基于WIN10的64位系统演示
一、写在前面
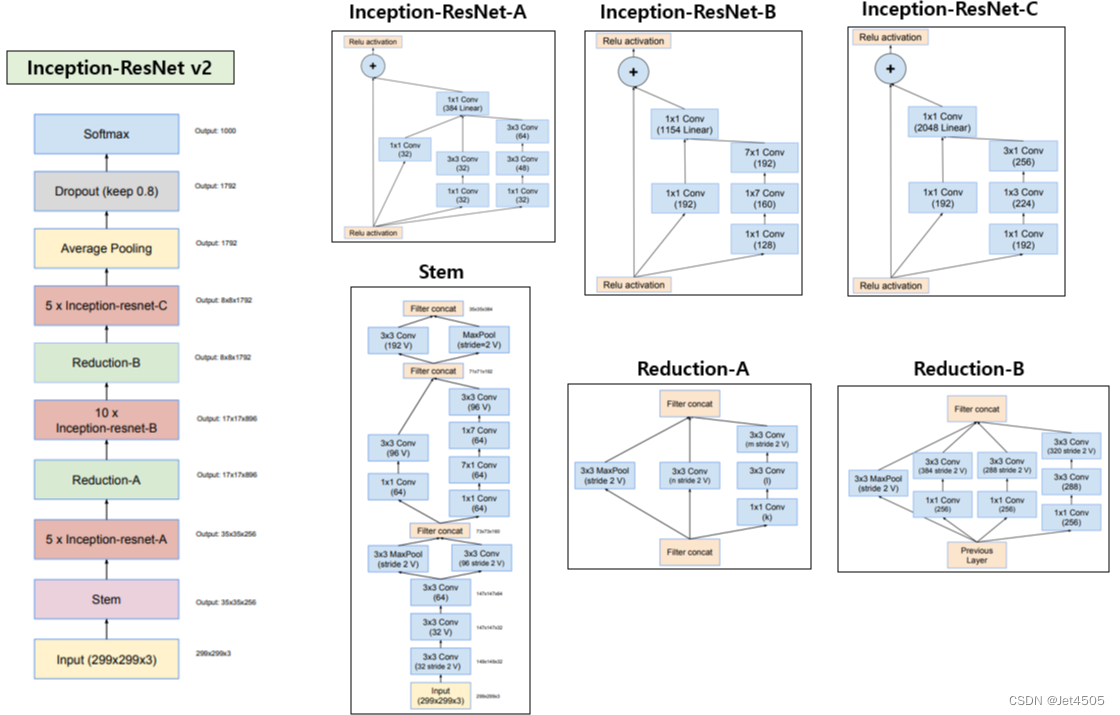
(1)InceptionResnetV2
InceptionResNetV2是一种由Google研究人员开发的深度学习模型,是一种混合了Inception和ResNet(残差网络)两种结构的卷积神经网络(CNN)。它在ImageNet竞赛中取得了非常优秀的成绩,并广泛应用于图像识别、对象检测等领域。
InceptionResNetV2的主要特点是将Inception结构(也称为网络中的网络)和残差连接(ResNet)结合在一起,旨在提高模型的性能和稳定性。Inception模块能够在多个尺度上提取特征,而残差连接可以帮助网络更好地学习复杂的映射关系,防止训练深度网络时出现的梯度消失问题。
InceptionResNetV2的结构相比于其前身InceptionV3更加复杂,包含了许多Inception模块和ResNet模块,从而使得模型具有更大的容量和更好的性能。不过这也导致了模型的计算量相对较大,需要更多的计算资源和时间进行训练。
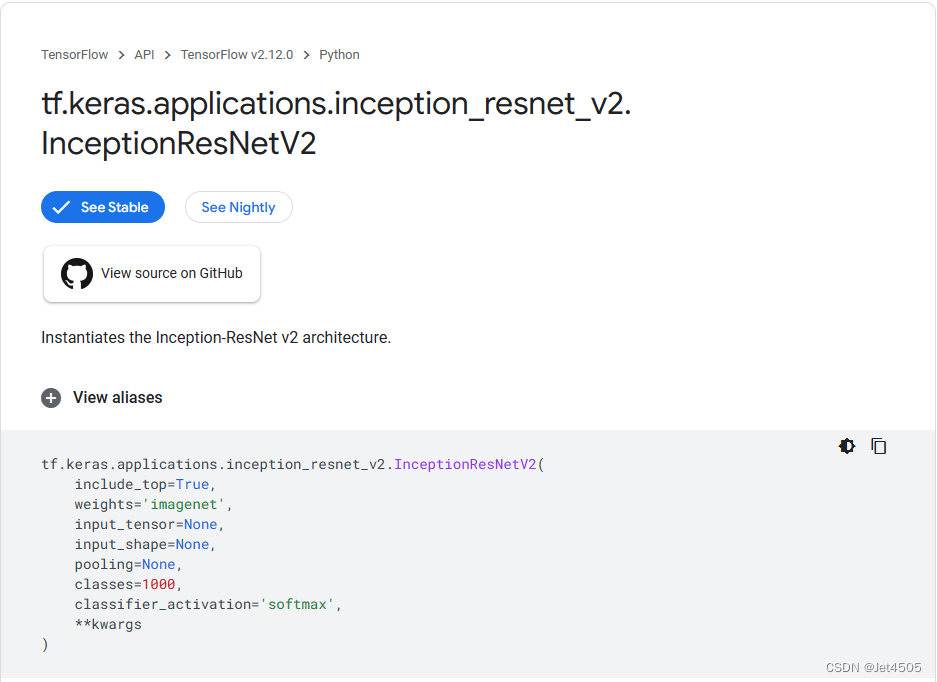
(2)InceptionResnetV2的预训练版本
Keras有InceptionResnetV2的各种变体预训练模型,省事:
二、InceptionResnetV2迁移学习代码实战
我们继续胸片的数据集:肺结核病人和健康人的胸片的识别。其中,肺结核病人700张,健康人900张,分别存入单独的文件夹中。使用的是Mobilenet V2这个网络。
from tensorflow import keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Dropout, Activation, Reshape, Softmax, GlobalAveragePooling2D, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D
from tensorflow.python.keras import Sequential, initializers
from tensorflow.python.keras import Model
from tensorflow.python.keras.optimizers import adam_v2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, image_dataset_from_directory
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers.preprocessing.image_preprocessing import RandomFlip, RandomRotation, RandomContrast, RandomZoom, RandomTranslation
import os,PIL,pathlib
import warnings
#设置GPU
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] #如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0, True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU")
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号(b)导入数据集
#1.导入数据
data_dir = "./MTB"
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*')))
print("图片总数为:",image_count)
batch_size = 32
img_height = 100
img_width = 100
"""
关于image_dataset_from_directory()的详细介绍可以参考文章:https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/article/details/117018789
"""
train_ds = image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="training",
seed=12,
image_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
