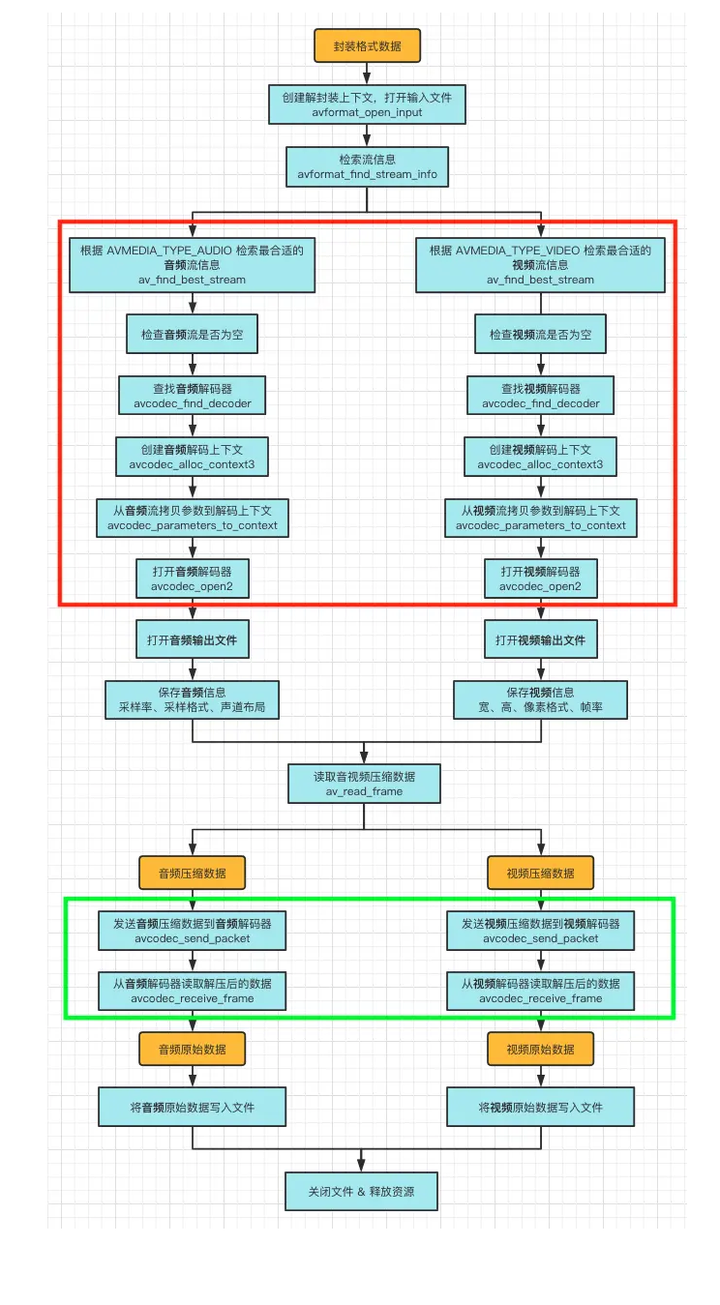
Nginx Rewrite–重写跳转
Nginx Rewrite--重写跳转
- 一、概述:
- 1.Rewrite 跳转场景:
- 2.Rewrite 跳转实现:
- 3.Rewrite 实际场景:
- 4.Nginx正则表达式:
- 5.Rewrite 命令:
- 6.location分类:
- 7.比较rewrite和location:
- 二、实际操作运用:
- 1.rewrite示例:
- 三、总结:
- 1.本章掌握:
- 2.实操中遇到的问题:
- 3.rewrite和location:
一、概述:
1.Rewrite 跳转场景:
(1)URL看起来更规范,合理。
① URL:指的是一个具体的路径/位置。
② URI:一个拥有相同类型/特性的对象集合。
③ URN:用名称定位。
(2)企业会将动态URL地址伪装成静态地址提供服务。
(3)网址换新域名后,让旧的访问跳转到新的域名上。
(4)服务端某些业务调整。
2.Rewrite 跳转实现:
(1)实现过程:

