【强化学习原理+项目专栏】必看系列:单智能体、多智能体算法原理+项目实战、相关技巧(调参、画图等、趣味项目实现、学术应用项目实现

专栏详细介绍:【强化学习原理+项目专栏】必看系列:单智能体、多智能体算法原理+项目实战、相关技巧(调参、画图等、趣味项目实现、学术应用项目实现
对于深度强化学习这块规划为:
- 基础单智能算法教学(gym环境为主)
- 主流多智能算法教学(gym环境为主)
- 主流算法:DDPG、DQN、TD3、SAC、PPO、RainbowDQN、QLearning、A2C等算法项目实战
- 一些趣味项目(超级玛丽、下五子棋、斗地主、各种游戏上应用)
- 单智能多智能题实战(论文复现偏业务如:无人机优化调度、电力资源调度等项目应用)
本专栏主要方便入门同学快速掌握强化学习单智能体|多智能体算法原理+项目实战。后续会持续把深度学习涉及知识原理分析给大家,让大家在项目实操的同时也能知识储备,知其然、知其所以然、知何由以知其所以然。
声明:部分项目为网络经典项目方便大家快速学习,后续会不断增添实战环节(比赛、论文、现实应用等)
-
专栏订阅(个性化选择):
-
强化学习原理+项目专栏大合集-《推荐订阅☆☆☆☆☆》
-
强化学习单智能体算法原理+项目实战《推荐订阅☆☆☆☆》
-
强化学习多智能体原理+项目实战《推荐订阅☆☆☆☆☆》
-
强化学习相关技巧(调参、画图等《推荐订阅☆☆☆》)
-
tensorflow_gym-强化学习:免费《推荐订阅☆☆☆☆》
-
强化学习从基础到进阶-案例与实践:免费《推荐订阅☆☆☆☆☆》
-
强化学习从基础到进阶-案例与实践[4.1]:深度Q网络-DQN项目实战CartPole-v0
1、定义算法
相比于Q learning,DQN本质上是为了适应更为复杂的环境,并且经过不断的改良迭代,到了Nature DQN(即Volodymyr Mnih发表的Nature论文)这里才算是基本完善。DQN主要改动的点有三个:
- 使用深度神经网络替代原来的Q表:这个很容易理解原因
- 使用了经验回放(Replay Buffer):这个好处有很多,一个是使用一堆历史数据去训练,比之前用一次就扔掉好多了,大大提高样本效率,另外一个是面试常提到的,减少样本之间的相关性,原则上获取经验跟学习阶段是分开的,原来时序的训练数据有可能是不稳定的,打乱之后再学习有助于提高训练的稳定性,跟深度学习中划分训练测试集时打乱样本是一个道理。
- 使用了两个网络:即策略网络和目标网络,每隔若干步才把每步更新的策略网络参数复制给目标网络,这样做也是为了训练的稳定,避免Q值的估计发散。想象一下,如果当前有个transition(这个Q learning中提过的,一定要记住!!!)样本导致对Q值进行了较差的过估计,如果接下来从经验回放中提取到的样本正好连续几个都这样的,很有可能导致Q值的发散(它的青春小鸟一去不回来了)。再打个比方,我们玩RPG或者闯关类游戏,有些人为了破纪录经常Save和Load,只要我出了错,我不满意我就加载之前的存档,假设不允许加载呢,就像DQN算法一样训练过程中会退不了,这时候是不是搞两个档,一个档每帧都存一下,另外一个档打了不错的结果再存,也就是若干个间隔再存一下,到最后用间隔若干步数再存的档一般都比每帧都存的档好些呢。当然你也可以再搞更多个档,也就是DQN增加多个目标网络,但是对于DQN则没有多大必要,多几个网络效果不见得会好很多。
1.1 定义模型
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
!pip uninstall -y parl
!pip install parl
import parl
from parl.algorithms import DQN
class MLP(parl.Model):
""" Linear network to solve Cartpole problem.
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of observation space.
output_dim (int): Dimension of action space.
