1. 基于前面一节netty学习(1):1个客户端与服务器通信
只需要把服务器的handler改造一下即可,通过ChannelGroup 找到所有的客户端channel,发送消息即可。
package server;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.DefaultChannelGroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.GlobalEventExecutor;
/**
* 自定义处理Handler
*/
public class NettyServiceHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
// 创建一个ChannelGroup,其是一个线程安全的集合,其中存放着与当前服务器相连接的所有Active状态的Channel
// GlobalEventExecutor是一个单例、单线程的EventExecutor,是为了保证对当前group中的所有Channel的处理
// 线程是同一个线程
private static ChannelGroup group = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
// 只要有客户端Channel与服务端连接成功就会执行这个方法
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 获取到当前与服务器连接成功的channel
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
System.out.println(channel.remoteAddress() + "---上线");
group.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress() + "---上线\n");
// 将当前channel添加到group中
group.add(channel);
// NettyService.remoteAddressMap.put(channel.remoteAddress().toString(), ctx);
}
// 只要有客户端Channel断开与服务端的连接就会执行这个方法
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 获取到当前要断开连接的Channel
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
System.out.println(channel.remoteAddress() + "------下线");
group.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress() + "下线,当前在线人数:" + group.size() + "\n");
// group中存放的都是Active状态的Channel,一旦某Channel的状态不再是Active,
// group会自动将其从集合中踢出,所以,下面的语句不用写
// remove()方法的应用场景是,将一个Active状态的channel移出group时使用
// group.remove(channel);
}
/**
* channelRead,这个方法当有数据读写的时候,会触发,可以读取客户端的消息
* 只要有客户端Channel给当前的服务端发送了消息,那么就会触发该方法的执行
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
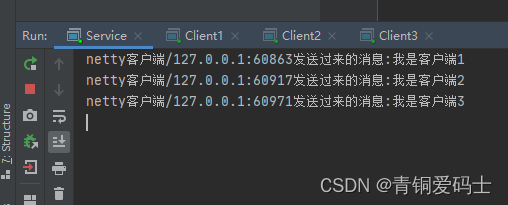
System.out.println("netty客户端" + channel.remoteAddress() + "发送过来的消息:" + msg);
// channel.writeAndFlush("自己发的消息:" + msg + "\n");
group.forEach(ch -> { // JDK8 提供的lambda表达式
if (ch != channel) {
ch.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress() + ":" + msg + "\n");
} else {
channel.writeAndFlush("自己发的消息:" + msg + "\n");
}
});
// String[] split = msg.split(":");
// if (split.length >= 2) { //指定客户端时发送给指定客户
// System.out.println("发送给客户:" + split[0]);
// if (NettyService.userIdMap.get(split[0]) != null) {
// NettyService.userIdMap.get(split[0]).writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress() + ":" + split[1] + "\n");
// } else {
// NettyService.userIdMap.put(split[0], ctx); //第一次发送消息时注册客户端的channel
// }
// } else { //否则发送给所有的客户端
// System.out.println("广播");
// // 遍历channelGroup,从而区分“我”和“别人”发出的消息,如果消息是自己发出的就显示“我”
// group.forEach(ch -> { // JDK8 提供的lambda表达式
// if (ch != channel) {
// ch.writeAndFlush(channel.remoteAddress() + ":" + msg + "\n");
// } else {
// channel.writeAndFlush("自己发的消息:" + msg + "\n");
// }
// });
// }
}
/**
* channelReadComplete,数据读取完毕之后,需要做的业务操作,回消息
*/
// public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext) throws Exception {
// //消息出站
// System.out.println("Netty服务端读取消息完毕");
// channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("--over", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// }
/**
* exceptionCaught,发生异常的handler
*/
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Throwable throwable) throws Exception {
throwable.printStackTrace();
channelHandlerContext.close();
}
}
2. 测试
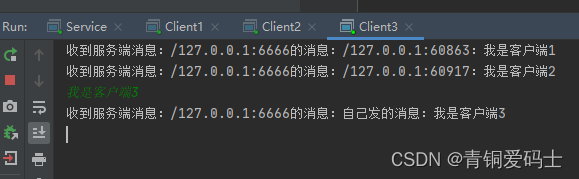
创建3个客户端
package test;
import client.NettyClient;
public class Client3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new NettyClient("127.0.0.1",6666).createNettyClient();
}
}
每个客户端都发送消息
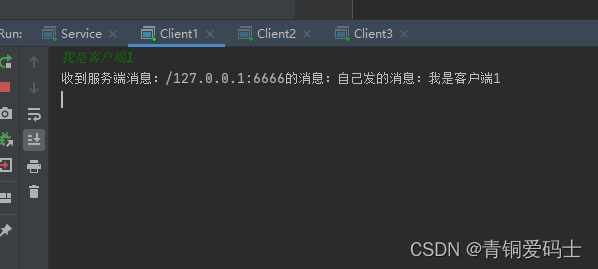
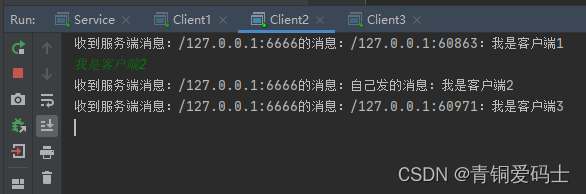
服务器