A 最长奇偶子数组


枚举满足条件的左端点能延续的最长右端点
class Solution {
public:
int longestAlternatingSubarray(vector<int> &nums, int threshold) {
int res = 0;
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n;) {
if (nums[i] % 2 == 0 && nums[i] <= threshold) {
int j = i + 1;
while (j < n && nums[j] <= threshold && nums[j] % 2 != nums[j - 1] % 2)
j++;
res = max(res, j - i);
i = j;
} else
i++;
}
return res;
}
};
B 和等于目标值的质数对

线性筛: 预处理求出1~n中的各数是否是质数, 然后枚举x
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findPrimePairs(int n) {
vector<int> pri;
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i])//vis[i]==0且i!=1 则i为质数
pri.push_back(i);
for (auto pi: pri) {
if (pi * i > n)
break;
vis[pi * i] = 1;
if (i % pi == 0)
break;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (int i = 2; i <= n - i; i++)
if (!vis[i] && !vis[n - i])
res.push_back({i, n - i});
return res;
}
};
C 不间断子数组
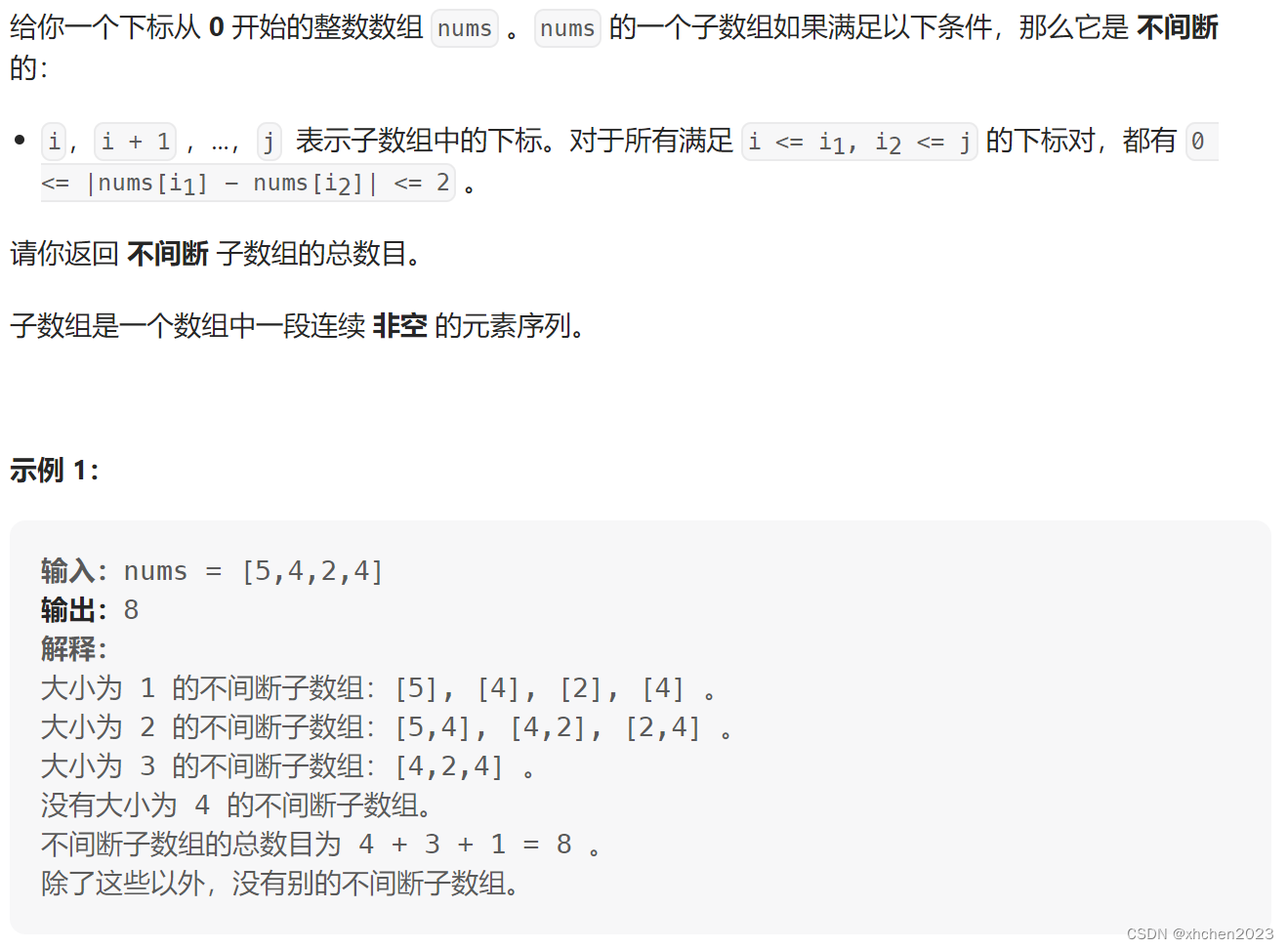

