Java压缩图片以及获取缩略图
- 前言
- 使用到的类
- Toolkit
- MediaTracker
- Image
- BufferedImage
- ImageWriter
- ImageIO
- ImageWriteParam
- Graphics2D
- 工具类ImageUtil
- 测试
- 测试代码
- 测试结果
- 遇到的问题
前言
这个应该就没啥多说的了,接触过图片操作的基本都知道上述功能为常用功能。
原因有两个:
服务器存储空间有限,除开部分特殊图片(比如医院的一些检查图片,壁纸网站的原图),基本不需要存储特别清晰的原图。比如我的服务器上原本存储原图只能存储1000张,但是现在我在上传时,对上传图片进行压缩,能压缩到原来的一半大小(并不绝对,有的可能压缩后图像更大),存储压缩后的图片可以来到2000张。网页加载时不加载原图,而是加载缩略图。这就很简单了,服务器带宽有限,如果每个原图十几M,那一个首页如果存在十几张图加载速度就非常非常慢了。
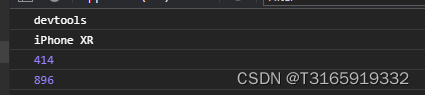
以WallHaven举例,WallHaven首页上展示的图片大小仅仅只有29K
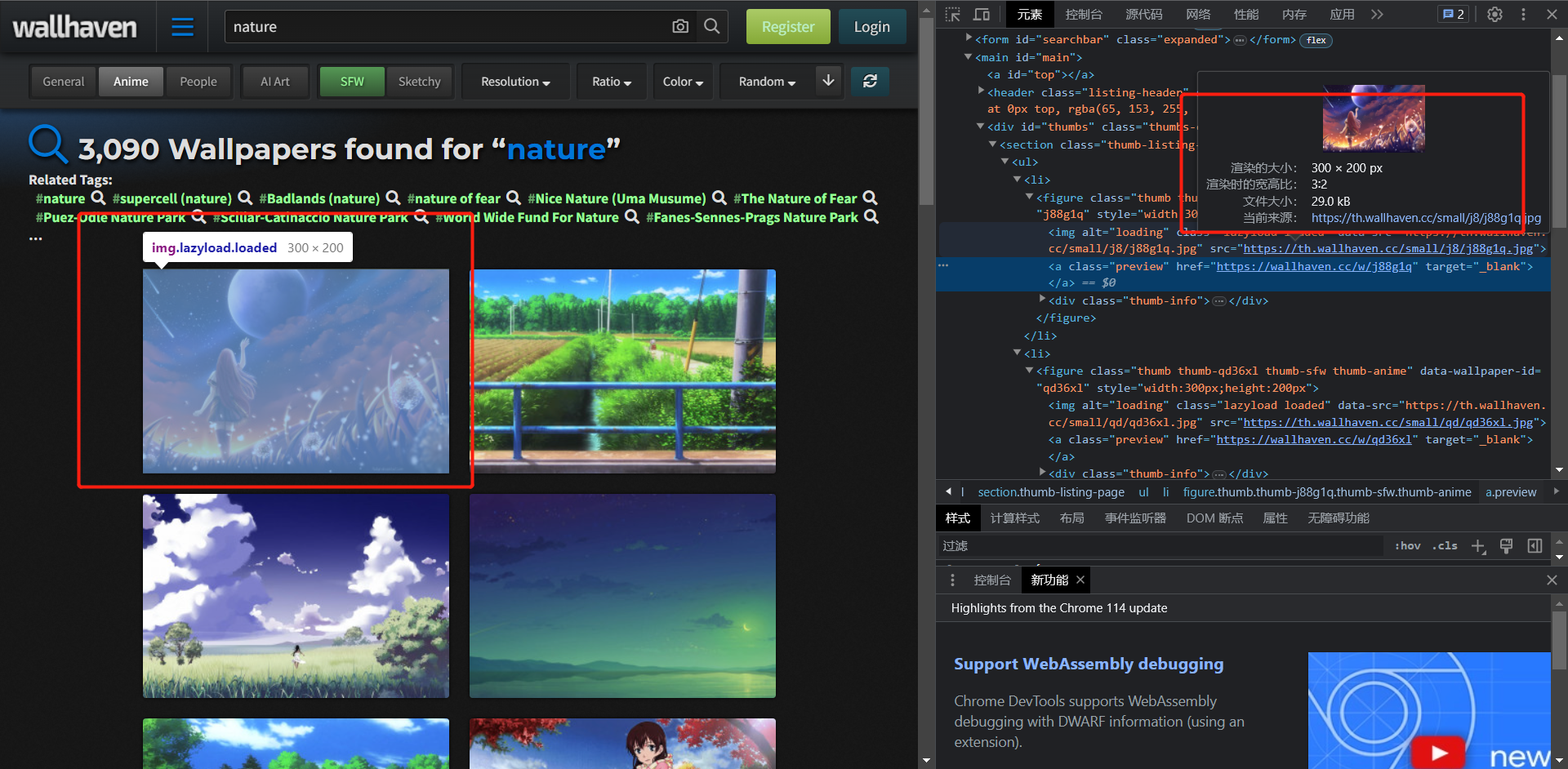
但详情页中的原图大小将近17M:
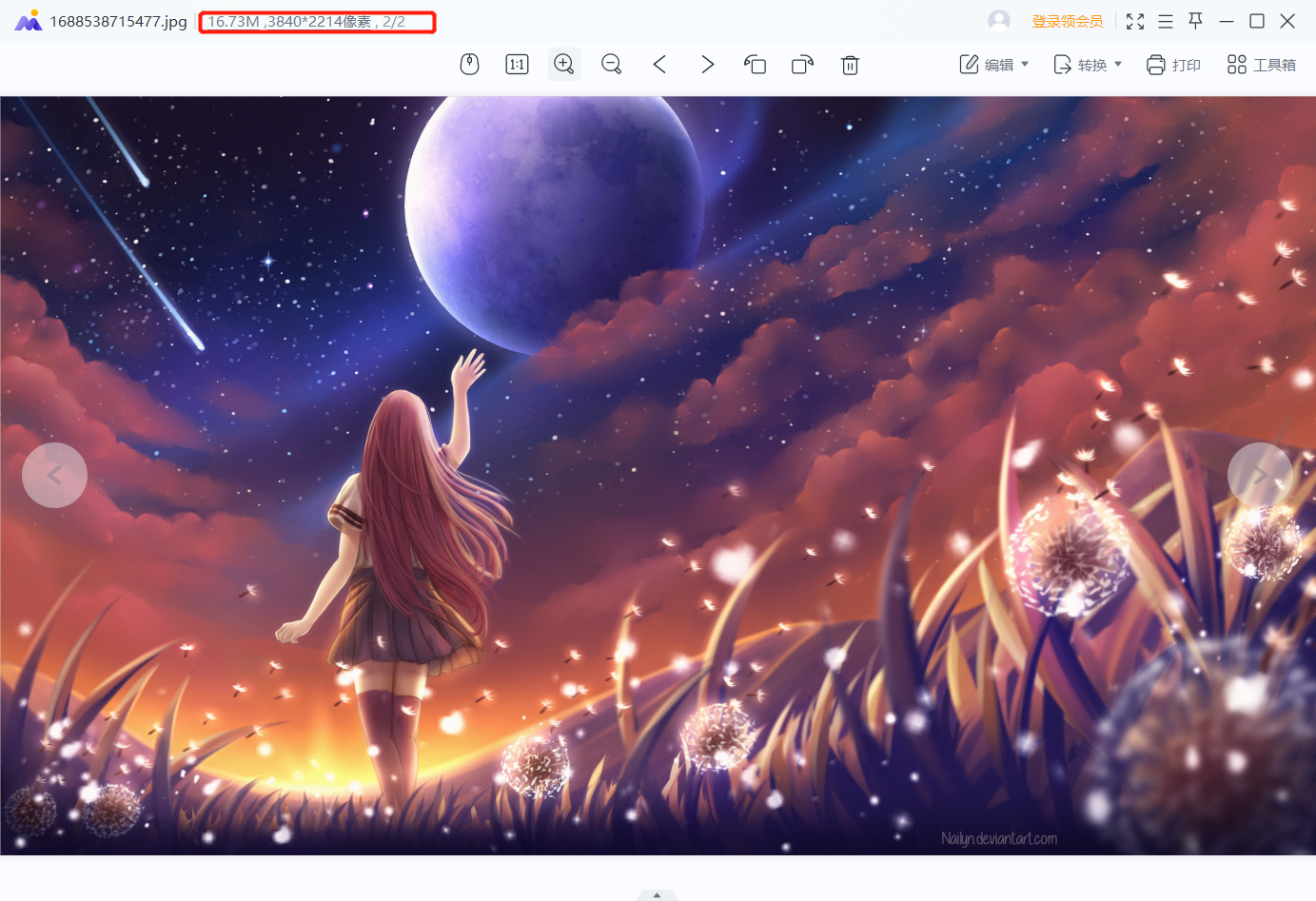
可想而知,如果全部加载原图到首页响应会有多慢,但是加载缩略图就会很快,因为一张可能只需要几十K。
使用到的类
以下是本工具类–ImageUtil:用于压缩图片以及生成缩略图,用到的一些类的简单介绍,具体信息请参见JavaDoc
Toolkit
在本文中主要用于获取图像资源。
Toolkit类的主要作用是提供了访问与本机窗口系统交互的方法,以及访问与窗口系统相关的资源和功能。
MediaTracker
在本文中主要用于确保图像加载完成。
MediaTracker类的主要作用是确保媒体资源完全加载后再进行使用,以避免在资源未完全加载时显示空白或错误的情况。它提供了一种简单的方式来跟踪媒体资源的加载过程,并在资源加载完成后进行通知。
Image
一个抽象类,它用于表示图像对象,并提供了基本的图像处理和显示功能。
BufferedImage
用于操作图像数据的类,它是Image类的一个子类,提供了更高级和灵活的图像操作功能。
ImageWriter
在本文中用于将生成的图像写出成图片文件。
ImageWriter类的主要功能是将图像数据写入到特定的图像文件格式中,如JPEG、PNG、GIF等。它提供了一些方法和参数,以控制图像编码的细节和选项。
ImageIO
