一、概念
定义:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
LinkedHashMap 继承 HashMap 的功能,增加保证了元素的有效
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
* 双向列表,表头
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
* 双向列表,表尾
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
* 从构造方法中看出,默认为 false 插入顺序决定了元素的有序
* 可以自定义为 true,表示 访问顺序,最近访问的元素放置列表尾部
* @serial
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
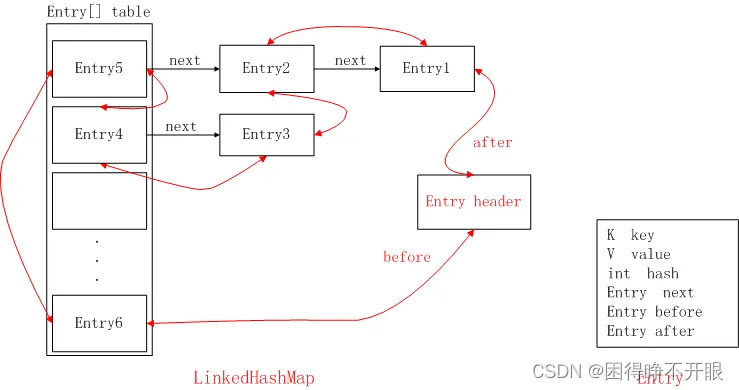
特点:
1、HashMap+双向链表 的特点,增删改查效率高
2、插入元素有序
3、除了继承 HashMap 的结构,还对所有 Entry 节点维护了双向链表。当put元素时,不但要把它加入到HashMap中去,还要加入到双向链表中
二、举例演示
public static void test3() {
log.info("1、默认按照插入顺序排序");
LinkedHashMap<Student, Integer> studentInfoMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
studentInfoMap.put(new Student("小王", 9), 88);
studentInfoMap.put(new Student("小张", 10), 80);
studentInfoMap.put(new Student("小李", 11), 90);
studentInfoMap.put(new Student("小赵", 8), 100);
studentInfoMap.forEach((key,value) ->{
log.info("key:{},value:{}",key,value);
});
log.info("2、按照访问顺序排序");
LinkedHashMap<Student, Integer> studentInfoMap1 = new LinkedHashMap<>(16,0.75f,true);
Student student1 = new Student("小王", 9);
studentInfoMap1.put(student1,88);
studentInfoMap1.put(new Student("小张", 10), 80);
studentInfoMap1.put(new Student("小李", 11), 90);
studentInfoMap1.put(new Student("小赵", 8), 100);
log.info("这里访问 key 为 student1的元素 小王");
studentInfoMap1.get(student1);
studentInfoMap1.forEach((key,value) ->{
log.info("key:{},value:{}",key,value);
});
}
输出: