建议从这里开始看:Elasticsearch快速入门及使用
Elasticsearch进阶
- 一.Elasticsearch检索方式
- 1.uri + 检索参数(不常用)
- 2.uri + 请求体(常用,也叫Query DSL)
- 二.Query DSL语法举例
- 1.match全文匹配
- 2.match_phrase短语匹配
- 3.multi_match多字段匹配
- 4.bool复合查询
- 5.term查询
- 三.Elasticsearch分析功能
- 1.aggregations聚合(相当于group by和聚合函数)
- 四.Elasticsearch映射
- 1.查看字段的映射(添加数据的时候,es会默认猜测字段的类型并保存)
- 2.创建映射
- 3.添加新的字段映射
- 4.更新映射
- 五.分词
- 1.安装IK分词器
- 2.分词模式
- (1) ik_smart(最少切分拆分)
- (2) ik_max_word(最细粒度拆分)
- 3.自定义拓展词库
一.Elasticsearch检索方式
1.uri + 检索参数(不常用)
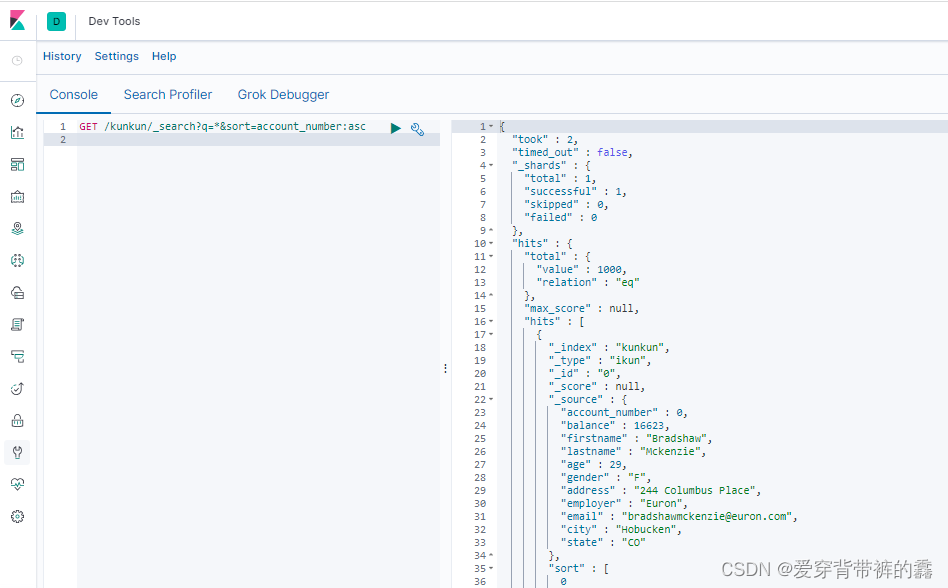
//查询kunkun库下的以account_number升序排序的所有数据,默认查询10条,相当于分页
GET /kunkun/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc
解释:
_search:查询关键字
q=*:查询所有数据