滑动窗口: 若一个数组是不间断子数组则其任意子数组都是不间断子数组, 所以可以用滑动窗口来枚举窗口的右端点 r r r, 设此时窗口的左端点最小为 l l l, 则以 r r r为子数组右端点的不间断子数组的数目为 r − l + 1 r-l+1 r−l+1. 中途用堆维护窗口内的最大值和最小值, 同时用哈希表记录一个数值在窗口内出现的次数.
class Solution {
public:
long long continuousSubarrays(vector<int> &a) {
int n = a.size();
long long res = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> cnt;//哈希表记录窗口内数出现次数
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minheap;//最小堆
priority_queue<int> maxheap;//最大堆
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < n; r++) {//枚举窗口右端点为r的情况
minheap.push(a[r]);
maxheap.push(a[r]);
cnt[a[r]]++;
while (1) {// 可能需要更新窗口左端点
while (!cnt[maxheap.top()])//删除不在窗口内的元素
maxheap.pop();
while (!cnt[minheap.top()])//删除不在窗口内的元素
minheap.pop();
if (!maxheap.empty() && !minheap.empty() && maxheap.top() - minheap.top() > 2)//更新窗口左端点
cnt[a[l++]]--;
else
break;
}
res += r - l + 1;
}
return res;
}
};
D 所有子数组中不平衡数字之和


滑动窗口+多重集: 枚举子数组的长度
l
e
n
len
len, 对相同长度的子数组使用滑动窗口的方式从左往右遍历, 用多重集维护当前窗口内的元素, 在窗口移动过程(右端点右移和左端点右移)中维护当前的不平衡数字.
class Solution {
public:
int sumImbalanceNumbers(vector<int> &a) {
int n = a.size();
int res = 0;
multiset<int> s;//多重集中可以含相同元素
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len++) {//枚举子数组的长度len
s.clear();//清0
int cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
s.insert(a[i]);
for (auto x = s.begin(); next(x) != s.end(); x++)//对应[0,len-1)区间
if (*next(x) - *x > 1)
cur++;
for (int l = 0, r = len - 1; r < n; l++, r++) {//枚举长为len的子数组的右端点r
int d = 0;
auto loc = s.upper_bound(a[r]);// a[r]需要插入至loc处
if (loc != s.begin()) {
if (loc != s.end() && *loc - *prev(loc) > 1)// 多重集插入前 loc与其前驱不平衡, 所以变化量 -1
d--;
if (a[r] - *prev(loc) > 1)// 多重集插入后 a[r]与其前驱不平衡, 所以变化量 +1
d++;
}
if (loc != s.end() && *loc - a[r] > 1)// 多重集插入后 a[r]与其后驱不平衡, 所以变化量 +1
d++;
s.insert(loc, a[r]);//添加a[r]
cur += d;//更新当前的不平衡数
res += cur;
d = 0;
loc = s.lower_bound(a[l]);//多重集中loc处的a[l]需要被删除
if (loc != s.begin() && *loc - *prev(loc) > 1)// 删除前loc与其前驱不平衡, 所以变化量 -1
d--;
if (next(loc) != s.end() && *next(loc) - *loc > 1)// 删除前loc与其后驱不平衡, 所以变化量 -1
d--;
if (loc != s.begin() && next(loc) != s.end() && *next(loc) - *prev(loc) > 1)//loc前驱与其后驱在删除后不平衡, 所以变化量 +1
d++;
cur += d;//更新当前的不平衡数
s.erase(loc);//删除a[l]
}
}
return res;
}
};