前言
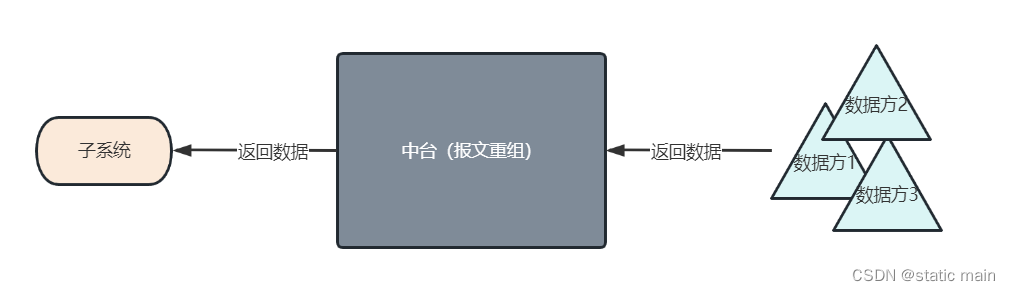
在一个平平无奇的下午,接到一个需求,需要给公司的中台系统做一个json报文重组的功能。
因为公司的某些业务需要外部数据的支持,所以会采购一些其它公司的数据,而且为了保证业务的连续性,同一种数据会采购多方的数据源
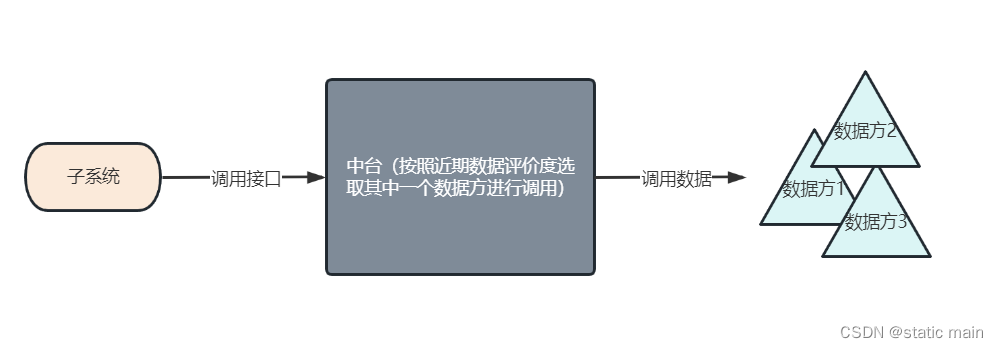
这里就出现了一个问题:
1.每个数据源的返回报文并不是一样的,所以需要在中台去进行转换,将不同数据源返回数据的结构重新组合
1.需求分析
首先,返回数据的格式为JSON,需要对原始数据的结构进行重组,也就是将原报文的值,放到新报文中,我将这个功能点拆成了两点:
① 取出原报文的值
② 构建新报文并将原报文的值放进去
根据上面这两点,我一下就想到使用递归算法来完成这个功能点
我们来看看递归算法是什么
递归算法
1.递归的基本思想:将一个大问题分解为若干个小问题,每个小问题都和原问题类似,但规模更小,直到最终问题可以轻易地被解决。
2.递归的终止条件:递归算法必须有一个明确的终止条件,否则算法将无限递归下去,导致程序崩溃。
3.递归的调用方式:在递归算法中,每次递归调用都会将问题的规模缩小,并将结果传递给下一次递归调用,直到最终得到问题的解。
4.递归的优势和劣势:递归算法可以使代码更加简洁清晰,同时也能够更自然地表达数学和物理模型等自然现象。但是,递归算法也存在一些劣势,比如可能会出现栈溢出等问题,同时递归算法的性能通常也不如迭代算法。
2.取出原报文的值
配置信息
首先,我们使用 . 来区分层级
例如:
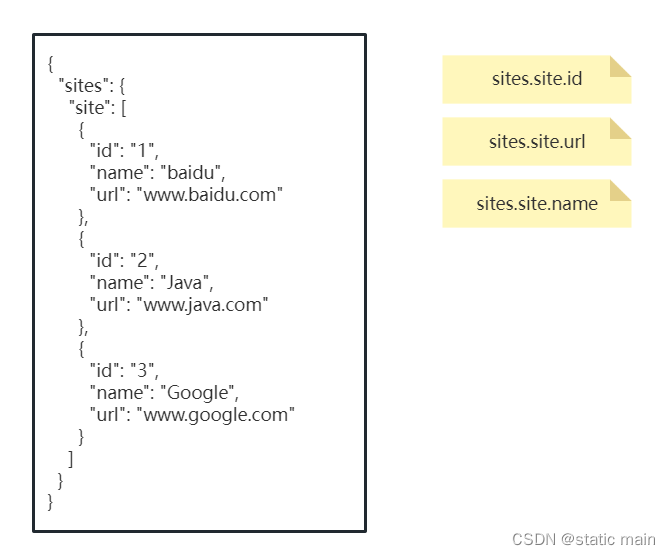
这里我们注意三点:
1.判断原报文的节点为JSONArray还是JSONObject
2.是否为最后一层
3.要有明确中断条件,这里我们中断条件就是sourceKey不包含. 也就是挖掘报文到达了配置的最后一层
private static JSONObject getSourceJSON(Object obj, String sourceKey) {
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
//如果最后一层则没有.
