进程与线程
程序>进程>线程
程序是一段静止的代码,只有真正运行时的程序,才被称为进程。一个程序运行至少有一个进程
从操作系统底层来说,进程只是一个概念,真正执行的是线程。

进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,而线程是CPU的基本调度单位。
线程是进程中的一个执行路径,共享同一个进程内存空间。
线程之间可以自由切换,并发执行,一个进程最少有一个一个线程。线程是CPU的基本调度单位。
进程之间不能共享数据段地址,但同进程的线程之间可以。
单核CPU在任何时间点上,只能运行一个进程:宏观并行,微观串行。
进程由多个线程组成,彼此之间完成不同的工作,交替执行,被称为多线程。
对于一个Java程序,至少有两个线程。
main方法,也称主线程。- 垃圾回收器
GC,在JVM启动时自动启动。
线程的组成
任何一个线程都具有的基本组成部分:
CPU时间片:操作系统会为每个线程分配执行时间。
- 不是我们去控制CPU,而是CPU根据操作系统为我们分配执行时间。
运行数据:
- 堆空间:存储线程需使用的对象,多个线程可以共享堆中的对象。
- 栈空间:存储线程需使用的局部变量,每个线程都拥有独立的栈。

线程的两种实现方式
并行与并发
并行:多个任务同时执行(多个CPU)。
并发:多个任务同时请求运行,而处理器一次只能接受一个任务,就会把两个任务安排轮流执行,由于CPU时间片运行时间较短,就会感觉两个任务在同时执行。

创建线程一共有两种方式,分别是:继承Thread类和实现Runable方法。
启动线程是通过调用start()方法,表示线程已经准备就绪,等待CPU分配时间片。一旦CPU分配了时间片,线程就会自动运行。
start()方法不是启动线程,而是说这个线程已经准备就绪,等待CPU调度。
继承Thread类
- 继承
Thread类 - 覆盖
run()方法 - 创建子类对象
- 调用
start()方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建子类对象
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
//调用start()方法
myThread.start();
}
}
//继承Thread类
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
//重写run方法
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
实现Runable方法
- 实现
Runable接口类 - 覆盖
run()方法 - 创建实现类对象
- 创建线程对象
- 调用
start()方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建实现类对象
MyRunable myRunable = new MyRunable();
//创建线程对象
Thread thread = new Thread(myRunable);
//调用start方法
thread.start();
}
}
//实现Runable接口类
class MyRunable implements Runnable {
@Override
//重写run方法
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
如果使用类的方式来创建线程,代码看起来更加方便简单。
如果使用接口的方式来创建线程,要先编写任务,然后将任务交给线程类才能启动。要多一个步骤,看起来更加麻烦。
但更常用的还是接口的方式,因为接口更加灵活,可以继承多个。
如果使用类的方法,那么将无法继承其他的类。而如果使用接口,那么仍然可以继承其他的类,不会被因承继Thread类限制住。
接口回调
我们通过线程往外返回结果的时候,直接返回是没有办法返回数据的。可以通过接口调用的方法传递数据。
也就是在线程内部定义一个接口,谁需要返回数据,谁里面就定义一个接口,来做数据的返回。
模拟一个系统登陆功能,使用随机验证码来防止暴力破解方式进行不断的登陆尝试。
实现要求:
利用线程实现生成4位验证码,要求验证码由数字、字母组成,生成后显示出来。然后用户输入验证码,判断验证码是否正确。
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ValidateCodeThread validateCodeThread = new ValidateCodeThread();
ValidateCodeThread.OnResultListener onResultListener = new ValidateCodeThread.OnResultListener() {
@Override
public void onResult(String result) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入验证码:");
String userCode = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(result.equals(userCode));
}
};
validateCodeThread.setOnResultListener(onResultListener);
Thread thread = new Thread(validateCodeThread);
thread.start();
}
}
//创建验证码的线程任务
class ValidateCodeThread implements Runnable {
private String codes = "23456789abcdefghjkmnpqrstuvwxyz";
private OnResultListener onResultListener;
public void setOnResultListener(OnResultListener onResultListener) {
this.onResultListener = onResultListener;
}
Random r = new Random();
int num = 4;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(4);
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int index = r.nextInt(codes.length());
sb.append(codes.charAt(index));
}
System.out.println("生成的验证码是" + sb);
if (onResultListener != null) {
onResultListener.onResult(sb.toString());
}
}
interface OnResultListener {
public void onResult(String result);
}
}
线程休眠
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
只要使用native修饰的方法都是本地方法。此方法不是由Java实现,而是由底层的C/C++实现,然后回调到sleep方法。
数列中随机生成不重复数
需求:从1~100中随机产生10个不重复的数。
普通的算法逻辑:
- 随机生成第一个数,放到结果数组的第0个位置。
- 随机生成第二个数,与结果数组中已存在的数比较,如果相同,重新生成,直到不同,放到结果数组中。
- 重复第2步,直到生成10个数结束。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
ints[i] = i + 1;
}
int[] result = new int[10];
boolean flag = true;
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
flag = true;
while (flag) {
boolean b = true;
int index = random.nextInt(ints.length);
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (ints[index] == result[j]) {
b = false;
break;
}
}
if (b) {
result[i] = ints[index];
flag = false;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
}
优化后的算法逻辑
我们可以将随机的元素与数组末尾的元素进行交换,下次取值的时候通过数组元素个数减1的方式来随机产生一个数。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++) {
ints[i] = i + 1;
}
int[] result = new int[10];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(ints.length - i);
result[i] = ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[index] + ints[ints.length - 1 - i];
ints[index] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
}
添加休眠功能
使用Thread.sleep(long millis)方法实现线程休眠。
使用Thread.sleep(long millis)可能返回中断,需要用try-catch语句包裹。
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenRandomNums genRandomNums = new GenRandomNums();
Thread thread = new Thread(genRandomNums);
thread.start();
}
}
class GenRandomNums implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
int[] ints = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++) {
ints[i] = i + 1;
}
int[] result = new int[10];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(ints.length - i);
result[i] = ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[index] + ints[ints.length - 1 - i];
ints[index] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
}
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
System.out.print(result[i] + " ");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
自定义标记中断线程
中断线程可以利用方法对象.interrupt();为线程打上中断标记,在线程内使用Thread.interrupted()方法判断是否中断,该方法的返回值为Boolean类型,根据返回值判断接下来的操作。
Java提供的中断方法并不会强行结束线程,只是为线程打上中断标记。如何中断交由线程自己决定。
也可以在类内添加标记flag,通过在类外手动为flag赋值,根据不同的值进行不同的操作,实现中断功能。
class GenRandomNums implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Boolean flag = true;
int[] ints = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++) {
ints[i] = i + 1;
}
int[] result = new int[10];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length && flag; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(ints.length - i);
result[i] = ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[index] + ints[ints.length - 1 - i];
ints[index] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
ints[ints.length - 1 - i] = ints[ints.length - 1 - i] - ints[index];
}
for (int i = 0; i < result.length && flag; i++) {
System.out.print(result[i] + " ");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
获取线程名称
Thread.currentThread().getName()会返回当前线程的名称。
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThraedName thraedName = new ThraedName();
Thread thread = new Thread(thraedName);
thread.start();
//main:main
System.out.println("main:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
//thread:Thread-0
System.out.println("thread:" + thread.getName());
}
}
class ThraedName implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//GenRandomNums:Thread-0
System.out.println("GenRandomNums:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
线程同步与安全性
线程安全问题
多个线程操作同一个数据出现的数据不统一问题。

