安装Python程序
官网Python下载地址:Python Releases for Windows | Python.org
安装3.7版本即可,版本升级可能会有较小的改动,下面要学习的都以python3.7为例
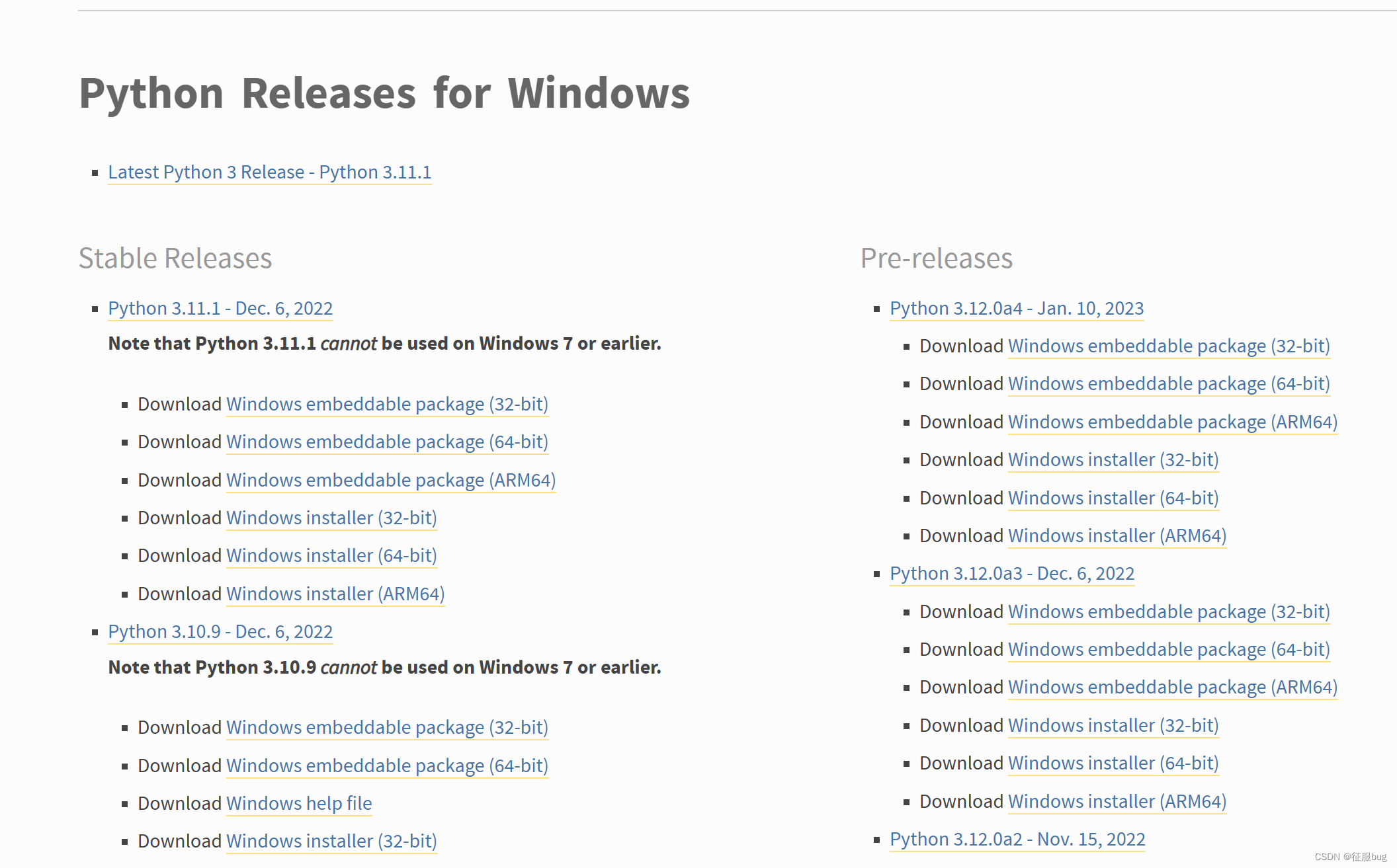
下载安装包之后直接双击无脑安装即可
新手经常遇到的问题:
1.符号使用的是中文字符
2.代码的缩进
3.python中的内置函数打错
安装完成后,使用python自带的工具即可进行学习编程

基础语法学习
dir(__builtins__) #查看python中的内置函数
>>> dir(__builtins__)
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'BlockingIOError', 'BrokenPipeError', 'BufferError', 'BytesWarning', 'ChildProcessError', 'ConnectionAbortedError', 'ConnectionError', 'ConnectionRefusedError', 'ConnectionResetError', 'DeprecationWarning', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'EnvironmentError', 'Exception', 'False', 'FileExistsError', 'FileNotFoundError', 'FloatingPointError', 'FutureWarning', 'GeneratorExit', 'IOError', 'ImportError', 'ImportWarning', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'InterruptedError', 'IsADirectoryError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'ModuleNotFoundError', 'NameError', 'None', 'NotADirectoryError', 'NotImplemented', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'PendingDeprecationWarning', 'PermissionError', 'ProcessLookupError', 'RecursionError', 'ReferenceError', 'ResourceWarning', 'RuntimeError', 'RuntimeWarning', 'StopAsyncIteration', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SyntaxWarning', 'SystemError', 'SystemExit', 'TabError', 'TimeoutError', 'True', 'TypeError', 'UnboundLocalError', 'UnicodeDecodeError', 'UnicodeEncodeError', 'UnicodeError', 'UnicodeTranslateError', 'UnicodeWarning', 'UserWarning', 'ValueError', 'Warning', 'WindowsError', 'ZeroDivisionError', '__build_class__', '__debug__', '__doc__', '__import__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'ascii', 'bin', 