它是Java Image I/O框架的一部分,提供了方便的方法来读取和写出图像文件。
ImageWriteParam
ImageWriteParam类的主要功能是允许开发人员设置图像写出过程中的一些参数,以控制图像的压缩质量、图像格式、元数据等细节。
Graphics2D
可以理解为画笔,用于绘制图像
它是Graphics类的子类,提供了更强大和灵活的绘图功能。
工具类ImageUtil
import io.jsonwebtoken.lang.Assert;
import javax.imageio.IIOImage;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.imageio.ImageWriteParam;
import javax.imageio.ImageWriter;
import javax.imageio.stream.ImageOutputStream;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @Description 用于有损压缩图片以及获取缩略图
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Data 2023/7/5 10:02
*/
public class ImageUtil {
/**
* @Description 以JPEG格式压缩图片
* @Param inputImage 输入的图片
* @Param outputImage 输出的图片
* @Return boolean 压缩成功则返回true 否则返回false
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:04
**/
public static boolean compressWithJPEG (String inputPath , String outputPath) {
File inputImage = new File(inputPath);
File outputImage = new File(outputPath);
//图像的输出流
ImageOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
//防止红色调 不再使用ImageIO.read()读取
//getImage方法读取方式为异步读取 所以需要媒体跟踪器确保图片加载完成
Image image1 = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().
getImage(inputImage.getAbsolutePath());
