1.Bean的生命周期底层原理
AppConfig
package com.zhouyu;
import com.zhouyu.service.OrderService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@ComponentScan("com.zhouyu")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public OrderService orderService1(){
return new OrderService();
}
@Bean
public OrderService orderService2(){
return new OrderService();
}
}
OrderService
package com.zhouyu.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
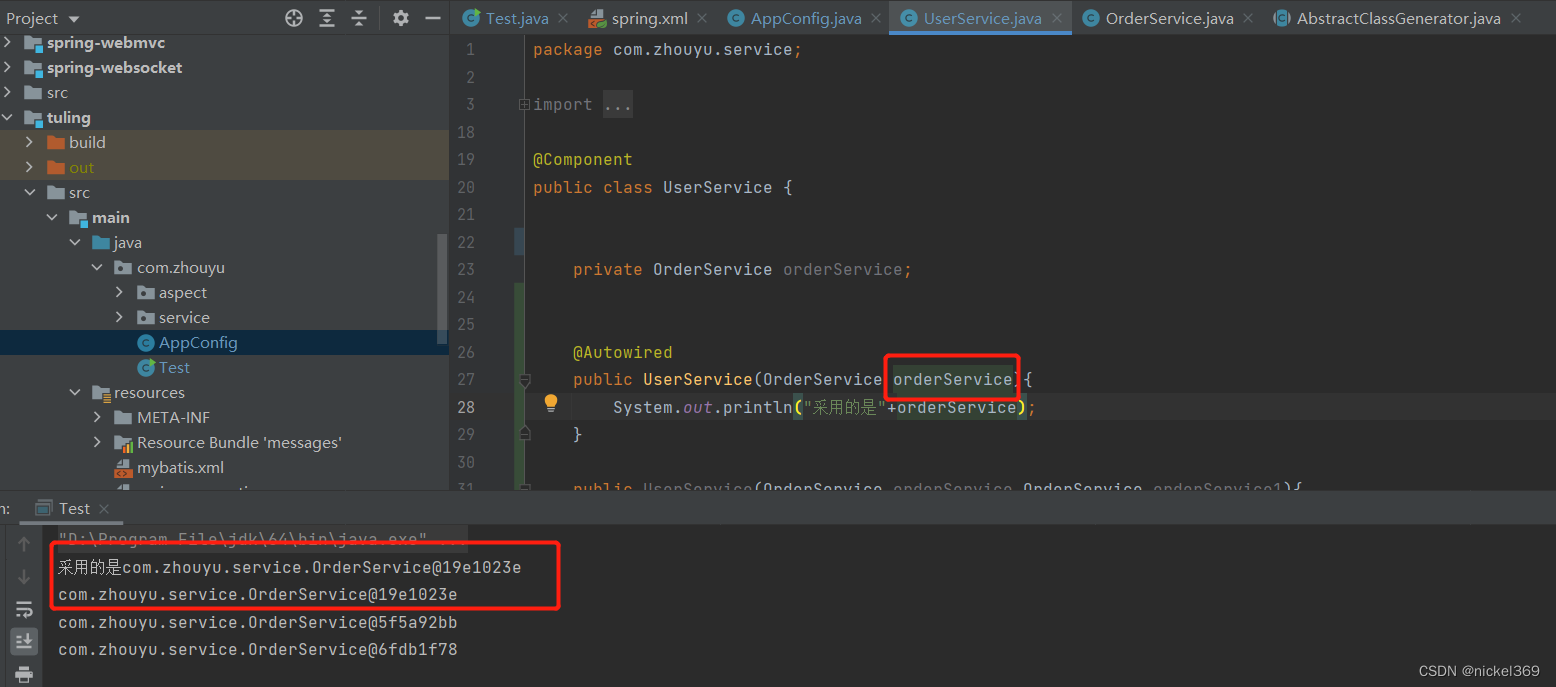
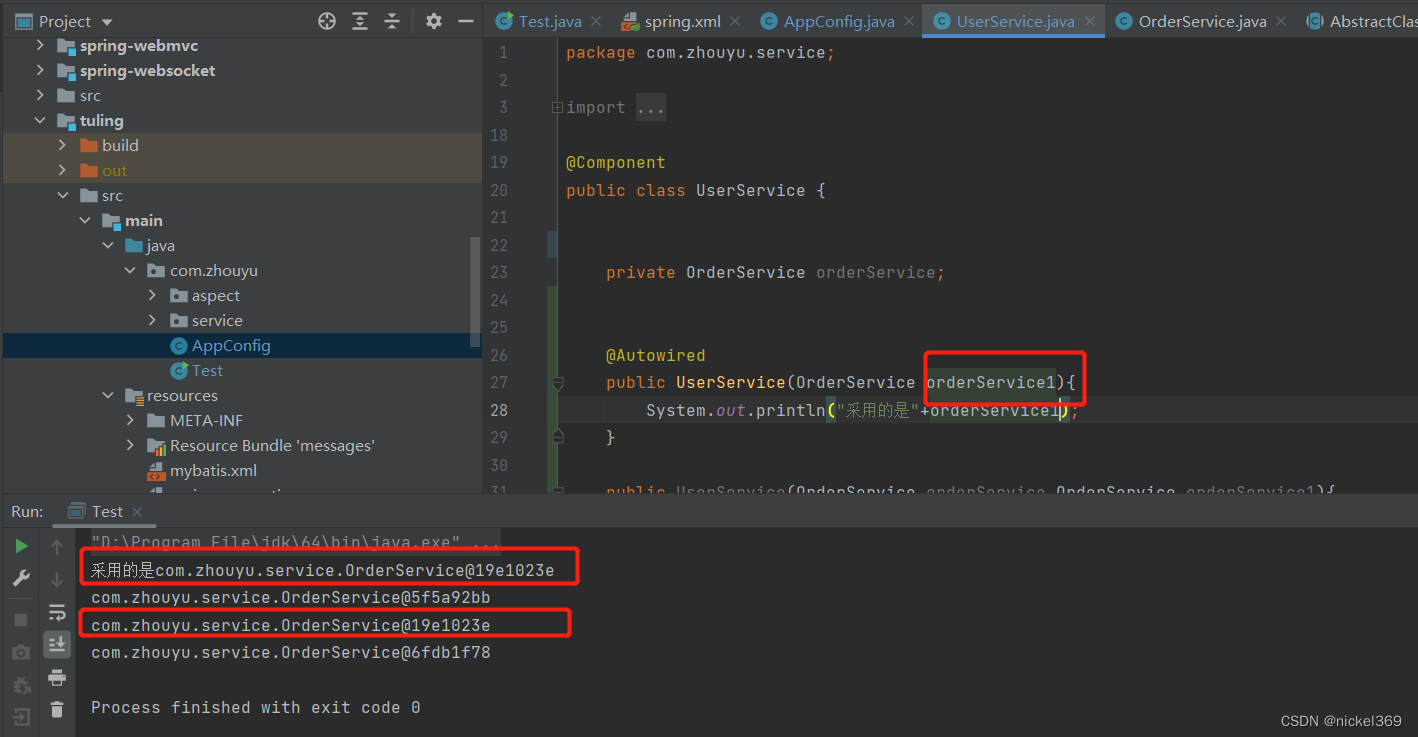
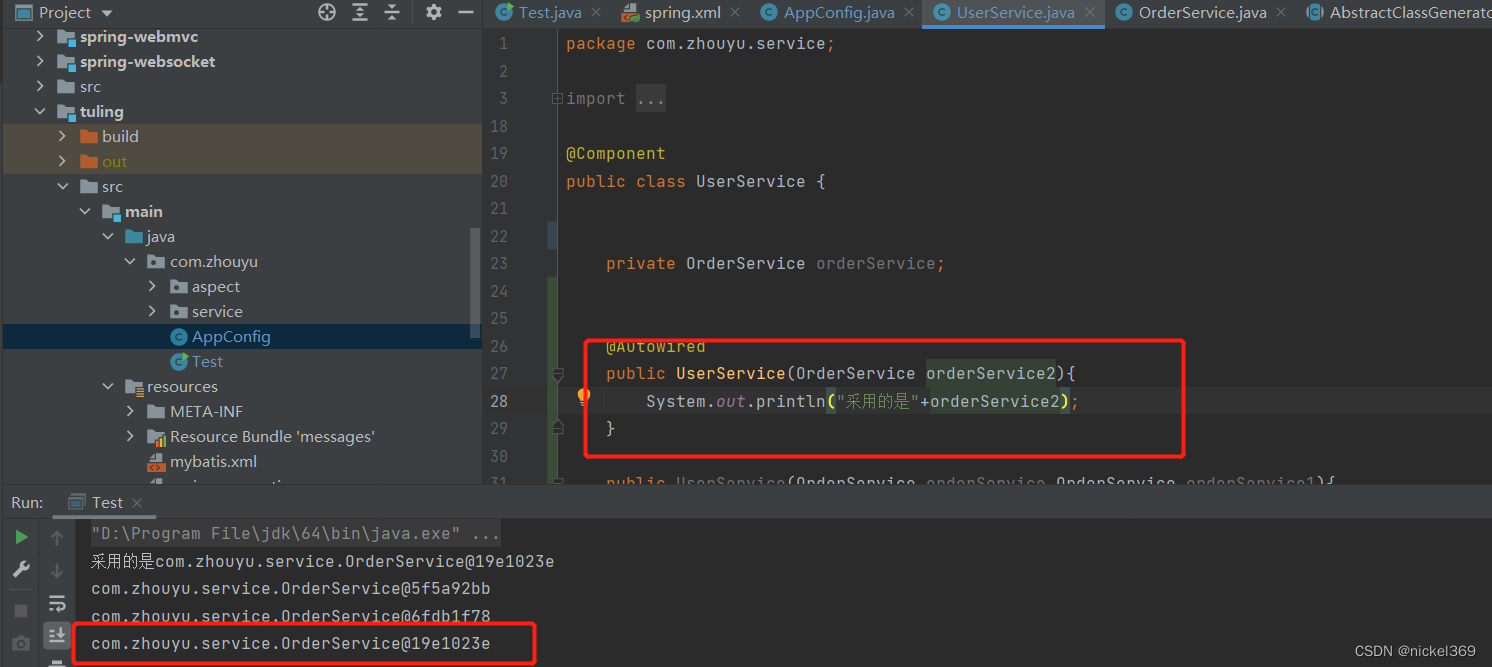
