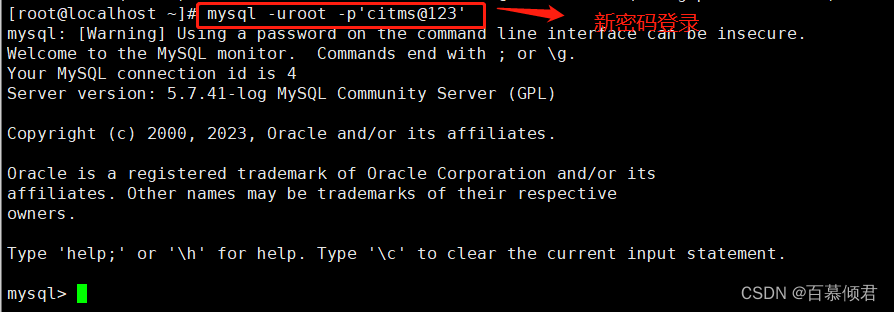
人体姿势骨架以图形格式表示人的方向。本质上,它是一组坐标,可以连接起来描述人的姿势。骨架中的每个坐标都被称为一个部分(或一个关节,或一个关键点)。两个部分之间的有效连接称为一对(或分支)。下面是一个人体姿势骨架样本。
因此,在本文中,我们将研究如何使用深度神经网络模型在OpenCV中执行人体姿态估计。
AI Dance based on Human Pose Estimation
- 1、数据集
- 2、模型架构
- 3、实验和结果
- 加载网络结构
- 读取图像和准备输入到网络
- 做出预测并分析关键点
- 画出骨架
1、数据集
由于缺乏高质量的数据集,人体姿态估计一直是一个具有挑战性的问题。如今,每一个AI挑战都是需要一个好的数据集来完成的。在过去的几年里,有挑战性的数据集已经发布,这使得研究人员更容易有效地解决这个问题。
以下是常用的数据集:
- COCO Key-points 数据集
- MPII 人体姿态估计数据集
- VGG姿态数据集
- SURREAL(实际任务下的人体姿态数据集)
- UP-3D数据集
本文中我们采用的是COCO数据集进行人体姿态估计任务。
2、模型架构
OpenPose首先检测属于图像中每个人的部分(关键点),然后将部分分配给不同的个体。下图是OpenPose模型的架构。

该模型将尺寸为w × h的彩色图像作为输入,并生成图像中每个人关键点的二维位置作为输出。检测分三个阶段进行:
- 阶段一:VGGNet的前10层用于为输入图像创建特征映射。
- 阶段二:使用2分支多级CNN,其中第一个分支预测身体部位位置(例如肘部,膝盖等)的一组2D置信度图(S)。下面给出了关键点的置信度图和亲和度图。第二个分支预测部分亲和度的一组二维向量场(L),它编码了部分之间的关联程度。
- 阶段三:通过贪婪推理对置信度图和亲和度图进行解析,生成图像中所有人的二维关键点。

3、实验和结果
在本节中,为了简单起见,我们将加载用于理解单个人的人体姿态估计的训练模型。步骤如下:
下载模型的权重: 权重下载
加载网络结构
我们正在使用在Caffe深度学习框架上训练的模型。Caffe模型有2个文件:
- Prototxt文件,它指定了神经网络的体系结构
- Caffemodel文件,存储训练模型的权重
读取图像和准备输入到网络
我们使用OpenCV读取的输入帧应该转换为输入blob(如Caffe),以便它可以馈送到网络。这是使用blobFromImage函数完成的,该函数将图像从OpenCV格式转换为Caffe blob格式。首先,我们将像素值归一化为(0,1)。然后我们指定图像的尺寸。接下来,要减去的平均值,即(0,0,0)。
做出预测并分析关键点
一旦将图像传递给模型,就可以进行预测。输出为4D矩阵:
- 第一个维度是图像ID(如果向网络传递多个图像)。
- 第二个维度表示关键点的索引。该模型生成的置信度图和部件关联图都是连接在一起的。对于COCO模型,它由57部分组成- 18关键点置信度图+ 1背景+ 19*2部分亲和图。
- 第三个维度是输出映射的高度。
- 第四个维度是输出映射的宽度。
画出骨架
当我们有关键点的时候我们就可以画骨架了只要把它们对连接起来。
# 2.Load the network
# Specify the paths for the 2 files
protoFile = "pose/mpi/pose_deploy_linevec_faster_4_stages.prototxt"
weightsFile = "pose/mpi/pose_iter_160000.caffemodel"
# Read the network into Memory
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile, weightsFile)
#3.Read Image and Prepare Input to the Network
# Read image
frame = cv2.imread("single.jpg")
# Specify the input image dimensions
inWidth = 368
inHeight = 368
# Prepare the frame to be fed to the network
inpBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 255, (inWidth, inHeight), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
# Set the prepared object as the input blob of the network
net.setInput(inpBlob)
# 4. Make Predictions and Parse Keypoints
output = net.forward()
H = out.shape[2]
W = out.shape[3]
# Empty list to store the detected keypoints
points = []
for i in range(len()):
# confidence map of corresponding body's part.
probMap = output[0, i, :, :]
# Find global maxima of the probMap.
minVal, prob, minLoc, point = cv2.minMaxLoc(probMap)
# Scale the point to fit on the original image
x = (frameWidth * point[0]) / W
y = (frameHeight * point[1]) / H
if prob > threshold :
cv2.circle(frame, (int(x), int(y)), 15, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame, "{}".format(i), (int(x), int(y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.4, (0, 0, 255), 3, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# Add the point to the list if the probability is greater than the threshold
points.append((int(x), int(y)))
else :
points.append(None)
cv2.imshow("Output-Keypoints",frame)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 5. Draw Skeleton
for pair in POSE_PAIRS:
partA = pair[0]
partB = pair[1]
if points[partA] and points[partB]:
cv2.line(frameCopy, points[partA], points[partB], (0, 255, 0), 3)
Human Pose Estimation.py hosted with by GitHub
输出结果如下:

视频结果如下:Youtobe:Human-Pose-Estimation
上述源码开源,已经上传☞此链接: 代码传送门