pandas模块使用介绍
1.pandas简介
pandas 是基于NumPy 的一种工具,该工具是为解决数据分析任务而创建的。Pandas 纳入了大量库和一些标准的数据模型,提供了高效地操作大型数据集所需的工具。pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。
-
Python在数据处理和准备⽅⾯⼀直做得很好,但在数据分析和建模⽅⾯就差⼀些。pandas帮助填补了这⼀空⽩,使您能够在Python中执⾏整个数据分析⼯作流程,⽽不必切换到更特定于领域的其它语⾔
-
与出⾊的 jupyter⼯具包和其他库相结合,Python中⽤于进⾏数据分析的环境在性能、⽣产率和协作能⼒⽅⾯都是卓越的
-
pandas是 Python 的核⼼数据分析⽀持库,提供了快速、灵活、明确的数据结构,旨在简单、直观地处理关系型、标记型数据。pandas是Python进⾏数据分析的必备⾼级⼯具。
-
pandas的主要数据结构是 Series(⼀维数据)与 DataFrame (⼆维数据),这两种数据结构⾜以处理⾦融、统计、社会科学、⼯程等领域⾥的⼤多数案例
-
处理数据⼀般分为⼏个阶段:
-
数据整理与清洗
-
数据分析与建模
-
数据可视化与制表
-
-
pandas模块安装:pip install pandas -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
-i 指定pip源,使用国内pip提高下载安装速度、
2.pandas数据结构
2-1.Series(⼀维数据)
⽤列表⽣成 Series时,Pandas 默认⾃动⽣成整数索引,也可以指定索引
代码示例1:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
list_info = [0, 1, 7, 9, np.NAN, None, 1024, 512]
s1 = pd.Series(data=list_info)
print(s1)
""" 输出结果
0 0.0
1 1.0
2 7.0
3 9.0
4 NaN
5 NaN
6 1024.0
7 512.0
dtype: float64
"""
- ⽆论是numpy中的np.NAN,还是Python中的None在pandas中都以缺失数据NaN对待
- pandas⾃动添加索引项
- 不指定dtype,默认值为dtype=‘float64’
代码示例2:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
list_info = [0, 1, 7, 9, np.NAN, None, 1024, 512]
s2 = pd.Series(data=list_info, index=list('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')[:len(list_info)], dtype='float32')
print(s2)
""" 输出结果
a 0.0
b 1.0
c 7.0
d 9.0
e NaN
f NaN
g 1024.0
h 512.0
dtype: float32
"""
1.可以自行指定⾏索引
代码示例3:
import pandas as pd
s3 = pd.Series(data={'wow': "魔兽世界", 'ow': "守望先锋", 'diablo': "暗黑破坏神"}, name='Blizzard_game', dtype='str')
print(s3)
""" 输出结果
wow 魔兽世界
ow 守望先锋
diablo 暗黑破坏神
Name: Blizzard_game, dtype: object
"""
1.可以传⼊字典创建,key⾏为索引,value为数据
2-2.DataFrame(二维数据)
DataFrame是由多种类型的列构成的⼆维标签数据结构,类似于 Excel 、SQL 表,或 Series 对象构成的字典
代码示例1:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data={'腾讯': ["英雄联盟", "王者荣耀", "地下城与勇士"],
'网易': ["魔兽世界", "守望先锋", "暗黑破坏神"],
'盛大': ["龙之谷", "传奇世界", "星辰变"]},
index=['小美', '小丽', '小兔'])
print(df1)
""" 输出结果
腾讯 网易 盛大
小美 英雄联盟 魔兽世界 龙之谷
小丽 王者荣耀 守望先锋 传奇世界
小兔 地下城与勇士 暗黑破坏神 星辰变
"""
1.index 作为⾏索引
2.字典中的key作为列索引
3.通过数据创建了3*3的DataFrame表格⼆维数组
代码示例2:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 151, size=(5, 3)),
index=['周杰伦', '林俊杰', '周润发', '张绍忠', '唐国强'],
columns=['语文', '数学', '外语'])
print(df2)
""" 输出结果
语文 数学 外语
周杰伦 107 59 114
林俊杰 148 137 24
周润发 83 3 19
张绍忠 89 147 56
唐国强 123 30 123
"""
3.查看数据
查看DataFrame的常⽤属性和DataFrame的概览和统计信息
代码示例:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 101, size=(12, 3)), index=None, columns=['语文', '数学', '外语'])
print("----- print(df) -----")
print(df)
print("----- df.head(4) -----")
print(df.head(4))
print("----- df.tail(4) -----")
print(df.tail(4))
# 查看形状,⾏数和列数
print("----- df.shape -----")
print(df.shape)
# 查看数据类型
print("----- df.dtypes -----")
print(df.dtypes)
# 查看行索引
print("----- df.index -----")
print(df.index)
# 查看列索引
print("----- df.columns -----")
print(df.columns)
# 对象值,⼆维ndarray数组
print("----- df.values -----")
print(df.values)
# # 查看数值型列的汇总统计,计数、平均值、标准差、最⼩值、四分位数、最⼤值
print("----- df.describe() -----")
print(df.describe())
# 查看列索引、数据类型、⾮空计数和内存信息
print("----- df.info() -----")
print(df.info())
""" 输出结果
----- print(df) -----
语文 数学 外语
0 27 19 30
1 56 2 92
2 81 42 24
3 72 18 44
4 50 23 3
5 18 4 94
6 13 83 96
7 90 76 73
8 38 12 86
9 39 8 52
10 18 0 10
11 68 30 48
----- df.head(4) -----
语文 数学 外语
0 27 19 30
1 56 2 92
2 81 42 24
3 72 18 44
----- df.tail(4) -----
语文 数学 外语
8 38 12 86
9 39 8 52
10 18 0 10
11 68 30 48
----- df.shape -----
(12, 3)
----- df.dtypes -----
语文 int32
数学 int32
外语 int32
dtype: object
----- df.index -----
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=12, step=1)
----- df.columns -----
Index(['语文', '数学', '外语'], dtype='object')
----- df.values -----
[[27 19 30]
[56 2 92]
[81 42 24]
[72 18 44]
[50 23 3]
[18 4 94]
[13 83 96]
[90 76 73]
[38 12 86]
[39 8 52]
[18 0 10]
[68 30 48]]
----- df.describe() -----
语文 数学 外语
count 12.000000 12.000000 12.000000
mean 47.500000 26.416667 54.333333
std 26.182923 27.628899 33.499887
min 13.000000 0.000000 3.000000
25% 24.750000 7.000000 28.500000
50% 44.500000 18.500000 50.000000
75% 69.000000 33.000000 87.500000
max 90.000000 83.000000 96.000000
----- df.info() -----
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 12 entries, 0 to 11
Data columns (total 3 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 语文 12 non-null int32
1 数学 12 non-null int32
2 外语 12 non-null int32
dtypes: int32(3)
memory usage: 272.0 bytes
None
"""
4.数据的输入与输出
4-1.CSV
4-1-1.数据写入CSV
代码示例:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[3, 5]),
columns=['IT', '化⼯', '⽣物', '教师', '⼠兵'])
# 查看数据
print(df)
df.to_csv('./20221205_info.csv',
sep=',',
header=True,
index=True)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
0 31 24 49 23 3
1 9 1 27 31 4
2 20 30 7 32 24
"""
sep = ‘,’ # ⽂本分隔符,默认是逗号
header = True # 是否保存列索引
index = True # 是否保存⾏索引,保存⾏索引,⽂件被加载时,默认⾏索引会作为⼀列

- 找到文件所在路径打开文件
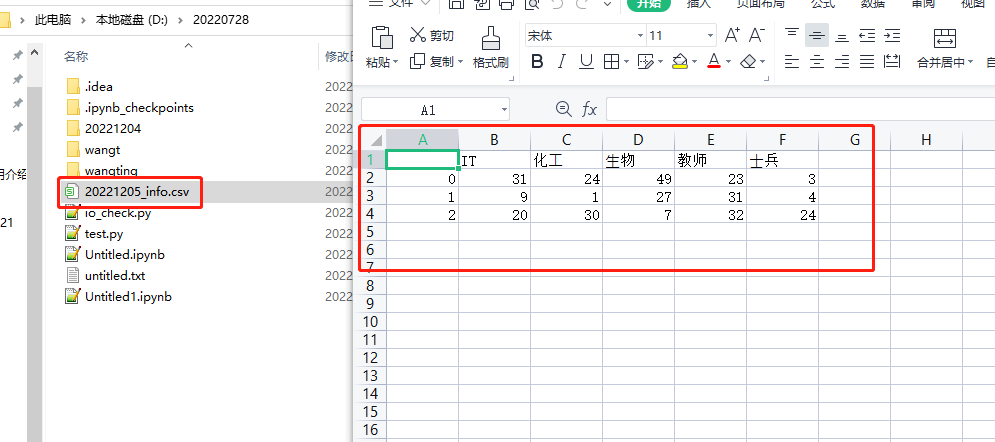
4-1-2.读取CSV
- 使用read_csv
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('./20221205_info.csv',
sep=',',
header=[0],
index_col=0)
print(df)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
0 31 24 49 23 3
1 9 1 27 31 4
2 20 30 7 32 24
"""
- 使用read_table
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_table('./20221205_info.csv',
sep=',',
header=[0],
index_col=0)
print(df)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
0 31 24 49 23 3
1 9 1 27 31 4
2 20 30 7 32 24
"""
4-2.Excel
操作Excel文件需要安装相关的模块工具
pip install xlrd -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install xlwt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install openpyxl -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
xlwt包可以正常使用,但是在使用时官方会提示警告:
FutureWarning: As the xlwt package is no longer maintained, the xlwt engine will be removed in a future version of pandas. This is the only engine in pandas that supports writing in the xls format. Install openpyxl and write to an xlsx file instead. You can set the option io.excel.xls.writer to ‘xlwt’ to silence this warning. While this option is deprecated and will also raise a warning, it can be globally set and the warning suppressed.
