1.
添加
Spring Data Redis
依赖启动器。在
chapter06
项目的
pom.xml
文件中添加
Spring Data Redis
依赖 启动器。
<!-- 引入整合 Redis 缓存的依赖启动器 --><dependency><groupId> org.springframework.boot </groupId><artifactId> spring-boot-starter-data-redis </artifactId></dependency>
2.Redis
服务连接配置。使用类似
Redis
的第三方缓存组件进行缓存管理时,缓存数据并不是像
Spring
Boot
默认缓存管理那样存储在内存中,而是需要预先搭建类似
Redis
服务的数据仓库进行缓存存储。所
以,这里首先需要安装并启动
Redis
服务;然后在项目的全局配置文件
application.properties
中添加
Redis
服务的连接配置。
# Redis 服务器地址spring.redis.host = 127.0.0.1# Redis 服务器连接端口spring.redis.port = 6379# Redis 服务器连接密码 ( 默认为空 )spring.redis.password =
或yml格式
spring: # MySQL数据库连接配置 datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootdata?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123 jpa: # 显示使用JPA进行数据库查询的SQL语句 show-sql: true redis: host: 192.168.48.67 port: 6379 password:
开启缓存机制
@EnableCaching//开启了SpringBoot基于注解的缓存管理实现

1 @EnableCaching注解
@EnableCaching
是由
Spring
框架提供的,
Spring Boot
框架对该注解进行了继承,该注解需要配置在类
上(在
Spring Boot
中,通常配置在项目启动类上),用于开启基于注解的缓存支持。
2 @Cacheable注解
@Cacheable
注解也是由
Spring
框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据查询方法上),用于
对方法的查询结果进行缓存存储。
@Cacheable
注解的执行顺序是,先进行缓存查询,如果为空则进行
方法查询,并将结果进行缓存;如果缓存中有数据,不进行方法查询,而是直接使用缓存数据。
Cacheable
注解提供了多个属性,用于对缓存存储进行相关配置,具体属性及说明如下表所示。
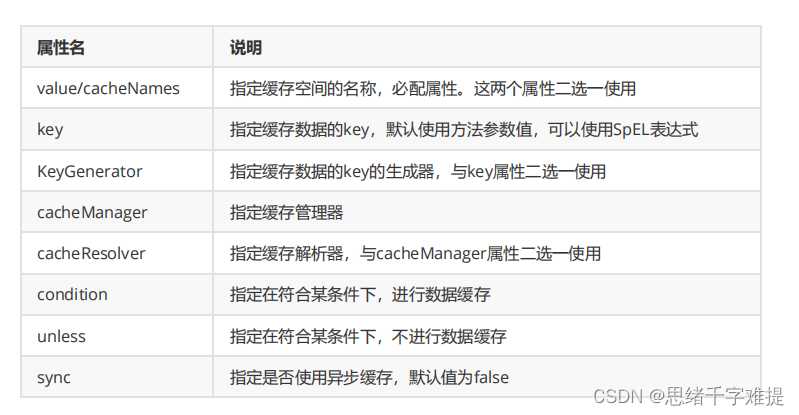
下面我们针对@Cacheable注解的属性进行具体讲解。
1.value/cacheNames属性
value
和
cacheNames
属性作用相同,用于指定缓存的名称空间,可以同时指定多个名称空间(例如
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"comment1", "comment2"})
)。如果
@Cacheable
注解只配置
value
(或
者
cacheNames
)的一个属性,那么这两个属性名可以省略,例如
@Cacheable("comment")
指定了缓存
的名称空间为
comment
。
2.key属性
key
属性的作用是指定缓存数据对应的唯一标识,默认使用注解标记的方法参数值,也可以使用
SpEL
表
达式。缓存数据的本质是
Map
类型数据,
key
用于指定唯一的标识,
value
用于指定缓存的数据。
如果缓存数据时,没有指定
key
属性,
Spring Boot
默认提供的配置类
SimpleKeyGenerator
会通过
generateKey(Object...params)
方法参数生成
key
值。默认情况下,如果
generateKey()
方法有一个参
数,参数值就是
key
属性的值;如果
generateKey()
方法没有参数,那么
key
属性是一个空参的
SimpleKey[]
对象;如果有多个参数,那么
key
属性是一个带参的
SimpleKey[params1,[param2,...]]
