第8章 模式匹配
-
基本概念和用法

-
模式守卫

package chapter08 object Test01_PatternMatchBase { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 1. 基本定义语法 val x = 5 val y = x match { case 1 => "one" case 2 => "two" case 3 => "three" case _ => "other" } println(y) // 2. 示例:用模式匹配实现简单的二元运算 val a = 25 val b = 13 def matchDualOp(op: String) = { op match { case "+" => a + b case "-" => a - b case "*" => a * b case "/" => a / b case "%" => a % b case _ => "非法运算符" } } println(matchDualOp("%")) println(matchDualOp("-")) println(matchDualOp("/")) println(matchDualOp("\\")) // 3. 模式守卫 // 求一个整数的绝对值 def abs(num: Int) = { num match { case i if i >= 0 => i case i if i < 0 => -i } } println(abs(19)) println(abs(-109)) } } -
模式匹配的不同用法
package chapter08 object Test02_MatchTypes { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 1. 匹配常量 def describeConst(x: Any) = { x match { case 1 => "Int one" case "hello" => "String hello" case true => "Boolean hello" case '+' => "Char +" case _ => "" // 不能省略,否则匹配不上时,报Match Error // case abc => "" // 和case _ 等价 } } println(describeConst("hello")) println(describeConst('+')) println(describeConst(0.3)) // 2. 匹配类型 println("================2. 匹配类型================") def describeType(x: Any): String = { x match { case i: Int => s"Int $i" case s: String => s"String $s" case list: List[String] => s"List String $list" case array: Array[Int] => s"Array Int ${array.mkString("---")}" case a => s"Something else ${a}" } } /** * ================2. 匹配类型================ * Int 2 * String hello * List String List(hello, world) * List String List(1, 2) * Array Int 1---2 * Something else [Ljava.lang.String;@7a0ac6e3 */ println(describeType(2)) println(describeType("hello")) println(describeType(List("hello", "world"))) println(describeType(List(1, 2))) // 由于jvm里面有泛型擦除,只能判断当前类型为List类型,里面的泛型会被擦除,可以匹配List String, println(describeType(Array(1, 2))) // array 没有泛型擦除 println(describeType(Array("hello world"))) // 3. 匹配数组 println("================3. 匹配数组================") /** * 0 * Array(1, 0) * 以0开头的数组 * 中间为1的三元素数组 * Something else * Array hello,20 */ for (arr <- List( Array(0), Array(1, 0), Array(0, 1, 0), Array(1, 1, 0), Array(2, 3, 7, 15), Array("hello", 20) )) { val result = arr match { case Array(0) => "0" case Array(1, 0) => "Array(1, 0)" // 匹配只有两个变量的Array case Array(x, y) => s"Array ${x},${y}" // 匹配两元素数组 case Array(0, _*) => s"以0开头的数组" // 匹配以0开头的数组 case Array(x, 1, z) => s"中间为1的三元素数组" // 匹配中间为1的三元素数组 case _ => "Something else" } println(result) } // 4. 匹配列表 // 方式1 println("================4. 匹配列表================") for (list <- List( List(0), List(1, 0), List(0, 1, 0), List(1, 1, 0), List(2, 3, 7, 15), List("hello", 20) )) { val result = list match { case List(0) => "0" case List(1, 0) => "List(1, 0)" case List(x, y) => s"List ${x},${y}" // 匹配两元素列表 case List(0, _*) => s"以0开头的列表" // 匹配以0开头的列表 case List(x, 1, z) => s"中间为1的三元素列表" // 匹配中间为1的三元素列表 case _ => "Something else" } println(result) } // 方式2 val list1 = List(1, 2, 5, 7, 24) val list = List(24) println(list) list match { case first :: second :: rest => println(s"first: $first, second: $second, rest:$rest") case _ => println("Something else") } // 5. 