Attachments - The 14th Jilin Provincial Collegiate Programming Contest - Codeforces
目录
Problem A. Chord
Problem B. Problem Select
Problem C. String Game
Problem E. Shorten the Array
Problem F. Queue
Problem G. Matrix
Problem J. Situation
Problem L. Swimmer
Problem A. Chord

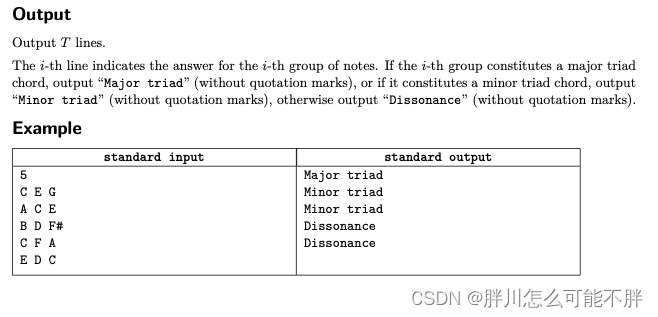
题意:
输入三个音阶,判断在钢琴上俩俩之间差是否满足条件,满足条件输出对应内容
思路:
按照顺序找到位置,由于不一定要一个区域所以+12 再 %12,就能得出差
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
string s[15] = {"C","C#","D","D#","E","F","F#","G","G#","A","A#","B"};
void solve()
{
string s1,s2,s3;
cin >> s1 >> s2 >> s3;
int x,y,z;
rep(i,0,11)
{
if(s[i] == s1) x = i;
}
rep(i,0,11)
{
if(s[i] == s2) y = i;
}
rep(i,0,11)
{
if(s[i] == s3) z = i;
}
// 5
// C E G
// A C E
// cout << x<<' ' << y<<' ' << z<<endl;
if((y-x + 12) % 12==4 && (z-y+12)%12==3)
{
cout<<"Major triad"<<endl;
}else if((y-x + 12) % 12==3 && (z-y+12)%12==4)
{
cout<<"Minor triad"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"Dissonance"<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Problem B. Problem Select

题意:
按照顺序输出前k个数字,数字就是最后的
思路:倒着直接输出
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
void solve()
{
cin>>n>>m;
vector<ll>ve;
rep(i,1,n)
{
string s;
cin>> s;
ll len = s.size();
ll ant= 0;
ll res=1;
per(i,len-1,0)
{
if(s[i]== '/')break;
ant += (s[i] - '0')*res;
res *= 10;
}
ve.push_back(ant);
}
sort(ve.begin(),ve.end());
int flag=0;
for(auto it : ve)
{
cout<<it<<' ';
flag++;
if(flag>=m)break;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Problem C. String Game
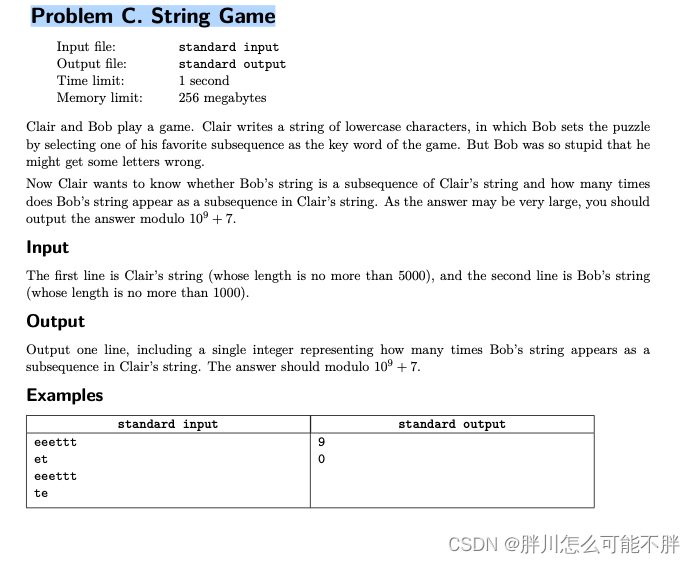
题意:
求有多少种方法是能从母串中得到子串
思路:
dp求方案数:
自前向后遍历s1的字符串
自后向前遍历s2的字符串
dp[j]代表s1前i个字符有dp[j]种子序列等于s2前j个字符
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
//ll dp[5500][1500];
ll dp[5500];
void solve()
{
string s1,s2;
while(cin >> s1 >> s2)
{
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
//cout<<s1 <<endl<<s2<<endl;
//rep(i,0,s1.size()-1)dp[i][0] = 1;
dp[0] = 1;
s1=' '+s1;
s2=' '+s2;
//cout<<s1<<endl<<s2<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=s1.size();i++)
{
for(int j=s2.size() ;j>=1;j--)
{
if(s1[i] == s2[j]) dp[j] = (dp[j] + dp[j-1]) % mod;
//cout<<dp[j]<<endl;
}
}
cout<<dp[s2.size()]<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Problem E. Shorten the Array

