一.什么是注解
1.Annotation是从JDK5开始引入的最新技术
2.Annotation的作用:
1)不是程序本身,可以对程序做出解释,(这一点和注释(comment)没什么区别)。
2)可以被其他程序(比如编译器)读取。
3.Annotation的格式:注解是以“@注释名”在代码中存在的,还可以添加一些参数值,例如:
@SuppressWarnings(value="unchecked").
4.Annotation可以使用在package,class,method,field等上面,相当于给他们添加额外的辅助信息,可以通过反射机制编程实现对这些元数据的访问。
二.内置注解
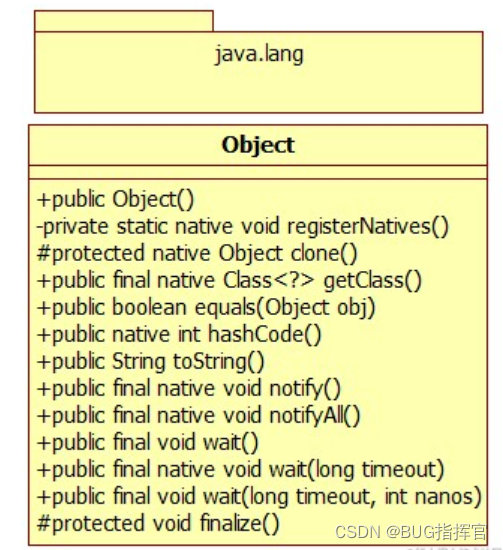
@Override :定义在java.lang.Override中,此注释只适用于修辞方法﹐表示一个方法声明打算重写超类中的另一个方法声明。
@Deprecated:定义在java.lang.Deprecated中,此注释可以用于修辞方法,属性,类,表示不鼓励程序员使用这样的元素﹐通常是因为它很危险或者存在更好的选择。
@SuppressWarnings:定义在java.lang.SuppressWarnings中,用来抑制编译时的警告信息.与前两个注释有所不同,你需要添加一个参数才能正确使用,这些参数都是已经定义好了的,我们选择性的使用就好了。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//什么是注解
public class Text01 extends Object{
//@Override 重写方法的注解
@Override
public String toString(){
return super.toString();
}
//@Deprecated 不推荐使用的方法,已经过时的方法,但是可以使用
@Deprecated
public static void text(){
System.out.println("过时的方法");
}
//@SuppressWarnings("all") 镇压警告,有不同的参数可以用来镇压不同的警告
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void text02(){
List list=new ArrayList(); //因为没有使用,会有警告
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
text();
}
}
三.元注解
元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解,Java定义了4个标准的meta-annotation类型,他们被用来提供对其他annotation类型作说明.
这些类型和它们所支持的类在java.lang.annotation包中可以找到.(@Target , @Retention ,@Documented , @lnherited )
@Target:用于描述注解的使用范围(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
@Retention :表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息﹐用于描述注解的生命周期(SOURCE<CLASS< RUNTIME)
@Document:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
@Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解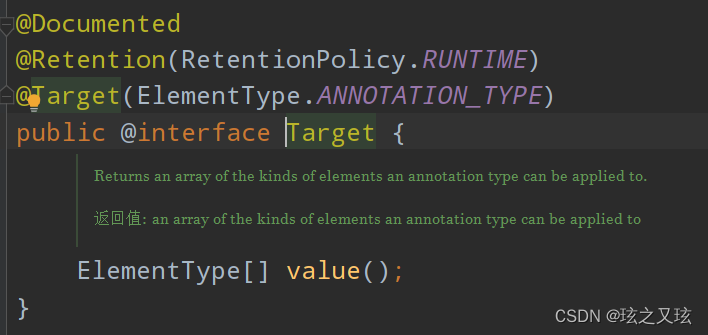
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//测试元注解
@MyAnnotation
public class Text02 {
@MyAnnotation
public void text(){
}
}
//定义一个注解
//Target 表示注解可以使用的地方
//@Target(value = ElementType.METHOD) 只能在方法上使用
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) //可以使用在类或者方法删上
//Retention 表示注解在什么阶段还有效
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//Documented 表示是否在Javadoc中生成我们的注解
@Documented
//Inherited 子类继承父类的注解
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation{
}四.自定义注解
使用@interface自定义注解时,自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口。
分析:
@interface用来声明一个注解,格式:public @interface注解名{定义内容}。
其中的每一个方法实际上时声明了一个配置参数。
方法的名称就是参数的名称。
返回值类型就是参数的类型(返回值只能是基本类型,Class,String,enum)。
可以通过default来声明参数的默认值
如果只有一个参数成员,一般参数名为value
注解元素必须要有值,我们定义注解元素时,经常使用空字符串,0作为默认值。
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//自定义注解
public class Text03 {
//若没有默认值必须赋值
@MyAnnotationo2(name = "李华",age = 19)
public void text(){}
@MyAnnotation03("李华") //只有一个值且为value时可以省略不写
public void text2(){
}
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotationo2{
//注解的参数 : 参数类型 + 参数名();
String name() default ""; //注解参数可以设置默认值,也可显示赋值
int age();
int id() default -1;
String[] school() default {"清华","北大"};
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation03{
String value();
}


![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计宿舍管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d9ed0bbba4d3433f968bfaef1662b39b.png)