val_ds = image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="validation",
seed=12,
image_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
class_names = train_ds.class_names
print(class_names)
print(train_ds)
#2.检查数据
for image_batch, labels_batch in train_ds:
print(image_batch.shape)
print(labels_batch.shape)
break
#3.配置数据
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
def train_preprocessing(image,label):
return (image/255.0,label)
train_ds = (
train_ds.cache()
.shuffle(800)
.map(train_preprocessing) # 这里可以设置预处理函数
# .batch(batch_size) # 在image_dataset_from_directory处已经设置了batch_size
.prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
)
val_ds = (
val_ds.cache()
.map(train_preprocessing) # 这里可以设置预处理函数
# .batch(batch_size) # 在image_dataset_from_directory处已经设置了batch_size
.prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
)
#4. 数据可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) # 图形的宽为10高为5
plt.suptitle("数据展示")
class_names = ["Tuberculosis","Normal"]
for images, labels in train_ds.take(1):
for i in range(15):
plt.subplot(4, 5, i + 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
# 显示图片
plt.imshow(images[i])
# 显示标签
plt.xlabel(class_names[labels[i]-1])
plt.show()(c)数据增强
data_augmentation = Sequential([
RandomFlip("horizontal_and_vertical"),
RandomRotation(0.2),
RandomContrast(1.0),
RandomZoom(0.5,0.2),
RandomTranslation(0.3,0.5),
])
def prepare(ds):
ds = ds.map(lambda x, y: (data_augmentation(x, training=True), y), num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)
return ds
train_ds = prepare(train_ds)(d)导入InceptionResnetV2
#获取预训练模型对输入的预处理方法
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications import inception_resnet_v2
from tensorflow.python.keras import Input, regularizers
IMG_SIZE = (img_height, img_width, 3)
base_model = inception_resnet_v2.InceptionResNetV2(input_shape=IMG_SIZE,
include_top=False, #是否包含顶层的全连接层
weights='imagenet')
inputs = Input(shape=IMG_SIZE)
#模型
x = base_model(inputs, training=False) #参数不变化
#全局池化
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