//媒体跟踪对象 用来跟踪图片的加载状态
MediaTracker mediaTracker = new MediaTracker(new Component() {});
//跟踪当前图片
mediaTracker.addImage(image1, 0);
//等待图片加载完成才能执行后续操作
mediaTracker.waitForAll();
//将Image对象转为BufferedImage对象便于后续操作
BufferedImage image = toBufferedImage(image1);
//获取JPEG格式的ImageWriter 来实现压缩 用于写出图片
ImageWriter writer = ImageIO.getImageWritersByFormatName("jpeg").next();
//创建ImageWriteParam 并设置压缩参数
ImageWriteParam param = writer.getDefaultWriteParam();
//设置压缩模式为有损压缩
param.setCompressionMode(ImageWriteParam.MODE_EXPLICIT);
//以最高质量压缩 0.0 - 1.0之间
param.setCompressionQuality(1.0f);
//使用图像文件中的元数据来确定是否使用平铺模式
param.setProgressiveMode(ImageWriteParam.MODE_COPY_FROM_METADATA);
//获取一个图像输出流
outputStream = ImageIO.createImageOutputStream(outputImage);
//设置写出的输出流
writer.setOutput(outputStream);
//写出
writer.write(
//图片额外数据为空
null,
new IIOImage(
//基本的image图像
image,
//缩略图为空
null,
//图片额外信息为空
null
),
//压缩参数
param
);
//释放资源
writer.dispose();
return true;
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
} finally {
if(outputStream != null) {
try {
outputStream.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* @Description 将image图像转为BufferedImage操作
* @Param image 需要转换的图像