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
hidden_dim1 = 256
hidden_dim2 = 256
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim1)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim1, hidden_dim2)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim2, output_dim)
def forward(self, state):
x = F.relu(self.fc1(state))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
1.2 定义经验回放
from collections import deque
class ReplayBuffer:
def __init__(self, capacity: int) -> None:
self.capacity = capacity
self.buffer = deque(maxlen=self.capacity)
def push(self,transitions):
'''_summary_
Args:
trainsitions (tuple): _description_
'''
self.buffer.append(transitions)
def sample(self, batch_size: int, sequential: bool = False):
if batch_size > len(self.buffer):
batch_size = len(self.buffer)
if sequential: # sequential sampling
rand = random.randint(0, len(self.buffer) - batch_size)
batch = [self.buffer[i] for i in range(rand, rand + batch_size)]
return zip(*batch)
else:
batch = random.sample(self.buffer, batch_size)
return zip(*batch)
def clear(self):
self.buffer.clear()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.buffer)
1.3 定义智能体
from random import random
import parl
import paddle
import math
import numpy as np
class DQNAgent(parl.Agent):
"""Agent of DQN.
"""
def __init__(self, algorithm, memory,cfg):
super(DQNAgent, self).__init__(algorithm)
self.n_actions = cfg['n_actions']
self.epsilon = cfg['epsilon_start']
self.sample_count = 0
self.epsilon_start = cfg['epsilon_start']
self.epsilon_end = cfg['epsilon_end']
self.epsilon_decay = cfg['epsilon_decay']
self.batch_size = cfg['batch_size']
self.global_step = 0
self.update_target_steps = 600
self.memory = memory # replay buffer
def sample_action(self, state):
self.sample_count += 1
# epsilon must decay(linear,exponential and etc.) for balancing exploration and exploitation
self.epsilon = self.epsilon_end + (self.epsilon_start - self.epsilon_end) * \
math.exp(-1. * self.sample_count / self.epsilon_decay)
if random.random() < self.epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(self.n_actions)
else:
action = self.predict_action(state)
return action
def predict_action(self, state):
state = paddle.to_tensor(state , dtype='float32')
q_values = self.alg.predict(state) # self.alg 是自带的算法
action = q_values.argmax().numpy()[0]
return action
def update(self):
"""Update model with an episode data
Args:
obs(np.float32): shape of (batch_size, obs_dim)
act(np.int32): shape of (batch_size)
reward(np.float32): shape of (batch_size)
next_obs(np.float32): shape of (batch_size, obs_dim)
terminal(np.float32): shape of (batch_size)
Returns:
loss(float)
"""
if len(self.memory) < self.batch_size: # when transitions in memory donot meet a batch, not update
return
if self.global_step % self.update_target_steps == 0:
self.alg.sync_target()
self.global_step += 1
state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, done_batch = self.memory.sample(
self.batch_size)
action_batch = np.expand_dims(action_batch, axis=-1)
reward_batch = np.expand_dims(reward_batch, axis=-1)
done_batch = np.expand_dims(done_batch, axis=-1)
state_batch = paddle.to_tensor(state_batch, dtype='float32')
action_batch = paddle.to_tensor(action_batch, dtype='int32')
reward_batch = paddle.to_tensor(reward_batch, dtype='float32')
next_state_batch = paddle.to_tensor(next_state_batch, dtype='float32')
done_batch = paddle.to_tensor(done_batch, dtype='float32')
loss = self.alg.learn(state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, done_batch)
2. 定义训练
def train(cfg, env, agent):
''' 训练
'''
print(f"开始训练!")
print(f"环境:{cfg['env_name']},算法:{cfg['algo_name']},设备:{cfg['device']}")
rewards = [] # record rewards for all episodes
steps = []
for i_ep in range(cfg["train_eps"]):
ep_reward = 0 # reward per episode
ep_step = 0
state = env.reset() # reset and obtain initial state
for _ in range(cfg['ep_max_steps']):
ep_step += 1
action = agent.sample_action(state) # sample action
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # update env and return transitions
agent.memory.push((state, action, reward,next_state, done)) # save transitions
state = next_state # update next state for env
agent.update() # update agent
ep_reward += reward #
if done:
break
steps.append(ep_step)
rewards.append(ep_reward)
if (i_ep + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(f"回合:{i_ep+1}/{cfg['train_eps']},奖励:{ep_reward:.2f},Epislon: {agent.epsilon:.3f}")
print("完成训练!")