#BatchNormalization
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
#Dropout
x = Dropout(0.8)(x)
#Dense
x = Dense(128, kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.2))(x) # 全连接层减少到128,添加 L2 正则化
#BatchNormalization
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
#激活函数
x = Activation('relu')(x)
#输出层
outputs = Dense(2, kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.2))(x) # 添加 L2 正则化
#BatchNormalization
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
#激活函数
outputs = Activation('sigmoid')(outputs)
#整体封装
model = Model(inputs, outputs)
#打印模型结构
print(model.summary())打印出模型的结构:
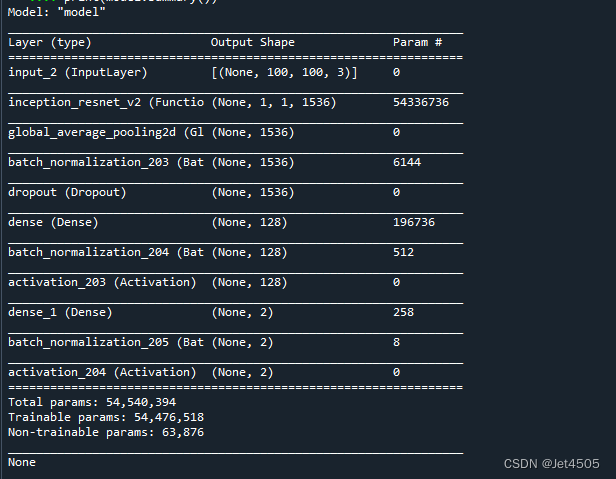
模型比较大,只是5400万的参数。
(e)编译模型
#定义优化器
from tensorflow.python.keras.optimizers import adam_v2, rmsprop_v2
#from tensorflow.python.keras.optimizer_v2.gradient_descent import SGD
optimizer = adam_v2.Adam()
#optimizer = SGD(learning_rate=0.001)
#optimizer = rmsprop_v2.RMSprop()
#编译模型
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer,
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
#训练模型
from tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, Callback, EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau, LearningRateScheduler
NO_EPOCHS = 20
PATIENCE = 10
VERBOSE = 1
# 设置动态学习率
annealer = LearningRateScheduler(lambda x: 1e-4 * 0.99 ** (x+NO_EPOCHS))
#性能不提升时,减少学习率
#reduce = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_accuracy',
# patience=PATIENCE,
# verbose=1,
# factor=0.8,
# min_lr=1e-6)
# 设置早停
earlystopper = EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', patience=PATIENCE, verbose=VERBOSE)
#
checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint('mtb_best_model_tm_inceptionrsenetv2.h5',
monitor='val_accuracy',
verbose=VERBOSE,
save_best_only=True,
save_weights_only=True,
mode='max')
train_model = model.fit(train_ds,
epochs=NO_EPOCHS,
verbose=1,
validation_data=val_ds,
callbacks=[earlystopper, checkpointer, annealer])
#保存模型
model.save('mtb_best_model_tm_inceptionrsenetv2.h5')
print("The trained model has been saved.")即使参数很多,但是模型训练依旧速度飞快!!!