index=False)由于xlwt包不再维护,未来版本的panda将删除xlwt引擎。这是panda中唯一支持xls格式编写的引擎。后续可以安装openpyxl并改为写入xlsx文件来替代原来使用习惯
代码示例1:
单分页sheet
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[3, 5]),
columns=['IT', '化⼯', '⽣物', '教师', '⼠兵'])
df1.to_excel('./20221206.xlsx',
sheet_name='salary',
header=True,
index=False)
df_info = pd.read_excel('./20221206.xlsx',
sheet_name='salary',
header=0,
index_col=0)
print(df_info)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
26 33 2 15 47
33 1 11 48 39
26 7 24 30 0
"""
代码示例2:
多分页sheet
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[3, 5]),
columns=['IT', '化⼯', '⽣物', '教师', '⼠兵'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[4, 3]),
columns=['Python', 'Tensorflow', 'Keras'])
with pd.ExcelWriter('./20221206_data.xlsx') as writer:
df1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='salary', index=False)
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='score', index=False)
data_salary = pd.read_excel('./20221206_data.xlsx',
sheet_name='salary')
print(data_salary)
data_score = pd.read_excel('./20221206_data.xlsx',
sheet_name='score')
print(data_score)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
0 43 31 17 33 28
1 17 15 44 26 43
2 47 21 15 19 3
Python Tensorflow Keras
0 48 32 16
1 14 30 3
2 10 28 36
3 42 1 1
"""
4-3.SQL
操作SQL需要安装相关的模块工具
安装依赖组件模块、准备MySQL实验环境
pip install sqlalchemy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install pymysql -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple

[root@wangting ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database pandas;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec)
代码示例:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[150, 3]),
columns=['Python', 'Tensorflow', 'Keras'])
conn = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@172.192.55.12/pandas?charset=UTF8MB4')
df.to_sql('score',
conn,
if_exists='append')
data = pd.read_sql('select * from score limit 5', conn,index_col=None)
print(data)
""" 输出结果
index Python Tensorflow Keras
0 0 1 1 14
1 1 43 40 43
2 2 0 3 31
3 3 27 0 10
4 4 38 45 24
"""
从MySQL中查看验证
MariaDB [(none)]> use pandas;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
MariaDB [pandas]> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_pandas |
+------------------+
| score |
+------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [pandas]> select * from score limit 3;
+-------+--------+------------+-------+
| index | Python | Tensorflow | Keras |
+-------+--------+------------+-------+
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 14 |
| 1 | 43 | 40 | 43 |
| 2 | 0 | 3 | 31 |
+-------+--------+------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [pandas]> desc score;
+------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| index | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| Python | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| Tensorflow | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| Keras | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
4-4.HDF5
-
HDF5是⼀个独特的技术套件,可以管理⾮常⼤和复杂的数据收集。
-
HDF5,可以存储不同类型数据的⽂件格式,后缀通常是.h5,它的结构是层次性的。
-
⼀个HDF5⽂件可以被看作是⼀个组包含了各类不同的数据集


对于HDF5⽂件中的数据存储,有两个核⼼概念:group 和 dataset
dataset 代表数据集,⼀个⽂件当中可以存放不同种类的数据集,这些数据集如何管理,就⽤到了group
最直观的理解,可以参考我们的⽂件管理系统,不同的⽂件位于不同的⽬录下。
⽬录就是HDF5中的group, 描述了数据集dataset的分类信息,通过group 有效的将多种dataset 进⾏管
理和区分;⽂件就是HDF5中的dataset, 表示的是具体的数据。
安装相关HDF5模块:
pip install tables -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
代码示例:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[4, 5]), columns=['IT', '化⼯', '⽣物', '教师', '⼠兵'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 50, size=[6, 3]), columns=['Python', 'Tensorflow', 'Keras'])
df1.to_hdf('./data.h5', key='salary')
df2.to_hdf('./data.h5', key='score')
salary_info = pd.read_hdf('./data.h5', key='salary')
print(salary_info)
score_info = pd.read_hdf('./data.h5', key='score')
print(score_info)
""" 输出结果
IT 化⼯ ⽣物 教师 ⼠兵
0 30 43 4 21 23
1 9 39 37 48 41
2 29 36 39 31 46
3 7 40 27 14 48
Python Tensorflow Keras
0 22 49 23
1 47 18 25
2 17 17 31
3 2 1 24
4 33 38 16
5 14 21 47
"""
5.数据选取
5-1.获取数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[8, 3]), columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print("----- print(df) -----")
print(df)
# 获取单列,Series
print("----- df['Chinese'] -----")
print(df['Chinese'])
# 获取单列,Series
print("----- df.English -----")
print(df.English)
# 获取多列,DataFrame
print("----- df[['Chinese', 'English']] -----")
print(df[['Chinese', 'English']])
# 行切片
print("----- df[3:15] -----")
print(df[3:15])
""" 输出结果
----- print(df) -----
Chinese Math English
0 87 24 107
1 37 55 8
2 28 22 77
3 77 138 76
4 16 98 57
5 93 63 60
6 120 26 52
7 84 8 110
----- df['Chinese'] -----
0 87
1 37
2 28
3 77
4 16
5 93
6 120
7 84
Name: Chinese, dtype: int32
----- df.English -----
0 107
1 8
2 77
3 76
4 57
5 60
6 52
7 110
Name: English, dtype: int32
----- df[['Chinese', 'English']] -----
Chinese English
0 87 107
1 37 8
2 28 77
3 77 76
4 16 57
5 93 60
6 120 52
7 84 110
----- df[3:15] -----
Chinese Math English
3 77 138 76
4 16 98 57
5 93 63 60
6 120 26 52
7 84 8 110
"""
5-2.标签选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[10, 3]),
index=list('ABCDEFGHIJ'), columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print("----- df -----")
print(df)
# 选取指定⾏标签数据
print("----- df.loc[['A', 'C', 'D', 'F']] -----")
print(df.loc[['A', 'C', 'D', 'F']])
# 根据⾏标签切⽚,选取指定列标签的数据
print("----- df.loc['A':'E', ['Chinese', 'English']] -----")
print(df.loc['A':'E', ['Chinese', 'English']])
# :默认保留所有⾏
print("----- df.loc[:, ['English', 'Math']] -----")
print(df.loc[:, ['English', 'Math']])
# ⾏切⽚从标签E开始每2个中取⼀个,列标签进⾏切⽚
print("----- df.loc['E'::2, 'Chinese':'Math'] -----")
print(df.loc['E'::2, 'Chinese':'Math'])
# 选取标量值
print("----- df.loc['A', 'Chinese'] -----")
print(df.loc['A', 'Chinese'])
""" 输出结果
----- df -----
Chinese Math English
A 64 46 107
B 115 104 9
C 30 78 27
D 30 52 47
E 120 38 143