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TicketThread ticketThread = new TicketThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(ticketThread);
Thread t2 = new Thread(ticketThread);
Thread t3 = new Thread(ticketThread);
Thread t4 = new Thread(ticketThread);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
class TicketThread implements Runnable {
private int num = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (num != 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-当前:" + num-- + "剩余" + num);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
线程同步
只有拥有对象互斥锁标记的线程,才能进入该对象加锁的同步代码块。
线程退出同步代码块时,会释放相应的互斥锁标记。
需要注意的是,sleep()方法不会释放锁。
synchronized()同步代码块
synchronized(要同步的对象){要同步的操作}
括号内"要同步的对象"只是一个标记作用,没有其他含义。
//同步代码块
synchronized (this) {
while (num != 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-当前:" + num-- + "剩余" + num);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
同步方法
同步的对象是当前对象。
//同步方法,同步的对象是当前对象
private synchronized void ticket() {
while (num != 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-当前:" + num-- + "剩余" + num);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Lock.lock();锁同步
更加灵活,可以自定义同步区域。
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
if (lock.tryLock()) {
lock.lock();
}
while (num != 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-当前:" + num-- + "剩余" + num);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
同步规则
只有在调用包含同步代码块的方法,或者同步方法时,才需要对象的锁标记。
如调用不包含同步代码块的方法,或普通方法时,则不需要锁标记,可直接调用。
Java中线程安全的类包括:StringBuffer类、集合类等,这些类的公开方法均为synchonized修饰的同步方法。

