1.底层是用什么实现的?
JDK8用的char数组,JDK9开始使用byte数组,而且都是final型,所以不同字符串(值)的地址必然不同。


char和byte的区别:char是2个字节表示,而byte是一个字节。
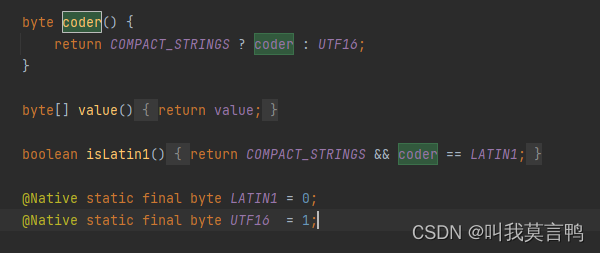
JDK17中,String使用2种编码方式 LATIN1和UTF-16.
但是转byte时就是用UTF-8进行保存了
LATIN1是单字节
UTF-16是双字节
所以当存汉字的时候,String的数据扩容就不同了,这样看,

2.String的构造方法
// private final byte[] value;
//1. 空串
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
this.coder = "".coder;
}
// 2.字符串赋值
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.coder = original.coder;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
// 3. char 转String char数组 开头 长度 编码方式(默认8)
public String(char value[]) {
this(value, 0, value.length, null);
}
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
this(value, offset, count, rangeCheck(value, offset, count));
}
String(byte[] value, byte coder) {
this.value = value;
this.coder = coder;
}
// 4.第四个VOID 没有用,作为执行添头吧
String(char[] value, int off, int len, Void sig) {
if (len == 0) {
this.value = "".value;
this.coder = "".coder;
return;
}
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] val = StringUTF16.compress(value, off, len);
if (val != null) {
this.value = val;
this.coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
}
this.coder = UTF16;
this.value = StringUTF16.toBytes(value, off, len);
}
// int只有这一种,数组 开始位置 长度
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
checkBoundsOffCount(offset, count, codePoints.length);
if (count == 0) {
this.value = "".value;
this.coder = "".coder;
return;
}
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] val = StringLatin1.toBytes(codePoints, offset, count);
if (val != null) {
this.coder = LATIN1;
this.value = val;
return;
}
}
this.coder = UTF16;
this.value = StringUTF16.toBytes(codePoints, offset, count);
}
// 4个参数 byte数组 截取开始位置 截取长度 编码方式
// 代码长是因为要转换编码方式
public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, Charset charset) {
Objects.requireNonNull(charset);
checkBoundsOffCount(offset, length, bytes.length);
if (length == 0) {
this.value = "".value;
this.coder = "".coder;
} else if (charset == UTF_8.INSTANCE) {
if (COMPACT_STRINGS && !StringCoding.hasNegatives(bytes, offset, length)) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, offset, offset + length);
this.coder = LATIN1;
} else {
int sl = offset + length;
int dp = 0;
byte[] dst = null;
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
dst = new byte[length];
while (offset < sl) {
int b1 = bytes[offset];
if (b1 >= 0) {
dst[dp++] = (byte)b1;
offset++;
continue;
}
if ((b1 == (byte)0xc2 || b1 == (byte)0xc3) &&
offset + 1 < sl) {
int b2 = bytes[offset + 1];
if (!isNotContinuation(b2)) {
dst[dp++] = (byte)decode2(b1, b2);
offset += 2;
continue;
}
}
// anything not a latin1, including the repl
// we have to go with the utf16
break;
}
if (offset == sl) {
if (dp != dst.length) {
dst = Arrays.copyOf(dst, dp);
}
this.value = dst;
this.coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
}
if (dp == 0 || dst == null) {
dst = new byte[length << 1];
} else {
byte[] buf = new byte[length << 1];
StringLatin1.inflate(dst, 0, buf, 0, dp);
dst = buf;
}
dp = decodeUTF8_UTF16(bytes, offset, sl, dst, dp, true);
if (dp != length) {
dst = Arrays.copyOf(dst, dp << 1);
}
this.value = dst;
this.coder = UTF16;
}
} else if (charset == ISO_8859_1.INSTANCE) {
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, offset, offset + length);
this.coder = LATIN1;
} else {
this.value = StringLatin1.inflate(bytes, offset, length);
this.coder = UTF16;
}
} else if (charset == US_ASCII.INSTANCE) {
if (COMPACT_STRINGS && !StringCoding.hasNegatives(bytes, offset, length)) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, offset, offset + length);
this.coder = LATIN1;
} else {
byte[] dst = new byte[length << 1];
int dp = 0;
while (dp < length) {
int b = bytes[offset++];
StringUTF16.putChar(dst, dp++, (b >= 0) ? (char) b : REPL);
}
this.value = dst;
this.coder = UTF16;
}
} else {
// (1)We never cache the "external" cs, the only benefit of creating
// an additional StringDe/Encoder object to wrap it is to share the
// de/encode() method. These SD/E objects are short-lived, the young-gen
// gc should be able to take care of them well. But the best approach
// is still not to generate them if not really necessary.