F 14 32 22
G 63 146 106
H 78 22 17
I 31 63 147
J 26 110 78
----- df.loc[['A', 'C', 'D', 'F']] -----
Chinese Math English
A 64 46 107
C 30 78 27
D 30 52 47
F 14 32 22
----- df.loc['A':'E', ['Chinese', 'English']] -----
Chinese English
A 64 107
B 115 9
C 30 27
D 30 47
E 120 143
----- df.loc[:, ['English', 'Math']] -----
English Math
A 107 46
B 9 104
C 27 78
D 47 52
E 143 38
F 22 32
G 106 146
H 17 22
I 147 63
J 78 110
----- df.loc['E'::2, 'Chinese':'Math'] -----
Chinese Math
E 120 38
G 63 146
I 31 63
----- df.loc['A', 'Chinese'] -----
64
"""
5-3.位置选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[10, 3]), index=list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 107 3 101
B 100 3 108
C 75 5 90
D 143 86 22
E 97 76 22
F 80 33 99
G 111 60 5
H 48 126 60
I 7 44 74
J 80 99 125
"""
# ⽤整数位置选择
print(df.iloc[4])
"""
Chinese 97
Math 76
English 22
Name: E, dtype: int32
"""
# ⽤整数切⽚,类似NumPy
print(df.iloc[2:8, 0:2])
"""
Chinese Math
C 75 5
D 143 86
E 97 76
F 80 33
G 111 60
H 48 126
"""
# 整数列表按位置切⽚
print(df.iloc[[1, 3, 5], [0, 2, 1]])
"""
Chinese English Math
B 100 108 3
D 143 22 86
F 80 99 33
"""
# ⾏切⽚
print(df.iloc[1:3, :])
"""
Chinese Math English
B 100 3 108
C 75 5 90
"""
# 列切⽚
print(df.iloc[:, :2])
"""
Chinese Math
A 107 3
B 100 3
C 75 5
D 143 86
E 97 76
F 80 33
G 111 60
H 48 126
I 7 44
J 80 99
"""
# 选取标量值
print(df.iloc[0, 2])
"""
101
"""
5-4.boolean索引
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[8, 3]),
index=list('ABCDEFGH'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 145 115 112
B 75 138 146
C 110 149 0
D 114 78 124
E 134 32 111
F 112 136 118
G 59 39 33
H 74 132 145
"""
print(df[df.Chinese > 100])
"""
Chinese Math English
A 145 115 112
C 110 149 0
D 114 78 124
E 134 32 111
F 112 136 118
"""
# 多个条件同时满足使用&符连接
print(df[(df.Chinese > 50) & (df['English'] > 50)])
"""
Chinese Math English
A 145 115 112
B 75 138 146
D 114 78 124
E 134 32 111
F 112 136 118
H 74 132 145
"""
# 选择DataFrame中满⾜条件的值,如果满⾜返回值,不满足则返回空数据NaN
print(df[df > 50])
"""
Chinese Math English
A 145 115.0 112.0
B 75 138.0 146.0
C 110 149.0 NaN
D 114 78.0 124.0
E 134 NaN 111.0
F 112 136.0 118.0
G 59 NaN NaN
H 74 132.0 145.0
"""
# isin判断是否在数组中,返回也是boolean类型值
print(df[df.index.isin(['A', 'C', 'F'])])
"""
Chinese Math English
A 145 115 112
C 110 149 0
F 112 136 118
"""
5-5.赋值操作
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[8, 3]),
index=list('ABCDEFGH'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 25 130 34
B 41 146 23
C 98 53 37
D 127 119 64
E 19 103 100
F 108 146 68
G 149 107 40
H 36 131 125
"""
s = pd.Series(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=8), index=list('ABCDEFGH'), name='Python')
df['Python'] = s
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English Python
A 25 130 34 49
B 41 146 23 5
C 98 53 37 76
D 127 119 64 139
E 19 103 100 38
F 108 146 68 59
G 149 107 40 41
H 36 131 125 122
"""
# 按标签赋值:索引A和科目索引Python赋值
df.loc['A', 'Python'] = 256
# 按位置赋值
df.iloc[3, 2] = 512
# 按NumPy数组进⾏赋值
df.loc[:, 'Chinese'] = np.array([128] * 8)
# 按照where条件进⾏赋值,⼤于等于128变成原来的负数,否则不变
df[df >= 128] = -df
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English Python
A -128 -130 34 -256
B -128 -146 23 5
C -128 53 37 76
D -128 119 -512 -139
E -128 103 100 38
F -128 -146 68 59
G -128 107 40 41
H -128 -131 125 122
"""

6.数据集成
6-1.concat数据串联拼接
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[3, 3]),
index=list('ABC'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=[3, 3]),
index=list('DEF'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=(3, 2)),
index=list('ABC'),
columns=['Python', 'Java'])
print(df1)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 148 143 47
B 16 50 31
C 121 75 95
"""
print(df2)
"""
Chinese Math English
D 120 97 67
E 94 99 59
F 67 64 78
"""
print(df3)
"""
Python Java
A 93 28
B 110 61
C 56 15
"""
print(pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=0))
"""
Chinese Math English
A 148 143 47
B 16 50 31
C 121 75 95
D 120 97 67
E 94 99 59
F 67 64 78
"""
print(df1.append(df2))
"""
Chinese Math English
A 148 143 47
B 16 50 31
C 121 75 95
D 120 97 67
E 94 99 59
F 67 64 78
"""
print(pd.concat([df1, df3], axis=1))
"""
Chinese Math English Python Java
A 148 143 47 93 28
B 16 50 31 110 61
C 121 75 95 56 15
"""
6-2.数据插入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 151, size=(3, 3)),
index=list('ABC'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
# 插⼊列
df.insert(loc=1, column='Python', value=1024)
print(df)
"""
Chinese Python Math English
A 32 1024 103 51
B 141 1024 120 62
C 148 1024 57 38
"""
# 注意:
# 1.对⾏的操作,使⽤追加append,默认在最后⾯追加,行插入⽆法指定位置
# 2.所以想要在指定位置插⼊⾏:切割-> 添加-> 合并
6-3.Join SQL风格合并
数据集的合并(merge)或连接(join)运算是通过⼀个或者多个键将数据链接起来的。这些运算是关系型数据库的核⼼操作。pandas的merge函数是数据集进⾏join运算的主要切⼊点
代码示例1:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data={'name':
['周淑怡', '沫子', '呆妹', '阿冷'], 'weight': [70, 55, 75, 65]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data={'name':
['周淑怡', '沫子', '呆妹', '阿冷'], 'height': [165, 164, 167, 166]})
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data={'名字':
['周淑怡', '沫子', '呆妹', '阿冷'], 'height': [165, 164, 167, 166]})
print(df1)
"""
name weight
0 周淑怡 70
1 沫子 55
2 呆妹 75
3 阿冷 65
"""
print(df2)
"""
name height
0 周淑怡 165
1 沫子 164
2 呆妹 167
3 阿冷 166
"""
print(df3)
"""
名字 height
0 周淑怡 165
1 沫子 164
2 呆妹 167
3 阿冷 166
"""
data1 = pd.merge(df1, df2,
how='inner',
on='name')
print(data1)
"""
name weight height
0 周淑怡 70 165
1 沫子 55 164
2 呆妹 75 167
3 阿冷 65 166
"""
data2 = pd.merge(df1, df3,
how='outer',
left_on='name',
right_on='名字')
print(data2)
"""
name weight 名字 height
0 周淑怡 70 周淑怡 165
1 沫子 55 沫子 164
2 呆妹 75 呆妹 167
3 阿冷 65 阿冷 166
"""
代码示例2:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 151, size=(3, 3)),
index=list('ABC'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 38 139 87
B 107 127 74
C 76 88 102
"""
score_mean = pd.DataFrame(df.mean(axis=1).round(1), columns=['平均分'])
data = pd.merge(left=df, right=score_mean,
