文章目录
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 234.回文链表
- 链表转数组+统计长度
- 反转后半部分链表 快慢指针
- 143. 重排链表
- 数组 双指针 超时
- 双队列
- 反转和插入链表
- 141. 环形链表
- 142.环形链表II
- 160.链表相交
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
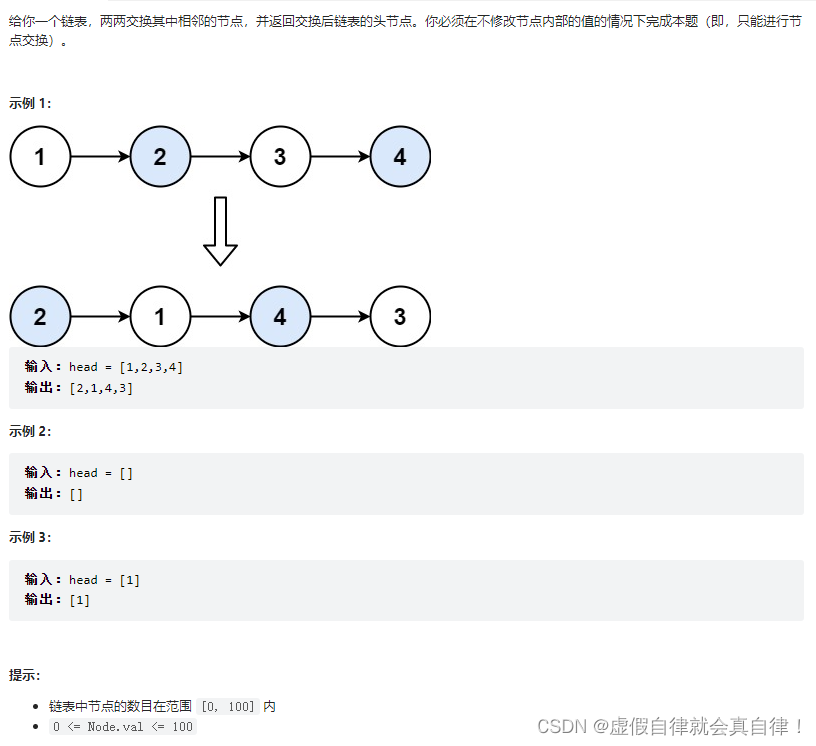
迭代法,时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n), 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
//1->2->3->4
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;//保存节点2
ListNode* temp1 = cur->next->next->next;//保存节点4
cur->next = cur->next->next;//1->3
cur->next->next = temp;//3->2
cur->next->next->next = temp1;//2->4
//cur移动两位 下一次交换
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
234.回文链表
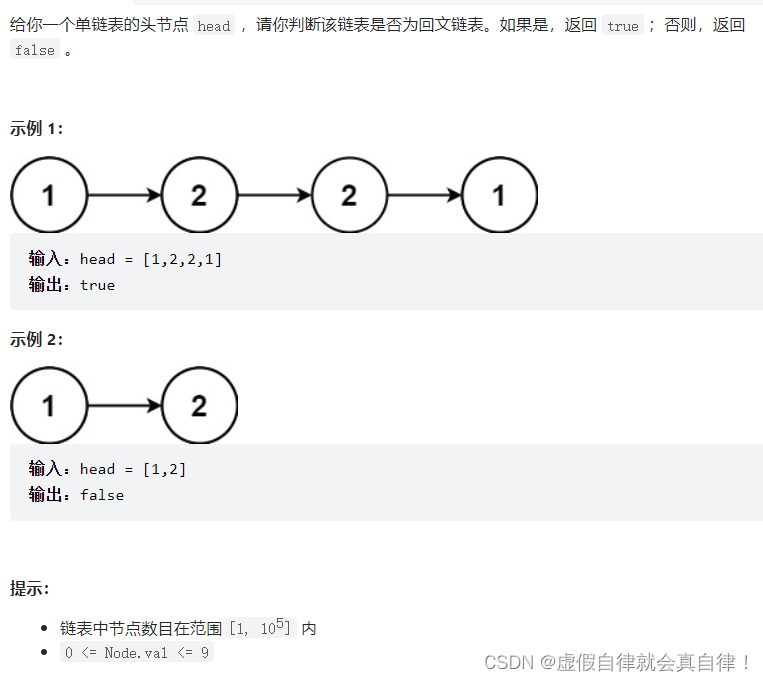
链表转数组+统计长度
时间复杂度、空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
//写法1 数组
/*
ListNode* cur = head;
vector<int> result;
while(cur)
{
result.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
//回文判断 双指针
for(int i=0, j=result.size()-1; i<j; i++,j--)
{
if(result[i] != result[j]) return false;
}
return true;*/
//写法2 统计长度+数组 避免多余空间开辟
ListNode* cur = head;
int n = 0;
while(cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
n++;
}
vector<int> result(n);
cur = head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
result[i] = cur->val;
cur = cur->next;
}
for(int i=0, j=result.size()-1; i<j; i++,j--)
{
if(result[i] != result[j]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
反转后半部分链表 快慢指针
- 止位置时,慢指针就在链表中间位置。
- 同时用pre记录慢指针指向节点的前一个节点,用来分割链表,将链表分为前后均等两部分,如果链表长度是奇数,那么后半部分多一个节点
- 将后半部分反转 ,得cur2,前半部分为cur1
- 按照cur1的长度,一次比较cur1和cur2的节点数值
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
//写法3 反转后半指针 快慢指针
if(head == nullptr && head->next == nullptr) return true;
ListNode* fast = head;//走两步 到终点时 slow在中间位置
ListNode* slow = head;//走一步 中间位置
ListNode* pre = head;//记录slow的上一个节点 前半段
//1.统计位置
while(fast && fast->next)
{
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
//2.分割链表
pre->next = nullptr;
//3.两段链表 奇数个节点 那么slow在奇数位cur2长度>cur1
ListNode* cur1 = head;
ListNode* cur2 = reverseList(slow);
while(cur1)
{
if(cur1->val != cur2->val) return false;
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* temp = head;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
//1->2->3 pre->cur->cur.next
temp = cur->next;//保存节点
cur->next = pre;//翻转节点
pre = cur;//更新pre 前移一步 原来cur的上一个节点
cur = temp;//更新cur 前移一步 原来cur的下一个节点
}
return pre;
}
};
143. 重排链表