* @Return {@link BufferedImage}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/4 9:46
**/
public static BufferedImage toBufferedImage(Image image) {
BufferedImage bufferedImage = new BufferedImage(
//传入图像的宽 不设置观察者
image.getWidth(null),
//传入图像的高 不设置观察者
image.getHeight(null),
//RGB颜色
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB
);
//获取用于绘图的画布对象
Graphics2D graphics2D = bufferedImage.createGraphics();
//相当与重新绘制原原图形一次
graphics2D.drawImage(image,
//x轴的开始坐标
0,
//y轴的开始坐标
0,
//观察者
null);
//释放资源
graphics2D.dispose();
return bufferedImage;
}
/**
* @Description 不设置宽高 按照同比例缩放 并且存储缩略图 生成的图片格式默认为jpeg
* @Param inFilePath 需要压缩的图片 路径
* @Param storePath 生成缩略图存储的图片路径
* @Return {@link boolean}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:43
**/
public static boolean storeThumbnailWithImage(
String inFilePath,
String storePath
) {
//默认为宽为500的同比例缩放 格式为jpeg
return storeImage(createThumbnail(inFilePath , 0 , 0),
storePath , "jpeg");
}
/**
* @Description 以指定宽高生成缩略图
* @Param inFilePath 同上
* @Param storePath 同上
* @Param width 缩略图宽度
* @Param height 缩略图高度
* @Return {@link boolean}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:46
