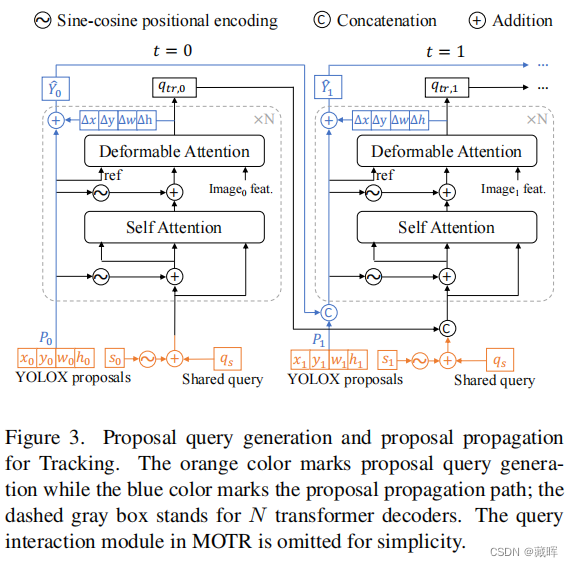
JUC阻塞队列BlockingQueue---ArrayBlockingQueue
- ArrayBlockingQueue
- 示例代码
- 原理
- 构造方法
- 内部常量
- 入队put方法
- 出队take方法
什么是阻塞队列?
ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue是典型的有界阻塞队列,其内部是用数组存储元素的,初始化时需要指定容量大小,利用 ReentrantLock 实现线程安全。
ArrayBlockingQueue可以用于实现数据缓存、限流、生产者-消费者模式等各种应用。
在生产者-消费者模型中使用时,如果生产速度和消费速度基本匹配的情况下,使用ArrayBlockingQueue是个不错选择;当如果生产速度远远大于消费速度,则会导致队列填满,大量生产线程被阻塞。
示例代码
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueueExample {
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 5;
private static final int PRODUCER_DELAY_MS = 1000;
private static final int CONSUMER_DELAY_MS = 2000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建一个容量为QUEUE_CAPACITY的阻塞队列
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY);
// 创建一个生产者线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
// 在队列满时阻塞
queue.put("producer");
System.out.println("生产了一个元素,队列中元素个数:" + queue.size());
Thread.sleep(PRODUCER_DELAY_MS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
// 创建一个消费者线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
// 在队列为空时阻塞
String element = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费了一个元素,队列中元素个数:" + queue.size());
Thread.sleep(CONSUMER_DELAY_MS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
原理
ArrayBlockingQueue使用独占锁ReentrantLock实现线程安全,入队和出队操作使用同一个锁对象,也就是只能有一个线程可以进行入队或者出队操作;这也就意味着生产者和消费者无法并行操作,在高并发场景下会成为性能瓶颈。
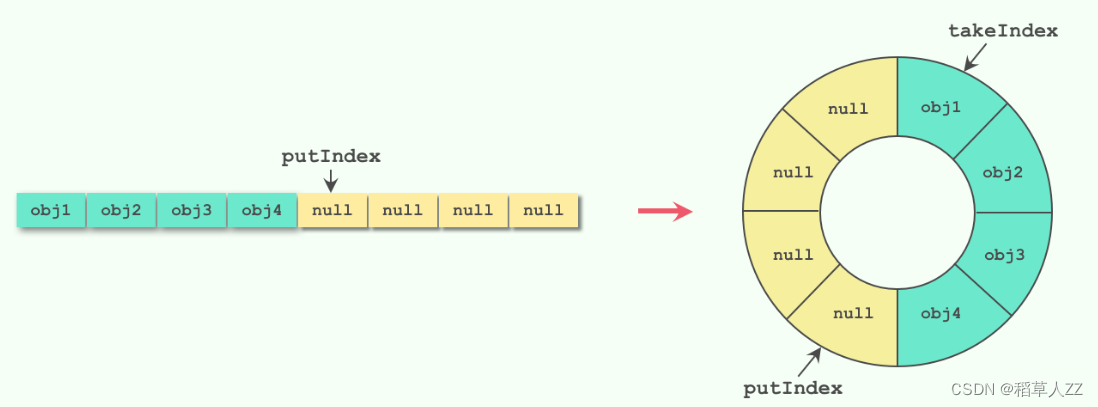
内部采用双指针对数组进行操作。使用双指针的好处在于可以避免数组的复制操作。如果使用单指针,每次删除元素时需要将后面的元素全部向前移动,这样会导致时间复杂度为 O(n)。而使用双指针,我们可以直接将 takeIndex 指向下一个元素,而不需要将其前面的元素全部向前移动。同样地,插入新的元素时,我们可以直接将新元素插入到 putIndex 所指向的位置,而不需要将其后面的元素全部向后移动。这样可以使得插入和删除的时间复杂度都是 O(1) 级别,提高了队列的性能。
构造方法
可以看到,在构建对象时,创建了一个独占锁ReentrantLock。同时,基于独占锁又创建了两个Condition,利用通知机制机进行阻塞控制。
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity and default access policy.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1}
*/
// 指定队列大小,创建非公平锁
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity and the specified access policy.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked
* on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order;
* if {@code false} the access order is unspecified.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1}
*/
// 指定队列大小,指定是否使用公平锁
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity, the specified access policy and initially containing the
* elements of the given collection,
* added in traversal order of the collection's iterator.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked
* on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order;
* if {@code false} the access order is unspecified.
* @param c the collection of elements to initially contain
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is less than
* {@code c.size()}, or less than 1.
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*/
// 指定队列大小,指定是否使用公平锁,同时添加指定元素集
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
内部常量
可以看到,有两个常量用来定义为双指针索引。
/** The queued items */
//数据元素数组
final Object[] items;
/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
//下一个待取出元素索引
int takeIndex;
/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
//下一个待添加元素索引
int putIndex;
/** Number of elements in the queue */
//元素个数
int count;
/*
* Concurrency control uses the classic two-condition algorithm
* found in any textbook.
*/
/** Main lock guarding all access */
//内部锁
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
//消费者
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
//生产者
private final Condition notFull;
入队put方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting
* for space to become available if the queue is full.
*
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 判断入队元素是否为空,为空则抛出空指针异常
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//加锁,如果线程中断抛出异常
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果元素个数等于数组长度(队列满了)
while (count == items.length)
// 等待出队后唤醒
notFull.await();
// 入队元素
enqueue(e);
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
// 将元素放到putIndex索引处
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length)
// 精髓所在--环形数组:putIndex 指针到数组尽头了,返回头部
putIndex = 0;
// 队列内元素个数加1
count++;
//notEmpty条件队列转同步队列,准备唤醒消费者线程,此时队列有数据
notEmpty.signal();
}
出队take方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//加锁,如果线程中断抛出异常
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
//如果队列为空,则消费者挂起
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
//出队
return dequeue();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//取出takeIndex位置的元素
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
//设计的精髓-- 环形数组:takeIndex 指针到数组尽头了,返回头部
takeIndex = 0;
// 队列内元素个数减1
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
//notFull条件队列转同步队列,准备唤醒生产者线程,此时队列有空位
notFull.signal();
return x;
}