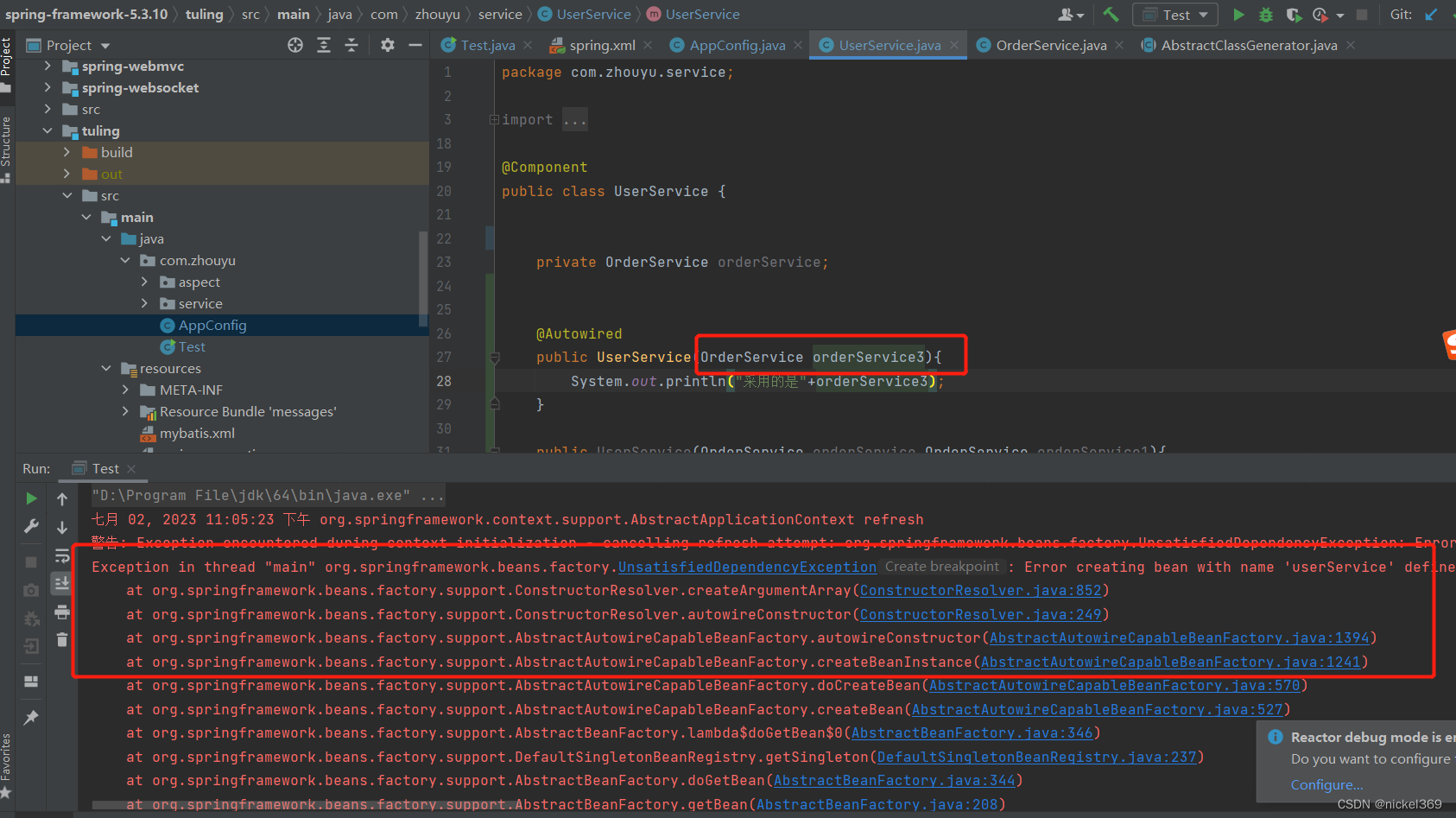
说明:在spring容器中存在多个bean对象时,bean在无参构造方法中引入某个bean,更改参数名称决定具体引入那一个bean,当参数的名称在bean中不存在时,此时程序就会报错。
2.依赖注入底层原理
2.1 通过spring.xml方式进行注入
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhouyu"/>
<bean id="user1" class="com.zhouyu.service.User" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="user2" class="com.zhouyu.service.User" parent="user1"/>
</beans>
java获取对象
package com.zhouyu;
import com.zhouyu.service.User;
import com.zhouyu.service.UserService;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.Nullable;