3.Rewrite 实际场景:
(1)Nginx跳转需求的实现方式:
①使用rewrite进行匹配跳转(防盗链)
②使用if匹配全局变量后调整(CentOS系统的全局变量,不是Nginx本身全局变量)
③使用location匹配再跳转(匹配的访问URL路径,location可匹配本地重写以及垮服务器跳转)
(2)rewrite在server {},if {},location {}段中
location只对域名后的除去传递参数外的字符串起作用
(3)对域名或参数字符串
① 使用if全局变量
② 使用proxy_pass反向代理
4.Nginx正则表达式:
(1)常用正则表达式元字符:
| 字符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 匹配输入字符串的起始位置 |
| $ | 匹配输入字符串的结束位置 |
| * | 匹配前面的字符零次或多次 |
| + | 匹配前面的字符一次或多次 |
| ? | 匹配前面的字符零次或一次 |
| . | 匹配除“\n”之外的任何单个字符 |
| \ | 将后面接的字符标记为一个特殊字符或一个原义字符或一个向后引用 |
| \d | 匹配纯数字 |
| {n} | 重复n次 |
| {n,} | 重复n次或更多次 |
| {c} | 匹配单个字符c |
| [a-z] | 匹配a-z小写字母任意一个 |
| [a-zA-Z] | 匹配(a-z)小写或(A-Z)大写字母中任意一个 |
| () | 表达式的开始和结束位置 |
| | | 或运算符 |
(2)小结:
从功能看,rewrite和location有点像,都能实现跳转。主要区别在于:
① rewrite是在同一域名内更改获取资源的路径,而location是对一类路径做控制访问或反向代理,还可以proxy_pass到其他机器。
② rewrite 对访问的域名或者域名内的URL路径地址重写
③ location对访问的路径做访问控制或者代理转发
5.Rewrite 命令:
(1)命令语法:
rewrite <regex> 正则 <replacement> 跳转后内容 [flag];(rewrite 支持的flag标记)
(2)flag标记说明:
| 标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| last | 相当于Apache的[l]标记,表示完成rewrite。 |
| break | 本条规则匹配完成即终止,不再匹配新的规则。 |
| redirect | 返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址,爬虫不会更新URL。 |
| permanent | 返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址,爬虫会更新URL。 |
- 标记总结:
① break和last类似,但不会重新发起一次处理过程,而是直接返回结果。
② redirect:该标记表示当前规则匹配成功后,立即进行重定向操作。
③ permanent:该标记和redirect类似,但它是永久重定向。
④ set:表示当前规则匹配成功设置一个变量,并把变量传入下一条规则。
(3)last和break比较:
| last | break | |
|---|---|---|
| 使用场景 | 一般写在server和if中 | 一般使用在location中 |
| URL匹配 | 不终止重写后的URL匹配 | 终止重写后的URL |
6.location分类:
(1)分类:
精确匹配:location = / {…}
一般匹配:location / {…}
正则匹配:location ~ / {…}
(2)正则匹配的常用表达式:
| 标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ~ | 执行一个正在匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 执行一个正在匹配,不区分大小写 |
| !~ | 执行一个正在匹配,区分大小写,不匹配 |
| !~* | 执行一个正在匹配,不区分大小写,不匹配 |
| ^~ | 普通字符匹配,使用前缀匹配。如匹配成功,则不再匹配其他location |
| = | 普通字符精确匹配,完全匹配 |
| @ | 定义一个命名的location,使用在内部定向时 |
(3)location优先级:
首先精确匹配=
其次前缀匹配 ^~
其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配 或*
然后匹配不带任何修饰的前缀匹配
最后是交给 /通用匹配
(4)location实例:
① location = / {}
=为精确匹配 / ,主机名后面不能带任何字符串,比如访问 / 和 /data,则 / 匹配,/data 不匹配,再比如 location = /abc,则只匹配/abc ,/abc/或 /abcd不匹配。若 location /abc,则即匹配/abc 、/abcd/ 同时也匹配 /abc/。② location / {}
因为所有的地址都以 / 开头,所以这条规则将匹配到所有请求 比如访问 / 和 /data, 则 / 匹配, /data 也匹配,但若后面是正则表达式会和最长字符串优先匹配(最长匹配)③ location /documents/ {}
匹配任何以 /documents/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location,只有其它 location后面的正则表达式没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条④ location /documents/abc {}