**/
public static boolean storeThumbnailWithImage(
String inFilePath,
String storePath,
int width ,
int height
) {
return storeImage(createThumbnail(inFilePath , width , height),
storePath , "jpeg");
}
/**
* @Description 同上
* @Param inFilePath 同上
* @Param storePath 同上
* @Param width 同上
* @Param height 同上
* @Param type 以什么格式生成缩略图 一般是jpg或者jpeg png格式的大小是前者的十倍
* @Return {@link boolean}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:47
**/
public static boolean storeThumbnailWithImage(
String inFilePath,
String storePath,
int width ,
int height ,
String type
) {
return storeImage(createThumbnail(inFilePath , width , height),
storePath , type);
}
/**
* @Description 获取一个缩略图的BufferedImage 宽高决定了图像文件的大小
* @Param filePath 原图像路径
* @Param width 缩略图宽度
* @Param height 缩略图高度
* @Return {@link BufferedImage}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:49
**/
public static BufferedImage createThumbnail (
String filePath,
int width,
int height
) {
try {
//获取一个对应路径的图像
File imageFile = new File(filePath);
//false才触发
Assert.isTrue(imageFile.exists() , "文件不存在!");
BufferedImage originalImage = ImageIO.read(imageFile);
if(width == 0 && height ==0) {
int defaultWidth = 0;