import org.springframework.aop.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AbstractPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
}
2.2 通过注解方式进行注入
AppConfig
package com.zhouyu;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@ComponentScan("com.zhouyu")
@EnableScheduling
@PropertySource("classpath:spring.properties")
public class AppConfig {
}
java获取对象
package com.zhouyu;
import com.zhouyu.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
}
说明:spring通过解析appConfig.class得到扫描路径,然后遍历该路径下的含有@Component、@Service注解对象记录下来,放在一个map集合中,通过beanName作为key,当前类作为value。
3.初始化底层原理
3.1 初始化前
User对象
package com.zhouyu.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
UserService 对象的test方法
package com.zhouyu.service;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class UserService{
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private User admin;
public void test(){
System.out.println(admin.getName());
}
@PostConstruct
public User getAdmin(){
admin.setPassword("123");
admin.setName("LiMing");
return admin;
}
}
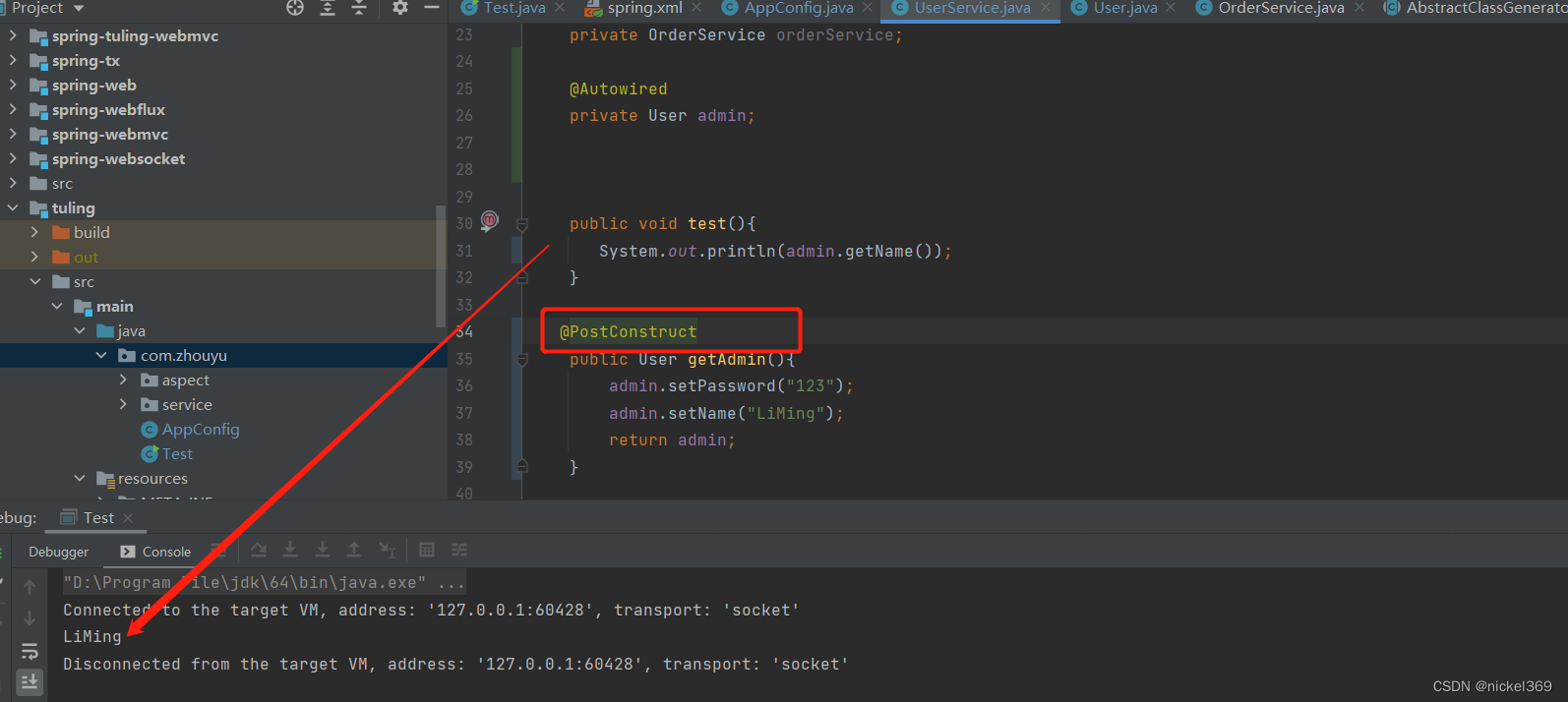