匹配任何以 /documents/abc 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location,只有其它 location后面的正则表达式没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条⑤ location ^~ /images/ {}
匹配任何以 /images/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,停止往下搜索正则,采用这一条⑥ location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {}
匹配所有以 gif、jpg或jpeg 结尾的请求。然而,所有请求 /images/ 下的图片会被 location ^~ /images/ 处理,因为 ^~ 的优先级更高,所以到达不了这一条正则。⑦ location /images/abc {}
最长字符匹配到 /images/abc,优先级最低,继续往下搜索其它 location,会发现 ^~ 和 ~ 存在⑧ location ~ /images/abc {}
匹配以/images/abc 开头的,优先级次之,只有去掉 location ^~ /images/ 才会采用这一条⑨ location /images/abc/1.html {}
匹配/images/abc/1.html 文件,如果和正则location ~ /images/abc/1.html 相比,正则优先级更高
(5)小结:
① (location=完整路径)>(location ^~ 路径)>(location,*正则顺序)>(location不分起始路径)>(location /)
② location匹配:
首先看 优先级:精确= > 前缀^~ > 正则,* > 一般 > 通用/
优先级相同:正则看上下顺序,上面的优先,一般匹配看长度,最长匹配的优先
精确,前缀,正则,一般 都没有匹配到,最后在看通用匹配
(6)实际网站使用中,至少有三个匹配规则定义:
① 第一个必选规则:
直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁,使用这个会加速处理,比如说官网。可以是一个静态首页,也可以直接转发给后端应用服务器
location = / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}② 第二个必选规则:
处理静态文件请求,这是nginx作为http服务器的强项。有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用
location ^~ /static/ {
root /webroot/static/;
}location ~* .(html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /webroot/res/;
}③ 第三个规则就是通用规则:
用来转发带.php、.jsp后缀的动态请求到后端应用服务器,非静态文件请求就默认是动态请求。
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat_server;
}
7.比较rewrite和location:
(1)相同点:都能实现跳转。
(2)不同点:
① rewrite是同一域名内更改获取资源的路径。
② location是对同一路径做控制访问或反向代理,还可以proxy_pass到其他机器。
(3)rewrite写在location里,执行顺序:
① 执行server块里的rewrite指令
② 执行location匹配
③ 执行选定的location中的rewrite指令
(4)rewrite和location比较:
① rewrite会改写访问URL路径(被访问的HTML/HTM/CSS文件)
② location对一类地址进行权限控制(认证控制)+跳转(跨服务器进行URL跳转)
二、实际操作运用:
1.rewrite示例:
(1)基于域名跳转:
- 要求:现在公司旧域名www.exo.com有业务需求变更,需要使用新域名www.bkpp.com代替,但是旧域名不能废除,需要跳转到新域名上,而且后面的参数保持不变。
[root@wang3 conf]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.exo.com; #域名修改
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.exo.com-access.log; #日志修改
location / { #添加域名重定向
if ($host = 'www.exo.com'){ #$host为rewrite全局变量,代表请求主机头字段或主机名
rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.bkpp.com/$1 permanent; #$1为正则匹配的内容,即“域名/”之后的字符串
}
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
[root@wang3 conf]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@wang3 conf]# echo "192.168.174.15 www.exo.com www.bkpp.com" >> /etc/hosts
[root@wang3 conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service