sort=account_number:asc:以account_number字段为排序条件
2.uri + 请求体(常用,也叫Query DSL)
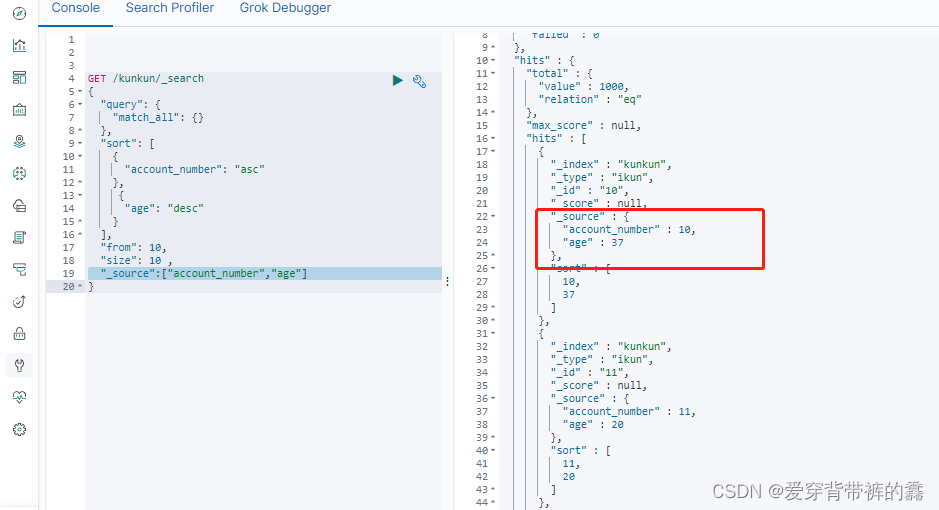
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": { //匹配所有
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"account_number": "asc" //升序排序
},
{
"age": "desc" //降序排序
}
],
"from": 10,//从第十条开始
"size": 10 //查十条
"_source":["account_number","age"] //查出的数据只有account_number和age字段
}
二.Query DSL语法举例
Query DSL官网文档
1.match全文匹配
//全文检索按照相关性得分进行排序
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"match": { //匹配条件 address包含'Court'或'ikun'的数据
"address": "Court ikun"
}
}
}
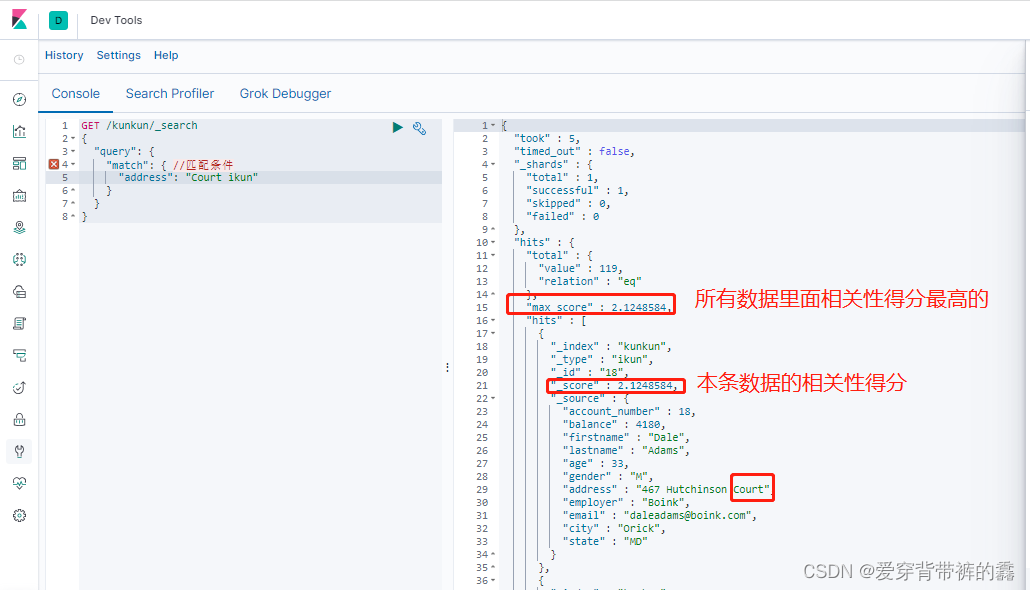
2.match_phrase短语匹配