env.close()
res_dic = {'episodes':range(len(rewards)),'rewards':rewards,'steps':steps}
return res_dic
def test(cfg, env, agent):
print("开始测试!")
print(f"环境:{cfg['env_name']},算法:{cfg['algo_name']},设备:{cfg['device']}")
rewards = [] # record rewards for all episodes
steps = []
for i_ep in range(cfg['test_eps']):
ep_reward = 0 # reward per episode
ep_step = 0
state = env.reset() # reset and obtain initial state
for _ in range(cfg['ep_max_steps']):
ep_step+=1
action = agent.predict_action(state) # predict action
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
state = next_state
ep_reward += reward
if done:
break
steps.append(ep_step)
rewards.append(ep_reward)
print(f"回合:{i_ep+1}/{cfg['test_eps']},奖励:{ep_reward:.2f}")
print("完成测试!")
env.close()
return {'episodes':range(len(rewards)),'rewards':rewards,'steps':steps}
3、定义环境
OpenAI Gym中其实集成了很多强化学习环境,足够大家学习了,但是在做强化学习的应用中免不了要自己创建环境,比如在本项目中其实不太好找到Qlearning能学出来的环境,Qlearning实在是太弱了,需要足够简单的环境才行,因此本项目写了一个环境,大家感兴趣的话可以看一下,一般环境接口最关键的部分即使reset和step。
import gym
import paddle
import numpy as np
import random
import os
from parl.algorithms import DQN
def all_seed(env,seed = 1):
''' omnipotent seed for RL, attention the position of seed function, you'd better put it just following the env create function
Args:
env (_type_):
seed (int, optional): _description_. Defaults to 1.
'''
print(f"seed = {seed}")
env.seed(seed) # env config
np.random.seed(seed)
random.seed(seed)
paddle.seed(seed)
def env_agent_config(cfg):
''' create env and agent
'''
env = gym.make(cfg['env_name'])
if cfg['seed'] !=0: # set random seed
all_seed(env,seed=cfg["seed"])
n_states = env.observation_space.shape[0] # print(hasattr(env.observation_space, 'n'))
n_actions = env.action_space.n # action dimension
print(f"n_states: {n_states}, n_actions: {n_actions}")
cfg.update({"n_states":n_states,"n_actions":n_actions}) # update to cfg paramters
model = MLP(n_states,n_actions)
algo = DQN(model, gamma=cfg['gamma'], lr=cfg['lr'])
memory = ReplayBuffer(cfg["memory_capacity"]) # replay buffer
agent = DQNAgent(algo,memory,cfg) # create agent
return env, agent
4、设置参数
到这里所有qlearning模块就算完成了,下面需要设置一些参数,方便大家“炼丹”,其中默认的是笔者已经调好的~。另外为了定义了一个画图函数,用来描述奖励的变化。
import argparse
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_args():
"""
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="hyperparameters")
parser.add_argument('--algo_name',default='DQN',type=str,help="name of algorithm")
parser.add_argument('--env_name',default='CartPole-v0',type=str,help="name of environment")
parser.add_argument('--train_eps',default=200,type=int,help="episodes of training") # 训练的回合数
parser.add_argument('--test_eps',default=20,type=int,help="episodes of testing") # 测试的回合数
parser.add_argument('--ep_max_steps',default = 100000,type=int,help="steps per episode, much larger value can simulate infinite steps")
parser.add_argument('--gamma',default=0.99,type=float,help="discounted factor") # 折扣因子
parser.add_argument('--epsilon_start',default=0.95,type=float,help="initial value of epsilon") # e-greedy策略中初始epsilon