if (!sourceKey.contains(".")) {
result.put("keyName", sourceKey);
result.put("data", obj);
} else {
//否则就不断向下递归
//取出配置项中的第一节点,每一次递归,我们的第一节点也在这一层被消耗
String tmpKey = sourceKey.substring(0, sourceKey.indexOf(" ."));
String sourceKeyAfter = sourceKey.substring(sourceKey.indexOf(". ") + 1, sourceKey.length());
String keyName = sourceKey.substring(sourceKey.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, sourceKey.length());
//判断报文的数据类型
if (obj instanceof JSONArray) {
JSONArray ja = (JSONArray) obj;
JSONArray tmpJA = new JSONArray();
for (int i = 0; 1 < ja.size(); i++) {
JSONObject jo = ja.getJSONObject(i);
//不断向下挖掘
JSONObject tmpJO = getSourceJSON(jo.get(tmpKey), sourceKeyAfter);
Object o = tmpJO.get("data");
if (o instanceof JSONArray) {
JSONArray array = (JSONArray) o;
for (int j = 0; j < array.size(); j++) {
tmpJA.add(array.get(j));
}
} else {
tmpJA.add(o);
}
}
result.put("keyName", keyName);
result.put("data", tmpJA);
} else if (obj instanceof JSONObject) {
JSONObject jo = (JSONObject) obj;
return getSourceJSON(jo.get(tmpKey), sourceKeyAfter);
}
}
return result;
}
最后返回的是一个JSONObject,里面有两个key
① keyName:节点名称
② data:源数据
目的就是通过keyName能保证能从data直接取出数据
验证例子:
我们直接拿上面的JSON报文来进行演示,获取报文中url片段
String source = "{\"sites\":{\"site\":[{\"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"baidu\",\"url\":\"www.baidu.com\"},{\"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"Java\",\"url\":\"www.java.com\"},{\"id\":\"3\",\"name\":\"Google\",\"url\":\"www.google.com\"}]}}";
JSONObject sourceJSON = JSONObject.parseObject(source);
//直接打印结果
System.out.println(getSourceJSON(sourceJSON, "sites.site.url"));
输出:

通过keyName,判断data中的数据格式,JSONObject直接获取,JSONArray循环获取,这样我们就可以拿到url的值了
构建新报文并赋值
这也是一层层的构建,最后返回一整个重构后的报文,依旧使用我们的递归算法
由于是一层层,所以我们针对每一层,都需要配置它的数据类型
先给出配置
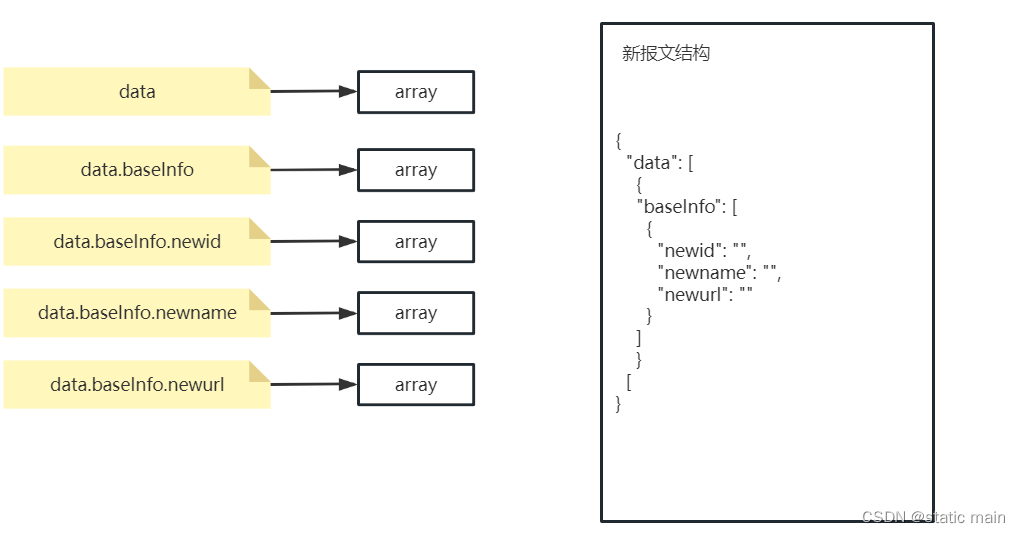
我们将此配置放到Map里,结构如下
JSONObject jo1 = new JSONObject(),jo2 = new JSONObject(),jo3 = new JSONObject(),jo4 = new JSONObject(),jo5 = new JSONObject();
jo1.put("type", "array");
jo1.put("sourceKey", "");
map.put("data", jo1);
jo2.put("type", "array");
jo2.put("sourceKey", "");
map.put("data.baseInfo", jo2);
jo3.put("type", "array");
jo3.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.id");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newid", jo3);
jo4.put("type", "array");
jo4.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.name");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newname", jo4);
jo5.put("type", "array");
jo5.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.url");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newurl", jo5);