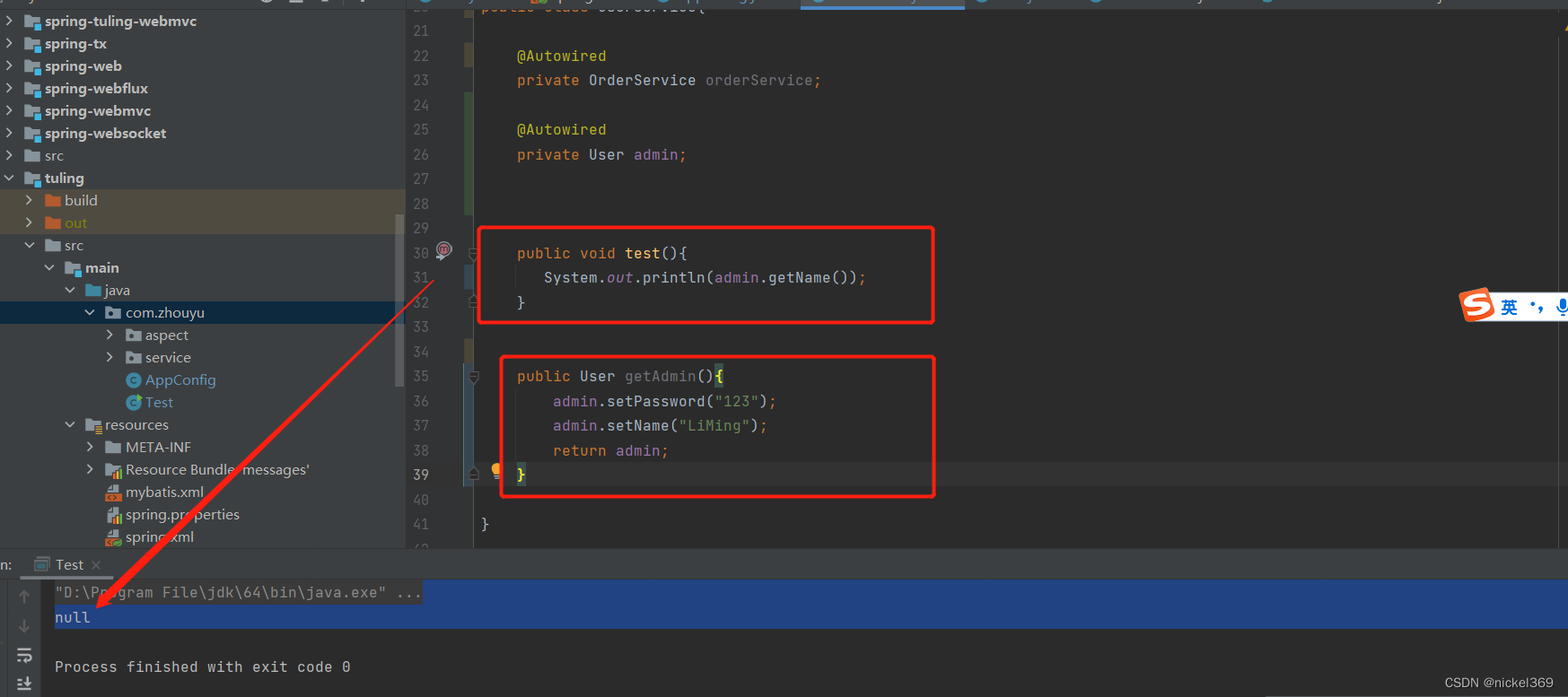
说明:User对象必须加上Component注解,这样才能被Spring容器进行管理,此时在getAdmin方法中加上PostConstruct注解后,此时对admin进行赋值,才其他方法中就能获取admin赋值的对象。
3.2 初始化
package com.zhouyu.service;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class UserService implements InitializingBean{
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private User user;
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
user.setPassword("123");
user.setName("LiMing");
}
}
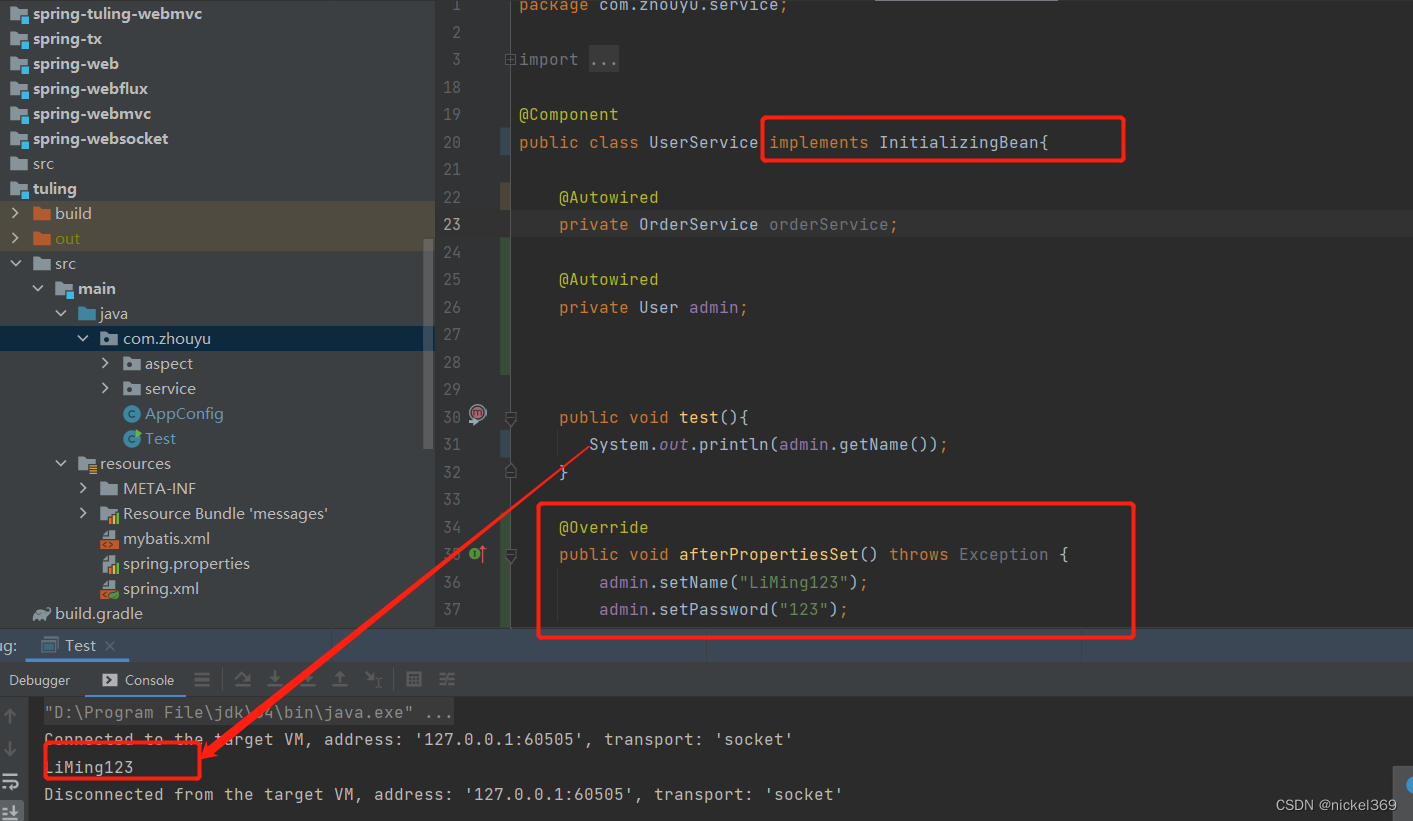