width = originalImage.getWidth();
height = originalImage.getHeight();
if(width > 2000) {
defaultWidth = width/5;
} else if (width >= 1000) {
defaultWidth = width/3;
} else if (width >= 500) {
defaultWidth = width/2;
} else {
defaultWidth = 100;
}
//同比例缩放
height = (int) (((double)height/(double)width)*defaultWidth);
width = defaultWidth;
}
// 创建一个缩略图 BufferedImage 对象
BufferedImage thumbnailImage = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// 使用 Graphics2D 进行绘制操作
Graphics2D graphics2D = thumbnailImage.createGraphics();
//设置渲染提示
graphics2D.setRenderingHint(
//用于在缩放或变换图像时进行像素之间的插值 它影响图像的平滑度和细节保留程度
RenderingHints.KEY_INTERPOLATION,
//该值表示使用双线性插值算法进行图像的插值。双线性插值是一种平滑的插值方法
//会在缩放时通过对周围像素的加权平均来计算新像素的值,以产生更平滑的图像。
RenderingHints.VALUE_INTERPOLATION_BILINEAR
);
//绘制缩略图
graphics2D.drawImage(
//原始图像
originalImage,
//绘制x轴的起点
0,
//y轴起点
0,
//x轴终点
width,
//y轴终点
height,
//观察者设置为空
null
);
//释放画布资源
graphics2D.dispose();
return thumbnailImage;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* @Description 以指定格式写出图像存储到指定路径 文件后缀名最好与存储格式一致
* @Param storeImage 需要存储的图像
* @Param storePath 存储路径
* @Param type 存储格式
* @Return {@link boolean}
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Date 2023/7/5 10:50