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": { //短语匹配 address包含'Court ikun'的数据
"address": "Court ikun"
}
}
}
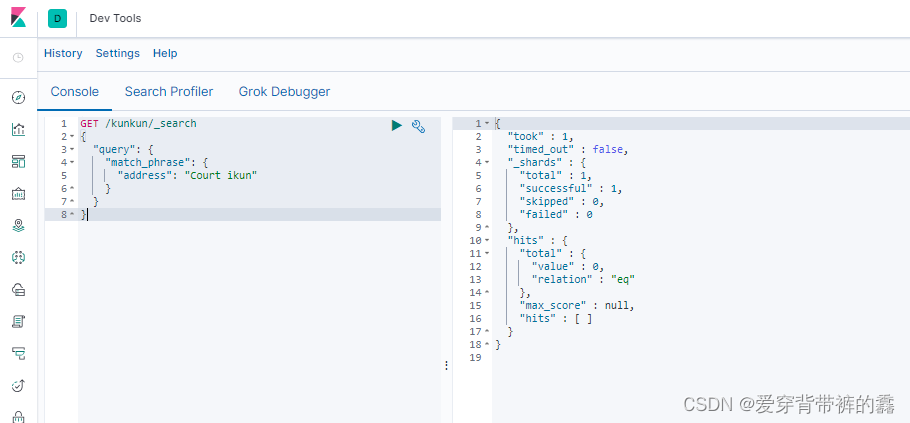
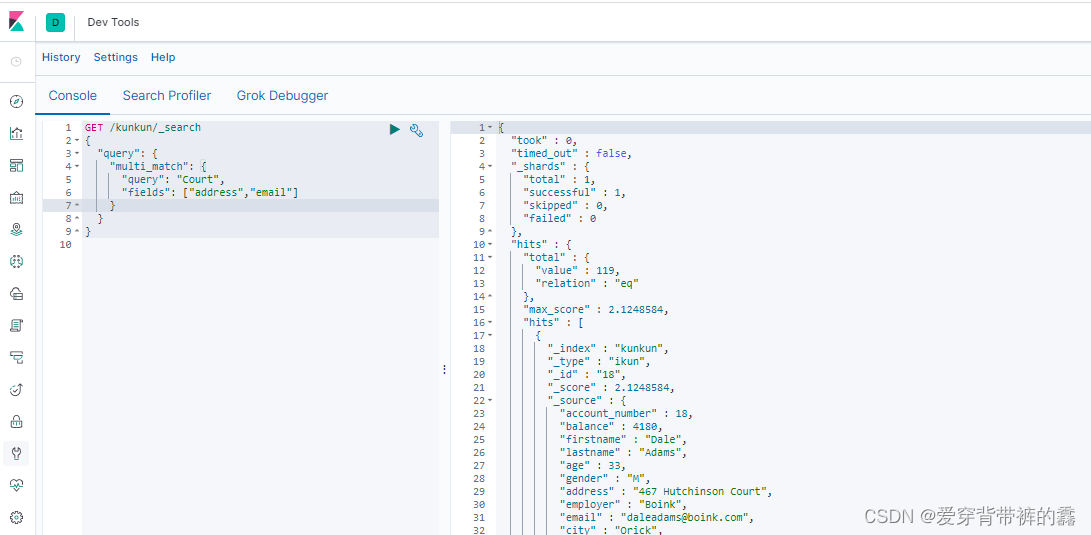
3.multi_match多字段匹配
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "Court", //匹配条件 匹配'address'和'email'字段包含'Court'的数据
"fields": ["address","email"] //匹配字段
}
}
}
4.bool复合查询
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [ //lastname必须是ikun(满足的话,相关性得分会更高)
{ "match": { "lastname": "ikun" } }
],
"must_not": [//email必须不是xiaoheizi(满足的话,相关性得分会更高)
{ "match": { "email": "xiaoheizi" } }
],
"should":[//年龄是不是25都可以(满足的话,相关性得分会更高)
{"match": {
"age": "25"
}}
],
"filter": { //过滤年龄在10-30之间的结果(满足也不计算相关性得分)