(2)基于客户端 IP 访问跳转:
公司业务新版本上线,要求所有 IP 访问任何内容都显示一个固定维护页面,只有公司 IP :192.168.174.15访问正常。
[root@wang3 conf]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
access_log logs/www.exo.com-access.log;
set $rewrite true; #设置变量$rewrite,变量值为boole值true
if ($remote_addr = "192.168.174.15"){ #当客户端IP为192.168.174.15时,将变量值设为false,不进行重写
set $rewrite false;
} #除了合法IP,其它都是非法IP,进行重写跳转维护页面
if ($rewrite = true){ #当变量值为true时,进行重写
rewrite (.+) /sehun.html; #将域名后边的路径重写成/sehun.html,例如www.exo.com/sehun.html
}
location = /sehun.html {
root /var/www/html; ##网页返回/var/www/html/sehun.html的内容
}
[root@wang3 conf]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@wang3 html]# mkdir -p /var/www/html/
[root@wang3 html]# echo '<h1>Shimmie Shimmie Ko Ko Bop I think I like it!</h1>' > /var/www/html/sehun.html
[root@wang3 html]# systemctl restart nginx


(3)基于旧域名跳转到新域名后面加目录:
现在访问的是 http://bbs.exo.com/post/,现在需要将这个域名下面的访问都跳转到http://www.exo.com/bbs/post/
[root@wang3 html]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.exo.com; #域名修改
charset utf-8;
access_log /var/log/nginx/www.exo.com-access.log;
#添加
location /post {
rewrite (.+) http://www.exo.com/bbs/$1 permanent; #这里的$1为位置变量,代表/post
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@wang3 html]# mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/html/bbs/post
[root@wang3 html]# echo "this is 1.html" >> /usr/local/nginx/html/bbs/post/1.html
[root@wang3 html]# echo "192.168.174.15 bbs.exo.com www.exo.com" >> /etc/hosts
[root@wang3 html]# systemctl restart nginx

(4)基于参数匹配的跳转:
现在访问http://www.exo.com/100-(100|200)-100.html 跳转到http://www.exo.com页面。
[root@wang3 post]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.kgc.com; #域名修改
charset utf-8;
access_log /var/log/nginx/www.kgc.com-access.log;
if ($request_uri ~ ^/100-(100|200)-(\d+).html$) {
rewrite (.+) http://www.kgc.com permanent;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@wang3 post]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@wang3 post]# systemctl restart nginx.service
- 使用浏览器访问 http://www.exo.com/100-200-100.html 跳转到http://www.exo.com页面。

(5)基于目录下所有 php 结尾的文件跳转:
要求访问 http://www.exo.com/upload/123.php 跳转到首页。
[root@wang3 post]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.exo.com; #域名修改
charset utf-8;
access_log /var/log/nginx/www.kgc.com-access.log;
location ~* /upload/.*\.php$ {
rewrite (.+) http://www.exo.com permanent;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@wang3 post]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@wang3 post]# systemctl restart nginx.service
- 浏览器访问 http://www.exo.com/upload/123.php 跳转到http://www.exo.com页面。

(6)基于最普通一条 url 请求的跳转:
要求访问一个具体的页面如 http://www.exo.com/abc/123.html 跳转到首页
[root@wang3 post]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.exo.com; #域名修改
charset utf-8;
access_log /var/log/nginx/www.exo.com-access.log;
location ~* ^/abc/123.html {
rewrite (.+) http://www.exo.com permanent;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@wang3 post]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@wang3 post]# systemctl restart nginx.service
访问一个具体的页面如 http://www.exo.com/abc/123.html 跳转到首页

三、总结:
1.本章掌握:
(1)跳转场景,跳转实现,nginx正则表达式,rewrite语法格式。
(2)last,break,permanent,redirect标记说明。
(3)location分类,优先级,location和rewrite比较。
2.实操中遇到的问题:
(1)Nginx服务无法启动。
- 解决方案:关闭防火墙,安全机制。
(2)网页正常跳转,但显示无法找到路径。
- DNS重释,
3.rewrite和location:
(1)rewrite指令允许对 URL 进行转换或修改。当 Nginx 收到一个请求时,会检查请求的 URI 是否与 rewrite 指令匹配,如果是,则这个 URI 将被重写为一个新的 URI。这个重写后的 URI 将被用于后续的处理。
(2)location指令用于匹配 HTTP 请求的 URI。当 Nginx 收到一个请求时,会检查请求的 URI 是否与 location 指令匹配。如果匹配,则该指令块中的指令将被执行。 location指令通常用于配置网站页面和后端服务的访问规则、安全设置等。