// (2)The defensive copy of the input byte/char[] has a big performance
// impact, as well as the outgoing result byte/char[]. Need to do the
// optimization check of (sm==null && classLoader0==null) for both.
CharsetDecoder cd = charset.newDecoder();
// ArrayDecoder fastpaths
if (cd instanceof ArrayDecoder ad) {
// ascii
if (ad.isASCIICompatible() && !StringCoding.hasNegatives(bytes, offset, length)) {
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, offset, offset + length);
this.coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
this.value = StringLatin1.inflate(bytes, offset, length);
this.coder = UTF16;
return;
}
// fastpath for always Latin1 decodable single byte
if (COMPACT_STRINGS && ad.isLatin1Decodable()) {
byte[] dst = new byte[length];
ad.decodeToLatin1(bytes, offset, length, dst);
this.value = dst;
this.coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
int en = scale(length, cd.maxCharsPerByte());
cd.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE)
.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE);
char[] ca = new char[en];
int clen = ad.decode(bytes, offset, length, ca);
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] bs = StringUTF16.compress(ca, 0, clen);
if (bs != null) {
value = bs;
coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
}
coder = UTF16;
value = StringUTF16.toBytes(ca, 0, clen);
return;
}
// decode using CharsetDecoder
int en = scale(length, cd.maxCharsPerByte());
cd.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE)
.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE);
char[] ca = new char[en];
if (charset.getClass().getClassLoader0() != null &&
System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
bytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, offset, offset + length);
offset = 0;
}
int caLen = decodeWithDecoder(cd, ca, bytes, offset, length);
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] bs = StringUTF16.compress(ca, 0, caLen);
if (bs != null) {
value = bs;
coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
}
coder = UTF16;
value = StringUTF16.toBytes(ca, 0, caLen);
}
}
/*
* Throws iae, instead of replacing, if malformed or unmappable.
*/
String(char[] value, int off, int len, Void sig) {
if (len == 0) {
this.value = "".value;
this.coder = "".coder;
return;
}
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] val = StringUTF16.compress(value, off, len);
if (val != null) {
this.value = val;
this.coder = LATIN1;
return;
}
}
this.coder = UTF16;
this.value = StringUTF16.toBytes(value, off, len);
}
小总结一下
这里暂时不考虑int型
参数 :1.直接数组(char byte)2.数组+2个参数(第一个参数是截取的开始位置,第二个位置是截取长度)3。带编码方式的(只有byte可以) 数组+编码方式 或者编码方式放在最后
注意,编码方式既可以是String型,也可以是CharSet型,因为lookupCharset(charsetName) 可以转换编码方式
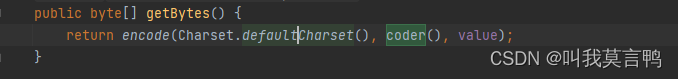
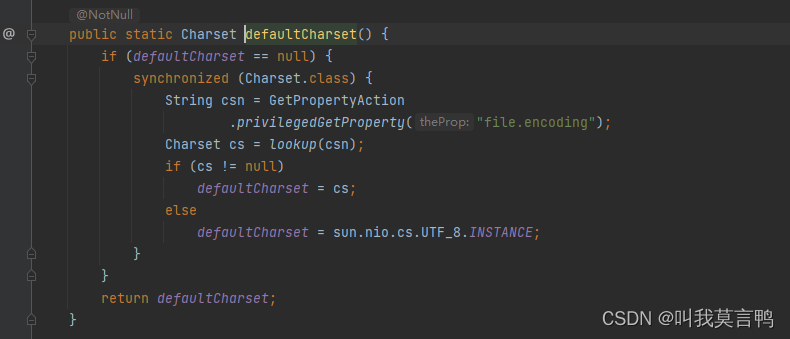
2.获取想要的编码方式的byte数组
public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset) {
if (charset == null) throw new NullPointerException();
return encode(charset, coder(), value);
}
// CharSet格式 StandardCharSet.
