nacos的实例分为临时实例和永久实例两种,相应的不同的实例会用有不同的心跳机制.
临时实例基于心跳方式做健康检测,永久实例是有Nacos主动探测实例状态.
可以通过在yaml文件配置.
spring:
application:
name: order-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
ephemeral: false # 设置实例为永久实例。true:临时; false:永久
server-addr: 192.168.150.1:8845
Nacos提供的心跳的API接口为:/nacos/v1/ns/instance/beat
客户端
NacosNamingService这个接口实现了服务心跳的功能
@Override
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
if (instance.isEphemeral()) {
BeatInfo beatInfo = new BeatInfo();
beatInfo.setServiceName(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName));
beatInfo.setIp(instance.getIp());
beatInfo.setPort(instance.getPort());
beatInfo.setCluster(instance.getClusterName());
beatInfo.setWeight(instance.getWeight());
beatInfo.setMetadata(instance.getMetadata());
beatInfo.setScheduled(false);
beatInfo.setPeriod(instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval());
// 发送心跳到 Nacos 服务
beatReactor.addBeatInfo(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), beatInfo);
}
serverProxy.registerService(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), groupName, instance);
}
BeatInfo
从上面的代码可以看到BeatInfo就是包含心跳需要的各种信息,
/**
* @author nkorange
*/
public class BeatInfo {
private int port;
private String ip;
private double weight;
private String serviceName;
private String cluster;
private Map<String, String> metadata;
private volatile boolean scheduled;
private volatile long period;
private volatile boolean stopped;
}
BeatReactor
这个类中维护了一个线程池;
public BeatReactor(NamingProxy serverProxy, int threadCount) {
this.serverProxy = serverProxy;
executorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(threadCount, new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.naming.beat.sender");
return thread;
}
});
}
当调用addBeatInfo方法的时候,就会执行心跳:
public void addBeatInfo(String serviceName, BeatInfo beatInfo) {
NAMING_LOGGER.info("[BEAT] adding beat: {} to beat map.", beatInfo);
String key = buildKey(serviceName, beatInfo.getIp(), beatInfo.getPort());
BeatInfo existBeat = null;
//fix #1733
if ((existBeat = dom2Beat.remove(key)) != null) {
existBeat.setStopped(true);
}
dom2Beat.put(key, beatInfo);
// 利用线程池,定期执行心跳任务,周期为 beatInfo.getPeriod()
// 心跳周期的默认值在 com.alibaba.nacos.api.common.Constants 类中
// public static final long DEFAULT_HEART_BEAT_INTERVAL = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(5);
// 可以看到是5秒,默认5秒一次心跳
// BeatTask:是一个Runnable
executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), beatInfo.getPeriod(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
MetricsMonitor.getDom2BeatSizeMonitor().set(dom2Beat.size());
}
BeatTask
心跳的任务封装在 BeatTask这个类中,是一个Runnable,其run方法如下:
public void run() {
if (beatInfo.isStopped()) {
return;
}
// 获取心跳周期
long nextTime = beatInfo.getPeriod();
try {
// 发送心跳
JSONObject result = serverProxy.sendBeat(beatInfo, BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled);
long interval = result.getIntValue("clientBeatInterval");
boolean lightBeatEnabled = false;
if (result.containsKey(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED)) {
lightBeatEnabled = result.getBooleanValue(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED);
}
BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled = lightBeatEnabled;
if (interval > 0) {
nextTime = interval;
}
// 判断心跳结果
int code = NamingResponseCode.OK;
if (result.containsKey(CommonParams.CODE)) {
code = result.getIntValue(CommonParams.CODE);
}
if (code == NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND) {
// 如果失败,则需要 重新注册实例
Instance instance = new Instance();
instance.setPort(beatInfo.getPort());
instance.setIp(beatInfo.getIp());
instance.setWeight(beatInfo.getWeight());
instance.setMetadata(beatInfo.getMetadata());
instance.setClusterName(beatInfo.getCluster());
instance.setServiceName(beatInfo.getServiceName());
instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId());
instance.setEphemeral(true);
try {
serverProxy.registerService(beatInfo.getServiceName(),
NamingUtils.getGroupName(beatInfo.getServiceName()), instance);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
// 捕获异常,什么都不干
}
}
} catch (NacosException ne) {
NAMING_LOGGER.error("[CLIENT-BEAT] failed to send beat: {}, code: {}, msg: {}",
JSON.toJSONString(beatInfo), ne.getErrCode(), ne.getErrMsg());
}
executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), nextTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
发送心跳
public JSONObject sendBeat(BeatInfo beatInfo, boolean lightBeatEnabled) throws NacosException {
if (NAMING_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("[BEAT] {} sending beat to server: {}", namespaceId, beatInfo.toString());
}
// 组织请求参数
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>(8);
