放。
3. 子线程能不能new handler?怎么能在子线程new Handler?
子线程不能直接创建Handler对象,如果需要在子线程new Handler需要调用Looper.prepare()
4 .子线程维护Looper的时候需要注意什么?
注意内存泄露的问题;使用完毕后 记得调用quitSafely的方法
5 .MessageQueue是怎么保证线程安全的
通过synchronized同步关键字来对入队操作进行限定
6 .removeMessage的时候是移除队列中的还是队列外的
remove的时候只能移除队列中的数据
7 .Looper能够prepare两次,为什么?
不能prepare两次,因为Looper在创建过程中就加了约束,如果prepare两次会报错。