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 30
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.term查询
注意: term用于查询非文本字段
//匹配age是22的数据
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": "22"
}
}
}
三.Elasticsearch分析功能
1.aggregations聚合(相当于group by和聚合函数)
aggregations聚合官网文档
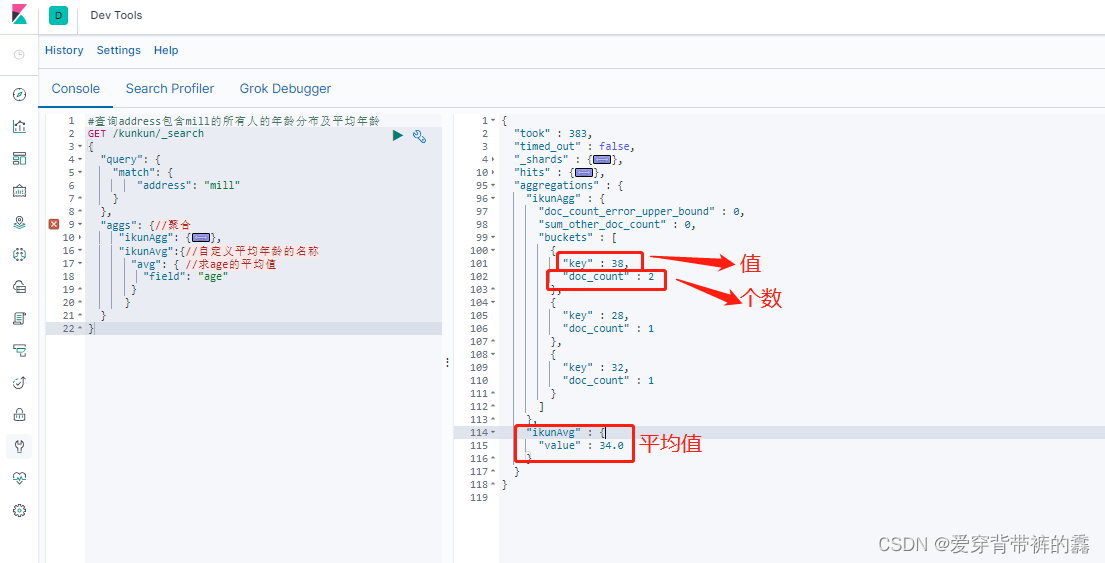
/**
* (1) 查询address包含mill的所有人的年龄分布及平均年龄
*/
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
},
"aggs": {//聚合
"ikunAgg": {//聚合操作名称可以自定义
"terms": {//查看age的分布
"field": "age",
"size": 10 //取出age前10种分布
}
},
"ikunAvg":{//自定义平均年龄的名称
"avg": { //求age的平均值
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
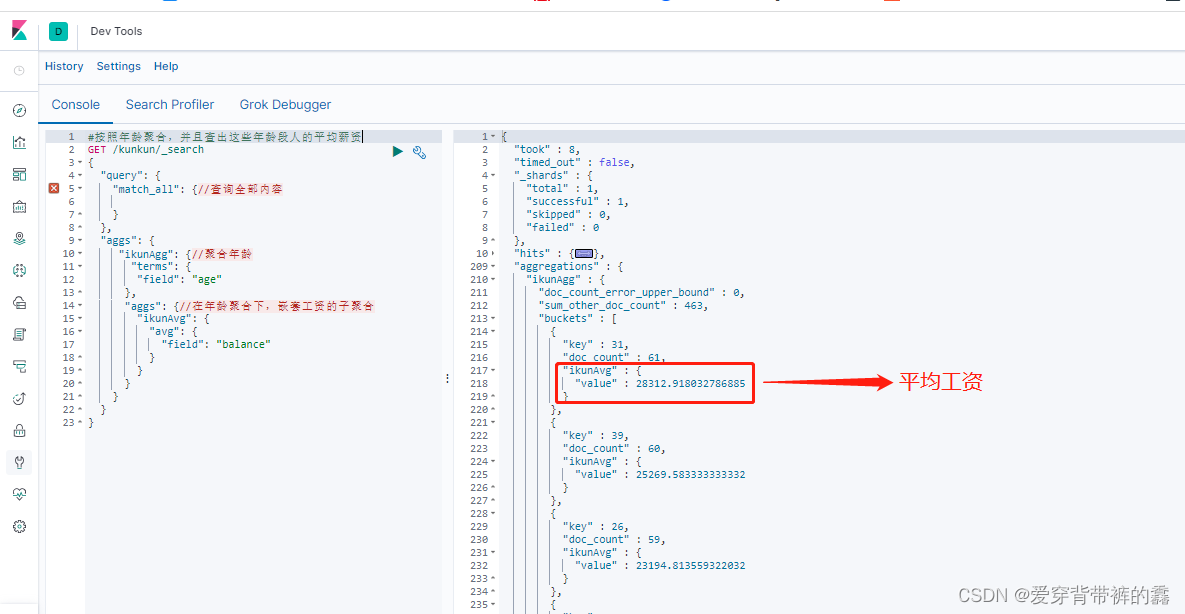
/**
* (2) 按照年龄聚合,并且查出这些年龄段人的平均薪资