left_index=True,
right_index=True)
print(data)
"""
Chinese Math English 平均分
A 38 139 87 88.0
B 107 127 74 102.7
C 76 88 102 88.7
"""
7.数据清洗
数据样例:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'color':
['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', None, 'red'],
'price': [10, 20, 10, 15, 20, 0, np.NaN]})
print(df)
"""
color price
0 red 10.0
1 blue 20.0
2 red 10.0
3 green 15.0
4 blue 20.0
5 None 0.0
6 red NaN
"""
- 重复数据删除过滤
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'color':
['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', None, 'red'],
'price': [10, 20, 10, 15, 20, 0, np.NaN]})
# 判断是否存在重复数据
df.duplicated()
# 删除重复数据
df_new = df.drop_duplicates()
print(df_new)
"""
color price
0 red 10.0
1 blue 20.0
3 green 15.0
5 None 0.0
6 red NaN
"""
7-1.空数据删除过滤
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'color':
['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', None, 'red'],
'price': [10, 20, 10, 15, 20, 0, np.NaN]})
# 判断是否存在空数据,存在返回True,否则返回False
df.isnull()
# 删除空数据
data1 = df.dropna(how='any')
print(data1)
"""
color price
0 red 10.0
1 blue 20.0
2 red 10.0
3 green 15.0
4 blue 20.0
"""
7-2.空数据填充替换
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'color':
['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', None, 'red'],
'price': [10, 20, 10, 15, 20, 0, np.NaN]})
# 判断是否存在空数据,存在返回True,否则返回False
df.isnull()
# 将空数据替换成默认值500
data2 = df.fillna(value=500)
print(data2)
"""
color price
0 red 10.0
1 blue 20.0
2 red 10.0
3 green 15.0
4 blue 20.0
5 500 0.0
6 red 500.0
"""
7-3.筛选指定行或列数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'color':
['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', None, 'red'],
'price': [10, 20, 10, 15, 20, 0, np.NaN]})
# 直接删除某列
# del df['color']
# print(df)
"""
price
0 10.0
1 20.0
2 10.0
3 15.0
4 20.0
5 0.0
6 NaN
"""
# 删除指定列
# data1 = df.drop(labels=['price'], axis=1)
# print(data1)
"""
color
0 red
1 blue
2 red
3 green
4 blue
5 None
6 red
"""
# 删除指定⾏
data2 = df.drop(labels=[0, 1, 5], axis=0)
print(data2)
"""
color price
2 red 10.0
3 green 15.0
4 blue 20.0
6 red NaN
"""
7-4.函数filter使用
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(([3, 7, 1], [2, 8, 256])),
index=['dog', 'cat'],
columns=['China', 'America', 'France'])
print(df)
"""
China America France
dog 3 7 1
cat 2 8 256
"""
print(df.filter(items=['China', 'France']))
"""
China France
dog 3 1
cat 2 256
"""
# 根据正则表达式删选列标签
print(df.filter(regex='a$', axis=1))
""" 列索引中以a结尾的数据
China America
dog 3 7
cat 2 8
"""
# 选择⾏中包含og
print(df.filter(like='og', axis=0))
""" 行索引中包含og关键词
China America France
dog 3 7 1
"""
7-5.异常值的剔除过滤
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randn(10000, 3))
# 根据条件找出不满⾜条件数据
data = (df > 3 * df.std()).any(axis=1) # std()标准差
# 找出不满⾜条件的⾏索引
index = df[data].index
# 再根据⾏索引,进⾏数据删除
data_new = df.drop(labels=index, axis=0)
print(data_new)
"""
[9943 rows x 3 columns]
原数据10000行
"""
8.数据转换
8-1.轴和元素替换
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(5, 3)),
index=list('ABCDE'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 3 8 0
B 0 2 5
C 0 4 1
D 1 2 9
E 2 2 0
"""
# 定义指定位置为空数值
df.iloc[3, [1, 2]] = None
print(df)
""" 行索引3,列索引1和2的改为空
Chinese Math English
A 3 8.0 0.0
B 0 2.0 5.0
C 0 4.0 1.0
D 1 NaN NaN
E 2 2.0 0.0
"""
# 重命名行与列索引
data1 = df.rename(index={'A': 'AAA', 'B': 'BBB'}, columns={'Chinese': '语文'})
print(data1)
""" 行索引和列索引替换
语文 Math English
AAA 3 8.0 0.0
BBB 0 2.0 5.0
C 0 4.0 1.0
D 1 NaN NaN
E 2 2.0 0.0
"""
# 替换值
print(df.replace(3, 33333))
""" 3替换为33333
Chinese Math English
A 33333 8.0 0.0
B 0 2.0 5.0
C 0 4.0 1.0
D 1 NaN NaN
E 2 2.0 0.0
"""
print(df.replace([0, 7], 777000))
""" 将值为0或7替换为777000
Chinese Math English
A 3 8.0 777000.0
B 777000 2.0 5.0
C 777000 4.0 1.0
D 1 NaN NaN
E 2 2.0 777000.0
"""
print(df.replace({0: 512, np.nan: 666}))
""" 数值为0的值替换为512,空值替换为666
Chinese Math English
A 3 8.0 512.0
B 512 2.0 5.0
C 512 4.0 1.0
D 1 666.0 666.0
E 2 2.0 512.0
"""
print(df.replace({'Chinese': 0}, -666))
""" Chinese列中数值为0的替换为-666
Chinese Math English
A 3 8.0 0.0
B -666 2.0 5.0
C -666 4.0 1.0
D 1 NaN NaN
E 2 2.0 0.0
"""
8-2.map Series元素改变
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 3, size=(5, 3)),
index=list('ABCDE'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 1 0 1
B 0 1 0
C 1 1 0
D 0 2 0
E 2 2 2
"""
# map批量元素改变,Series专有
data1 = df['English'].map({0: '低', 1: '中', 2: '高'})
print(data1)
"""
A 中
B 低
C 低
D 低
E 高
"""
data2 = df['Chinese'].map(lambda x: True if x >= 1 else False)
print(data2)
"""
A True
B False
C True
D False
E True
"""
def convert(x):
if x == 0:
return "低"
elif x == 1:
return "中"
else:
return "高"
data3 = df['Math'].map(convert)
print(data3)
"""
A 低
B 中
C 中
D 高
E 高
"""
8-3.apply元素改变
既⽀持Series,也⽀持DataFrame
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 3)),
index=list('ABCDEF'),
columns=['语文', '数学', '外语'])
print(df)
"""
语文 数学 外语
A 3 2 5
B 6 4 4
C 2 8 8
D 7 6 4
E 1 0 3
F 5 1 0
"""
data1 = df['外语'].apply(lambda x: True if x > 5 else False)
print(data1)
"""
A False
B False
C True
D False
E False
F False
"""
# 列的中位数
data2 = df.apply(lambda x: x.median(), axis=0)
print(data2)
"""
语文 4.0
数学 3.0
外语 4.0
"""
# ⾏平均值,计数
def convert(x):
return x.mean().round(1), x.count()
print(df.apply(convert, axis=1))
"""
A (3.3, 3)
B (4.7, 3)
C (6.0, 3)
D (5.7, 3)
E (1.3, 3)
F (2.0, 3)
"""
# 计算DataFrame中每个元素
print(df.applymap(lambda x: x + 100))
""" 每个值增加100
语文 数学 外语
A 103 102 105
B 106 104 104
C 102 108 108
D 107 106 104
E 101 100 103
F 105 101 100
"""
8-4.transform变形
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 3)),
index=list('ABCDEF'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 8 6 5
B 3 4 4
C 7 7 5
D 8 7 5
E 1 9 6
F 2 8 3
"""
# 单列执⾏多项计算
data1 = df['Chinese'].transform([np.sqrt, np.exp])
print(data1)
"""
sqrt exp
A 2.828427 2980.957987
B 1.732051 20.085537
C 2.645751 1096.633158
D 2.828427 2980.957987
E 1.000000 2.718282
F 1.414214 7.389056
"""
def convert_aa(x):
return x + 100
