文章目录
- 一、硬件准备
- 1.1 DFRobot RGB多彩发光板
- 1.2 龙芯2K0500开发板
- 二、背景知识
- 三、实现点灯
- 3.1 手动点亮
- 3.2 手动熄灭
- 3.3 实现PwmController
- 3.4 实现呼吸灯效果
- 四、效果演示
- 五、完整代码
- 六、参考链接
前段时间乔帮主送了几个DFRobot的RGB多彩发光板,官方的演示视频看起来很绚丽,今天准备用龙芯开发板点亮这个RGB多彩发光板,实现炫彩呼吸灯。
本文接下来将会介绍——如何使用Linux系统在龙芯2K0500先锋板上,输出PWM方波点亮多彩LED发光板。本文介绍的发方法同样可以用于控制LED的亮度、三色LED的亮度、控制舵机旋转角度等其他使用PWM信号驱动的外设。
一、硬件准备
本文所需硬件包括:
- 龙芯2K500先锋板
- DFRobot RGB多彩发光板
1.1 DFRobot RGB多彩发光板
多彩发光板长这样:

多彩发光板引脚说明:

内部是三个共阳极的发光二极管,和三色LED很相似。
1.2 龙芯2K0500开发板
龙芯2K0500开发板的IO扩展口上预留了PWM的引脚,具体如下图:
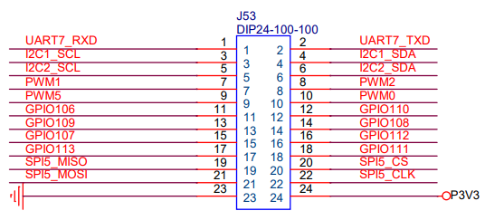
这里使用PWM0、PWM1、PWM2三个引脚连接到多彩发光板,连接关系如下:
- 10号针(PWM0)连接到 多彩发光板的R脚;
- 7号针(PWM1)连接到 多彩发光板的G脚;
- 8号针(PWM2)连接到 多彩发光板的B脚;
- 24号针(P3V3)连接到 多彩发光板的**+脚**;
二、背景知识
开始之前,先简单介绍一点背景知识。这里主要参考的是Linux内核文档《Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) interface》。
以下是用户层sysfs接口一段文档的翻译(PS:水平有限,如有错误,烦请指正):
用户空间通过sysfs来使用pwm功能,相关文件都暴露在 /sys/class/pwm/ 目录下。主芯片(我们这里的龙芯2K0500)的每个PWM控制器体现为pwmchipN目录(其中N是主芯片的第几个PWM控制器),这个目录里面会有:
- npwm 表示这个PWM控制器有几个通道(只读的)
- export 用于将一个PWM通道导出到sysfs(只写的,PS:导出之后才有pwm0之类的子目录,如果导出0的话);
- unexport 用于将PWM通道的sysfs目录隐藏;
PWM通道的数字是,从0开始到npwm-1;
当一个PWM通道导出后,pwmX目录将会在pwmchipN目录下被创建,X就是导出的PWM通道编号;同时伴随着以下属性可用:
- period PWM信号的总周期(可读可写)。它的值是纳秒为单位的并且是PWM一整个周期的时间(包括active和inactive的);
- duty_cycle PWM信号的active状态的时间(可读可写);也是纳秒为单位,并且必须小于period的值;
- polarity 用于改变PWM信号的极性(可读可写);写这个属性仅在PWM芯片支持修改时才有用(work),polarity只能在PWM还没有使能时修改。值是字符串“normal”或者“inversed”;
- enable 启用或禁用PWM信号(可读可写);
- 0 禁用
- 1 启用
三、实现点灯
有了以上知识,我们就可以在龙芯2K0500开发板上使用PWM点亮多彩发光板了。
3.1 手动点亮
开机后,在shell中使用ls命令查看/sys/class/pwm目录:
# ls /sys/class/pwm/
pwmchip0 pwmchip1 pwmchip2 pwmchip3 pwmchip4 pwmchip5
#
跳转到 /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0 目录,查看文件:
# cd /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/
#
# ls
device export npwm power subsystem uevent unexport
#
向export写入0之后,查看:
# echo 0 > export
#
# ls -al
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:20 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:20 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:21 device -> ../../../1ff5c000.pwm
--w------- 1 root root 16384 2022-06-01 10:24 export
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 16384 2022-06-01 10:21 npwm
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:20 power
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:24 pwm0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2022-06-01 10:21 subsystem -> ../../../../../../class/pwm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 16384 2022-06-01 10:20 uevent
--w------- 1 root root 16384 2022-06-01 10:24 unexport
#
可以看到,多出来一个pwm0目录;
跳转到pwm0目录后,使用echo分别写文件:
# echo 1000000000 > period
#
# echo 500000000 > duty_cycle
#
# echo 1 > enable
#
此时将会看到多彩发光板红色闪烁,频率为每秒一次。
这里写入的period值1000000000,产生的PWM信号周期正好是1秒(纳秒为单位),duty_cycle值500000000是它的一半,方便观察。
3.2 手动熄灭
类似的,使用echo也可以停止PWM信号,从而熄灭多彩发光板;
# echo 0 > enable
类似的,向duty_cycle写入其他值,可以改变PWM信号的占空比:
# echo 100000000 > duty_cycle
# echo 1 > enable
3.3 实现PwmController
有了上面的实验,我们就可以实现用代码控制输出PWM信号了。
class PwmController
{
public:
PwmController(int chip, int chan = 0) : chip_(chip)