*/
GET /kunkun/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {//查询全部内容
}
},
"aggs": {
"ikunAgg": {//聚合年龄
"terms": {
"field": "age"
},
"aggs": {//在年龄聚合下,嵌套工资的子聚合
"ikunAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
四.Elasticsearch映射
mapping映射官网文档
Mapping是用来定义一个文档,以及它包含的属性是如何储存和索引的(就是给字段指定类型)。
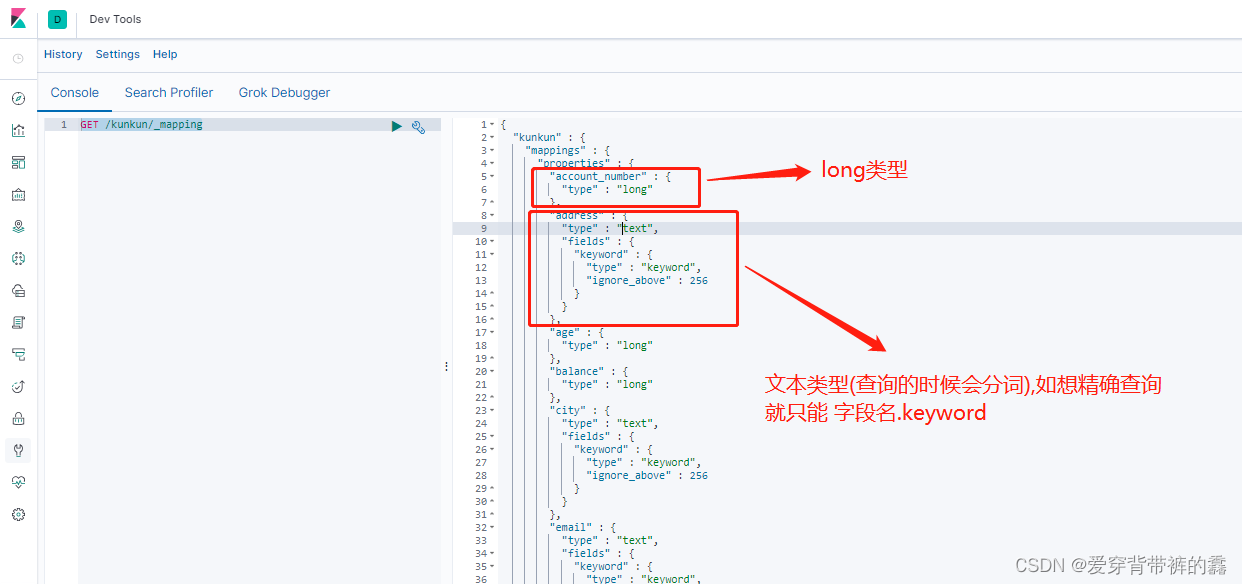
1.查看字段的映射(添加数据的时候,es会默认猜测字段的类型并保存)
//查看字段的类型
GET /kunkun/_mapping
2.创建映射
PUT /my-index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": { "type": "integer" },
//keyword:是精准匹配。
"email": { "type": "keyword" },
//text:保存的时候会进行分词,然后检索的时候按照分词进行匹配。
"name": { "type": "text" }
}
}
}
3.添加新的字段映射