def convert_bb(x):
return x + 200
def convert_cc(x):
return x + 300
# 多列分别执⾏不同的计算
data2 = df.transform({'Chinese': convert_aa, 'Math': convert_bb, 'English': convert_cc})
print(data2)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 108 206 305
B 103 204 304
C 107 207 305
D 108 207 305
E 101 209 306
F 102 208 303
"""
8-5.重排随机抽样哑变量(虚拟变量)
代码示例1:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 3)),
index=list('ABCDEF'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 9 8 0
B 6 2 1
C 4 5 5
D 9 8 5
E 1 1 3
F 6 8 7
"""
# 获取随机排序数
ran = np.random.permutation(6)
print(ran)
"""
[3 0 2 1 5 4]
"""
# 根据ran获取随机排序数来随机重排DataFrame
df1 = df.take(ran)
print(df1)
"""
Chinese Math English
D 9 8 5
A 9 8 0
C 4 5 5
B 6 2 1
F 6 8 7
E 1 1 3
"""
# 随机抽样
print(df.take(np.random.randint(0, 6, size=4)))
"""
Chinese Math English
F 6 8 7
D 9 8 5
D 9 8 5
C 4 5 5
"""
代码示例2:
import pandas as pd
# 哑变量,独热编码,1表示有,0表示没有
df = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['b', 'b', 'a', 'c', 'a', 'b']})
print(pd.get_dummies(df, prefix='', prefix_sep=''))
"""
a b c
0 0 1 0
1 0 1 0
2 1 0 0
3 0 0 1
4 1 0 0
5 0 1 0
"""
9.数据重塑
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(5, 3)),
index=list('ABCDE'),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df1)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 93 32 14
B 55 79 84
C 14 10 36
D 4 42 88
E 91 81 20
"""
# 转置
print(df1.T)
"""
A B C D E
Chinese 93 55 14 4 91
Math 32 79 10 42 81
English 14 84 36 88 20
"""
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(10, 3)),
index=pd.MultiIndex.from_product([list('ABCDE'), ['期中', '期末']]),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df2)
"""
Chinese Math English
A 期中 80 56 98
期末 86 46 53
B 期中 72 81 22
期末 98 99 23
C 期中 75 38 91
期末 11 95 28
D 期中 98 13 29
期末 46 23 87
E 期中 6 33 70
期末 44 30 67
"""
# ⾏旋转成列,level指定哪⼀层,进⾏变换
print(df2.unstack(level=-1))
"""
Chinese Math English
期中 期末 期中 期末 期中 期末
A 80 86 56 46 98 53
B 72 98 81 99 22 23
C 75 11 38 95 91 28
D 98 46 13 23 29 87
E 6 44 33 30 70 67
"""
# 列旋转成⾏
print(df2.stack())
"""
A 期中 Chinese 80
Math 56
English 98
期末 Chinese 86
Math 46
English 53
B 期中 Chinese 72
Math 81
English 22
期末 Chinese 98
Math 99
English 23
C 期中 Chinese 75
Math 38
English 91
期末 Chinese 11
Math 95
English 28
D 期中 Chinese 98
Math 13
English 29
期末 Chinese 46
Math 23
English 87
E 期中 Chinese 6
Math 33
English 70
期末 Chinese 44
Math 30
English 67
"""
# ⾏列互换
print(df2.stack().unstack(level=1))
"""
期中 期末
A Chinese 80 86
Math 56 46
English 98 53
B Chinese 72 98
Math 81 99
English 22 23
C Chinese 75 11
Math 38 95
English 91 28
D Chinese 98 46
Math 13 23
English 29 87
E Chinese 6 44
Math 33 30
English 70 67
"""
# 各学科平均分
print(df2.mean())
"""
Chinese 61.6
Math 51.4
English 56.8
"""
# 各学科,每个⼈期中期末平均分
print(df2.groupby(level=0).mean())
"""
Chinese Math English
A 83.0 51.0 75.5
B 85.0 90.0 22.5
C 43.0 66.5 59.5
D 72.0 18.0 58.0
E 25.0 31.5 68.5
"""
# 各学科,期中期末所有⼈平均分
print(df2.groupby(level=1).mean())
"""
Chinese Math English
期中 66.2 44.2 62.0
期末 57.0 58.6 51.6
"""
10.数学和统计⽅法
pandas对象拥有⼀组常⽤的数学和统计⽅法。它们属于汇总统计,对Series汇总计算获取mean、max值或者对DataFrame⾏、列汇总计算返回⼀个Series。
10-1.简单统计指标
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(10, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
0 16 4 24
1 13 78 31
2 15 79 75
3 25 18 29
4 77 6 41
5 53 32 32
6 7 37 16
7 60 61 29
8 56 76 0
9 59 39 86
"""
# ⾮NA值的数量
print(df.count())
"""
Chinese 10
Math 10
English 10
"""
# 轴0最⼤值,即每⼀列最⼤值
print(df.max(axis=0))
"""
Chinese 77
Math 79
English 86
"""
# 默认计算轴0最⼩值
print(df.min())
"""
Chinese 7
Math 4
English 0
"""
# 中位数
print(df.median())
"""
Chinese 39.0
Math 38.0
English 30.0
"""
# 求和
print(df.sum())
"""
Chinese 381
Math 430
English 363
"""
# 轴1平均值,即每⼀⾏的平均值
print(df.mean(axis=1))
"""
0 14.666667
1 40.666667
2 56.333333
3 24.000000
4 41.333333
5 39.000000
6 20.000000
7 50.000000
8 44.000000
9 61.333333
"""
# 分位数
print(df.quantile(q=[0.2, 0.4, 0.8]))
"""
Chinese Math English
0.2 14.6 15.6 22.4
0.4 21.4 35.0 29.0
0.8 59.2 76.4 47.8
"""
# 查看数值型列的汇总各类统计
print(df.describe())
"""
Chinese Math English
count 10.000000 10.000000 10.000000
mean 38.100000 43.000000 36.300000
std 25.304589 29.101355 25.871692
min 7.000000 4.000000 0.000000
25% 15.250000 21.500000 25.250000
50% 39.000000 38.000000 30.000000
75% 58.250000 72.250000 38.750000
max 77.000000 79.000000 86.000000
"""
10-2.索引标签、位置获取
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(5, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
0 50 93 30
1 53 47 94
2 64 24 79
3 76 74 83
4 55 52 8
"""
# 计算最⼩值位置 : 0
print(df['Chinese'].argmin())
# 计算最⼤值位置 : 1
print(df['English'].argmax())
# 最⼤值索引标签
print(df.idxmax())
"""
Chinese 3
Math 0
English 1
"""
# 最⼩值索引标签
print(df.idxmin())
"""
Chinese 0
Math 2
English 4
"""
10-3.更多统计指标
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(12, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
0 0 3 2
1 7 8 1
2 4 3 9
3 5 5 0
4 4 5 5
5 8 0 4
6 4 1 2
7 8 0 4
8 0 0 1
9 2 7 0
10 7 2 0
11 1 8 0
"""
# 统计元素出现次数
print(df['Chinese'].value_counts())
"""
4 3
0 2
7 2
8 2
5 1
2 1
1 1
"""
# 去重
print(df['English'].unique())
"""
[2 1 9 0 5 4]
"""
# 累加
print(df.cumsum())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 0 3 2
1 7 11 3
2 11 14 12
3 16 19 12
4 20 24 17
5 28 24 21
6 32 25 23
7 40 25 27
8 40 25 28
9 42 32 28
10 49 34 28
11 50 42 28
"""
# 累乘
print(df.cumprod())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 0 3 2
1 0 24 2
2 0 72 18
3 0 360 0
4 0 1800 0
5 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
10 0 0 0
11 0 0 0
"""
# 标准差
print(df.std())
"""
Chinese 2.949063
Math 3.060006
English 2.741378
"""
# ⽅差
print(df.var())
"""
Chinese 8.696970
Math 9.363636
English 7.515152
"""
# 累计最⼩值
print(df.cummin())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 0 3 2
1 0 3 1
2 0 3 1
3 0 3 0
4 0 3 0
5 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
10 0 0 0
11 0 0 0
"""
# 累计最⼤值
print(df.cummax())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 0 3 2