(f)Accuracy和Loss可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loss = train_model.history['loss']
acc = train_model.history['accuracy']
val_loss = train_model.history['val_loss']
val_acc = train_model.history['val_accuracy']
epoch = range(1, len(loss)+1)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10,4))
ax[0].plot(epoch, loss, label='Train loss')
ax[0].plot(epoch, val_loss, label='Validation loss')
ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[0].set_ylabel('Loss')
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].plot(epoch, acc, label='Train acc')
ax[1].plot(epoch, val_acc, label='Validation acc')
ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax[1].legend()
plt.show()观察模型训练情况:
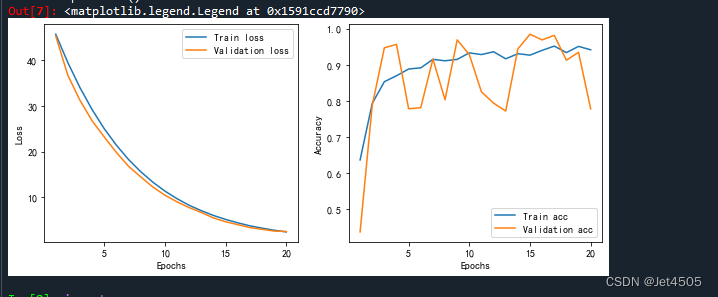
蓝色为训练集,橙色为验证集。可以看到,验证集的准确率波动较大,但是整体还是往上升的。
(g)混淆矩阵可视化以及模型参数
没啥好说的,都跟之前的ML模型类似:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.python.keras.models import load_model
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import math
# 定义一个绘制混淆矩阵图的函数
def plot_cm(labels, predictions):
# 生成混淆矩阵
conf_numpy = confusion_matrix(labels, predictions)
# 将矩阵转化为 DataFrame
conf_df = pd.DataFrame(conf_numpy, index=class_names ,columns=class_names)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,7))
sns.heatmap(conf_df, annot=True, fmt="d", cmap="BuPu")
plt.title('混淆矩阵',fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('真实值',fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('预测值',fontsize=14)
val_pre = []
val_label = []
for images, labels in val_ds:#这里可以取部分验证数据(.take(1))生成混淆矩阵
for image, label in zip(images, labels):
# 需要给图片增加一个维度
img_array = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
# 使用模型预测图片中的人物
prediction = model.predict(img_array)
val_pre.append(np.argmax(prediction))
val_label.append(label)
plot_cm(val_label, val_pre)
cm_val = confusion_matrix(val_label, val_pre)
a_val = cm_val[0,0]
b_val = cm_val[0,1]
c_val = cm_val[1,0]
d_val = cm_val[1,1]
acc_val = (a_val+d_val)/(a_val+b_val+c_val+d_val) #准确率:就是被分对的样本数除以所有的样本数