PUT /my-index/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"chang":{ //新加字段名字
"type":"text", //映射类型
"index":"false" //该字段不参与检索
}
}
}
4.更新映射
对于已存在的字段映射我们不能直接去更新,我们需要创建新的索引进行数据迁移。
//1.创建新的索引并更新字段映射
PUT /my-index—new
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": { "type": "long" },
"email": { "type": "text" },
"name": { "type": "text" }
}
}
}
//2.把旧索引数据迁移到新索引
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "my-index", //旧索引名称
"type": "account" //旧索引的类型(6.0版本之前,6.0之后版本不需要写类型)
},
"dest": {
"index": "my-index—new" //新索引的名称
}
}
五.分词
es内置的分词器文档
IK分词器7.3.1 提取码:0221
IK其他版本
一个 tokenizer (分词器) 接收一个字符流,将之分割为独立的 tokens (词元,通常是独立的单词),然后输出 tokens 流。
//默认是standard分词器
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard", //分词器类型
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone." //分词的语句
}
注意:因为es内嵌的分词器都是对英文的分词,所以我们还要下载中文的分词器(IK分词器插件的版本要和ElasticSearch的版本一致)。
1.安装IK分词器
把你下载下来的分词器放在 elasticsearch目录下 -> plugins

2.分词模式
(1) ik_smart(最少切分拆分)
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "我是小黑子"
}

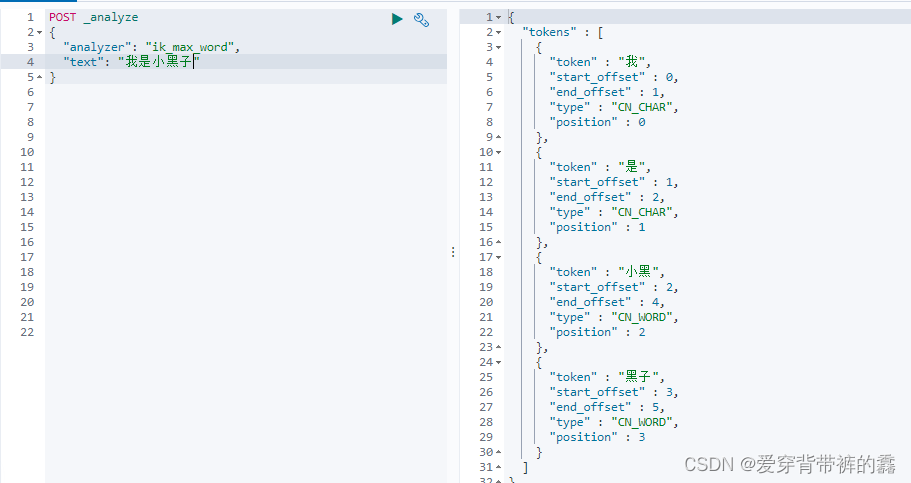
(2) ik_max_word(最细粒度拆分)
3.自定义拓展词库
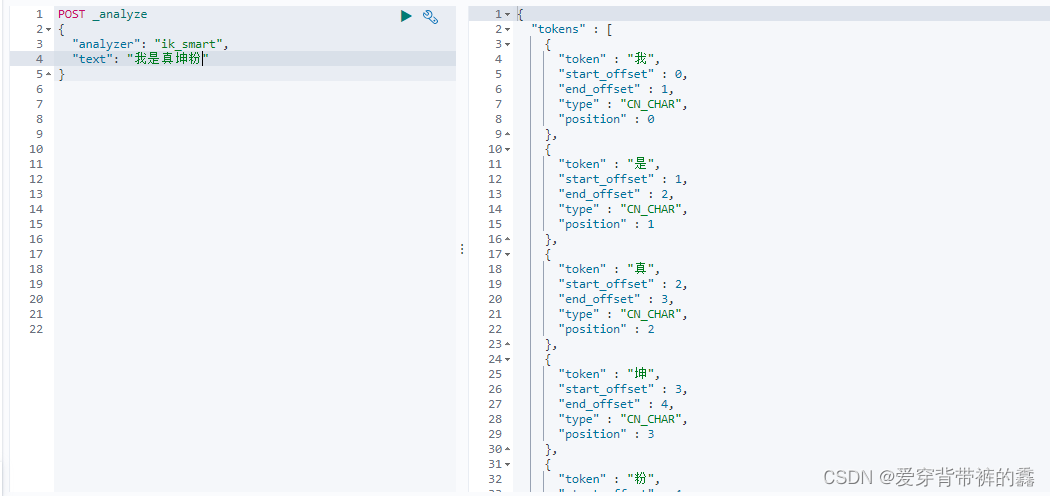
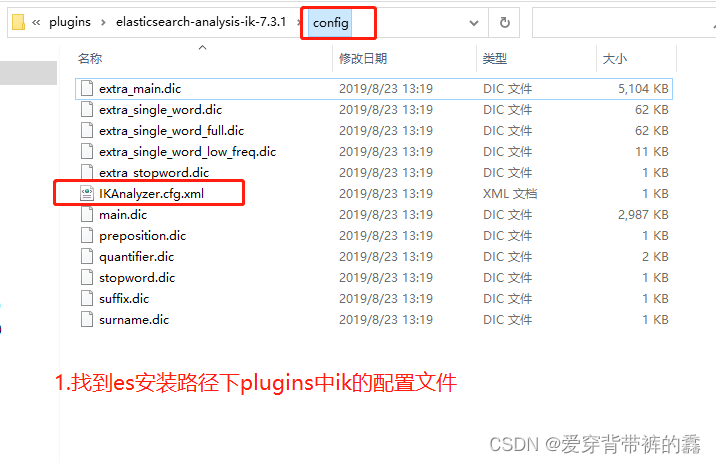
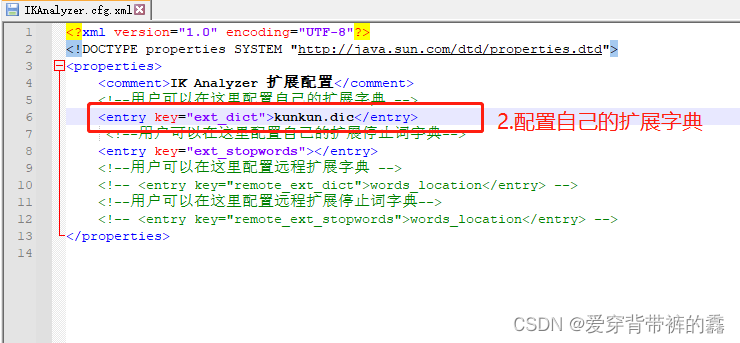
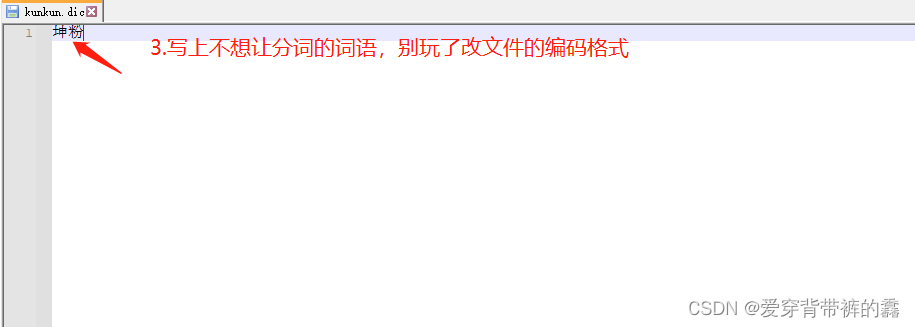
说明: 因为有一些词,识别不了。比如:我是真爱坤和一些网络用语分词就不准确,所以咱们要自定义拓展词库。
(1) 没自定义拓展词库之前
(2) 自定义词库
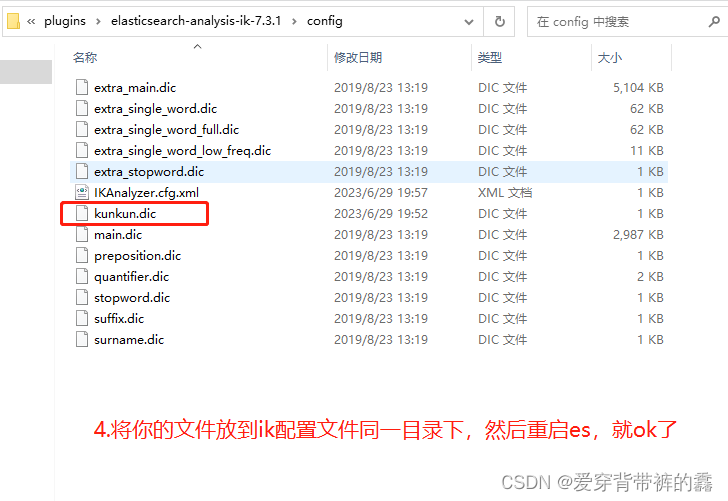
(3) 加了自定义词库之后