目录
- yolo格式转换
- 1. Visdrone2019格式转换
yolo格式转换
1. Visdrone2019格式转换
数据集下载地址https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/115729
如果是visdrone数据集,直接使用txt2xml.py去转换,修改annotation和img的路径,运行即可,运行后会在新建的xml文件夹下生成6471个xml文件,我们把xml文件转换为json,json再转成yolo
"""
该脚本用于visdrone数据处理;
将annatations文件夹中的txt标签文件转换为XML文件;
txt标签内容为:
<bbox_left>,<bbox_top>,<bbox_width>,<bbox_height>,<score>,<object_category>,<truncation>,<occlusion>
类别:
ignored regions(0), pedestrian(1),
people(2), bicycle(3), car(4), van(5),
truck(6), tricycle(7), awning-tricycle(8),
bus(9), motor(10), others(11)
"""
#visdrone转为yolo格式
import os
import cv2
import time
from xml.dom import minidom
name_dict = {'0': 'ignored regions', '1': 'pedestrian', '2': 'people',
'3': 'bicycle', '4': 'car', '5': 'van', '6': 'truck',
'7': 'tricycle', '8': 'awning-tricycle', '9': 'bus',
'10': 'motor', '11': 'others'}
def transfer_to_xml(pic, txt, file_name):
xml_save_path = 'xml' # 生成的xml文件存储的文件夹
if not os.path.exists(xml_save_path):
os.mkdir(xml_save_path)
img = cv2.imread(pic)
img_w = img.shape[1]
img_h = img.shape[0]
img_d = img.shape[2]
doc = minidom.Document()
annotation = doc.createElement("annotation")
doc.appendChild(annotation)
folder = doc.createElement('folder')
folder.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('visdrone'))
annotation.appendChild(folder)
filename = doc.createElement('filename')
filename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(file_name))
annotation.appendChild(filename)
source = doc.createElement('source')
database = doc.createElement('database')
database.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("Unknown"))
source.appendChild(database)
annotation.appendChild(source)
size = doc.createElement('size')
width = doc.createElement('width')
width.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(img_w)))
size.appendChild(width)
height = doc.createElement('height')
height.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(img_h)))
size.appendChild(height)
depth = doc.createElement('depth')
depth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(img_d)))
size.appendChild(depth)
annotation.appendChild(size)
segmented = doc.createElement('segmented')
segmented.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("0"))
annotation.appendChild(segmented)
with open(txt, 'r') as f:
lines = [f.readlines()]
for line in lines:
for boxes in line:
box = boxes.strip('\n')
box = box.split(',')
x_min = box[0]
y_min = box[1]
x_max = int(box[0]) + int(box[2])
y_max = int(box[1]) + int(box[3])
object_name = name_dict[box[5]]
# if object_name is 'ignored regions' or 'others':
# continue
object = doc.createElement('object')
nm = doc.createElement('name')
nm.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(object_name))
object.appendChild(nm)
pose = doc.createElement('pose')
pose.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("Unspecified"))
object.appendChild(pose)
truncated = doc.createElement('truncated')
truncated.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("1"))
object.appendChild(truncated)
difficult = doc.createElement('difficult')
difficult.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("0"))
object.appendChild(difficult)
bndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
xmin = doc.createElement('xmin')
xmin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(x_min))
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)
ymin = doc.createElement('ymin')
ymin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(y_min))
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)
xmax = doc.createElement('xmax')
xmax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(x_max)))
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)
ymax = doc.createElement('ymax')
ymax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(y_max)))
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)
object.appendChild(bndbox)
annotation.appendChild(object)
with open(os.path.join(xml_save_path, file_name + '.xml'), 'w') as x:
x.write(doc.toprettyxml())
x.close()
f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = time.time()
print('Transfer .txt to .xml...ing....')
