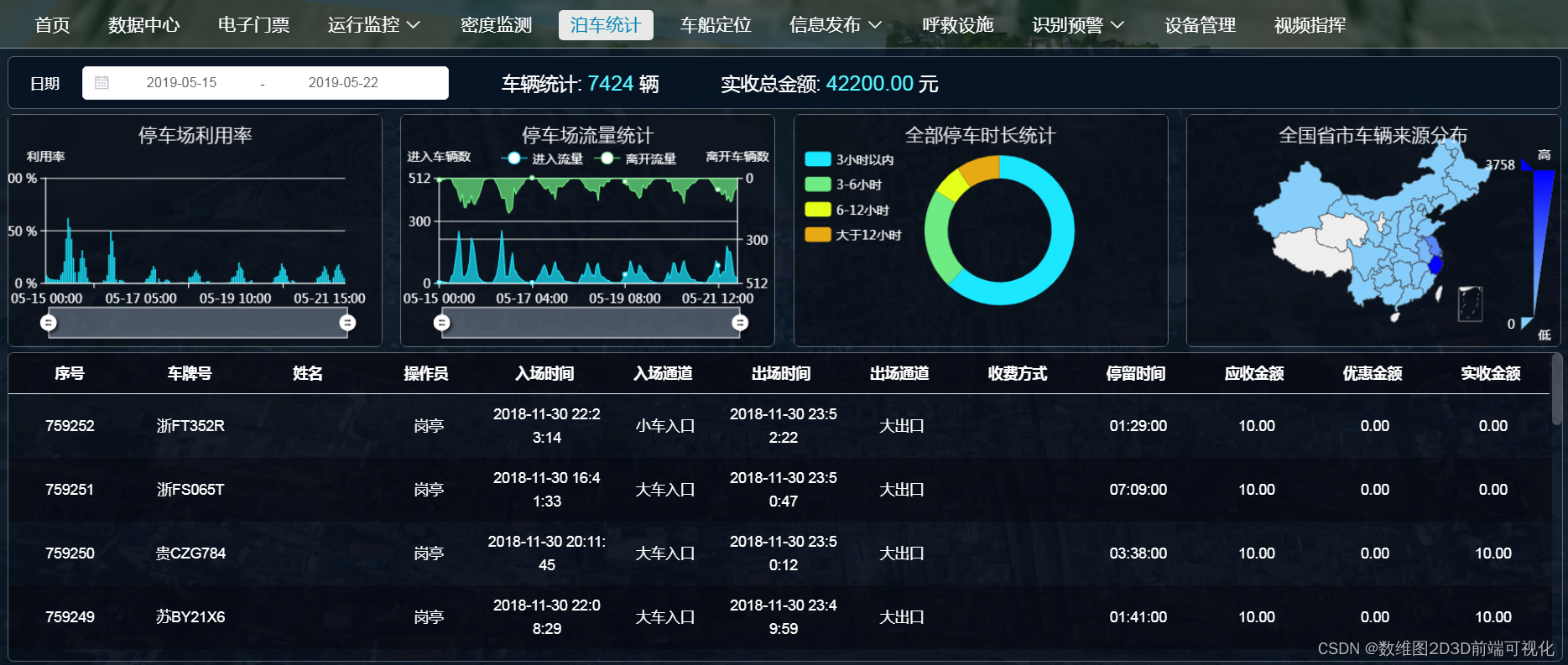
1 硬件连接(使用Arduino Uno):
CS -> 10
SCK -> 13
MOSI -> 11
MISO -> 12
VCC ->5V
GND -> GND
2 让Arduino检测到SD卡
官方测试程序:检测SD卡连接并输出卡型号
/*
SD card test
This example shows how use the utility libraries on which the'
SD library is based in order to get info about your SD card.
Very useful for testing a card when you're not sure whether its working or not.
The circuit:
SD card attached to SPI bus as follows:
** MOSI - pin 11 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** MISO - pin 12 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** CLK - pin 13 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** CS - depends on your SD card shield or module.
Pin 4 used here for consistency with other Arduino examples
created 28 Mar 2011
by Limor Fried
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe
*/
// include the SD library:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// set up variables using the SD utility library functions:
Sd2Card card;
SdVolume volume;
SdFile root;
// change this to match your SD shield or module;
// Arduino Ethernet shield: pin 4
// Adafruit SD shields and modules: pin 10
// Sparkfun SD shield: pin 8
// MKRZero SD: SDCARD_SS_PIN
const int chipSelect = 4;
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
Serial.print("\nInitializing SD card...");
// we'll use the initialization code from the utility libraries
// since we're just testing if the card is working!
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("* is a card inserted?");
Serial.println("* is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("* did you change the chipSelect pin to match your shield or module?");
while (1);
} else {
Serial.println("Wiring is correct and a card is present.");
}
// print the type of card
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Card type: ");
switch (card.type()) {
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
Serial.println("SD1");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
Serial.println("SD2");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
Serial.println("SDHC");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Unknown");
}
// Now we will try to open the 'volume'/'partition' - it should be FAT16 or FAT32
if (!volume.init(card)) {
Serial.println("Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.\nMake sure you've formatted the card");
while (1);
}
Serial.print("Clusters: ");
Serial.println(volume.clusterCount());
Serial.print("Blocks x Cluster: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster());
Serial.print("Total Blocks: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster() * volume.clusterCount());
Serial.println();
// print the type and size of the first FAT-type volume
uint32_t volumesize;
Serial.print("Volume type is: FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(), DEC);
volumesize = volume.blocksPerCluster(); // clusters are collections of blocks
volumesize *= volume.clusterCount(); // we'll have a lot of clusters
volumesize /= 2; // SD card blocks are always 512 bytes (2 blocks are 1KB)
Serial.print("Volume size (Kb): ");
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Mb): ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Gb): ");
Serial.println((float)volumesize / 1024.0);
Serial.println("\nFiles found on the card (name, date and size in bytes): ");
root.openRoot(volume);
// list all files in the card with date and size
root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);
}
void loop(void) {
}
如果测试失败,要注意以下操作:
1 Initializing failed:
确认接线:对于Arduino Uno,SD卡读卡器的CS引脚要连接4.
如果接线正确,确认chipSelect值也为4
2 Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.\nMake sure you’ve formatted the card:
这一步需要对SD卡进行格式化,一定要选择FAT16或FAT32格式。对于内存大于32G的SD卡,windows自带的格式化工具不会提供FAT32选项,因此需要借用第三方工具:
http://ridgecrop.co.uk/index.htm?guiformat.htm