如果需求中存在多线程同时访问,那么建议使用StringBuffer类。如果只有一个线程,那么建议使用StringBuilder类。
同步会增加性能的消耗,但在多线程的时候又不得不使用同步,否则会出现数据错乱、数据不安全的问题。通常是用确保数据安全换取性能的牺牲。性能和安全是相辅相成的。
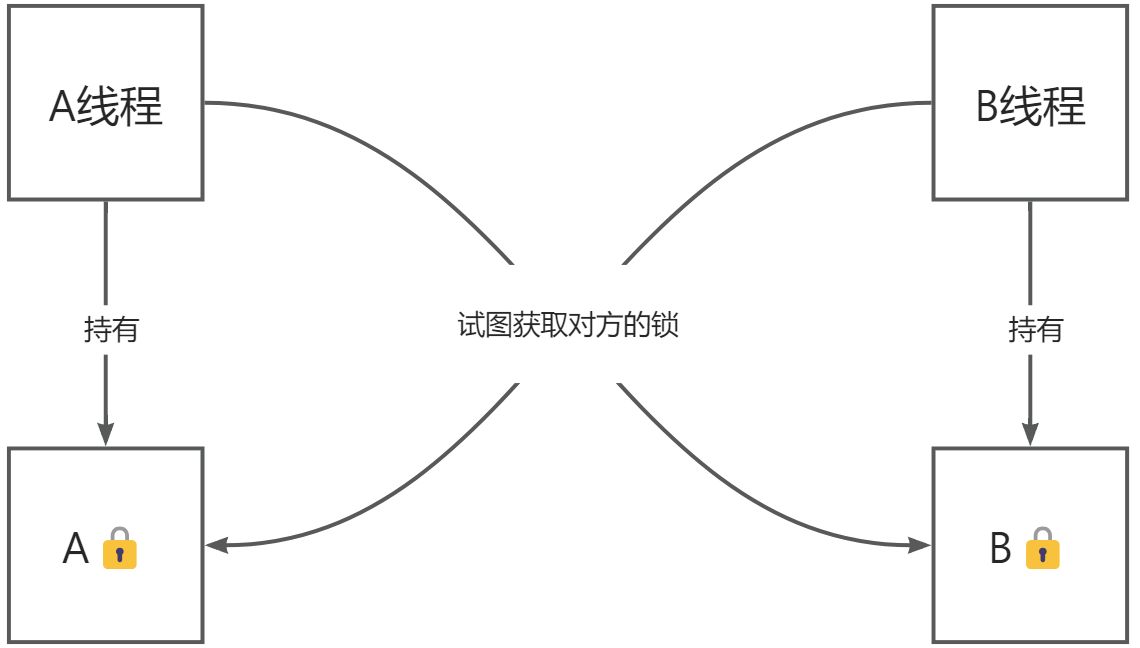
死锁问题
如果线程进行同步,那么他就会上锁,此时如果其他线程如果要执行,就要在门口等待,就会出现死锁:想要获取这个锁,但一直获取不到。
线程池
线程是宝贵的内存资源,单个线程占用约1M左右的内存空间,过多分配容易造成内存溢出。
频繁的创建和销毁线程会增加虚拟机回收频率造成程序性能下降。
线程池
线程容器,可设定线程分配的数量上限。将预先创建的线程对象存入池中,并重用线程池中的线程对象。避免频繁的创建和销毁。
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建三个线程的线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//提交到任务队列
executorService.submit(new TicketThread());
executorService.submit(new TicketThread());
executorService.submit(new TicketThread());
executorService.submit(new TicketThread());
}
}
class TicketThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
多线程应用
生产者与消费者的协作案例
this.wait();//线程进入等待状态,把CPU时间片让出去,释放监视器所有权(对象锁),等待其他方法使用notify()方法唤醒。
Thread.sleep();///线程进入休眠状态,把CPU时间片让出去,但不会释放对象锁
this.notify();//按优先级唤醒等待中的一个线程
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Food food = new Food();
Producter p = new Producter(food);
Customers c = new Customers(food);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(p);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(c);
thread2.start();
thread1.start();
}
}
class Customers implements Runnable {
private Food food;
public Customers(Food food) {
this.food = food;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
food.get();
}
}
}
class Producter implements Runnable {
private Food food;
public Producter(Food food) {
this.food = food;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
food.set("牛肉拉面", "味道美极了");
} else {
food.set("韭菜炒鸡蛋", "大补啊");
}
}
}
}
class Food {
private String name;
private String desc;
Boolean flag = true;//true表示可以生产,false表示可以消费
//生产食物
public synchronized void set(String name, String desc) {
//如果能消费不能生产
if (!flag) {
try {
//线程进入等待状态,释放监视器所有权(对象锁)
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.name = name;
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.desc = desc;
//生产完成,可以消费
flag = false;
//按优先级唤醒等待中的一个线程
this.notify();
}
//获取食物
public synchronized void get() {
//如果能生产不能消费
if (flag) {
try {
//线程进入等待状态,释放监视器所有权(对象锁)
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + "->" + desc);
//消费完成,可以生产
flag = true;
//按优先级唤醒等待中的一个线程
this.notify();
}
}
线程隔离
ThreadLocal提供一个线程Thread局部变量,访问到某个变量的每一个线程都拥有自己的局部变量。可以在多线程环境下保证成员变量的安全。
ThreadLocal并不是用来解决多线程环境下共享变量的问题。而是用来提供线程内部共享变量的问题。
对比
synchronized
ThreadLocal是采用空间换时间的方式,为每一个线程都提供一份变量的副本,实现同时访问、互不干扰,在多线程当中让每个线程之间的数据相互隔离。
synchronized同步机制采用的是时间换空间的方式,只提供一份,让线程排队访问,在多线程之间访问资源同步。
import java.lang.Thread;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(myThread);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myThread);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
threadLocal.set(i);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "threadLocal.get()=" + threadLocal.get());
}
}
}