目录
八、MyBatis小技巧
8.1#{}和${}
8.2别名机制:typeAliases
8.3mappers
编辑
8.4IDEA配置文件模板
8.5插入数据时获取自动生成的主键
九、MyBatis参数处理
9.1单个简单参数类型
9.2Map参数
9.3实体类参数
9.4多参数
9.5@Param注解(命名参数)
9.6@Param源码分析
八、MyBatis小技巧
8.1#{}和${}
#{}和${}的区别
-
#{}:底层使用PreparedStatement。特点:先进行SQL语句的编译,然后给SQL语句的占位符?传值,可以避免SQL注入的风险。
-
${}:底层使用Statement。特点:先进行SQL语句的拼接,然后再对SQL语句进行编译。存在SQL注入的风险。
-
如果需要SQL语句的关键字放入SQL语句中,只用使用${},因为#{}是以值的形式放到SQL语句当中的。例如:
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
order by produce_time ${AscOrDesc};拼接表名
-
业务背景:实际开发中,有的表数据量非常庞大,可能会采用分表方式进行存储,比如每天生成一张表,表的名字与日期挂钩,例如:2022年8⽉1⽇⽣成的表:t_log_20220801。
-
使用#{}:
select * from 't_log_20220801' -
使用${}:
select * from t_log_20220801 -
正确形式:
<select id="selectAllByTable" resultType="com.hhb.pojo.Log"> select * from t_log_${date} </select>
批量删除
-
对应的sql语句:
-
delete from t_car where id=1 or id=2 or id=3;
-
delete from t_car where id in(1,2,3)
-
-
使用#{}:
delete from t_car where id in('1,2,3');-
执行错误:1292 - Truncated incorrect DOUBLE value: '1,2,3'
-
-
使用${}:
delete from t_user where id in(1, 2, 3); -
delete from t_car where id in(${ids})
模糊查询:like
-
对应的sql语句:
-
select * from t_car where brand like '%奔驰%';
-
-
第一张方案:
-
'%${brand}%'
-
-
第二种方案:concat函数,这个是mysql数据库中的一个函数,专门进行字符串拼接
-
concat('%',#{brand},'%')
-
-
第三种方案:
-
concat('%','${brand}','%')
-
-
第四种方案:常用
-
"%"#{brand}"%"
-
8.2别名机制:typeAliases
<typeAliases>
<!--别名自己指定的-->
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="aaa"/>
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" alias="bbb"/>
<!--采用默认的别名机制-->
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"/>
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log"/>
<!--包下所有的类自动起别名。使用简名作为别名。-->
<package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>所有别名不区分大小写。 namespace不能使用别名机制。
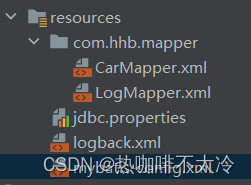
8.3mappers
resource
<mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/>
这种方式是从类的根路径下开始查找资源,要求类的根路径下必须有:CarMapper.xml。
url
<mapper url="file:///d:/CarMapper.xml"/>
这种方式是一种绝对路径的方式,这种方式不要求配置文件必须放到类路径当中,哪里都行,只要提供一个绝对路径就行,这种方式极少使用,因为移植性太差。
class
<mapper class="com.hhb.mapper.CarMapper"/>
-
这种方式class中提供的是mapper接口的全限定接口名,必须带有包名。
-
使用这种方式的前提:CarMapper.xml文件的位置不能随便放,必须和CarMapper接口放在一起,XML文件的名字必须和接口一致。
<package name="com.hhb.mapper"/>
-
这种方式是实际开发中使用的。
-
使用这种方式的前提:CarMapper.xml文件的位置不能随便放,必须和CarMapper接口放在一起,XML文件的名字必须和接口一致。
-
注意:在IDEA的resources目录下新建多重目录的话,必须这样创建:
com/hhb/mapper,不能这样创建:com.hhb.mapper
8.4IDEA配置文件模板
mybatis-config.xml和SqlMapper.xml⽂件可以在IDEA中提前创建好模板,以后通过模板创建配置⽂件。

8.5插入数据时获取自动生成的主键
<insert id="insertCarUseGeneratedKeys" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
</insert>-
useGeneratedKeys="true":使用自动生成的主键值
-
keyProperty="id":指定主键值赋给对象的哪个属性,这个就表示将主键值赋值给Car对象的id属性。
九、MyBatis参数处理
9.1单个简单参数类型
-
简单类型包括:
-
byte short int long float double char
-
Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Character
-
String
-
java.util.Date
-
java.sql.Date
-
<select id="selectByName" resultType="student" parameterType="java.lang.String">
select * from t_student where name = #{name, javaType=String, jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</select>-
sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,parameterType属性都是用来帮助mybatis进行类型确定的,不过这些配置多数是可以省略的,因为mybatis它有强大的自动类型推断机制。
-
如果参数只有一个的话,#{}里面的内容可以随便写。
9.2Map参数
-
需求:插⼊⼀条Student数据
StudentMapper.xml
<!--<insert id="insertStudentByMap" parameterType="map">-->
<insert id="insertStudentByMap">
insert into t_student(id, name, age, height, birth, sex)
values (null, #{姓名}, #{年龄}, #{身高}, #{日期}, #{性别});
</insert>StudentMapperTest
@Test
public void testInsertStudentByMap() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("姓名","赵云");
map.put("年龄",25);
map.put("身高",186.0);
map.put("日期",new Date());
map.put("性别","男");
int count = mapper.insertStudentByMap(map);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}-
sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,parameterType属性可以省略。
-
insert语句中的value值必须是map中的key值。
9.3实体类参数
-
需求:插⼊⼀条Student数据
StudentMapper.xml
<!--<insert id="insertStudentByPojo" parameterType="student">-->
<insert id="insertStudentByPojo">
insert into t_student(id, name, age, height, birth, sex)
values (null, #{name}, #{age}, #{height}, #{birth}, #{sex});
</insert>StudentMapperTest
@Test
public void testInsertStudentByPojo() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student(null, "刘备", 36, 180.0, new Date(), '男');
int count = mapper.insertStudentByPojo(student);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}-
sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,parameterType属性可以省略。
9.4多参数
-
需求:根据学生姓名和性别进行查询
StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student">
select *
from t_student
where name = #{arg0}
and sex = #{arg1};
</select>-
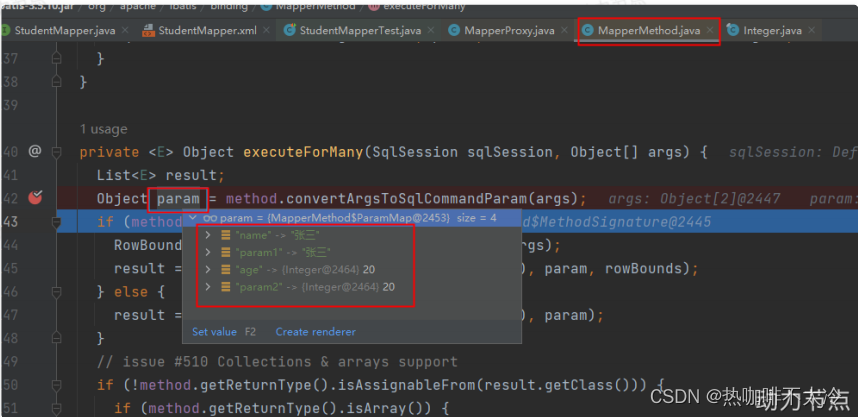
这是多参数,mybatis框架会自动创建一个map集合,并且将map集合以如下方式存储:
map.put("arg0", name); map.put("arg1", sex); map.put("param1", name); map.put("param2", sex); -
低版本的mybatis中,使用的是:#{0}和#{1}...
-
高版本的mybatis中,使用的是:#{arg0}和#{arg1}...或者:#{param1}和#{param2}...两者可以混合使用。
StudentMapperTest
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndSex() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex("张三", "男");
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}9.5@Param注解(命名参数)
-
需求:根据学生姓名和性别进行查询。
-
使用@param注解增强可读性。
StudentMapper
List<Student> selectByNameAndSex2(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") Character sex);
-
核心:@Param("这里填写的其实是map集合的key")。
StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndSex2" resultType="student">
select *
from t_student
where name = #{name}
and sex = #{sex};
</select>9.6@Param源码分析