parser.add_argument('--epsilon_end',default=0.01,type=float,help="final value of epsilon") # e-greedy策略中的终止epsilon
parser.add_argument('--epsilon_decay',default=200,type=int,help="decay rate of epsilon") # e-greedy策略中epsilon的衰减率
parser.add_argument('--memory_capacity',default=200000,type=int) # replay memory的容量
parser.add_argument('--memory_warmup_size',default=200,type=int) # replay memory的预热容量
parser.add_argument('--batch_size',default=64,type=int,help="batch size of training") # 训练时每次使用的样本数
parser.add_argument('--targe_update_fre',default=200,type=int,help="frequency of target network update") # target network更新频率
parser.add_argument('--seed',default=10,type=int,help="seed")
parser.add_argument('--lr',default=0.0001,type=float,help="learning rate")
parser.add_argument('--device',default='cpu',type=str,help="cpu or gpu")
args = parser.parse_args([])
args = {**vars(args)} # type(dict)
return args
def smooth(data, weight=0.9):
'''用于平滑曲线,类似于Tensorboard中的smooth
Args:
data (List):输入数据
weight (Float): 平滑权重,处于0-1之间,数值越高说明越平滑,一般取0.9
Returns:
smoothed (List): 平滑后的数据
'''
last = data[0] # First value in the plot (first timestep)
smoothed = list()
for point in data:
smoothed_val = last * weight + (1 - weight) * point # 计算平滑值
smoothed.append(smoothed_val)
last = smoothed_val
return smoothed
def plot_rewards(rewards,cfg,path=None,tag='train'):
sns.set()
plt.figure() # 创建一个图形实例,方便同时多画几个图
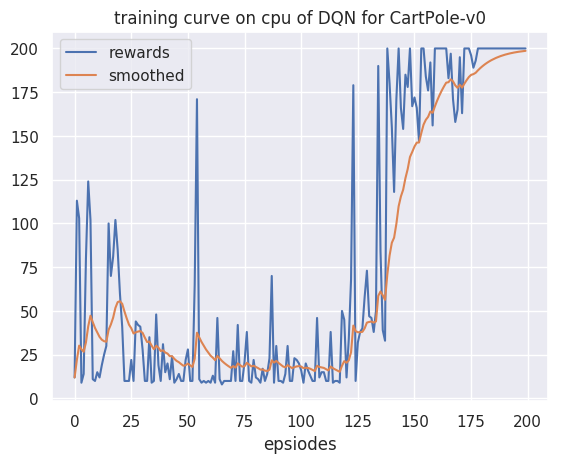
plt.title(f"{tag}ing curve on {cfg['device']} of {cfg['algo_name']} for {cfg['env_name']}")
plt.xlabel('epsiodes')
plt.plot(rewards, label='rewards')
plt.plot(smooth(rewards), label='smoothed')
plt.legend()
5、训练
# 获取参数
cfg = get_args()
# 训练
env, agent = env_agent_config(cfg)
res_dic = train(cfg, env, agent)
plot_rewards(res_dic['rewards'], cfg, tag="train")
# 测试
res_dic = test(cfg, env, agent)
plot_rewards(res_dic['rewards'], cfg, tag="test") # 画出结果
seed = 10
n_states: 4, n_actions: 2
开始训练!
环境:CartPole-v0,算法:DQN,设备:cpu
回合:10/200,奖励:10.00,Epislon: 0.062
回合:20/200,奖励:85.00,Epislon: 0.014
回合:30/200,奖励:41.00,Epislon: 0.011
回合:40/200,奖励:31.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:50/200,奖励:22.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:60/200,奖励:10.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:70/200,奖励:10.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:80/200,奖励:22.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:90/200,奖励:30.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:100/200,奖励:20.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:110/200,奖励:15.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:120/200,奖励:45.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:130/200,奖励:73.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:140/200,奖励:180.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:150/200,奖励:167.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:160/200,奖励:200.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:170/200,奖励:165.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:180/200,奖励:200.00,Epislon: 0.010
回合:190/200,奖励:200.00,Epislon: 0.010