String body = StringUtils.EMPTY;
if (!lightBeatEnabled) {
body = "beat=" + JSON.toJSONString(beatInfo);
}
params.put(CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, namespaceId);
params.put(CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME, beatInfo.getServiceName());
params.put(CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, beatInfo.getCluster());
params.put("ip", beatInfo.getIp());
params.put("port", String.valueOf(beatInfo.getPort()));
// 发送请求,这个地址就是:/v1/ns/instance/beat
String result = reqAPI(UtilAndComs.NACOS_URL_BASE + "/instance/beat", params, body, HttpMethod.PUT);
return JSON.parseObject(result);
}
服务端
对于临时实例,服务端代码分了两部分:
(1) InstanceController提供了一个接口,处理客户端的心跳请求
(2) 定时检测实例心跳是否按期执行
可以根据客户端发起心跳检测的接口找到在InstanceController类中,定义了一个方法来处理心跳请求:
@CanDistro
@PutMapping("/beat")
@Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public JSONObject beat(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
result.put("clientBeatInterval", switchDomain.getClientBeatInterval());
// 解析心跳的请求参数
// 获取 serviceName
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
// 获取 namespaceId
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID,
Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
// 获取clusterName
String clusterName = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME,
UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME);
// 获取ip
String ip = WebUtils.optional(request, "ip", StringUtils.EMPTY);
// 获取port
int port = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "port", "0"));
String beat = WebUtils.optional(request, "beat", StringUtils.EMPTY);
RsInfo clientBeat = null;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beat)) {
clientBeat = JSON.parseObject(beat, RsInfo.class);
}
if (clientBeat != null) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(clientBeat.getCluster())) {
clusterName = clientBeat.getCluster();
}
ip = clientBeat.getIp();
port = clientBeat.getPort();
}
if (Loggers.SRV_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] full arguments: beat: {}, serviceName: {}", clientBeat, serviceName);
}
// 尝试从 Nacos 注册表中 获取实例
Instance instance = serviceManager.getInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, clusterName, ip, port);
// 如果获取失败,说明心跳失败,实例尚未注册
if (instance == null) {
if (clientBeat == null) {
// 对应客户端中,心跳失败,则注册实例的代码
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND);
return result;
}
instance = new Instance();
instance.setPort(clientBeat.getPort());
instance.setIp(clientBeat.getIp());
instance.setWeight(clientBeat.getWeight());
instance.setMetadata(clientBeat.getMetadata());
instance.setClusterName(clusterName);
instance.setServiceName(serviceName);
instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId());
instance.setEphemeral(clientBeat.isEphemeral());
// 重新注册一个实例
serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
}
// 尝试基于 namespaceId 和 serviceName 从注册表中获取 Service 服务
Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
// 如果不存在,说明服务不存在,返回404
if (service == null) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR,
"service not found: " + serviceName + "@" + namespaceId);
}
if (clientBeat == null) {
clientBeat = new RsInfo();
clientBeat.setIp(ip);
clientBeat.setPort(port);
clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName);
}
// 如果心跳没问题,开始处理心跳结果
service.processClientBeat(clientBeat);
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.OK);
result.put("clientBeatInterval", instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval());
result.put(SwitchEntry.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED, switchDomain.isLightBeatEnabled());
return result;
}
处理心跳请求
public void processClientBeat(final RsInfo rsInfo) {
ClientBeatProcessor clientBeatProcessor = new ClientBeatProcessor();
clientBeatProcessor.setService(this);
clientBeatProcessor.setRsInfo(rsInfo);
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(clientBeatProcessor);
}
HealthCheckReactor就是对线程池的封装,关键在于ClientBeatProcessor这个类中,他是一个Runnable,其中run方法:
public void run() {
Service service = this.service;
if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] processing beat: {}", rsInfo.toString());
}
String ip = rsInfo.getIp();
String clusterName = rsInfo.getCluster();
int port = rsInfo.getPort();
// 获取集群信息
Cluster cluster = service.getClusterMap().get(clusterName);
// 获取集群中的所有实例信息
List<Instance> instances = cluster.allIPs(true);
for (Instance instance : instances) {
// 找到心跳的这个实例
if (instance.getIp().equals(ip) && instance.getPort() == port) {
if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] refresh beat: {}", rsInfo.toString());
}
// 更新实例的最后依一次心跳时间 lastBeat
// lastBeat 是判断实例心跳是否过期的关键指标!