1 7 8 2
2 7 8 9
3 7 8 9
4 7 8 9
5 8 8 9
6 8 8 9
7 8 8 9
8 8 8 9
9 8 8 9
10 8 8 9
11 8 8 9
"""
# 计算差分
print(df.diff())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 NaN NaN NaN
1 7.0 5.0 -1.0
2 -3.0 -5.0 8.0
3 1.0 2.0 -9.0
4 -1.0 0.0 5.0
5 4.0 -5.0 -1.0
6 -4.0 1.0 -2.0
7 4.0 -1.0 2.0
8 -8.0 0.0 -3.0
9 2.0 7.0 -1.0
10 5.0 -5.0 0.0
11 -6.0 6.0 0.0
"""
# 计算百分⽐变化
print(df.pct_change())
"""
Chinese Math English
0 NaN NaN NaN
1 inf 1.666667 -0.50
2 -0.428571 -0.625000 8.00
3 0.250000 0.666667 -1.00
4 -0.200000 0.000000 inf
5 1.000000 -1.000000 -0.20
6 -0.500000 inf -0.50
7 1.000000 -1.000000 1.00
8 -1.000000 NaN -0.75
9 inf inf -1.00
10 2.500000 -0.714286 NaN
11 -0.857143 3.000000 NaN
"""
10-4.高级统计指标
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
0 6 1 8
1 7 8 5
2 9 0 4
3 4 0 3
4 5 0 5
5 6 0 5
"""
# 属性的协⽅差
print(df.cov())
"""
Chinese Math English
Chinese 2.966667 1.3 0.2
Math 1.300000 10.3 0.6
English 0.200000 0.6 2.8
"""
# Python和Keras的协⽅差 0.2
print(df['Chinese'].cov(df['English']))
# 所有属性相关性系数
print(df.corr())
"""
Chinese Math English
Chinese 1.000000 0.235175 0.069393
Math 0.235175 1.000000 0.111726
English 0.069393 0.111726 1.000000
"""
# 单⼀属性相关性系数
print(df.corrwith(df['Math']))
"""
Chinese 0.235175
Math 1.000000
English 0.111726
"""
11.数据排序
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 30, size=(6, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
print(df)
"""
Chinese Math English
0 20 25 13
1 15 2 18
2 15 17 27
3 7 18 21
4 14 11 24
5 22 10 21
"""
# 按索引排序,升序
print(df.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True))
# 按列名排序,降序
print(df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False))
"""
Math English Chinese
0 25 13 20
1 2 18 15
2 17 27 15
3 18 21 7
4 11 24 14
5 10 21 22
"""
# 按列名属性值排序
print(df.sort_values(by=['Chinese']))
"""
Chinese Math English
3 7 18 21
4 14 11 24
1 15 2 18
2 15 17 27
0 20 25 13
5 22 10 21
"""
# 先按Chinese排序,再按English继续排序
print(df.sort_values(by=['Chinese', 'English']))
"""
Chinese Math English
3 7 18 21
4 14 11 24
1 15 2 18
2 15 17 27
0 20 25 13
5 22 10 21
"""
# 根据属性English排序,返回最⼤10个数据
print(df.nlargest(2, columns='English'))
"""
Chinese Math English
2 15 17 27
4 14 11 24
"""
# 根据属性Chinese排序,返回最⼩3个数据
print(df.nsmallest(3, columns='Chinese'))
"""
Chinese Math English
3 7 18 21
4 14 11 24
1 15 2 18
"""
12.分箱操作
-
分箱操作就是将连续数据转换为分类对应物的过程
-
分箱操作分为等距分箱和等频分箱
-
分箱操作也叫⾯元划分或者离散化
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0, 150, size=(15, 3)),
columns=['Chinese', 'Math', 'English'])
# 等宽分箱
print(pd.cut(df.Chinese, bins=3))
"""
0 (76.0, 113.0]
1 (76.0, 113.0]
2 (39.0, 76.0]
3 (76.0, 113.0]
4 (1.889, 39.0]
5 (76.0, 113.0]
6 (76.0, 113.0]
7 (1.889, 39.0]
8 (76.0, 113.0]
9 (1.889, 39.0]
10 (39.0, 76.0]
11 (76.0, 113.0]
12 (1.889, 39.0]
13 (39.0, 76.0]
14 (76.0, 113.0]
"""
# 指定宽度分箱
data1 = pd.cut(df.English,
bins=[0, 60, 90, 120, 150],
right=False,
labels=['不及格', '中等', '良好', '优秀'])
print(data1)
"""
0 良好
1 良好
2 不及格
3 不及格
4 良好
5 不及格
6 优秀
7 良好
8 不及格
9 良好
10 中等
11 中等
12 良好
13 良好
14 不及格
"""
# 等频分箱
data2 = pd.qcut(df.Chinese, q=4,
labels=['差', '中', '良', '优'])
print(data2)
"""
0 优
1 优
2 中
3 中
4 差
5 良
6 优
7 差
8 良
9 差
10 中
11 优
12 差
13 中
14 良
"""
13.分组聚合

13-1.分组
代码示例1:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 准备数据
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=10),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=10),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10)})
# 将0,1映射成男⼥
df['sex'] = df['sex'].map({0: '男', 1: '⼥'})
print(df.head(3))
"""
sex class Python Keras Tensorflow Java C++
0 男 6 33 130 77 87 45
1 ⼥ 6 53 102 62 108 23
2 ⼥ 2 113 83 14 59 119
"""
# 1、分组->可迭代对象
# 单分组
g = df.groupby(by='sex')[['Python', 'Java']]
for name, data in g:
print('组名:', name)
print('数据:', data)
"""
组名: ⼥
数据: sex class Python Keras Tensorflow Java C++
1 ⼥ 6 53 102 62 108 23
2 ⼥ 2 113 83 14 59 119
4 ⼥ 4 28 16 115 127 37
5 ⼥ 5 68 149 36 80 31
8 ⼥ 2 67 58 120 60 90
9 ⼥ 2 109 109 49 72 6
组名: 男
数据: sex class Python Keras Tensorflow Java C++
0 男 6 33 130 77 87 45
3 男 2 110 47 17 29 143
6 男 3 113 24 70 90 78
7 男 5 141 90 90 133 102
"""
"""
df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Python']] # 多分组
df['Python'].groupby(df['class']) # 单分组
df['Keras'].groupby([df['class'], df['sex']]) # 多分组
df.groupby(df.dtypes, axis=1) # 按数据类型分组
"""
- 通过字典进⾏分组
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=10),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=10),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10)})
# 通过字典进⾏分组
m = {'sex': 'category', 'class': 'category', 'Python': 'IT', 'Keras': 'IT', 'Tensorflow': 'IT', 'Java': 'IT',
'C + +': 'IT'}
for name, data in df.groupby(m, axis=1):
print('组名', name)
print('数据', data)
"""
组名 IT
数据 Python Keras Tensorflow Java
0 89 59 29 82
1 150 7 128 4
2 127 15 25 66
3 83 67 126 16
4 83 120 101 109
5 29 116 18 87
6 34 40 123 137
7 9 11 105 79
8 29 117 25 140
9 63 33 47 71
组名 category
数据 sex class
0 0 2
1 0 8
2 0 6
3 0 7
4 1 5
5 0 8
6 1 7
7 0 7
8 0 7
9 1 6
"""
13-2.分组聚合
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=10),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=10),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=10)})
# 保留1位⼩数
print(df.groupby(by='sex').mean().round(1))
"""
class Python Keras Tensorflow Java C++
sex
0 3.2 38.8 45.2 94.6 115.0 68.0
1 2.6 50.4 61.6 88.0 53.0 89.8
"""
# 按照班级和性别进⾏分组,Python、Keras的最⼤值聚合
print(df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Python', 'Keras']].max())
"""
Python Keras
class sex
1 0 97 95
1 80 63
2 0 30 47
3 0 72 63
1 113 45
5 0 104 111
7 1 114 80
"""
# 按照班级和性别进⾏分组,计数聚合。统计每个班,男⼥⼈数
print(df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex']).size())
"""
class sex
1 0 1
2 1 1
3 1 1
5 0 1
6 0 2
1 2
8 0 2
"""
# 基本描述性统计聚合
print(df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex']).describe())
"""
Python ... C++
count mean std min ... 25% 50% 75% max
class sex ...