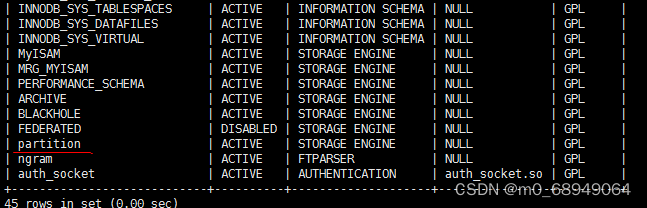
测试成功结果如下

2 利用SD卡读写文件
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>
const int chipSelect = 10;
String fileName = "test.txt";
File myFile;
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(chipSelect, OUTPUT);
// wait for Serial Monitor to connect. Needed for native USB port boards only:
while (!Serial);
Serial.print("Initializing SD card...");
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("1. is a card inserted?");
Serial.println("2. is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("3. did you change the chipSelect pin to match your shield or module?");
Serial.println("Note: press reset button on the board and reopen this Serial Monitor after fixing your issue!");
while (true);
}
Serial.println("initialization done.");
// open the file. note that only one file can be open at a time,
// so you have to close this one before opening another.
myFile = SD.open(fileName, FILE_WRITE);
// if the file opened okay, write to it:
if (myFile) {
Serial.print("Writing to test.txt...");
myFile.println("testing 1, 2, 3.");
if (SD.exists(fileName)) {
Serial.println("file exists");
}
// close the file:
myFile.close();
Serial.println("done.");
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
Serial.println("reopening...");
// re-open the file for reading:
myFile = SD.open(fileName);
if (myFile) {
Serial.println(fileName + ":");
// read from the file until there's nothing else in it:
while (myFile.available()) {
Serial.write(myFile.read());
}
// close the file:
Serial.println("done.");
myFile.close();
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
}
void loop() {
// nothing happens after setup
}
里面调用的SD类方法:
1
SD.begin(chipSelect)
启动SD类,chipSelect为SD读卡器CS引脚连接的Arduino引脚。返回值为boolean,代表SD卡是否成功启动
2
SD.open(fileName, FILE_WRITE)
打开文件,参数为(文件名,读取方式)。注意文件名采用8.3格式,即文件名最多8字符,文件拓展名最多3字符,不区分大小写。如果文件名长度超过限制可能造成文件创建失败。
读取方式分为FILE_READ和FILE_WRITE,如果该参数不填默认为FILE_READ。在FILE_READ为只读状态,而FILE_WRITE允许修改文件。在FILE_WRITE状态下如果open的文件名不存在会创建新文件。
在FILE_READ模式下默认从文件头读取,在FILE_WRITE模式下默认从文件末尾读取
该方法返回值为一个文件(File类型),代表打开的文件。File类型支持被作为boolean,true代表存在文件,false代表不存在文件
3
SD.exists(fileName)
判断文件是否存在,返回boolean
文件操作方法:
myFile.println()
在文件里打印信息
myFile.close()
关闭并退出当前文件
上述测试程序运行结果:

注:我在测试中调用了程序多次,导致test.txt里面有多行内容。第一次运行后test.txt中只会有一行testing 1 2 3