instance.setLastBeat(System.currentTimeMillis());
if (!instance.isMarked()) {
if (!instance.isHealthy()) {
instance.setHealthy(true);
Loggers.EVT_LOG.info("service: {} {POS} {IP-ENABLED} valid: {}:{}@{}, region: {}, msg: client beat ok",
cluster.getService().getName(), ip, port, cluster.getName(), UtilsAndCommons.LOCALHOST_SITE);
getPushService().serviceChanged(service);
}
}
}
}
}
心跳异常检测
在服务注册时,一定会创建一个Service对象,而Service中有一个init方法,会在注册的时候被调用
public void init() {
// 开启心跳检测的任务
// 执行心跳检测的定时任务
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleCheck(clientBeatCheckTask);
// 遍历注册表中的集群
for (Map.Entry<String, Cluster> entry : clusterMap.entrySet()) {
entry.getValue().setService(this);
// 完成集群初始化
entry.getValue().init();
}
}
public static void scheduleCheck(ClientBeatCheckTask task) {
// 5000ms一次,也就是5秒对实例的心跳状态做一次检测
// task:是一个 Runnable
futureMap.putIfAbsent(task.taskKey(), EXECUTOR.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task, 5000, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
ClientBeatCheckTask
public void run() {
try {
if (!getDistroMapper().responsible(service.getName())) {
return;
}
if (!getSwitchDomain().isHealthCheckEnabled()) {
return;
}
// 找到所有 临时 实例的列表
List<Instance> instances = service.allIPs(true);
// first set health status of instances:
for (Instance instance : instances) {
// 判断时间间隔(当前时间 - 最后一次心跳时间)是否大于 心跳超时时间,默认15秒
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getInstanceHeartBeatTimeOut()) {
if (!instance.isMarked()) {
if (instance.isHealthy()) {
// 如果超时,标记实例为不健康 healthy = false
instance.setHealthy(false);
Loggers.EVT_LOG.info("{POS} {IP-DISABLED} valid: {}:{}@{}@{}, region: {}, msg: client timeout after {}, last beat: {}",
instance.getIp(), instance.getPort(), instance.getClusterName(), service.getName(),
UtilsAndCommons.LOCALHOST_SITE, instance.getInstanceHeartBeatTimeOut(), instance.getLastBeat());
// 发布实例状态变更的事件
getPushService().serviceChanged(service);
SpringContext.getAppContext().publishEvent(new InstanceHeartbeatTimeoutEvent(this, instance));
}
}
}
}
if (!getGlobalConfig().isExpireInstance()) {
return;
}
// then remove obsolete instances:
for (Instance instance : instances) {
if (instance.isMarked()) {
continue;
}
// 判断心跳间隔(当前事件 - 最后一次心跳时间)是否大于 实例被删除的最长超时间,默认30秒
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getIpDeleteTimeout()) {
// delete instance
Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[AUTO-DELETE-IP] service: {}, ip: {}", service.getName(), JSON.toJSONString(instance));
// 如果超过了 30 秒,则删除实例
deleteIP(instance);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("Exception while processing client beat time out.", e);
}
}
主动健康检测
对于非实例,nacos会采用主动的健康检测,定时向实例发送请求,根据响应来判断实例健康状态.