map的key为目标构建路径,value为JSONObject,里面包含 ① 数据类型 ② 源路径
构建新报文的代码,需要注意以下几点
① 只有在最后一层才进行构建报文+赋值,前面全为构建
② 在构建之前判断节点是否存在,存在直接取出来进行递归,不存在再根据类型创建新节点
==③ 要有明确中断条件,这里我们中断条件就是targetKey不包含. ==
public static Object rebuildJSON(String targetKey, Object obj, Map<String, JSONObject> map, Object sourceObj,
String sourceKey, String oldKey) {
Object result = null;
if (targetKey.contains(".")) {
String tmpkey = targetKey.substring(0, targetKey.indexOf("."));
String tmpkeyType = "array";
if ("".equals(oldKey)) {
tmpkeyType = map.get(tmpkey).getString("type");
} else {
tmpkeyType = map.get(oldKey + "." + tmpkey).getString("type");
}
String afterkey = targetKey.substring(targetKey.indexOf(".") + 1, targetKey.length());
if (obj instanceof JSONArray) {
JSONArray ja = (JSONArray) obj;
JSONArray newJA = new JSONArray();
if (ja.size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < ja.size(); i++) {
JSONObject jo = ja.getJSONObject(i);
Object tmpO = jo.get(tmpkey);
if (tmpO == null) {
if ("array".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONArray tmpja = new JSONArray();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpja);
} else if ("object".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONObject tmpjo = new JSONObject();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpjo);
}
}
tmpO = rebuildJSON(afterkey, jo.get(tmpkey), map, sourceObj, sourceKey, tmpkey);
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpO);
newJA.add(jo);
}
} else {
JSONObject jo = new JSONObject();
if ("array".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONArray tmpja = new JSONArray();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpja);
} else if ("object".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONObject tmpjo = new JSONObject();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpjo);
}
Object tmpO = rebuildJSON(afterkey, jo.get(tmpkey), map, sourceObj, sourceKey, tmpkey);
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpO);
newJA.add(jo);
}
result = newJA;
} else if (obj instanceof JSONObject) {
JSONObject jo = (JSONObject) obj;
JSONObject newJo = jo;
Object tmpO = jo.get(tmpkey);
if (tmpO == null) {
if ("array".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONArray tmpja = new JSONArray();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpja);
} else if ("object".equals(tmpkeyType)) {
JSONObject tmpjo = new JSONObject();
jo.put(tmpkey, tmpjo);
}
}
tmpO = rebuildJSON(afterkey, jo.get(tmpkey), map, sourceObj, sourceKey, tmpkey);
newJo.put(tmpkey, tmpO);
result = newJo;
}
} else {
if (obj instanceof JSONArray) {