error_rate_val = 1 - acc_val #错误率:与准确率相反,描述被分类器错分的比例
sen_val = d_val/(d_val+c_val) #灵敏度:表示的是所有正例中被分对的比例,衡量了分类器对正例的识别能力
sep_val = a_val/(a_val+b_val) #特异度:表示的是所有负例中被分对的比例,衡量了分类器对负例的识别能力
precision_val = d_val/(b_val+d_val) #精确度:表示被分为正例的示例中实际为正例的比例
F1_val = (2*precision_val*sen_val)/(precision_val+sen_val) #F1值:P和R指标有时候会出现的矛盾的情况,这样就需要综合考虑他们,最常见的方法就是F-Measure(又称为F-Score)
MCC_val = (d_val*a_val-b_val*c_val) / (math.sqrt((d_val+b_val)*(d_val+c_val)*(a_val+b_val)*(a_val+c_val))) #马修斯相关系数(Matthews correlation coefficient):当两个类别具有非常不同的大小时,可以使用MCC
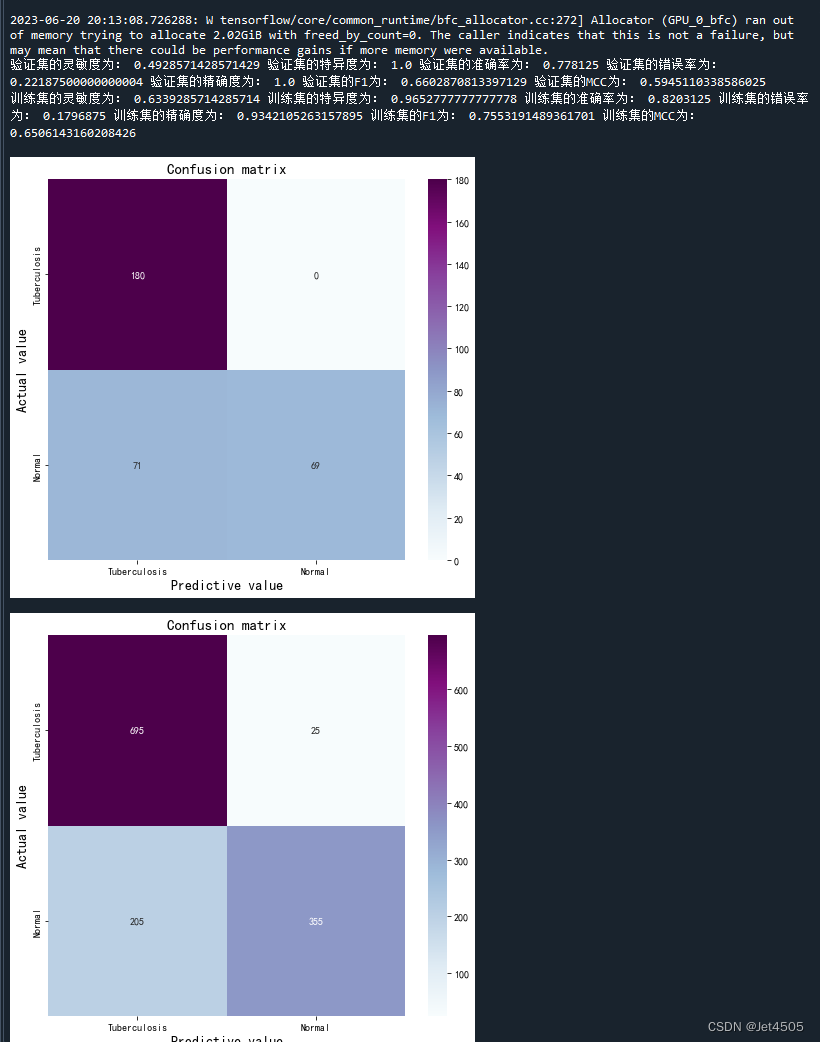
print("验证集的灵敏度为:",sen_val,
"验证集的特异度为:",sep_val,
"验证集的准确率为:",acc_val,
"验证集的错误率为:",error_rate_val,
"验证集的精确度为:",precision_val,
"验证集的F1为:",F1_val,
"验证集的MCC为:",MCC_val)
train_pre = []
train_label = []
for images, labels in train_ds:#这里可以取部分验证数据(.take(1))生成混淆矩阵
for image, label in zip(images, labels):
# 需要给图片增加一个维度
img_array = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
# 使用模型预测图片中的人物
prediction = model.predict(img_array)
train_pre.append(np.argmax(prediction))
train_label.append(label)
plot_cm(train_label, train_pre)
cm_train = confusion_matrix(train_label, train_pre)
a_train = cm_train[0,0]
b_train = cm_train[0,1]
c_train = cm_train[1,0]
d_train = cm_train[1,1]
acc_train = (a_train+d_train)/(a_train+b_train+c_train+d_train)
error_rate_train = 1 - acc_train
sen_train = d_train/(d_train+c_train)
sep_train = a_train/(a_train+b_train)
precision_train = d_train/(b_train+d_train)
F1_train = (2*precision_train*sen_train)/(precision_train+sen_train)
MCC_train = (d_train*a_train-b_train*c_train) / (math.sqrt((d_train+b_train)*(d_train+c_train)*(a_train+b_train)*(a_train+c_train)))
print("训练集的灵敏度为:",sen_train,
"训练集的特异度为:",sep_train,
"训练集的准确率为:",acc_train,
"训练集的错误率为:",error_rate_train,
"训练集的精确度为:",precision_train,
"训练集的F1为:",F1_train,
"训练集的MCC为:",MCC_train)灵敏度弱于特异度,因此需要根据实际调整阈值(当下是默认值0.5):
(h)AUC曲线绘制
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.python.keras.models import load_model
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import math
