A - New Scheme
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int a[N];
void solve()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) cin >> a[i];
if (a[0] < 100 || a[0]>675 || a[0] % 25 != 0) {
puts("No");
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) {
if (a[i] < a[i - 1]|| a[i] < 100 || a[i]>675 || a[i] % 25 != 0) {
puts("No");
return;
}
}
puts("Yes");
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
B - Default Price
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
string c[N],d[N];
int p[N];
map<string, int>mp;
int res;
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> c[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> d[i];
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) cin >> p[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) mp[d[i]] = p[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (mp[c[i]]) res += mp[c[i]];
else res += p[0];
}
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
C - Standings
会卡精度,double就不能过全部数据,改成long double就AC了
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
struct node {
long double a, b;
long double rate;
int idx;
bool operator<(const node& W)const {
if (rate!=W.rate) return rate>W.rate;
return idx<W.idx;
}
}q[N];
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> q[i].a >> q[i].b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
q[i].idx = i;
q[i].rate = q[i].a /(q[i].a + q[i].b);
}
sort(q + 1, q + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << q[i].idx << " ";
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
D - Snuke Maze
用dfs
原本写的代码,各种tle以及re:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=510;
char s[N][N];
bool check(char ch1,char ch2){
if(ch1=='s'&&ch2=='n') return true;
if(ch1=='n'&&ch2=='u') return true;
if(ch1=='u'&&ch2=='k') return true;
if(ch1=='k'&&ch2=='e') return true;
if(ch1=='e'&&ch2=='s') return true;
return false;
}
int res;
int h,w;
bool found;
void dfs(int x,int y){
if(x==h&&y==w){
res++;
found=true;
return;
}
if(found) return;
if(x-1>=1&&check(s[x][y],s[x-1][y])) dfs(x-1,y);
if(y-1>=1&&check(s[x][y],s[x][y-1])) dfs(x,y-1);
if(x+1<=h&&check(s[x][y],s[x+1][y])) dfs(x+1,y);
if(y+1<=w&&check(s[x][y],s[x][y+1])) dfs(x,y+1);
}
void solve()
{
cin>>h>>w;
for(int i=1;i<=h;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=w;j++){
cin>>s[i][j];
}
}
if(s[1][1]!='s'){
puts("No");
return;
}
dfs(1,1);
if(res) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}别人的代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=510;
char s[N][N];
int h,w;
string t="snuke";
int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0},dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
int vis[N][N][5];
int res;
void dfs(int x,int y,int cur){
if(x<1||y<1||x>h||y>w) return ;
if(s[x][y]!=t[cur]) return ;
if(x==h&&y==w){
res++;
return;
}
if(vis[x][y][cur]) return;
vis[x][y][cur]=1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
dfs(x+dx[i],y+dy[i],(cur+1)%5);
}
}
void solve()
{
cin>>h>>w;
for(int i=1;i<=h;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=w;j++){
cin>>s[i][j];
}
}
dfs(1,1,0);
if(res) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
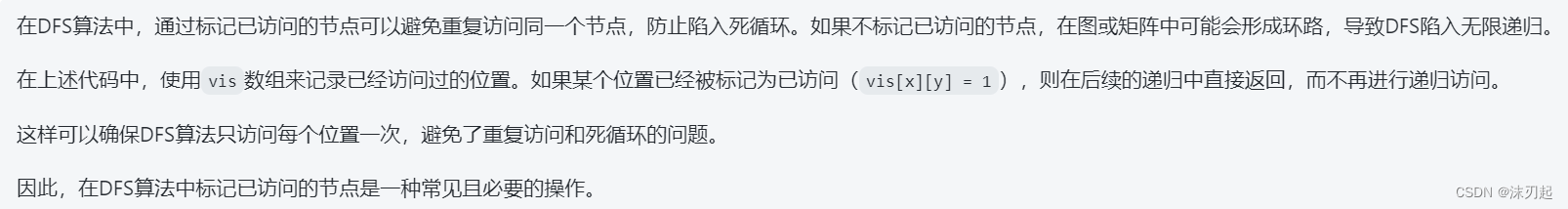
}对比之后发现我的代码少了标记已经走过的点
进行修正
中间要注意剪枝
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=510;
char s[N][N];
int vis[N][N];
bool check(char ch1,char ch2){
if(ch1=='s'&&ch2=='n') return true;
if(ch1=='n'&&ch2=='u') return true;
if(ch1=='u'&&ch2=='k') return true;
if(ch1=='k'&&ch2=='e') return true;
if(ch1=='e'&&ch2=='s') return true;
return false;
}
int res;
int h,w;
bool found;
void dfs(int x,int y){
if(x==h&&y==w){
res++;
found=true;
return;
}
if(vis[x][y]) return;
vis[x][y]=1;
if(found) return;
if(x-1>=1&&check(s[x][y],s[x-1][y])) dfs(x-1,y);
if(y-1>=1&&check(s[x][y],s[x][y-1])) dfs(x,y-1);
if(x+1<=h&&check(s[x][y],s[x+1][y])) dfs(x+1,y);
if(y+1<=w&&check(s[x][y],s[x][y+1])) dfs(x,y+1);
}
void solve()
{
cin>>h>>w;
for(int i=1;i<=h;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=w;j++){
cin>>s[i][j];
}
}
if(s[1][1]!='s'){
puts("No");
return;
}
dfs(1,1);
if(res) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
signed main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
然后我加了一个回溯算法,就会超时
至于为什么不用回溯,是因为不需要,因为它本来dfs就是往各个方向找,能找到就是能找到,只要找到一条路就行,所以找过的点就直接标记,只找一次,就不需要再找了