入口是从ServiceManager类中的registerInstance方法
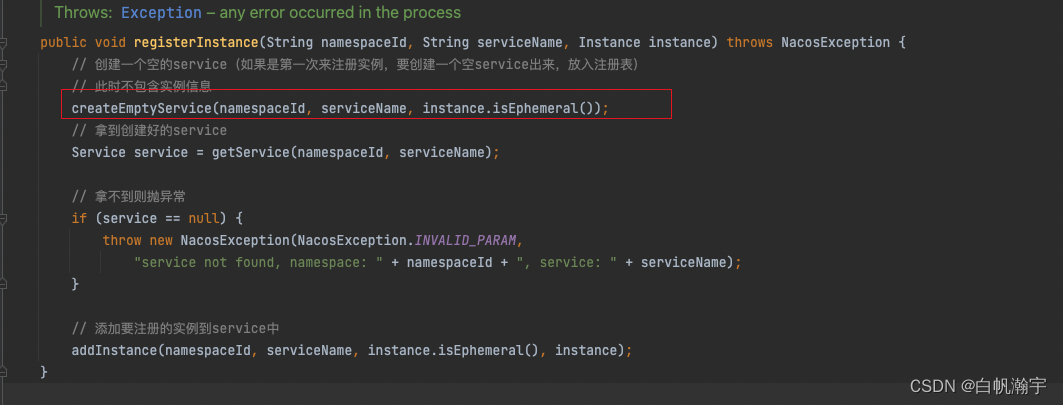
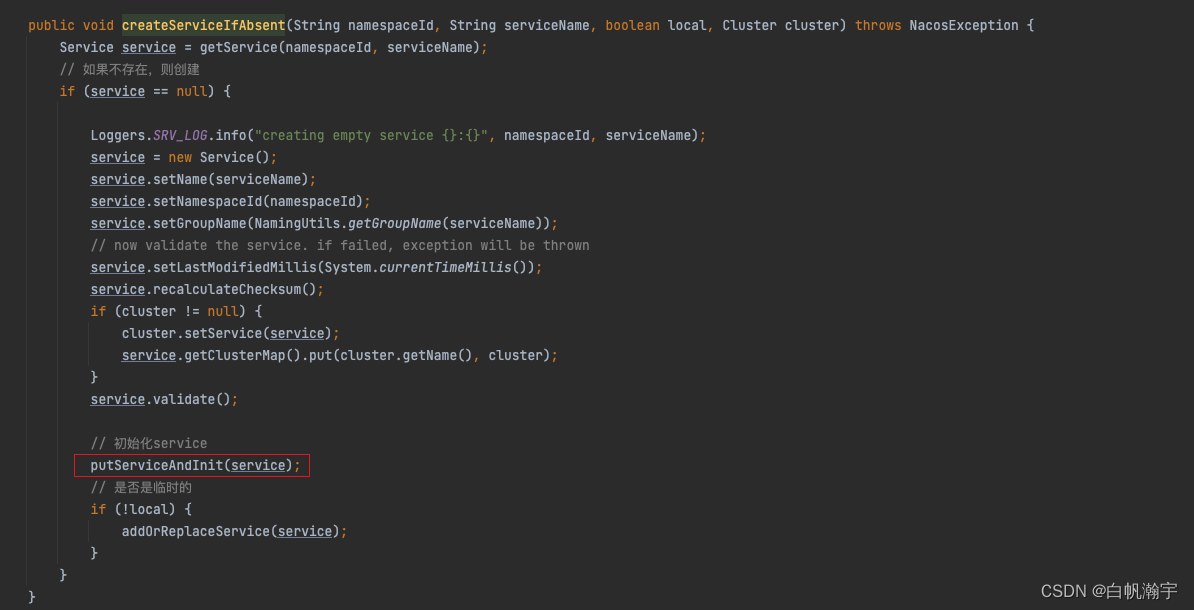
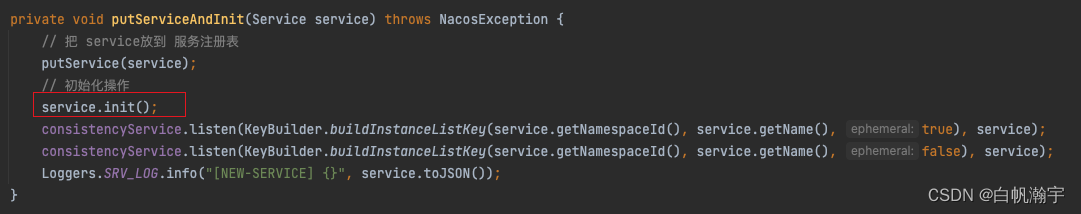
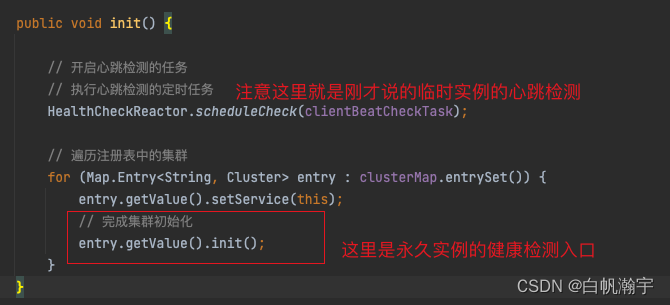
下面看一下集群初始化的init方法
public void init() {
if (inited) {
return;
}
// 创建健康检测的任务
checkTask = new HealthCheckTask(this);
// 这里会开启对 非临时实例的 定时健康检测
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleCheck(checkTask);
inited = true;
}
和上面的init方法一样,也是会创建一个任务HealthCheckTask,并且放到线程池里,进行定时检测
public void run() {
try {
if (distroMapper.responsible(cluster.getService().getName()) &&
switchDomain.isHealthCheckEnabled(cluster.getService().getName())) {
// 开启健康检测
healthCheckProcessor.process(this);
// 记录日志
if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[HEALTH-CHECK] schedule health check task: {}", cluster.getService().getName());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.error("[HEALTH-CHECK] error while process health check for {}:{}",
cluster.getService().getName(), cluster.getName(), e);
} finally {
if (!cancelled) {
// 结束后,再次进行任务调度,一定延迟后执行
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleCheck(this);
// worst == 0 means never checked
if (this.getCheckRTWorst() > 0
&& switchDomain.isHealthCheckEnabled(cluster.getService().getName())
&& distroMapper.responsible(cluster.getService().getName())) {
// TLog doesn't support float so we must convert it into long
long diff = ((this.getCheckRTLast() - this.getCheckRTLastLast()) * 10000)
/ this.getCheckRTLastLast();