{
Export(true);
}
~PwmController()
{
Export(false);
}
bool Start()
{
return Enable(true);
}
bool Stop()
{
return Enable(false);
}
bool SetFreq(int freq)
{
if (freq <= 0)
{
return false;
}
period_ = 1000000000uL / freq;
return WriteInt(periodPath_, period_);
}
bool SetDuty(float percent)
{
if (percent <= 0 || period_ <= 0)
{
return false;
}
int dutyCycle = period_ * (percent / 100.0f);
return WriteInt(dutyCyclePath_, dutyCycle);
}
private:
static bool WriteInt(const std::string &path, int value)
{
int fd = open(path.c_str(), O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s failed: %s!\n", path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
return false;
}
std::string str = std::to_string(value);
if (write(fd, str.data(), str.size()) < 0)
{
printf("write %d to %s failed: %s\n", value, path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
}
if (close(fd) < 0)
{
printf("close %s failed: %s\n", path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
return false;
}
// printf("write %d to %s: OK!\n", value, path.c_str());
return true;
}
bool Prepare()
{
if (chip_ < 0)
{
return false;
}
if (perpared_)
{
return true;
}
std::string path = "/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip" + std::to_string(chip_);
exportPath_ = path + "/export";
unexportPath_ = path + "/unexport";
path += "/pwm" + std::to_string(chan_);
enablePath_ = path + "/enable";
periodPath_ = path + "/period";
dutyCyclePath_ = path + "/duty_cycle";
perpared_ = true;
return true;
}
bool Export(bool on)
{
if (!Prepare())
{
return false;
}
return WriteInt(on ? exportPath_ : unexportPath_, chan_);
}
bool Enable(bool on)
{
if (!Prepare())
{
return false;
}
return WriteInt(enablePath_, on ? 1 : 0);
}
private:
int chip_ = -1;
int chan_ = 0; // 默认只用了 channel 0
int period_ = 0;
bool perpared_ = false;
std::string exportPath_;
std::string unexportPath_;
std::string enablePath_;
std::string periodPath_;
std::string dutyCyclePath_;
};
这里实现了一个通用的PwmController类,可以非常方便的操作一个PWM芯片的某个通道。
3.4 实现呼吸灯效果
使用上面的PwmController可以非常方便的实现呼吸灯效果,代码如下:
void TestPwm1(int id)
{
PwmController pwm(id);
printf("pwm%d test start ...\n", id);
pwm.SetFreq(100);
pwm.Start();
printf("pwm%d duty ratio up ...\n", id);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
pwm.SetDuty(i);
usleep(10 * 1000);
}
printf("pwm%d duty ratio down ...\n", id);
for (int i = 100; i >= 0; i--)
{
pwm.SetDuty(i);
usleep(10 * 1000);
}
pwm.Stop();
printf("pwm%d test done!\n", id);
}
这段代码中,第一个for循环逐渐增加PWM占空比,实现亮度递增,第二个循环实现逐渐降低PWM占空比,亮度递减。
四、效果演示
这里是使用上面的TestPwm1函数,分别控制多彩发光板红、绿、蓝颜色的代码:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
TestPwm1(0);
TestPwm1(1);
TestPwm1(2);
return 0;
}
演示效果见本贴末尾视频。
五、完整代码
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
class PwmController
{
public:
PwmController(int chip, int chan = 0) : chip_(chip)
{
Export(true);
}
~PwmController()
{
Export(false);
}
bool Start()
{
return Enable(true);
}
bool Stop()
{
return Enable(false);
}
bool SetFreq(int freq)
{
if (freq <= 0)
{
return false;
}
period_ = 1000000000uL / freq;
return WriteInt(periodPath_, period_);