对
象。
除了使用默认
key
属性值外,还可以手动指定
key
属性值,或者是使用
Spring
框架提供的
SpEL
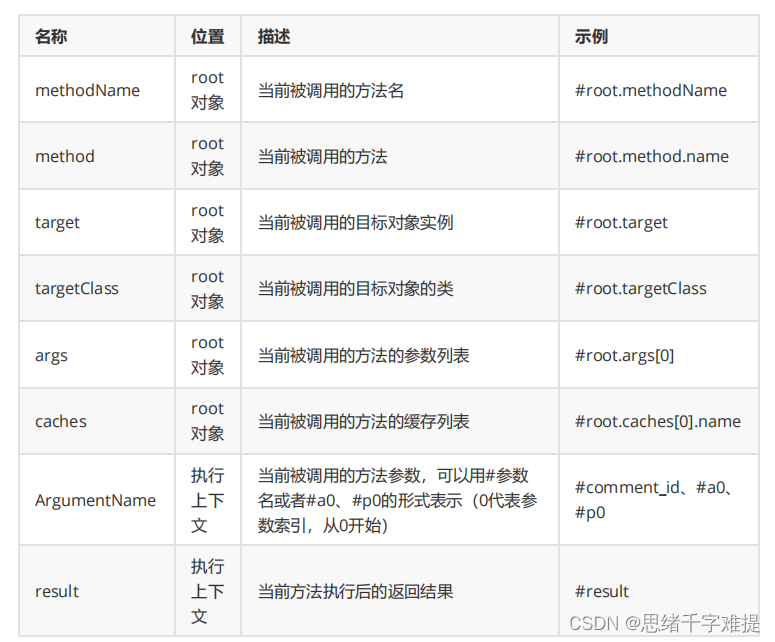
表达式。关
于缓存中支持的
SpEL
表达式及说明如下表所示。
3.keyGenerator属性
keyGenerator
属性与
key
属性本质作用相同,都是用于指定缓存数据的
key
,只不过
keyGenerator
属性
指定的不是具体的
key
值,而是
key
值的生成器规则,由其中指定的生成器生成具体的
key
。使用时,
keyGenerator
属性与
key
属性要二者选一。关于自定义
key
值生成器的定义,读者可以参考
Spring Boot
默认配置类
SimpleKeyGenerator
的定义方式,这里不做具体说明。
4.cacheManager/cacheResolver属性
cacheManager
和
cacheResolver
属性分别用于指定缓存管理器和缓存解析器,这两个属性也是二选一使
用,默认情况下不需要配置,如果存在多个缓存管理器(如
Redis
、
Ehcache
等)可以使用这两个属性分
别指定。
5.condition属性
condition
属性用于对数据进行有条件的选择性存储,只有当指定条件为
true
时才会对查询结果进行缓
存,可以使用
SpEL
表达式指定属性值。例如
@Cacheable(cacheNames="comment",condition="#comment_id>10")
表示方法参数
comment_id
的
值大于
10
才会对结果数据进行缓存。
6.unless属性
unless
属性的作用与
condition
属性相反,当指定的条件为
true
时,方法的返回值不会被缓存。
unless
属
性可以使用
SpEL
表达式指定。
@Cacheable(cacheNames="comment",unless="#result==null")
表示只
有查询结果不为空才会对结果数据进行缓存储。
7.sync属性
sync
属性表示数据缓存过程中是否使用异步模式,默认值为
false
3 @CachePut注解
@CachePut
注解是由
Spring
框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据更新方法上),该注解的
作用是更新缓存数据。
@CachePut
注解的执行顺序是,先进行方法调用,然后将方法结果更新到缓存
中。
@CachePut
注解也提供了多个属性,这些属性与
@Cacheable
注解的属性完全相同。
4 @CacheEvict注解
@CacheEvict
注解是由
Spring
框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据删除方法上),该注解
的作用是删除缓存数据。
@CacheEvict
注解的默认执行顺序是,先进行方法调用,然后清除缓存。
@CacheEvict
注解提供了多个属性,这些属性与
@Cacheable
注解的属性基本相同。除此之外,
@CacheEvict
注解额外提供了两个特殊属性
allEntries
和
beforeInvocation
,其说明如下。
1.allEntries属性
allEntries
属性表示是否清除指定缓存空间中的所有缓存数据,默认值为
false
(即默认只删除指定
key
对
应的缓存数据)。例如
@CacheEvict(cacheNames="comment",allEntries= true)
表示方法执行后会删除
缓存空间
comment
中所有的数据。
2.beforeInvocation属性
beforeInvocation
属性表示是否在方法执行之前进行缓存清除,默认值为
false
(即默认在执行方法后再
进行领存清除)例如
@CacheEvict(cacheNames="comment",beforeInvocation=true)
表示会在方法执
行之前进行缓存清除。
需要注意的是,如果将
@CacheEvict
注解的
beforeInvocation
属性设置为
true
,会存在一定的弊端。例
如在进行数据删除的方法中发生了异常,这会导致实际数据并没有被删除,但是缓存数据却被提前清除
了。
基于
API
的
Redis
缓存实现
package com.example.demo.service.imp;
import com.example.demo.domain.Comment;
import com.example.demo.repository.CommentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public Comment findById(int comment_id) {
//通过RedisTemplate查询缓存中的数据(Redis中的数据)
Object object = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("comment_" + comment_id);
if (object !=null){
return (Comment) object;
} else {
Optional<Comment> optional = commentRepository.findById(comment_id);
Comment comment = new Comment();
if (optional.isPresent()) {
comment = optional.get();
}
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment_id,comment,1,TimeUnit.DAYS);
return comment;
}
}
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
commentRepository.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(),
comment.getArticleId());
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment.getId(),comment);
return comment;
}
public void deleteComment(int comment_id) {
commentRepository.deleteById(comment_id);
redisTemplate.delete("comment_"+comment_id);
}
}


二.配置以下工具类 解决中文乱码
package com.example.demo.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
@Configuration // 定义一个配置类
public class RedisConfig {
//Api开发
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate();
//设置Redis模板类工厂
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 使用JSON格式序列化对象,对缓存数据key和value进行转换
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jacksonSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jacksonSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 设置RedisTemplate模板API的序列化方式为JSON
template.setDefaultSerializer(jacksonSerializer);
return template;
}
//注解开发
@Bean //返回值表示一个Redis缓存管理器对象,通过对象来管理和配置基于注解开发缓存的数据进行序列化转化
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 分别创建String和JSON格式序列化对象,对缓存数据key和value进行转换
RedisSerializer<String> strSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jacksonSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jacksonSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 定制缓存数据序列化方式及时效
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1)) //配置缓存数据的默认存活时间为1天
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(strSerializer))//指定key进行序列化
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jacksonSerializer))//
.disableCachingNullValues();//null值不参与序列化操作
//创建对象,作为返回值返回
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(config).build();
return cacheManager;
}
}