1 0 1.0 97.0 NaN 97.0 ... 56.00 56.0 56.00 56.0
3 0 1.0 73.0 NaN 73.0 ... 134.00 134.0 134.00 134.0
4 0 2.0 88.0 60.811183 45.0 ... 44.25 69.5 94.75 120.0
5 1 2.0 61.0 53.740115 23.0 ... 106.50 110.0 113.50 117.0
6 0 1.0 135.0 NaN 135.0 ... 120.00 120.0 120.00 120.0
7 1 2.0 109.5 50.204581 74.0 ... 24.75 38.5 52.25 66.0
8 0 1.0 31.0 NaN 31.0 ... 23.00 23.0 23.00 23.0
"""
13-3.分组聚合apply、transform


import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=300),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=300),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300)})
# 分组后调⽤apply,transform封装单⼀函数计算
data1 = df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Python', 'Keras']].apply(np.mean).round(1)
print(data1)
"""
Python Keras
class sex
1 0 70.6 66.8
1 76.3 85.6
2 0 75.8 74.2
1 74.8 72.1
3 0 83.3 86.9
1 65.5 85.6
4 0 69.5 70.8
1 76.8 52.1
5 0 69.7 71.0
1 82.1 53.4
6 0 79.3 96.7
1 75.9 68.5
7 0 71.6 88.3
1 63.4 69.8
8 0 85.7 60.0
1 76.1 100.9
"""
# 最⼤值最⼩值归⼀化
def normalization(x):
return (x - x.min()) / (x.max() - x.min())
# 返回全数据,返回DataFrame.shape和原DataFrame.shape⼀样。
data2 = df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Python', 'Tensorflow']].transform(normalization).round(3)
print(data2)
"""
Python Tensorflow
0 0.460 0.353
1 0.386 0.925
2 0.510 0.255
3 0.748 0.341
4 0.946 0.589
.. ... ...
295 0.366 0.627
296 0.301 0.310
297 0.500 0.883
298 0.564 0.837
299 0.241 0.294
"""
13-4.分组聚合agg

import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=300),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=300),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300)})
# agg 多中统计汇总操作
# 分组后调⽤agg应⽤多种统计汇总
data1 = df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Tensorflow', 'Keras']].agg([np.max, np.min, pd.Series.count])
print(data1)
"""
Tensorflow Keras
amax amin count amax amin count
class sex
1 0 150 20 20 146 10 20
1 140 12 18 145 6 18
2 0 139 21 11 141 45 11
1 132 11 16 150 14 16
3 0 148 15 16 149 18 16
1 143 0 26 145 1 26
4 0 148 7 17 144 5 17
1 135 6 17 129 7 17
5 0 146 31 18 145 0 18
1 139 33 17 144 17 17
6 0 148 3 23 144 4 23
1 141 2 27 147 0 27
7 0 125 1 19 149 6 19
1 140 4 21 142 0 21
8 0 126 2 16 127 7 16
1 135 1 18 148 8 18
"""
# 分组后不同属性应⽤多种不同统计汇总
data2 = df.groupby(by=['class', 'sex'])[['Python', 'Keras']].agg({'Python': [('最⼤值', np.max), ('最⼩值', np.min)],
'Keras': [('计数', pd.Series.count),
('中位数', np.median)]})
print(data2)
"""
Python Keras
最⼤值 最⼩值 计数 中位数
class sex
1 0 149 13 20 78.0
1 119 4 18 103.0
2 0 131 1 11 100.0
1 144 0 16 57.0
3 0 148 8 16 87.0
1 146 1 26 85.5
4 0 149 3 17 73.0
1 148 2 17 48.0
5 0 148 14 18 79.5
1 139 7 17 74.0
6 0 150 1 23 87.0
1 146 0 27 103.0
7 0 148 3 19 99.0
1 146 0 21 69.0
8 0 142 18 16 75.5
1 150 1 18 56.0
"""
13-5.透视表pivot_table
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data={'sex': np.random.randint(0, 2, size=300),
'class': np.random.randint(1, 9, size=300),
'Python': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Keras': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Tensorflow': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'Java': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300),
'C++': np.random.randint(0, 151, size=300)})
# 透视表
def count(x):
return len(x)
# 要透视分组的值
data = df.pivot_table(values=['Python', 'Keras', 'Tensorflow'],
index=['class', 'sex'],
aggfunc={'Python': [('最⼤值', np.max)],
'Keras': [('最⼩值', np.min), ('中位数', np.median)],
'Tensorflow': [('最⼩值', np.min), ('平均值', np.mean), ('计数', count)]})
print(data)
"""
Keras Python Tensorflow
中位数 最⼩值 最⼤值 平均值 最⼩值 计数
class sex
1 0 98.0 26.0 147 52.347826 4.0 23.0
1 50.0 4.0 126 89.562500 5.0 16.0
2 0 65.0 0.0 148 62.956522 0.0 23.0
1 91.0 9.0 146 84.850000 19.0 20.0
3 0 61.0 1.0 135 75.260870 6.0 23.0
1 85.0 2.0 139 44.250000 1.0 16.0
4 0 88.0 5.0 150 76.866667 6.0 15.0
1 101.0 20.0 142 76.125000 6.0 16.0
5 0 104.5 7.0 150 80.200000 1.0 20.0
1 55.0 1.0 150 77.238095 28.0 21.0
6 0 69.5 1.0 148 96.318182 31.0 22.0
1 81.0 16.0 138 74.800000 19.0 15.0
7 0 69.5 0.0 150 76.136364 2.0 22.0
1 67.0 2.0 141 56.142857 2.0 14.0
8 0 60.5 3.0 142 75.687500 10.0 16.0
1 72.5 5.0 135 79.111111 4.0 18.0
"""
14.时间序列
14-1.时间戳操作
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 时刻数据 2022-12-07 10:00:00
print(pd.Timestamp('2022-12-07 10')) # 2022-12-07 10:00:00
# 时期数据
print(pd.Period('2022-12-07 10:08:08', freq='Y')) # 2022
print(pd.Period('2022-12-07 10:08:08', freq='M')) # 2022-12