s2.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_16);
3.关于String初始化的思考
从String的初始化看,都是Value的直接赋值,那么问题来了。赋值的前提是Value存在,也就是说,我之前的玩意一定在,所以,他也要占空间
例如:String(“asda”) String(byte a[])
这两个,构造方法调用的前提都是,字符串String ="asda"存在,byte a[] 存在。
所以如果是new String 最起码会创建一个对象,也可能会创建两个。
4.方法学习
1.获取某个位置的字符
// index是要获取的字符下标
public char charAt(int index)
2.普通比较
2.比较
// 转成相同的字符编码,然后进行比较 先比长度,再逐个比较就完事了
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
byte v1[] = value;
byte v2[] = anotherString.value;
byte coder = coder();
if (coder == anotherString.coder()) {
return coder == LATIN1 ? StringLatin1.compareTo(v1, v2)
: StringUTF16.compareTo(v1, v2);
}
return coder == LATIN1 ? StringLatin1.compareToUTF16(v1, v2)
: StringUTF16.compareToLatin1(v1, v2);
}
3.无视大小写比较
还是先判断编码格式,按照编码格式先转码然后再去比较,不过这个比较之前,都先转化成了大写然后比较的
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
byte v1[] = s1.value;
byte v2[] = s2.value;
byte coder = s1.coder();
if (coder == s2.coder()) {
return coder == LATIN1 ? StringLatin1.compareToCI(v1, v2)
: StringUTF16.compareToCI(v1, v2);
}
return coder == LATIN1 ? StringLatin1.compareToCI_UTF16(v1, v2)
: StringUTF16.compareToCI_Latin1(v1, v2);
}
public static int compareToCI(byte[] value, byte[] other) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = other.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
for (int k = 0; k < lim; k++) {
if (value[k] != other[k]) {
char c1 = (char) CharacterDataLatin1.instance.toUpperCase(getChar(value, k));
char c2 = (char) CharacterDataLatin1.instance.toUpperCase(getChar(other, k));
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return len1 - len2;
}
4.concat 拼接
垃圾方法 因为我门可以直接使用+
5.contains查询某个字符或者字符串是否存在于这个字符串中
好笑的是,里面用的还是indexof方法
注意这里的charSequence 字符串和字符都继承了这个接口,所以s可以是字符和字符串
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) >= 0;
}
6.indexof
按照相应的编码方式去寻找,因为不同编码方式,长度不同,位置不同
public int indexOf(int ch) {
return indexOf(ch, 0);
}
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
return isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.indexOf(value, ch, fromIndex)
: StringUTF16.indexOf(value, ch, fromIndex);
}
7.判断是不是以某个字符串为结尾(开始)
思路:
1.按照编码方式进行对比,不符合要求直接pass
2.(转码)比较
//
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, length() - suffix.length());
}
// 2个参数 一个是字符串,一个是开始位置
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if (toffset < 0 || toffset > length() - prefix.length()) {
return false;
}
byte ta[] = value;
byte pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = 0;
int pc = pa.length;
byte coder = coder();
// 编码方式相同
// 编码方式不同的话, 必须传来的参数是拉丁的
//不同的话,如果传来的是UTF16,则本字符串就是拉丁,拉丁无汉字,直接不用比较了
if (coder == prefix.coder()) {
// 看编码格式相等不相等,相等就找到相应的位置,因为汉字UTF-16的位置需要双倍一下 如果是汉字 字母格式 就进行2位16进制的比较 2个16进制就是一个字节(8位二进制)
int to = (coder == LATIN1) ? toffset : toffset << 1;
while (po < pc) {
//走到相应位置直接开始比较
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
} else {
if (coder == LATIN1) { // && pcoder == UTF16
return false;
}
// coder == UTF16 && pcoder == LATIN1)
while (po < pc) {
if (StringUTF16.getChar(ta, toffset++) != (pa[po++] & 0xff)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
8.split 分割
处理符号 将每一段String都放到list中,最后返回String数组
如果没有分割符,就返回该字符串。
public String[] split(String regex) {
return split(regex, 0);
}
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
/* fastpath if the regex is a
* (1) one-char String and this character is not one of the
* RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or
* (2) two-char String and the first char is the backslash and
* the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter.