**/
public static boolean storeImage(BufferedImage storeImage , String storePath , String type) {
try {
Assert.notNull(storeImage , "图像不能为空!");
File storeFile = new File(storePath);
if(storeFile.exists()) {
Assert.isTrue(storeFile.delete() , "当前文件: "+storePath + " 已存在,且未能删除。");
}
//写出图片到文件 格式为type
ImageIO.write(storeImage, type, storeFile);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
测试
测试代码
/**
* @Description
* @Author 三文鱼先生
* @Data 2023/7/5 14:38
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String inputImagePath = "D:\\testFile\\comperessImage\\origin.png";
String thumbnailPath = "D:\\testFile\\comperessImage\\thumbnail.jpeg";
String compressPath = "D:\\testFile\\comperessImage\\compress.jpeg";
ImageUtil.compressWithJPEG(inputImagePath , compressPath);
ImageUtil.storeThumbnailWithImage(inputImagePath , thumbnailPath);
}
}
测试结果
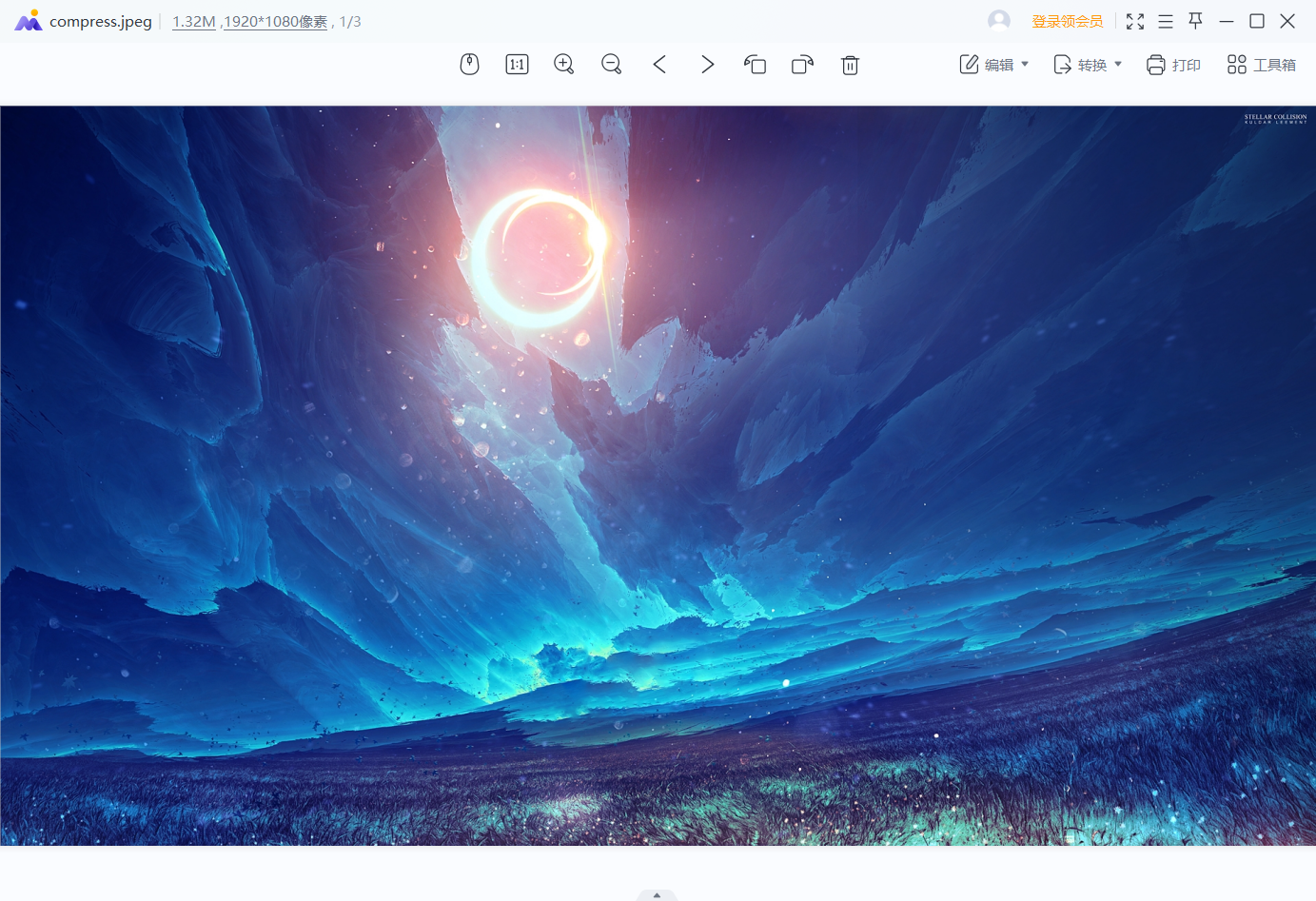
使用的测试图片大小是3.8M
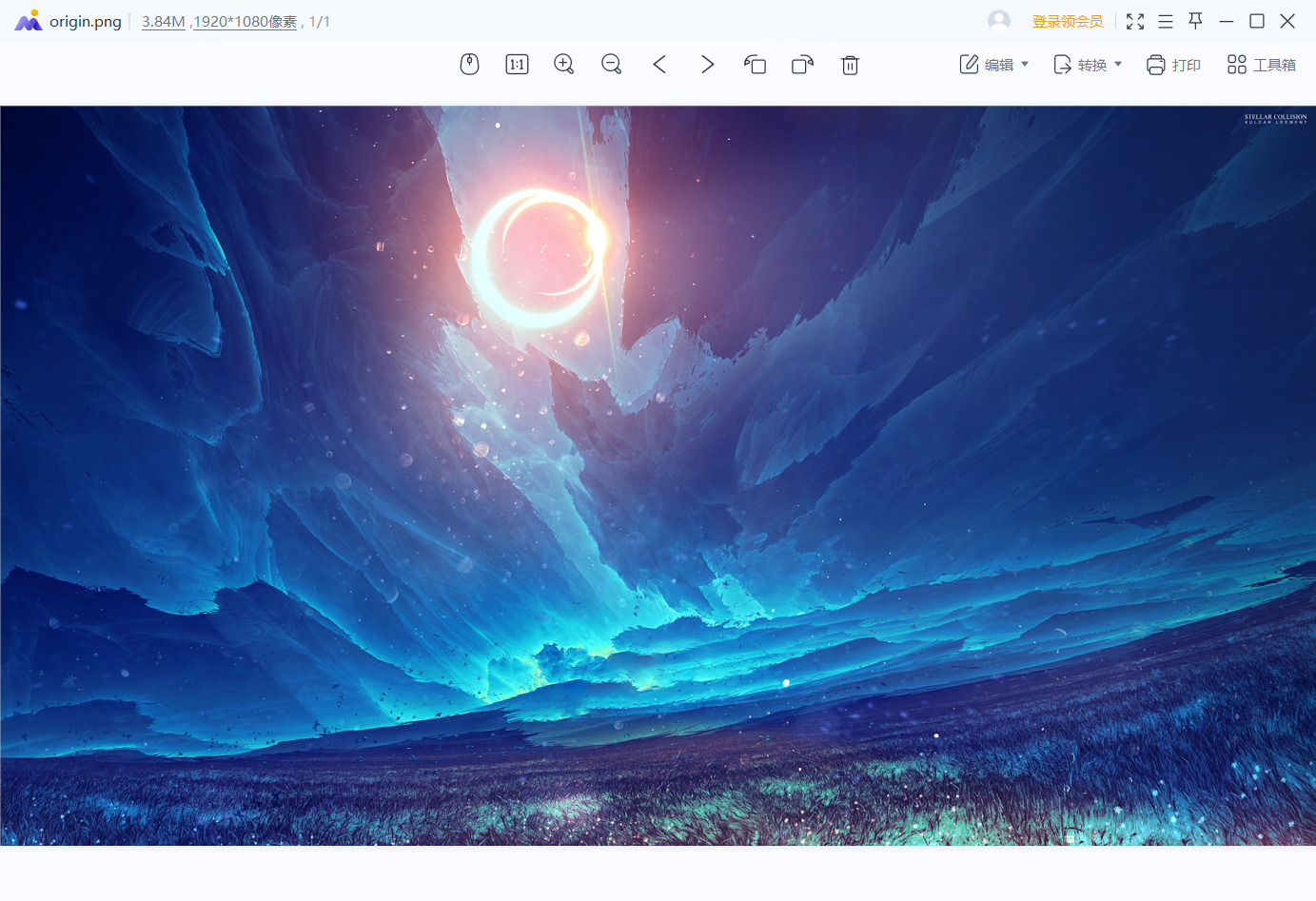
压缩后的图片为1.3M,大家可以自己测试后,找找压缩前后两张图片的不同之处
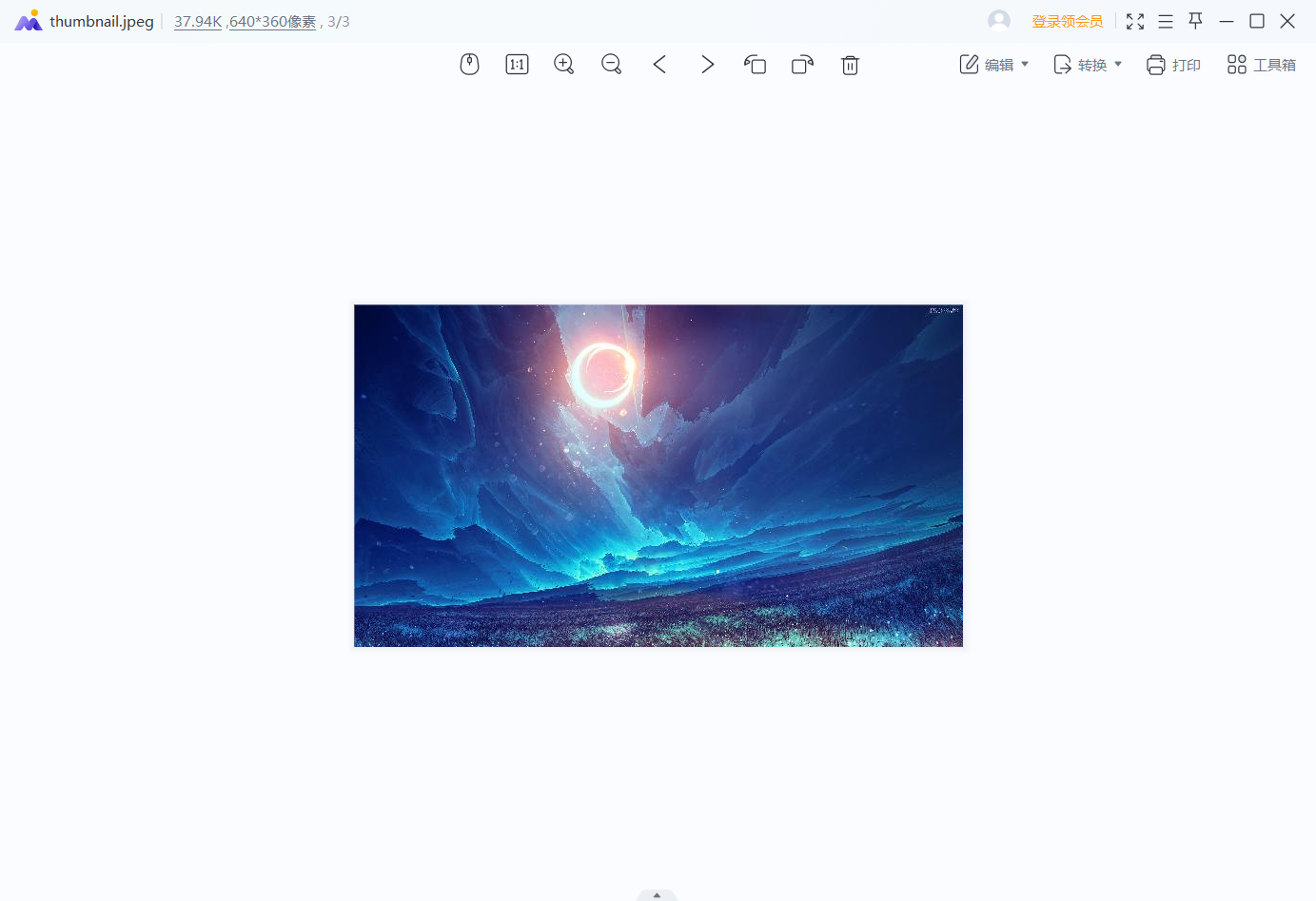
默认生成的缩略图大小为38K
遇到的问题
遇到比较懵13的问题,大概就是使用ImageIO.read()直接读取图像压缩时产生的红色调问题,我排查过程及解决方法放在了另一篇文章里:
ImageIO.read红色调问题