'bool', 'breakpoint', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'compile', 'complex', 'copyright', 'credits', 'delattr', 'dict', 'dir', 'divmod', 'enumerate', 'eval', 'exec', 'exit', 'filter', 'float', 'format', 'frozenset', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'help', 'hex', 'id', 'input', 'int', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'license', 'list', 'locals', 'map', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'next', 'object', 'oct', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'property', 'quit', 'range', 'repr', 'reversed', 'round', 'set', 'setattr', 'slice', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'vars', 'zip']1.变量
name = '张三'创建变量过程
首先是变量声明,其次是变量赋值
变量名称规则:
1.变量是区分大小写的,使用不同大小写的变量,python会认为是多个变量
2.不可以以数字开头,不光python不可以,大多数语言是都不可以的
3.不可以以特殊符号来进行开头,可以以下划线_来进行开头
定义不同的语句
>>> name = '张三'
>>> print (name)
张三
>>> age = 17
>>> print (age)
17
>>> description="hello world!"
>>> print (description)
hello world!
>>> description_two="'hello world!'"
>>> print (description_two)
'hello world!'2.转义
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| \\ | 反斜杠(\) |
| \' | 单引号(') |
| \" | 双引号(") |
| \a | 响铃 |
| \b | 退格符 |
| \n | 换行符 |
| \r | 回车符 |
| \t | 水平制表符 |
| \v | 垂直制表符 |
| \f | 换页符 |
| \ooo | ooo为八进制 |
| \xhh | hh为十六进制 |
3.变量与字符串
>>> print(520+1314)
1834
>>> print('520'+'1314')
5201314
>>> print(520+1314)
1834
>>> print('520'+'1314')
5201314从此几行代码可以看出,数字相加的话得出的是相加的和,但是字符串相加又叫做拼接,乘法用在字符串就是打印多次,字符串只可以使用+符号来进行拼接与*来使用,字符串这就是类型的不同
4.变量类型转义
1.int()
可以将数字型的字符串给转换为int整型,但是一些字母或者文字的话会报错
>>> age = '18'
>>> type (age)
<class 'str'>
>>> age_1 = int(age)
>>> type (age_1)
<class 'int'>2.abs()
将数字类型的转换成绝对值
>>> abs(-100)
1003.float()
将整数转换为浮点型
>>> float(1)