this.setCheckRTLastLast(this.getCheckRTLast());
Cluster cluster = this.getCluster();
if (Loggers.CHECK_RT.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.CHECK_RT.debug("{}:{}@{}->normalized: {}, worst: {}, best: {}, last: {}, diff: {}",
cluster.getService().getName(), cluster.getName(), cluster.getHealthChecker().getType(),
this.getCheckRTNormalized(), this.getCheckRTWorst(), this.getCheckRTBest(),
this.getCheckRTLast(), diff);
}
}
}
}
}
健康检测逻辑定义在里healthCheckProcessor.process(this);方法中,在HealthCheckProcessor中,这个接口的默认实现是TcpSuperSenseProcessor
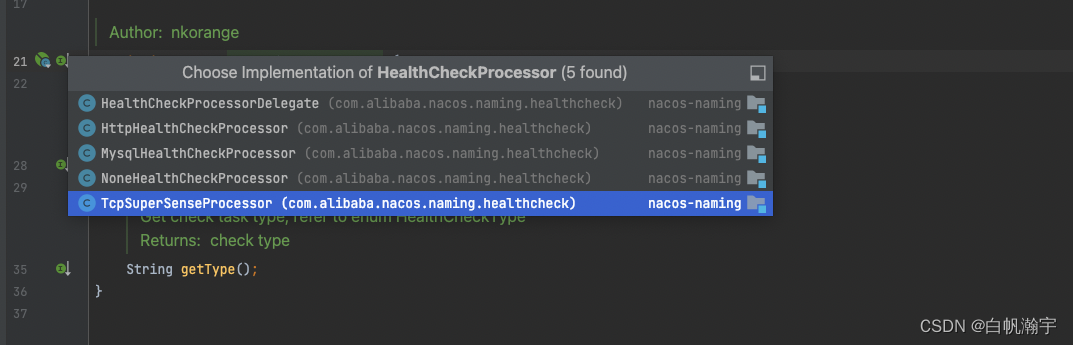
public void process(HealthCheckTask task) {
// 获取所有 非临时实例的 集合
List<Instance> ips = task.getCluster().allIPs(false);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(ips)) {
return;
}
for (Instance ip : ips) {
if (ip.isMarked()) {
if (SRV_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
SRV_LOG.debug("tcp check, ip is marked as to skip health check, ip:" + ip.getIp());
}
continue;
}
if (!ip.markChecking()) {
SRV_LOG.warn("tcp check started before last one finished, service: "
+ task.getCluster().getService().getName() + ":"
+ task.getCluster().getName() + ":"
+ ip.getIp() + ":"
+ ip.getPort());
healthCheckCommon.reEvaluateCheckRT(task.getCheckRTNormalized() * 2, task, switchDomain.getTcpHealthParams());
continue;
}
// 封装健康检测信息到 beat
Beat beat = new Beat(ip, task);
// 放入到一个阻塞队列中
taskQueue.add(beat);
MetricsMonitor.getTcpHealthCheckMonitor().incrementAndGet();
}
}
可以看到nacos中有很多这种操作,不是立即去执行,而是通过放到阻塞队列里面,进行异步执行.