匹配元组 println("================5. 匹配元组================") /** * 0, 1 * 1, 0 * (a, 1, _)0 * (a, 1, _)0 * (x, y, z) * (x, y, z) */ for (tuple <- List( (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, 1, 0), (0, 1, 1), (1, 23, 56), ("hello", true, 0.5) )) { val result = tuple match { case (a, b) => s"${a}, ${b}" case (0, _) => "(0, _)" case (a, 1, _) => s"(a, 1, _)" + a case (x, y, z) => s"(x, y, z)" case _ => "Something else" } println(result) } // 元组匹配扩展 // 5.1 在变量声明时,匹配 /** * x: 10, y: hello * first: 23, second: 15 * first: 23, second: 15, rest: List(9, 78) */ val (x, y) = (10, "hello") println(s"x: ${x}, y: ${y}") // val List(first,second,rest) = List(23,15,9,78) // error,需要使用val fir :: sec :: rest = List(23, 15, 9, 78) val List(first, second, _*) = List(23, 15, 9, 78) println(s"first: $first, second: ${second}") val fir :: sec :: rest = List(23, 15, 9, 78) println(s"first: $fir, second: ${sec}, rest: ${rest}") // 5.1 for 推导式中进行模式匹配 val list5: List[(String, Int)] = List(("a", 23), ("b", 13), ("c", 9), ("d", 78), ("a", 13)) // 直接打印 /** * a 23 * b 13 * c 9 * d 78 * a 13 */ for (elem <- list5) { println(elem._1 + " " + elem._2) } // 将list中元素直接定义为元组,对变量赋值 /** * word: a, count: 23 * word: b, count: 13 * word: c, count: 9 * word: d, count: 78 * word: a, count: 13 */ for ((word, count) <- list5) { println(s"word: $word, count: $count") } // 可以不考虑某个位置的变量,只遍历key或者value /** * word: a * word: b * word: c * word: d * word: a * count: 23 * count: 13 * count: 9 * count: 78 * count: 13 */ for ((word, _) <- list5) { println(s"word: $word") } for ((_, count) <- list5) { println(s"count: $count") } // 可以指定某个位置的值必须是多少 /** * word: a , count: 23 * word: a , count: 13 */ for (("a", count) <- list5) { println(s"word: a , count: $count") } // 6. 匹配对象 println("================6. 匹配对象================") } } -
匹配对象
package chapter08 object Test04_MatchObject { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val student = new Student("alice", 19) // 根据对象实例的内容进行匹配 val result: String = student match { case Student("alice", 18) => "Alice 18" case _ => "Else" } println(result) } } // 定义类 class Student(val name: String, val age: Int) // 定义伴生对象 object Student { def apply(name: String, age: Int): Student = { new Student(name, age) } // 必须实现一个unapply,实现对对象属性的拆解 def unapply(student: Student): Option[(String, Int)] = { if (student == null) { None } else { Some(student.name, student.age) } } }package chapter08 object Test05_MatchCaseClass { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val student = Student1("alice", 18) // 根据对象实例的内容进行匹配 val result: String = student match { case Student1("alice", 18) => "Alice 18" case _ => "Else" } println(result) } } // 定义样例类 case class Student1(name: String, age: Int) -
偏函数
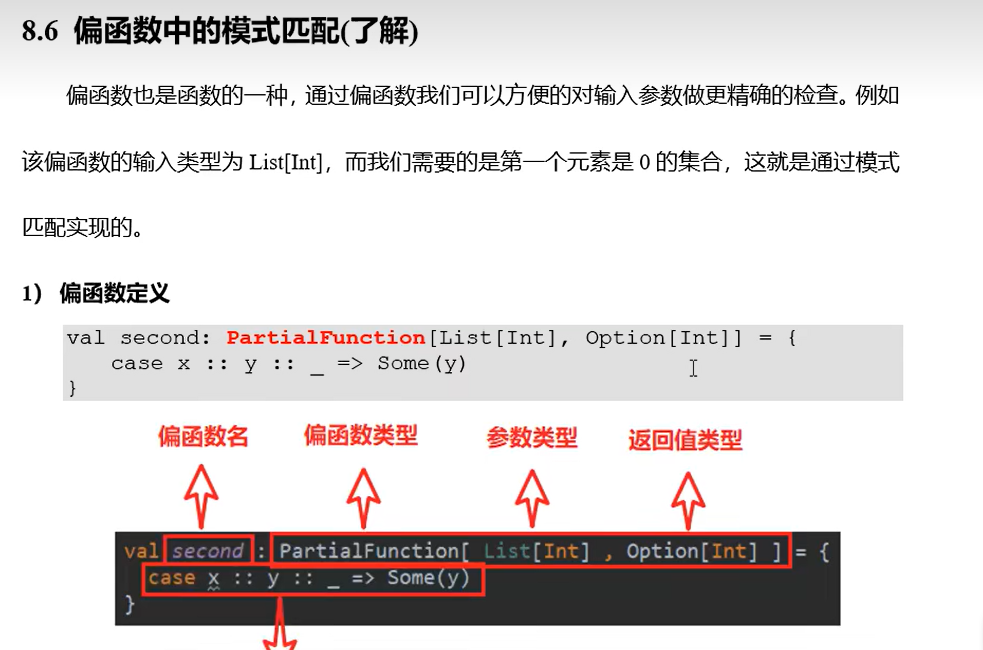
-