}
bool SetDuty(float percent)
{
if (percent <= 0 || period_ <= 0)
{
return false;
}
int dutyCycle = period_ * (percent / 100.0f);
return WriteInt(dutyCyclePath_, dutyCycle);
}
private:
static bool WriteInt(const std::string &path, int value)
{
int fd = open(path.c_str(), O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s failed: %s!\n", path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
return false;
}
std::string str = std::to_string(value);
if (write(fd, str.data(), str.size()) < 0)
{
printf("write %d to %s failed: %s\n", value, path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
}
if (close(fd) < 0)
{
printf("close %s failed: %s\n", path.c_str(), strerror(errno));
return false;
}
// printf("write %d to %s: OK!\n", value, path.c_str());
return true;
}
bool Prepare()
{
if (chip_ < 0)
{
return false;
}
if (perpared_)
{
return true;
}
std::string path = "/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip" + std::to_string(chip_);
exportPath_ = path + "/export";
unexportPath_ = path + "/unexport";
path += "/pwm" + std::to_string(chan_);
enablePath_ = path + "/enable";
periodPath_ = path + "/period";
dutyCyclePath_ = path + "/duty_cycle";
perpared_ = true;
return true;
}
bool Export(bool on)
{
if (!Prepare())
{
return false;
}
return WriteInt(on ? exportPath_ : unexportPath_, chan_);
}
bool Enable(bool on)
{
if (!Prepare())
{
return false;
}
return WriteInt(enablePath_, on ? 1 : 0);
}
private:
int chip_ = -1;
int chan_ = 0; // 默认只用了 channel 0
int period_ = 0;
bool perpared_ = false;
std::string exportPath_;
std::string unexportPath_;
std::string enablePath_;
std::string periodPath_;
std::string dutyCyclePath_;
};
void TestPwm1(int id)
{
PwmController pwm(id);
printf("pwm%d test start ...\n", id);
pwm.SetFreq(100);
pwm.Start();
printf("pwm%d duty ratio up ...\n", id);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
pwm.SetDuty(i);
usleep(10 * 1000);
}
printf("pwm%d duty ratio down ...\n", id);
for (int i = 100; i >= 0; i--)
{
pwm.SetDuty(i);
usleep(10 * 1000);
}
pwm.Stop();
printf("pwm%d test done!\n", id);
}
void TestPwm2(int id1, int id2)
{
PwmController pwm1(id1);
PwmController pwm2(id2);
printf("pwm%d,%d test start ...\n", id1, id2);
pwm1.SetFreq(10000);
pwm1.Start();
pwm2.SetFreq(10000);
pwm2.Start();
for (int i = -100; i <= 100; i += 10) {
pwm1.SetDuty(100 - std::abs(i));
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
pwm2.SetDuty(j);
usleep(10*1000);
}
for (int j = 100; j >= 0; j--) {
pwm2.SetDuty(j);
usleep(10*1000);
}
}
pwm1.Stop();
pwm2.Stop();
printf("pwm%d,%d test done!\n", id1, id2);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ncycle = argc > 1 ? atoi(argv[1]) : 1;
for (int i = 0; i < ncycle; i++)
{
TestPwm1(0);
TestPwm1(1);
TestPwm1(2);
TestPwm2(0, 1); // RG
TestPwm2(0, 2); // RB
TestPwm2(1, 2); // GB
}
return 0;
}
编译命令:
loongarch64-linux-gnu-g++ pwm_rgb_led.cpp -o pwm_test -Wall
将生成的pwm_test通过FTP或者U盘拷贝到龙芯2K0500开发板上之后,运行:
./pwm_test
六、参考链接
- RGB LCD多彩发光板-LED灯-DFRobot创客商城
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) interface — The Linux Kernel documentation