题意:
改变数组的长度然后输出最短长度
思路:
先找出数组中的最小元素,然后遍历数组看是否存在一个不是x的倍数的数,如果存在就代表存在 y 满足 gcd( x , y ) ≠ x.那么答案就是 1。
如果不存在,那么答案就是 num(x) / 2 (向上取整)。
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
ll mmin =INF;
rep(i,1,n)
{
cin>> arr[i];
// brr[i] = arr[i];
mmin = min( mmin, arr[i]);
}
//sort(brr+ 1,brr+1+n);
int flag = 0;
ll ant =0;
rep(i,1,n){
if(arr[i] % mmin !=0)
{
flag =1;
//break;
}else if(arr[i] == mmin)
{
ant ++;
}
}
if(flag)
{
cout<<1<<endl;
}else{
cout<<((ant+1)/2)<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Problem F. Queue

题意:
数组中有多少个逆序对,通过m次操作交换l,r之后,过程中逆序对做少是几个
思路:
数组数组求逆序对,同时在交换的过程中遍历交换的区间的逆序对,
(比赛的时候一点没看出来,以为是模拟,还是太菜了)
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
ll lowbit(ll x)
{
return x & (-x);
}
void insert(int x)
{
for(ll i = x;i <= 100000; i += lowbit(i)) ++ brr[i];
}
ll getsum(int x)
{
ll sum = 0;
for(int i = x ; i; i -= lowbit(i))sum += brr[i];
return sum;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
memset(brr,0,sizeof(brr));
rep(i,1,n)cin >> arr[i], ++ arr[i];
ll num = 0;
rep(i,1,n)
{
num += i - 1 - getsum(arr[i]);
insert(arr[i]);
}
cin >> m;
ll ans = num;
while(m--)
{
ll l,r;
cin >> l >> r;
if(arr[l] < arr[r])num++;
if(arr[l] > arr[r])num--;
rep(i,l+1,r-1)
{
if(arr[l] > arr[i])num--;
if(arr[l] < arr[i])num++;
if(arr[r] > arr[i])num++;
if(arr[r] < arr[i])num--;
}
ans = min ( ans, num);
swap(arr[l],arr[r]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Problem G. Matrix

题意:
给你一个矩阵的长和宽,每个格子起始都是0,遍历所有的格子,遍历到格子的坐标为(i,j),就将行为i的倍数,列为j的倍数的格子上的数字进行变化:如果原来是0,变成1,如果原来是1变成0,问你遍历完所有格子后,矩阵中1的个数是多少。
思路:
就。。。。。可奇怪了,多写了几个例子就看出来了,就sqrt(m) * sqrt(n)
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<stack> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<unordered_map> #include<map> #include<cstring> #include <unordered_set> //#include<priority_queue> #include<queue> #include<set> #include<stdlib.h> #define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl; #define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++) #define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--) #define no cout<<"NO"<<endl; #define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl; #define endl "\n" #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); //priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<ll, ll> PII; typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD; ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; //const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX; // int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) // { // return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1); // } const ll N = 2e6+ 10; const ll mod =998244353; ll t,n,m,x,y,ca; ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N]; // int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx; void solve() { cin >> n >>m; cout<<ll(sqrt(n))*ll(sqrt(m))<<endl;; } int main() { IOS; t=1; //scanf("%d",&t); cin>>t; ca=1; while(t--) { solve(); ca++; } return 0; }
Problem J. Situation