1.04.bool()
>>> bool(100)
True
>>> bool(-1)
True
>>> bool(0)
False
>>> bool('false')
True
>>> bool(False)
False5.运算符
算数运算符
| 运算符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| < | 判断左边的是否小于右边的 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| > | 大于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| == | 判断是否相等 |
| != | 是否不相等 |
| is | 判断两个对象的id是否相等 |
| is not | 判断两个对象的id是否不相等 |
>>> 1 > 2
False
>>> 3 <= 5
True
>>> 3 == 3
True
>>> 3 != 3
False逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| and | 左边和右边同时为true,结果为true |
| or | 左边或右边其中一个为true,结果为true |
| not | 如果为true,结果为false,如果是false,结果为true |
6.循环结构
for循环
结构:
for 变量 in 可迭代对象:
statement()循环取值:
>>> for i in "Curry":
print (i)
C
u
r
r
yrange()迭代函数
语法:
range(stop)
range(start,stop)
range(start,start,step)range用法:
>>> for i in range(5):
print (i)
0
1
2
3
4
>>> for i in range(2,5):
print(i)
2
3
4
>>> for i in range(1,5,2):
print(i)
1
3
>>> for i in range(5,0,-1):
print(i)
5
4
3
2
1while循环
格式:
while 条件:
条件为true的执行语句
第二种方式:
while 条件:
代码块
else:
当条件为假执行此代码块其他循环项:
brack; //结束当前循环
continue; //跳出当前一层循环7.基础常用模块
1.random随机数模块
>>> import random
>>> print (random.randint(1,10))
42.decimal精准浮点数模块
>>> import decimal
>>> 0.1 + 0.2
0.30000000000000004
>>> a = decimal.Decimal('0.1')
>>> b = decimal.Decimal('0.2')
>>> print (a+b)
0.33.len()获取长度
>>> len('Curry')
5
>>> test=[1,2,3,4,5,'Curry']
>>> len(test)
68.python中的类型
-
浮点型
-
整型
-
字符串
-
复数
-
布尔
9.业务逻辑
流程图
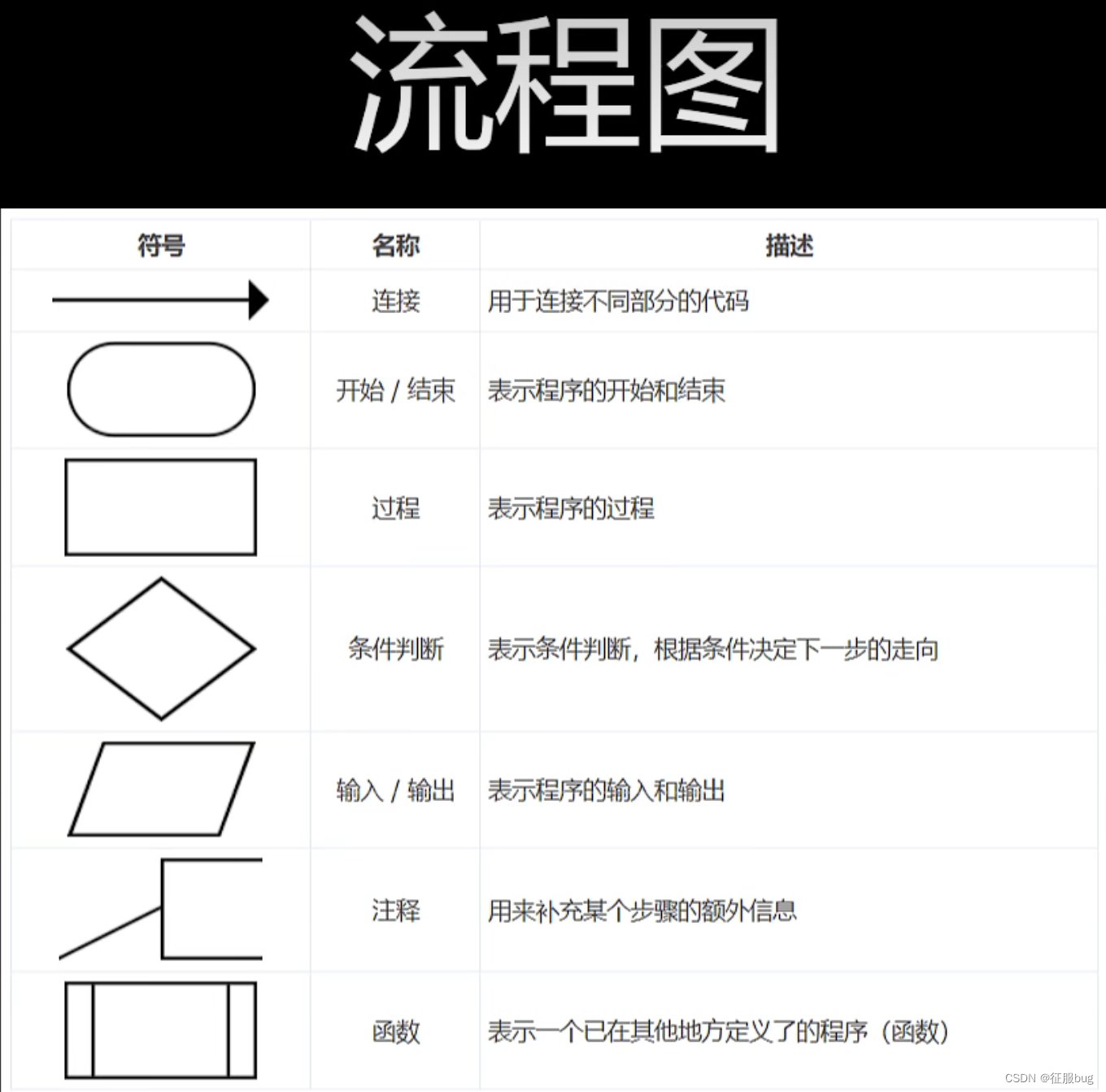
思维导图
10.了不起的判断分支
1.单支判断
if 条件:
代码块2.双分支判断
if 条件:
代码块
else:
代码块3.多分支判断
if 条件:
代码块
else if:
代码块
else if:
代码块
else:
代码块4.判断的特殊写法
格式:为true代码块 if 条件 else 为false结果
>>> if 0 < 1:
print ("True")
else:
print ("False")
True
>>> print ("True") if 0 < 1 else print ("False")
True