目录
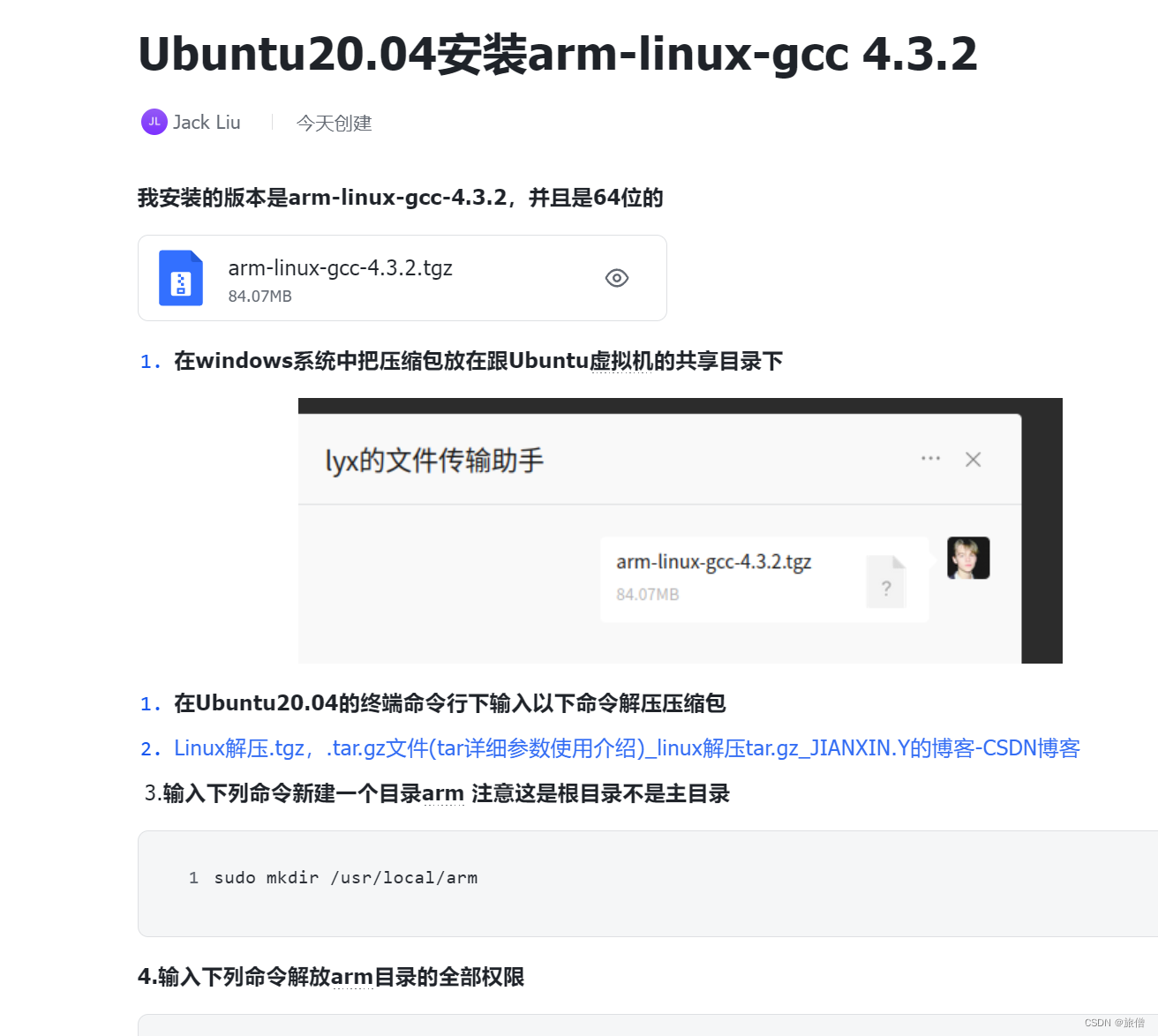
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
142. 环形链表 II
这题不是很难,目前除了从【.】变成了【->】之外,python和C++也没啥区别
另外就是对虚拟头结点的掌握了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while (cur->next != nullptr and cur->next->next != nullptr){
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next;
ListNode* tmp2 = cur->next->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur->next->next = tmp1;
tmp1->next = tmp2;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
双指针的经典应用,确实经典
写完我去看了一下卡哥的思路,二者基本一致,不过他多向前移动了一步,所以他的第二个while的条件只要cur != nullptr就可以了,这个小不同,不影响
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummy;
ListNode* tmp = dummy;
while (n--){
cur = cur->next;
}
while (cur->next != nullptr){
tmp = tmp->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
tmp->next = tmp->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};面试题 02.07. 链表相交
这道题主要注意下面两点
- 题目要求【函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构】,所以在计算完链表的长度后,需要重新复制指针指向原headA,headB,不能直接对headA和headB进行操作
- 卡哥的解法是将长的置换为A,使用了swap,我这边没有,用的if else判断,当然,这个不是核心,可以学习一下
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* cur_a = headA;
ListNode* cur_b = headB;
int cnt_a = 0;
int cnt_b = 0;
while (cur_a != NULL){
cnt_a++;
cur_a = cur_a->next;
}
while (cur_b != NULL){
cnt_b++;
cur_b = cur_b->next;
}
cur_a = headA;
cur_b = headB;
if (cnt_a > cnt_b){
int diff = cnt_a - cnt_b;
while(diff--){
cur_a = cur_a->next;
}
}
else{
int diff = cnt_b - cnt_a;
while(diff--){
cur_b = cur_b->next;
}
}
while (cur_a != NULL){
if(cur_a == cur_b){
return cur_a;
}
else{
cur_a = cur_a->next;
cur_b = cur_b->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};142. 环形链表 II
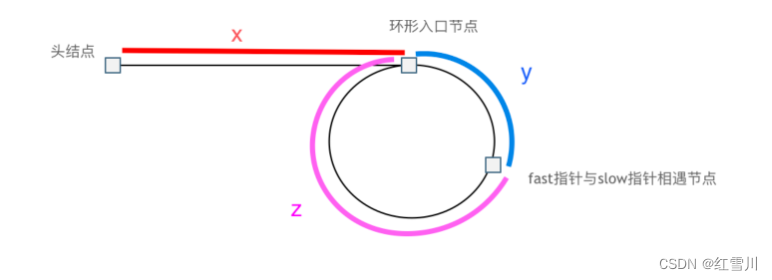
这道题还是蛮难的,主要难在找相遇点
判断环:快慢指针,每当慢指针前进一步,快指针前进两步。如果快指针遇到空指针,说明无环;如果快指针遇到慢指针,说明存在环
判断入口:从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。(可以理解为构建两轮相遇)
注意:这题就不用设置虚拟头指针了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL){
return head;
}
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
{
ListNode* index1 = slow; //这里其实没必要设定index1,直接用slow就行
ListNode* index2 = head;
while(index1 != index2){
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};