JSONArray ja = (JSONArray) obj;
JSONArray sourceja = (JSONArray) sourceObj;
JSONArray newJA = new JSONArray();
if (sourceja.size() > ja.size()) {
for (int i = 0; i < sourceja.size(); i++) {
JSONObject targetJO;
if (ja.size() > i) {
targetJO = ja.getJSONObject(i);
} else {
targetJO = new JSONObject();
}
JSONObject sourceJO = sourceja.getJSONObject(i);
targetJO.put(targetKey, sourceJO.get(sourceKey));
newJA.add(targetJO);
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < ja.size(); i++) {
if (sourceja.size() > i) {
JSONObject targetJO = ja.getJSONObject(i);
JSONObject sourceJO = sourceja.getJSONObject(i);
targetJO.put(targetKey, sourceJO.get(sourceKey));
newJA.add(targetJO);
}
}
}
result = newJA;
} else {
JSONObject jo = (JSONObject) obj;
JSONObject sourcejo = (JSONObject) sourceObj;
jo.put(targetKey, sourcejo.get(sourceKey));
result = jo;
}
}
return result;
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String source = "{\"sites\":{\"site\":[{\"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"baidu\",\"url\":\"www.baidu.com\"},{\"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"Java\",\"url\":\"www.java.com\"},{\"id\":\"3\",\"name\":\"Google\",\"url\":\"www.google.com\"}]}}";
JSONObject sourceJSON = JSONObject.parseObject(source);
Map<String,JSONObject> map = new HashMap<>();
JSONObject jo1 = new JSONObject(),jo2 = new JSONObject(),jo3 = new JSONObject(),jo4 = new JSONObject(),jo5 = new JSONObject();
jo1.put("type", "array");
jo1.put("sourceKey", "");
map.put("data", jo1);
jo2.put("type", "array");
jo2.put("sourceKey", "");
map.put("data.baseInfo", jo2);
jo3.put("type", "object");
jo3.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.id");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newid", jo3);
jo4.put("type", "object");
jo4.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.name");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newname", jo4);
jo5.put("type", "object");
jo5.put("sourceKey", "sites.site.url");
map.put("data.baseInfo.newurl", jo5);
Object result = new JSONObject();
for(Map.Entry<String,JSONObject> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String sourceKey = entry.getValue().getString("sourceKey");
//源路径为空我们不获取它的原值
if("".equals(sourceKey)) {
continue;
}
JSONObject sourceObj = getSourceJSON(sourceJSON, sourceKey);
result = rebuildJSON(entry.getKey(), result, map, sourceObj.get("data"), sourceObj.getString("keyName"), "");
}
System.out.println(result);
}
测试输出结果:
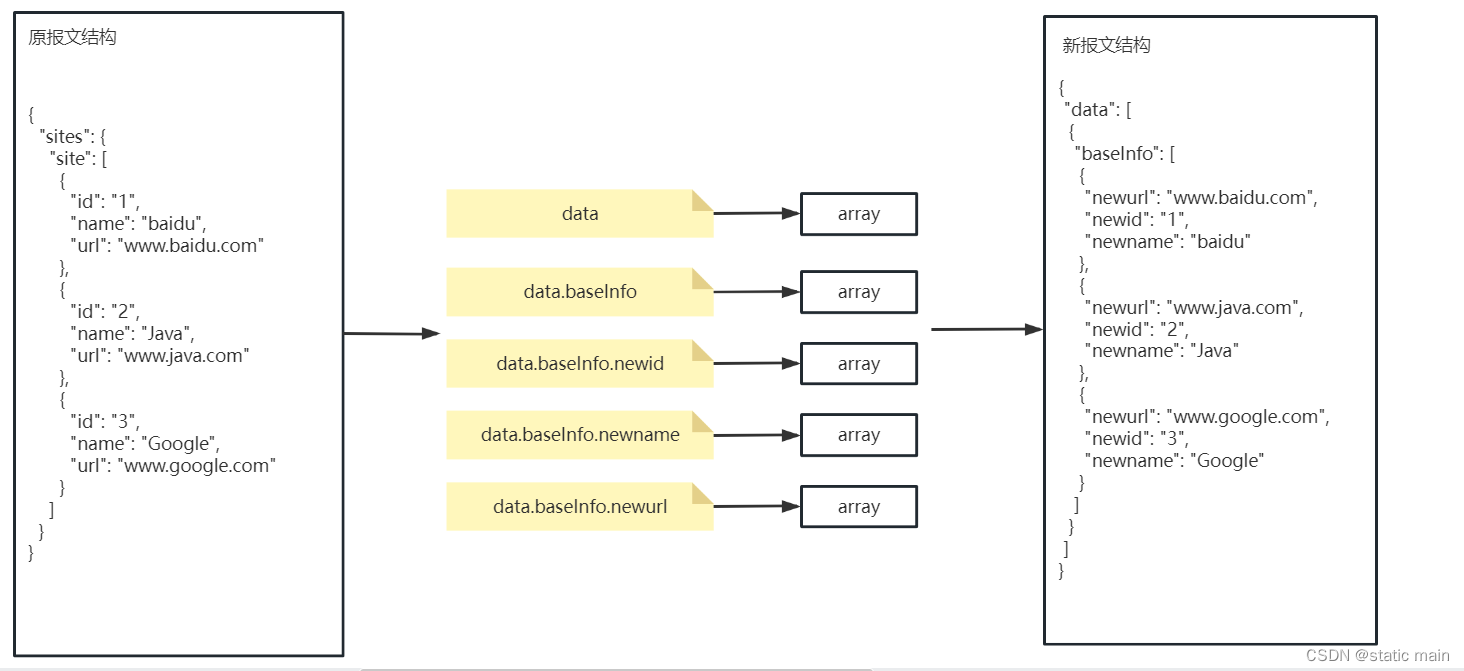
到这一步螺丝终于拧完了!
这个只能针对标准的JSON报文去处理,在这一步前我还利用了其它的算法将不标准的报文转化为标准的,详细代码关注我后续会讲解