因为TcpSuperSenseProcessor是一个Runnable,所以我们可以直接看他的run接口:
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
// 处理任务
processTask();
int readyCount = selector.selectNow();
if (readyCount <= 0) {
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
NIO_EXECUTOR.execute(new PostProcessor(key));
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
SRV_LOG.error("[HEALTH-CHECK] error while processing NIO task", e);
}
}
}
private void processTask() throws Exception {
Collection<Callable<Void>> tasks = new LinkedList<>();
do {
// 取出beat
Beat beat = taskQueue.poll(CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MS / 2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (beat == null) {
return;
}
// 将任务封装为一个TaskProcessor,并放入集合
tasks.add(new TaskProcessor(beat));
} while (taskQueue.size() > 0 && tasks.size() < NIO_THREAD_COUNT * 64);
// 批量处理集合中的任务
for (Future<?> f : NIO_EXECUTOR.invokeAll(tasks)) {
f.get();
}
}
接着看TaskProcessor,因为是一个callable的线程,所以直接看call方法
public Void call() {
// 获取检测任务已经等待的时长
long waited = System.currentTimeMillis() - beat.getStartTime();
if (waited > MAX_WAIT_TIME_MILLISECONDS) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("beat task waited too long: " + waited + "ms");
}
SocketChannel channel = null;
try {
// 获取实例信息
Instance instance = beat.getIp();
Cluster cluster = beat.getTask().getCluster();
BeatKey beatKey = keyMap.get(beat.toString());
if (beatKey != null && beatKey.key.isValid()) {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - beatKey.birthTime < TCP_KEEP_ALIVE_MILLIS) {
instance.setBeingChecked(false);
return null;
}
beatKey.key.cancel();
beatKey.key.channel().close();
}
// 通过NIO建立TCP连接
channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// only by setting this can we make the socket close event asynchronous
channel.socket().setSoLinger(false, -1);
channel.socket().setReuseAddress(true);
channel.socket().setKeepAlive(true);
channel.socket().setTcpNoDelay(true);
int port = cluster.isUseIPPort4Check() ? instance.getPort() : cluster.getDefCkport();
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(instance.getIp(), port));
// 注册连接、读取事件
SelectionKey key
= channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT | SelectionKey.OP_READ);
key.attach(beat);
keyMap.put(beat.toString(), new BeatKey(key));
beat.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
NIO_EXECUTOR.schedule(new TimeOutTask(key),
CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
beat.finishCheck(false, false, switchDomain.getTcpHealthParams().getMax(), "tcp:error:" + e.getMessage());
if (channel != null) {
try {
channel.close();
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
Nacos的健康检测有两种模式:
- 临时实例:
采用客户端心跳检测模式,心跳周期5秒
心跳间隔超过15秒则标记为不健康
心跳间隔超过30秒则从服务列表删除 - 永久实例:
采用服务端主动健康检测方式
周期为2000 + 5000毫秒内的随机数
检测异常只会标记为不健康,不会删除
以淘宝为例,双十一大促期间,流量会比平常高出很多,此时服务肯定需要增加更多实例来应对高并发,而这些实例在双十一之后就无需继续使用了,采用临时实例比较合适。而对于服务的一些常备实例,则使用永久实例更合适。
与eureka相比,Nacos与Eureka在临时实例上都是基于心跳模式实现,差别不大,主要是心跳周期不同,eureka是30秒,Nacos是5秒。
另外,Nacos支持永久实例,而Eureka不支持,Eureka只提供了心跳模式的健康监测,而没有主动检测功能。






![分布式文件存储系统FastDFS[3]-通过Docker安装并且从客户端进行上传下载测试](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c53df8d8240948b0a3894966c0ced8fa.png)