def plot_roc(name, labels, predictions, **kwargs):
fp, tp, _ = metrics.roc_curve(labels, predictions)
plt.plot(fp, tp, label=name, linewidth=2, **kwargs)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='orange', linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('False positives rate')
plt.ylabel('True positives rate')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_aspect('equal')
val_pre_auc = []
val_label_auc = []
for images, labels in val_ds:
for image, label in zip(images, labels):
img_array = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
prediction_auc = model.predict(img_array)
val_pre_auc.append((prediction_auc)[:,1])
val_label_auc.append(label)
auc_score_val = metrics.roc_auc_score(val_label_auc, val_pre_auc)
train_pre_auc = []
train_label_auc = []
for images, labels in train_ds:
for image, label in zip(images, labels):
img_array_train = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
prediction_auc = model.predict(img_array_train)
train_pre_auc.append((prediction_auc)[:,1])#输出概率而不是标签!
train_label_auc.append(label)
auc_score_train = metrics.roc_auc_score(train_label_auc, train_pre_auc)
plot_roc('validation AUC: {0:.4f}'.format(auc_score_val), val_label_auc , val_pre_auc , color="red", linestyle='--')
plot_roc('training AUC: {0:.4f}'.format(auc_score_train), train_label_auc, train_pre_auc, color="blue", linestyle='--')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
#plt.savefig("roc.pdf", dpi=300,format="pdf")
print("训练集的AUC值为:",auc_score_train, "验证集的AUC值为:",auc_score_val)ROC曲线:
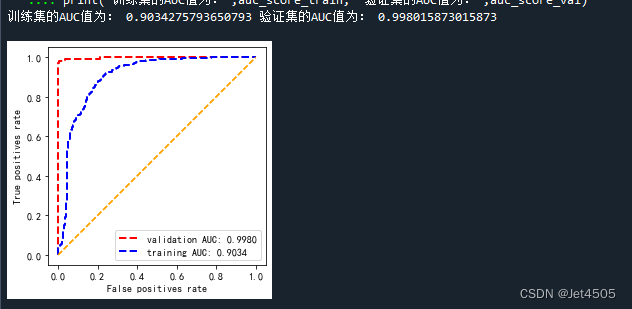
依旧赏心悦目的曲线啊!!!
三、写在最后
发挥了组合模型的优势吧,即使参数巨大,但是不影响训练速度,收敛得很快但又能保持相对较高的准确率,值得推荐!
四、InceptionResnetV2、Mobilenet、Efficientnet、DenseNet201、Inception V3和VGG19的对比
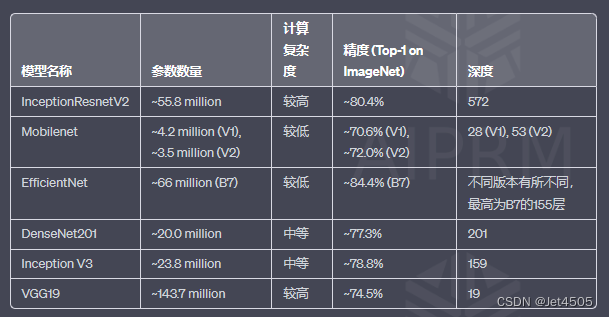
(1)“参数数量”代表模型大小;
(2)“计算复杂度”代表模型运行所需的计算资源;
(3)“精度”代表模型在特定任务上的性能;
(4)“深度”代表模型的层数(更深的网络可能需要更多的计算资源,但也可能有更好的性能)。
五、数据
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/15vSVhz1rQBtqNkNp2GQyVw?pwd=x3jf
提取码:x3jf