数组 双指针 超时
把链表放进数组中,然后通过双指针法,一前一后,来遍历数组,构造链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
//数组 超时
//1.节点存入数组
vector<ListNode*> vec;
ListNode* cur = head;
if(cur == nullptr) return;
while(cur)
{
vec.push_back(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
//2.前后指针 重新排链表
int i = 1, j = vec.size() - 1;
int count = 0;//统计奇偶数
cur = head;
while(i <= j)
{
if(count % 2 == 0)
{
cur->next = vec[j];
i--;
}
else
{
cur->next = vec[i];
i++;
}
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
cur->next = nullptr;
}
};
双队列
把链表放进双向队列,然后通过双向队列一前一后弹出数据,来构造新的链表。这种方法比操作数组容易一些,不用双指针模拟一前一后了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
//方法2 两头队列模拟
ListNode* cur = head;
deque<ListNode*> que;
if(cur==nullptr) return;
while(cur->next != nullptr)
{
que.push_back(cur->next);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
ListNode* temp;//获取队列节点
int count = 0;
while(que.size())
{
//偶数获取队列尾部节点
if(count % 2 == 0)
{
temp = que.back();
que.pop_back();
}
else
{
temp = que.front();
que.pop_front();
}
cur->next = temp;//连接
count++;
cur = cur->next;//cur更新
}
cur->next = nullptr;
}
};
反转和插入链表
将链表分割成两个链表,然后把第二个链表反转,之后在通过两个链表拼接成新的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
//方法2 链表
//1.分割链表 快慢指针
//如果链表长度是奇数 head1长度比head2多一个
if(head == nullptr) return;
ListNode* slow = head;//链表后半段的头部 相当于慢指针
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next && fast->next->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* head1 = head;//前半部分
ListNode* head2 = slow->next;//后半部分
head2 = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;//分割链表
//2.反转链表
head2 = reverseList(head2);
//3.合并链表
ListNode* cur1 = head1;
ListNode* cur2 = head2;
ListNode* cur = head;//合并后链表
cur1 = cur1->next;//第一次写的时候少了这一行
int count = 0;
while(cur1 && cur2)
{
//奇数取cur1 偶数取cur2
if(count % 2 == 0)
{
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
//4.结尾处理 先连接偶数再连接奇数节点
//如果长度是奇数最后一个肯定是奇数节点结尾
if (cur2 != nullptr) cur->next = cur2;
if(cur1 != nullptr) cur->next = cur1;
}
private:
//反转链表
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* temp;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;//反转
pre = cur;//先更新pre
cur = temp;//再更新cur
}
return pre;
}
};
141. 环形链表

快慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步, 相遇则说明有环
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
int result = 0;
if(head == nullptr) return result;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
142.环形链表II
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)//有环 找入口
{
ListNode* cur = slow;
ListNode* entrance = head;
//不相等一直更新
while(cur != entrance)
{
cur = cur->next;
entrance = entrance->next;
}
return entrance;//相等 返回环入口
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
160.链表相交
面试题 02.07. 链表相交

两个链表统计长度,保证两个指针在同一个起点同时移动
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int countList(ListNode* head)
{
int len = 0;
while(head)
{
head = head->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
//1.统计长度
int lena = countList(headA);
int lenb = countList(headB);
//2.让headA为长链表
if(lena < lenb) swap(headA, headB);
//3.长链表的节点先移动
int len = (lena < lenb) ? (lenb - lena) : (lena - lenb);
ListNode* cura = headA;
ListNode* curb = headB;
while(len--)
{
cura = cura->next;
}
while(cura && curb)
{
if(cura == curb) return cura;
cura = cura->next;
curb = curb->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};