题意:
井字游戏,不过是有初始状态的井字游戏,
先输入一个op,1表示是Alice先下,0表示是Bob先下
再输入一个3 * 3的初始状态的矩阵,.代表还没下,O是Alice下的,X表示是Bob下的
矩阵的最终价值是O的数量减去X的数量,Alice希望这个值尽可能大,Bob希望这个值尽可能小,两个人都聪明秃顶,问最终的价值是多少
思路:
佬那里学来的博弈树,我自己没写出来(还是太菜了)
对抗搜索的经典题目,使用min-max搜索
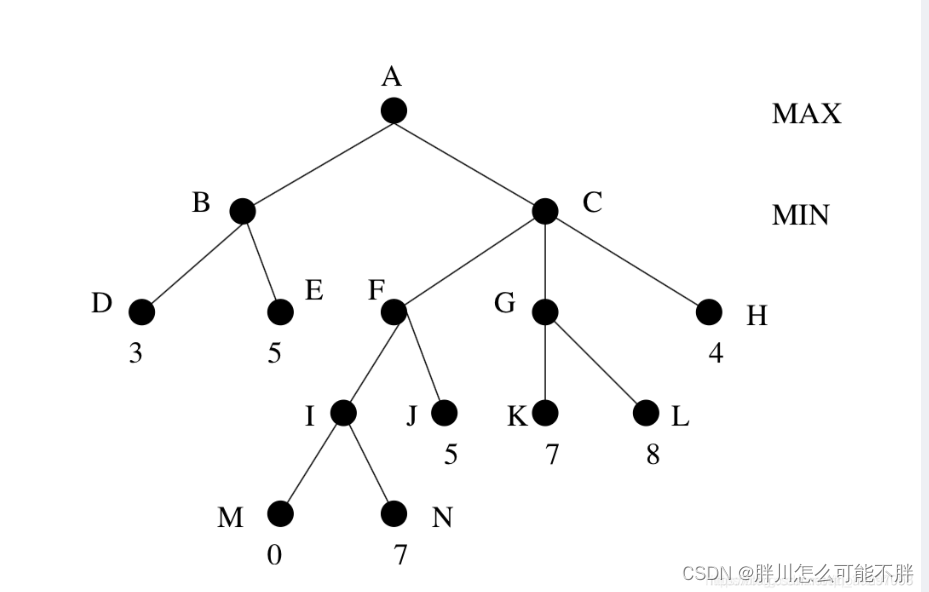
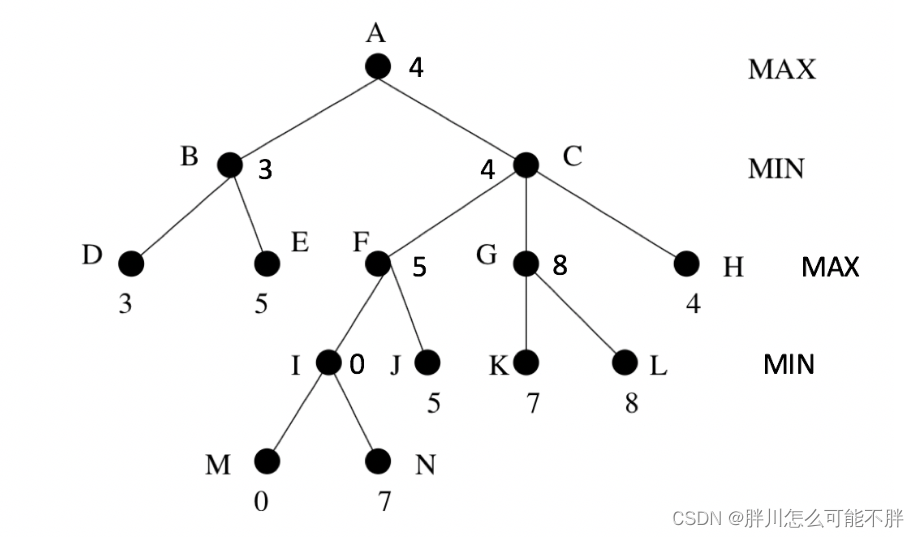
什么是最小最大搜索?就是在决策双方一个希望终值尽可能大,一个希望终值尽可能小的情况下,建立出一棵博弈树,根据子节点的值来确定父节点的值,如下:
从上往下,单数层是我方行动,双数层是对方行动,我方行动需要选择对我最有利的行动,即value大的行动,对方行动则是选择使我方最不利的行动,即value小的行动。
我们需要从最底层第四层开始考虑,双数层所以是对方行动。对于node I,会选择值更小的node M,node I的值更新为0。再考虑第三层,单数层是我方行动。node F会选择I,J中值更大的J,更新为5,G会选择K,L中值更大的L,更新为8。依次一层层向上类推,可以得到最终结果为:
所以这个题,我们可以枚举每个点放O还是X,来获得博弈树,来得到最终答案
因为有T组数组,我们可以开一个记忆化数组记录状态,将3*3的字符数组进行哈希后作为数组的第一维,第二维度记录当前是谁决策
其他的就去爆搜
佬玛
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
#define m_p(a,b) make_pair(a, b)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define debug(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n";
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair <int,int> pii;
#define MAX 300000 + 50
int n, m, k;
struct ran{
char tr[5][5];
int gethaxi(){
int haxi = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j){
if(tr[i][j] == '.')haxi = haxi * 3;
else if(tr[i][j] == 'O')haxi = haxi * 3 + 1;
else haxi = haxi * 3 + 2;
}
}
return haxi;
}
int fuck(){
int ans = 0;
if(tr[1][1] == tr[1][2] && tr[1][2] == tr[1][3] ){
if(tr[1][1] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[2][1] == tr[2][2] && tr[2][2] == tr[2][3]){
if(tr[2][1] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[3][1] == tr[3][2] && tr[3][2] == tr[3][3]){
if(tr[3][1] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[1][1] == tr[2][1] && tr[3][1] == tr[1][1] ){
if(tr[1][1] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[1][2] == tr[2][2] && tr[3][2] == tr[1][2] ){