print(pd.Period('2022-12-07 10:08:08', freq='D')) # 2022-12-07
print(pd.Period('2022-12-07 10:08:08', freq='H')) # 2022-12-07 10:00
# 批量时刻数据
index = pd.date_range('2022.12.07', periods=5, freq='M')
print(index)
"""
'2022-12-31',
'2023-01-31',
'2023-02-28',
'2023-03-31',
'2023-04-30'
"""
# 批量时期数据
print(pd.period_range('2022.12.07', periods=5, freq='M'))
"""
'2022-12', '2023-01', '2023-02', '2023-03', '2023-04'
"""
# 时间戳索引Series
index_info = pd.date_range('2022.12.07', periods=5, freq='D')
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 10, size=5), index=index_info)
print(ts)
"""
2022-12-07 4
2022-12-08 7
2022-12-09 4
2022-12-10 5
2022-12-11 1
"""
# 转换⽅法
print(pd.to_datetime(['2022.12.07', '2022-12-07', '07/12/2022', '2022/12/07']))
"""
'2022-12-07', '2022-12-07', '2022-07-12', '2022-12-07'
"""
print(pd.to_datetime([1670582232], unit='s')) # 2022-12-09 10:37:12
# 世界标准时间
dt = pd.to_datetime([1670582232401], unit='ms')
print(dt) # 2022-12-09 10:37:12.401000
# 东⼋区时间
print(dt + pd.DateOffset(hours=8)) # 2022-12-09 18:37:12.401000
# 3天后⽇期
print(dt + pd.DateOffset(days=3)) # 2022-12-12 10:37:12.401000
14-2.时间戳索引
import pandas as pd
index = pd.date_range("2022-12-05", periods=200, freq="D")
ts = pd.Series(range(len(index)), index=index)
# ⽇期访问数据: 3
print(ts['2022-12-08'])
# ⽇期切⽚
print(ts['2022-12-08':'2022-12-10'])
"""
2022-12-08 3
2022-12-09 4
2022-12-10 5
"""
# 传⼊年⽉
print(ts['2022-12'])
print(ts['2022'])
"""
2022-12-05 0
2022-12-06 1
2022-12-07 2
...
2022-12-29 24
2022-12-30 25
2022-12-31 26
"""
# 时间戳索引 : 3
print(ts[pd.Timestamp('2022-12-08')])
# 切⽚
print(ts[pd.Timestamp('2022-12-08'):pd.Timestamp('2022-12-08')])
"""
2022-12-08 3
"""
print(ts[pd.date_range('2022-12-08', periods=10, freq='D')])
"""
2022-12-08 3
2022-12-09 4
2022-12-10 5
2022-12-11 6
2022-12-12 7
2022-12-13 8
2022-12-14 9
2022-12-15 10
2022-12-16 11
2022-12-17 12
"""
# 获取年
print(ts.index.year)
"""
[2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022, 2022,
...
2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023]
"""
# 获取星期⼏
print(ts.index.dayofweek)
"""
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2,
...
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3]
"""
# ⼀年中第⼏个星期⼏
print(ts.index.weekofyear)
"""
[49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 50, 50, 50,
...
24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 25, 25, 25, 25]
"""
15.数据可视化
安装工具:
pip install matplotlib -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install jupyter -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
Matplotlib 是 Python 的绘图库,它能让使用者很轻松地将数据图形化,并且提供多样化的输出格式,Matplotlib 可以用来绘制各种静态,动态,交互式的图表。Matplotlib 是一个非常强大的 Python 画图工具,我们可以使用该工具将很多数据通过图表的形式更直观的呈现出来。Matplotlib 可以绘制线图、散点图、等高线图、条形图、柱状图、3D 图形、甚至是图形动画等等
Jupyter Notebook是一款开发工具,基于网页的用于交互计算的应用程序。其可被应用于全过程计算:开发、文档编写、运行代码和展示结果,经常可以大大增加调试代码效率,快速的展现数据输出结果和图像。
-
Jupyter启动命令行终端
- Windows----> 快捷键:win + R ----->输⼊:cmd回⻋------>命令⾏出来
- Mac ---->启动终端
-
命令行终端中启动jupyter
-
进⼊终端输⼊指令:jupyter notebook
-
[注意]:在哪⾥启动jupyter启动,浏览器上的⽬录,对应哪⾥
-
线形图
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randn(1000, 4),
index=pd.date_range(start='27/6/2012', periods=1000),
columns=list('ABCD'))
df1.cumsum().plot()

条形图
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.rand(10, 4),
columns=list('ABCD'))
df2.plot.bar(stacked=True)
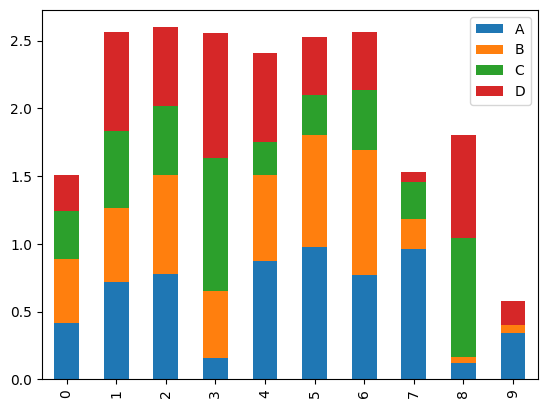
饼图
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.rand(4, 2),
index=list('ABCD'),
columns=['One', 'Two'])
df3.plot.pie(subplots=True, figsize=(8, 8))

散点图
df4 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(50, 4), columns=list('ABCD'))
df4.plot.scatter(x='A', y='B')
ax = df4.plot.scatter(x='A', y='C', color='DarkBlue', label='Group 1')
df4.plot.scatter(x='B', y='D', color='DarkGreen', label='Group 2', ax=ax)
df4.plot.scatter(x='A', y='B', s=df4['C'] * 200)



面积图
df5 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.rand(10, 4),
columns=list('ABCD'))
df5.plot.area(stacked=True)
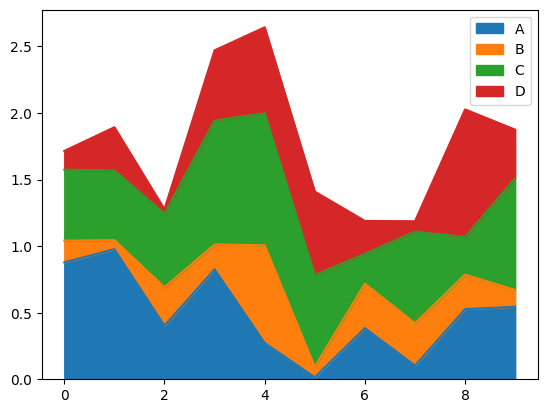
箱式图
df6 = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.rand(10, 5),
columns=list('ABCDE'))
df6.plot.box()

直方图
df7 = pd.DataFrame({'A': np.random.randn(1000) + 1, 'B': np.random.randn(1000),
'C': np.random.randn(1000) - 1})
df7.plot.hist(alpha=0.5)
df7.plot.hist(stacked=True)
df7.hist(figsize=(8, 8))









![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于智能推荐的胖达大码服装定制网(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9ddf0c5b227b472cbb917900318fdcdd.png)