说明:初始化时,查看方法是否实现了InitializingBean接口,假如实现了该方法,将会执行afterPropertiesSet方法。
3.3 初始化后实现AOP
ZhouyuAspect.java对象
package com.zhouyu.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class ZhouyuAspect {
@Before("execution(public void com.zhouyu.service.UserService.test())")
public void a(){
System.out.println("test Before");
}
@After("execution(public void com.zhouyu.service.UserService.test())")
public void b(){
System.out.println("test After");
}
}
test.java对象
package com.zhouyu;
import com.zhouyu.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
// 创建一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
}
UserService.java对象
package com.zhouyu.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserService implements InitializingBean{
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private User admin;
public void test(){
System.out.println(admin.getName());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
admin.setName("LiMing123");
admin.setPassword("123");
}
}
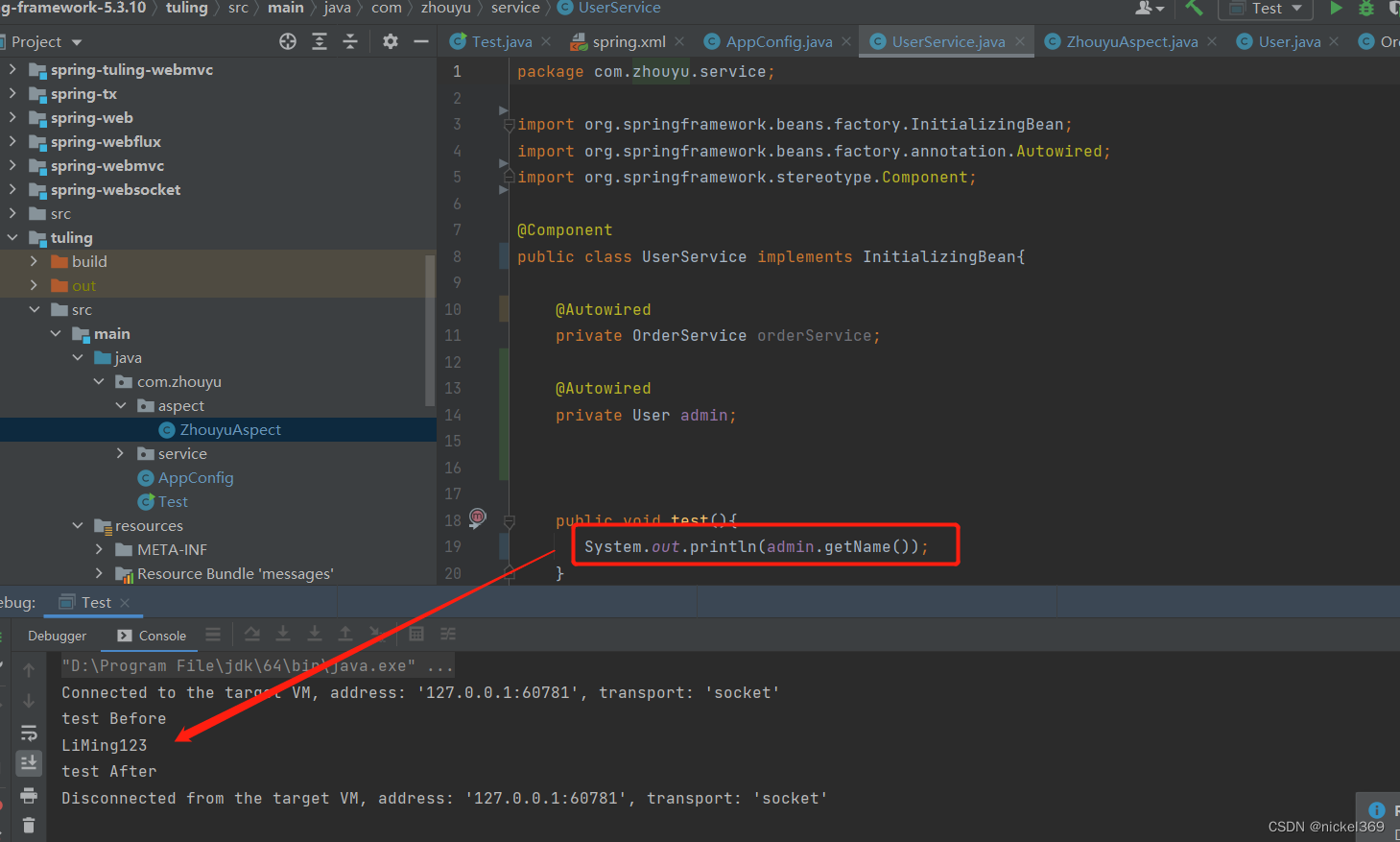
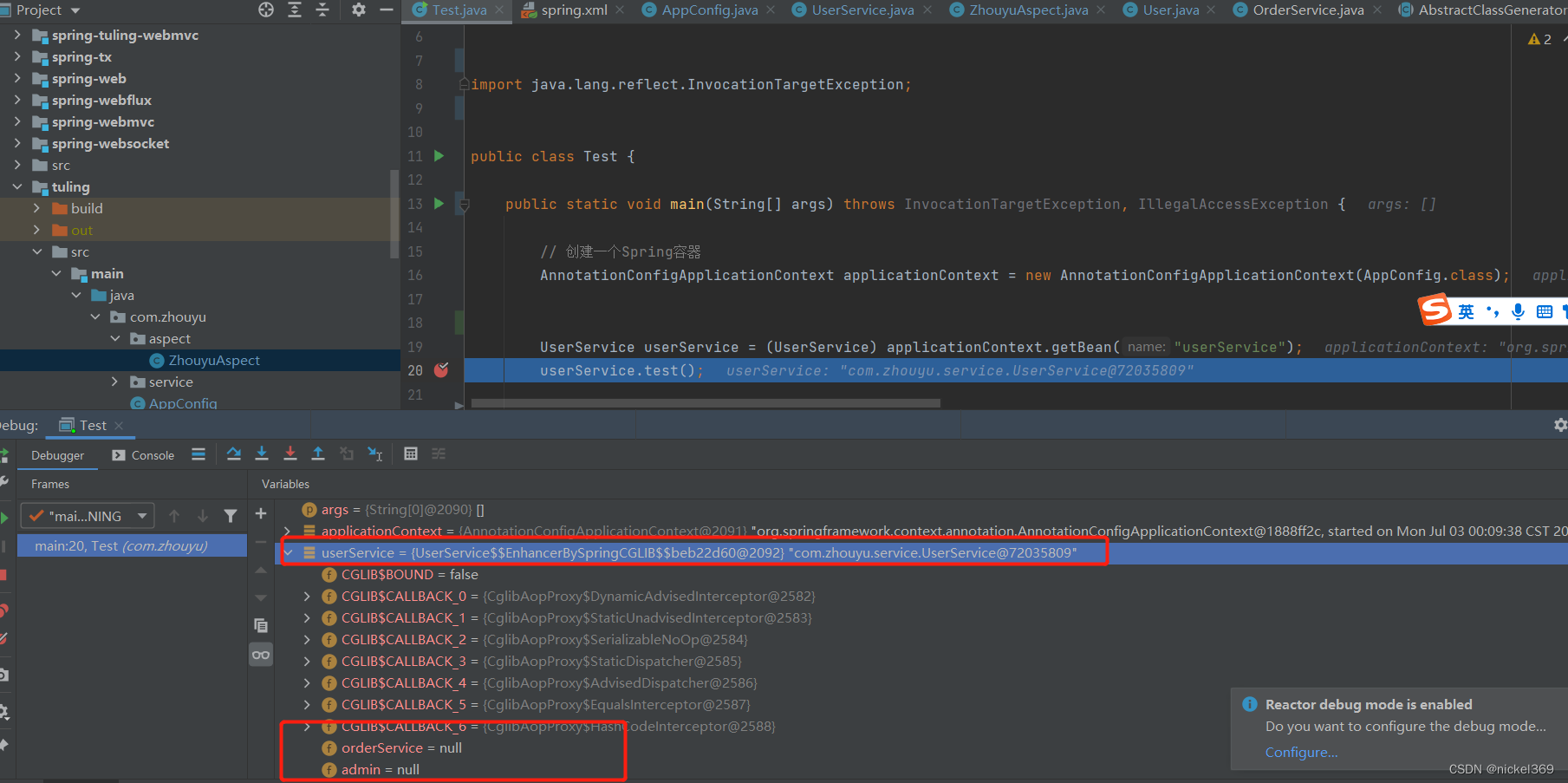
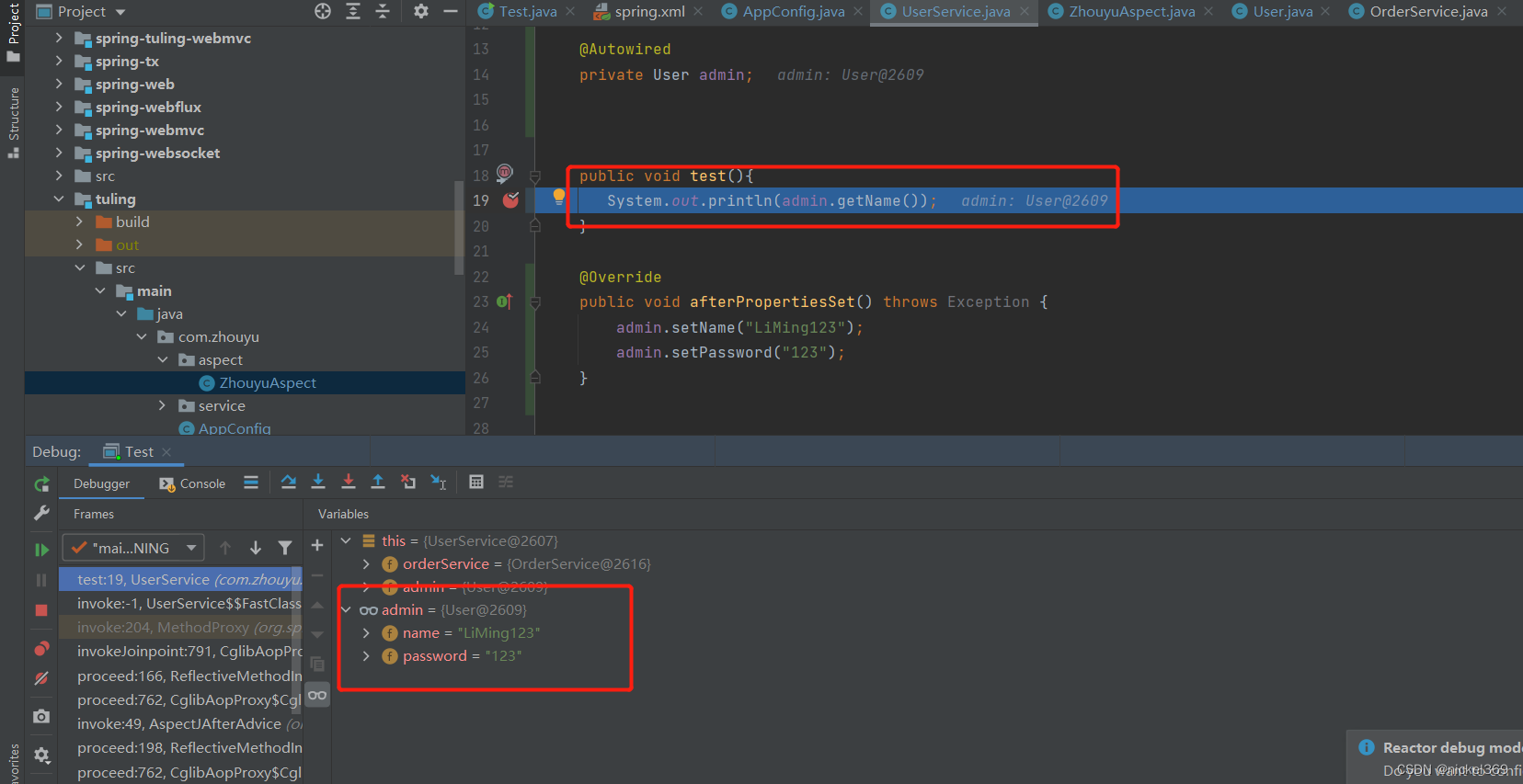