if(tr[1][2] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[1][3] == tr[2][3] && tr[3][3] == tr[1][3] ){
if(tr[1][3] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[1][1] == tr[2][2] && tr[2][2] == tr[3][3]){
if(tr[1][1] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
if(tr[2][2] == tr[1][3] && tr[2][2] == tr[3][1]){
if(tr[2][2] == 'O')++ans;
else --ans;
}
return ans;
}
bool judge(){
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j){
if(tr[i][j] == '.')return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
int dp[MAX][2];
int dfs(ran now, int op){
int haxi = now.gethaxi();
// cout << haxi << endl;
if(dp[haxi][op] != -inf)return dp[haxi][op];
if(!now.judge())return now.fuck();
if(op){//max
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j){
if(now.tr[i][j] == '.'){
ran nex = now;
nex.tr[i][j] = 'O';
dp[haxi][op] = max(dp[haxi][op], dfs(nex, 1 - op));
}
}
}
}
else{
dp[haxi][op] = inf;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j){
if(now.tr[i][j] == '.'){
ran nex = now;
nex.tr[i][j] = 'X';
dp[haxi][op] = min(dp[haxi][op], dfs(nex, 1 - op));
}
}
}
}
return dp[haxi][op];
}
void work(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 100000; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j <= 1; ++j){
dp[i][j] = -inf;
}
}
int t;cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int op;cin >> op;
ran p;
scanf("%s%s%s", p.tr[1]+1, p.tr[2]+1, p.tr[3]+1);
cout << dfs(p, op) << endl;
}
}
int main(){
work();
return 0;
}
Problem L. Swimmer

思路:
泳池一来回算一个行程,然后和泳池长度比较即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
void solve()
{
ll q;
cin >> n >> m >> q;
rep(i,1, n)
{
cin>>arr[i];
}
while(q--)
{
ll time;
ll op;
cin >>time>> op;
ll cnt = (time*arr[op]) % (2 * m);
if(cnt > m)cnt = 2 * m - cnt;
cout<<cnt<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}