*/
char ch = 0;
if (((regex.length() == 1 &&
".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
(regex.length() == 2 &&
regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
(((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
(ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE))
{
int off = 0;
int next = 0;
boolean limited = limit > 0;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
list.add(substring(off, next));
off = next + 1;
} else { // last one
//assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
int last = length();
list.add(substring(off, last));
off = last;
break;
}
}
// If no match was found, return this
if (off == 0)
return new String[]{this};
// Add remaining segment
if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
list.add(substring(off, length()));
// Construct result
int resultSize = list.size();
if (limit == 0) {
while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).isEmpty()) {
resultSize--;
}
}
String[] result = new String[resultSize];
return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
}
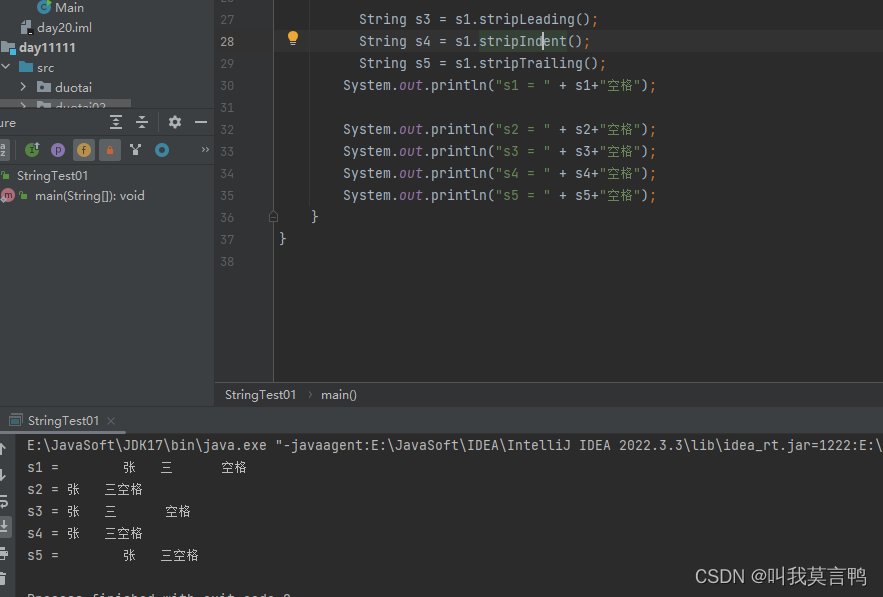
8. trip清除边缘空格
strip和stripIndent方法一样,都是去除两边空格
stripLeading 去除左边空格
stripTrailing 去除右边空格
9.截取字符串substring
取前不取后,因为方法中算的是长度(后-前)
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
return substring(beginIndex, length());
}
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
int length = length();
checkBoundsBeginEnd(beginIndex, endIndex, length);
if (beginIndex == 0 && endIndex == length) {
return this;
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
return isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.newString(value, beginIndex, subLen)
: StringUTF16.newString(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
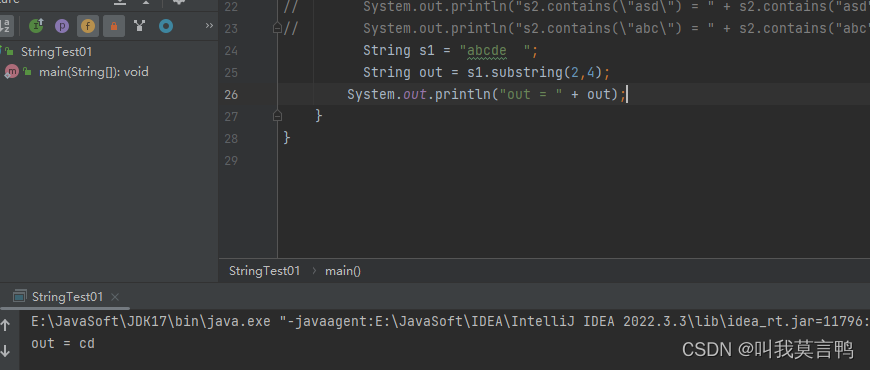
10.大小转换
public String toLowerCase() {
return toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
public String toUpperCase() {
return toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
![Vue3解决:[Vue warn]: Failed to resolve component: el-table(或el-button) 的三种解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ebc82a6622d42f9b9be7278d68a5ef8.png)