说明:当引用切面后,userService将会在底层生成一个userServiceProxy代理方法,代理对象此时也有test方法,在执行test方法之前执行切面@before方法,然后执行test方法,test方法将会调用父类里面test方法,所有当进去test方法里面时,此时属性又有值了。
4.推断构造方法底层原理
存在多个构造方法,其中一个是无参构造方法
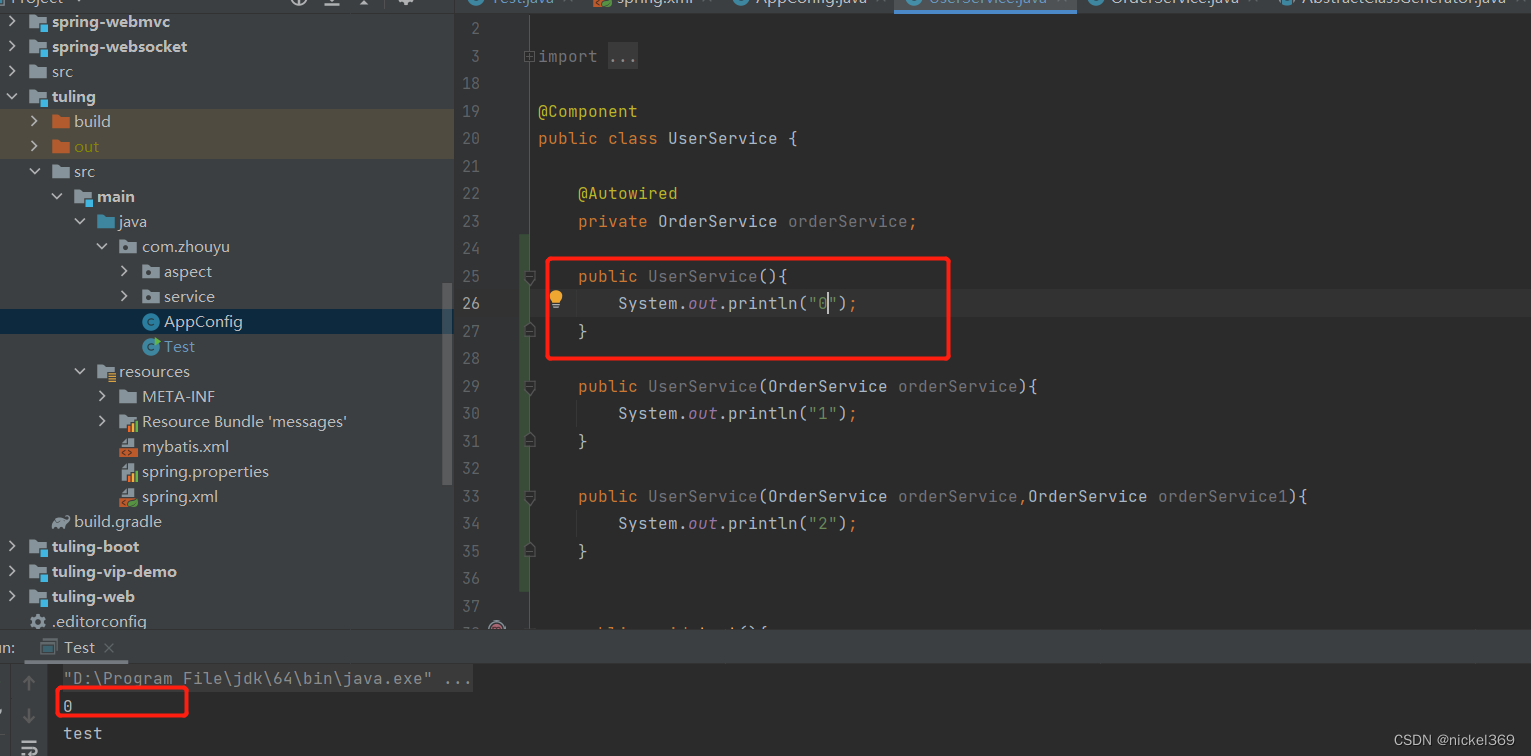
存在多个构造方法,无无参构造方法
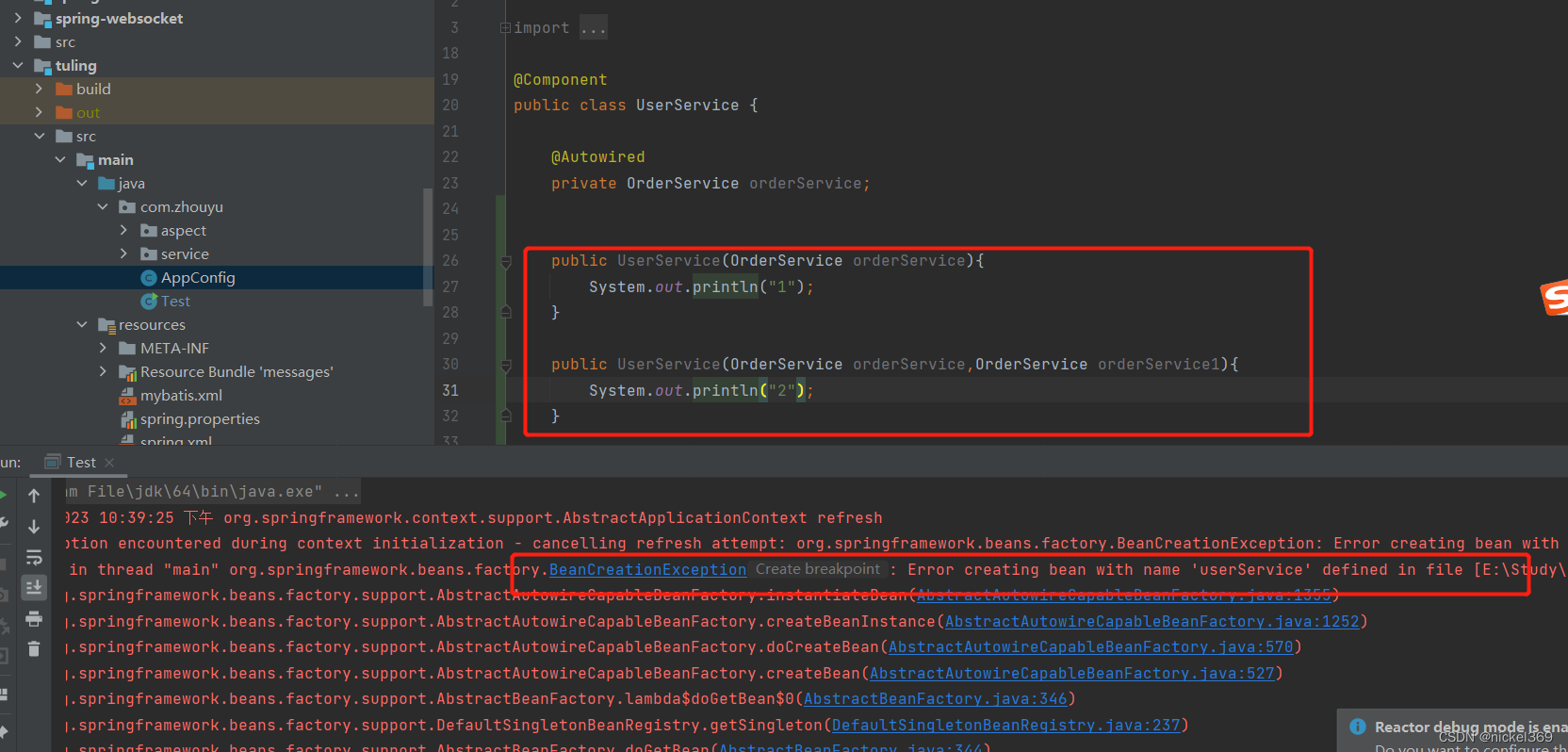
存在多个构造方法,其中一个构造方法含有Autowired注解
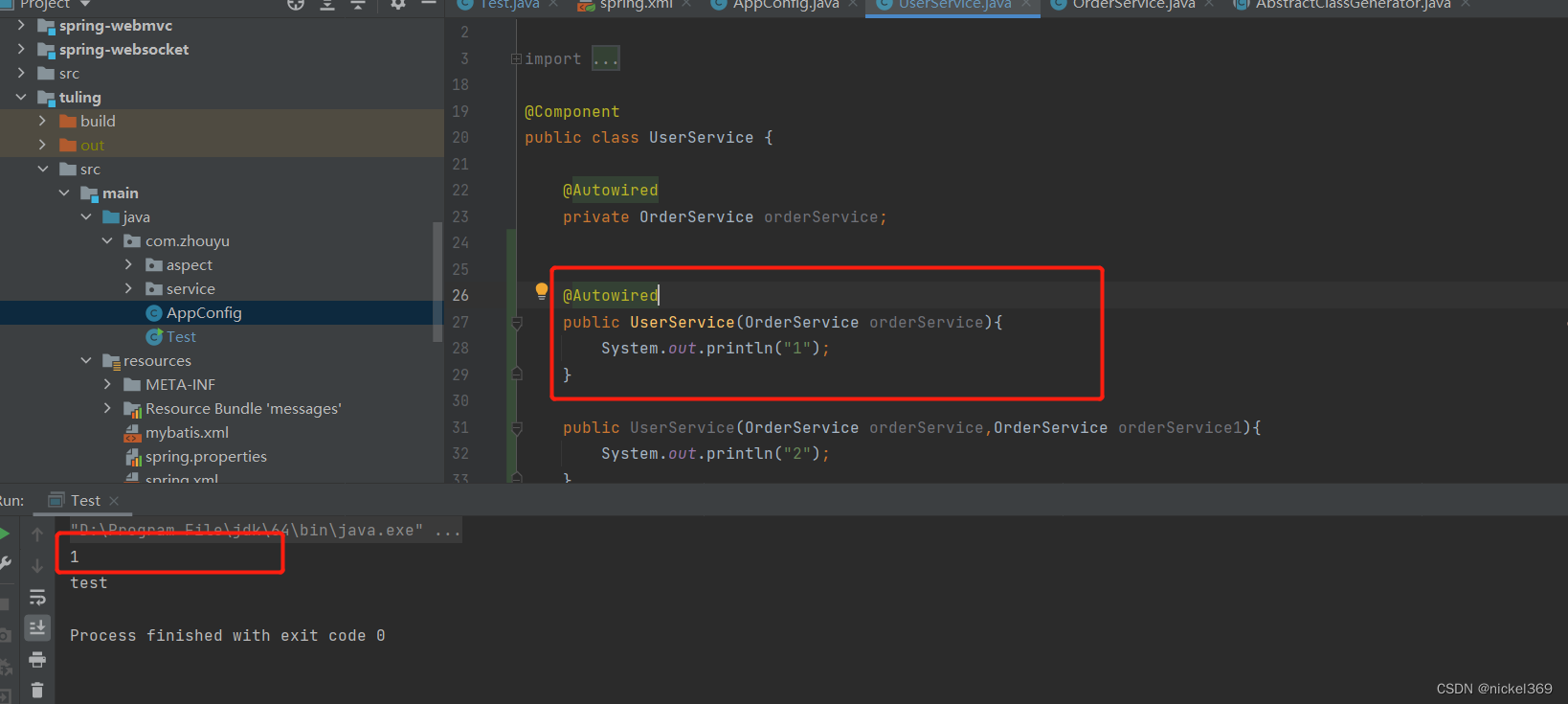
说明:创建对象时,通过该类的构造方法进行创建对象,假如该类只有一个构造方法时候,就采用这个构造方法,假如有多个构造方法,存在无参构造方法就用无参构造方法进行构造,假如不存在无参构造方法,存在多个有参构造方法就会报错,但是存在多个有参构造方法,其中一个构造方法有@Autowired,将会采用这个构造方法。同时也会判断是否有被Autowired注解的属性,有的话也会把属性找出来并由spring进行赋值。