txt_folder = 'E:\\YoloImg\\VisDrone2019-DET-train (1)\\VisDrone2019-DET-train\\annotations' # visdrone txt标签文件夹
txt_file = os.listdir(txt_folder)
img_folder = 'E:\\YoloImg\\VisDrone2019-DET-train (1)\\VisDrone2019-DET-train\\images' # visdrone 照片所在文件夹
count = 0
for txt in txt_file:
txt_full_path = os.path.join(txt_folder, txt)
img_full_path = os.path.join(img_folder, txt.split('.')[0] + '.jpg')
count = count + 1
print('txt to xml succeed:{}', count)
try:
transfer_to_xml(img_full_path, txt_full_path, txt.split('.')[0])
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("Transfer .txt to .XML sucessed. costed: {:.3f}s...".format(time.time() - t))
import json
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 这个文件可以把input_folder下的文件夹的xml文件全部转换成coco类型,并且输出到output_folder文件夹下
# 如果input_folder下的xml有多个类别,都可以挑出来
# 修改输入和输出文件夹的路径
input_folder = "刚刚转换好的xml文件夹的路径"
output_folder = "自己要保存的新路径"
# 列出输入文件夹中的所有文件
files = os.listdir(input_folder)
# 遍历所有文件并检查扩展名以仅处理 XML 文件
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".xml"):
# 读取原始标注 XML 文件
with open(os.path.join(input_folder, file), "r") as f:
xml_data = f.read()
# 解析 XML 数据
root = ET.fromstring(xml_data)
# 获取图像路径
# path = root.find("path").text
# 获取图像尺寸
width = int(root.find("size/width").text)
height = int(root.find("size/height").text)
if width == 0 or height == 0:
print(f"Invalid width or height in file: {file}")
continue
# 获取目标位置
objects = root.findall("object")
shapes = []
for obj in objects:
xmin = int(obj.find("bndbox/xmin").text)
#xmin = int(float(obj.find("bndbox/xmin").text))
ymin = int(obj.find("bndbox/ymin").text)
#ymin = int(float(obj.find("bndbox/ymin").text))
xmax = int(obj.find("bndbox/xmax").text)
#xmax = int(float(obj.find("bndbox/xmax").text))
ymax = int(obj.find("bndbox/ymax").text)
#ymax = int(float(obj.find("bndbox/ymax").text))
# 转换目标位置坐标为 COCO 格式
x_center = (xmin + xmax) / 2
y_center = (ymin + ymax) / 2
bbox_width = (xmax - xmin)
bbox_height = (ymax - ymin)
# 读取目标标签
label = obj.find("name").text
# 生成 COCO 格式的 JSON
shape = {
"label": label,
"points": [
[x_center - bbox_width / 2, y_center - bbox_height / 2],
[x_center + bbox_width / 2, y_center + bbox_height / 2],
],
"group_id": None,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {}
}
shapes.append(shape)
# 生成最终的 COCO 格式的 JSON 数据
coco_data = {
"version": "5.1.1",
"flags": {},
"imagePath": None,
"imageData": None,
"imageHeight": height,
"imageWidth": width,
"shapes": shapes
}
# 创建唯一的输出文件名
output_file = os.path.splitext(file)[0] + ".json"
# 将数据保存为 JSON 文件
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, output_file), "w") as f:
json.dump(coco_data, f, indent=4)
import os
import json
import random
import shutil
# json转成yolo格式,划分的时候把json和img全部放入input_dir里面
# 先用xml转json,再用json转为yolo格式
# 定义你的类别列表
classes = [
'ignored regions',
'pedestrian',
'people',
'bicycle',
'car',
'van',
'truck',
'tricycle',
'awning-tricycle',
'bus',
'motor',
'others'
] # 更新为你的类别
def convert_annotation(input_dir, output_dir, json_file):
with open(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file), 'r') as in_file:
data = json.load(in_file)
out_file = open(os.path.join(output_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.txt')), 'w')
img_width = data['imageWidth']
img_height = data['imageHeight']
for obj in data['shapes']:
cls = obj['label']
if cls not in classes:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
points = obj['points']
x_center = (points[0][0] + points[1][0]) / 2.0 / img_width
y_center = (points[0][1] + points[1][1]) / 2.0 / img_height
width = (points[1][0] - points[0][0]) / img_width
height = (points[1][1] - points[0][1]) / img_height
out_file.write(f"{cls_id} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}\n")
def convert_all(input_dir, output_dir):
json_files = [f for f in os.listdir(input_dir) if f.endswith('.json')]
random.shuffle(json_files)
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
train_output_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, 'train')
val_output_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, 'val')
train_images_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'train')
val_images_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'val')
if not os.path.exists(train_output_dir):
os.makedirs(train_output_dir)
if not os.path.exists(val_output_dir):
os.makedirs(val_output_dir)
if not os.path.exists(train_images_dir):
os.makedirs(train_images_dir)
if not os.path.exists(val_images_dir):
os.makedirs(val_images_dir)
train_split = int(len(json_files) * 0.9)
train_json_files = json_files[:train_split]
val_json_files = json_files[train_split:]
for json_file in train_json_files:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file), train_output_dir)
convert_annotation(input_dir, train_output_dir, json_file)
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.jpg'))):
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.jpg')), train_images_dir)
elif os.path.exists(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.png'))):
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.png')), train_images_dir)
for json_file in val_json_files:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file), val_output_dir)
convert_annotation(input_dir, val_output_dir, json_file)
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.jpg'))):
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.jpg')), val_images_dir)
elif os.path.exists(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.png'))):
shutil.copy(os.path.join(input_dir, json_file.replace('.json', '.png')), val_images_dir)
with open(os.path.join(output_dir, 'classes.txt'), 'w') as f:
for cls in classes:
f.write(cls + '\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_dir = 'D:\\Open-mmLab\\yolov5-master\\classify\\my_xml'
output_dir = 'D:\\Open-mmLab\\yolov5-master\\classify\\my_new_xml'
convert_all(input_dir, output_dir)
转换的时候,图片和json要在一个文件夹下,代码才会分开,不然会没有图片,完成之后就是标准的格式了,可以训练了,运行完后如下,把val和train里面json文件全部删除即可
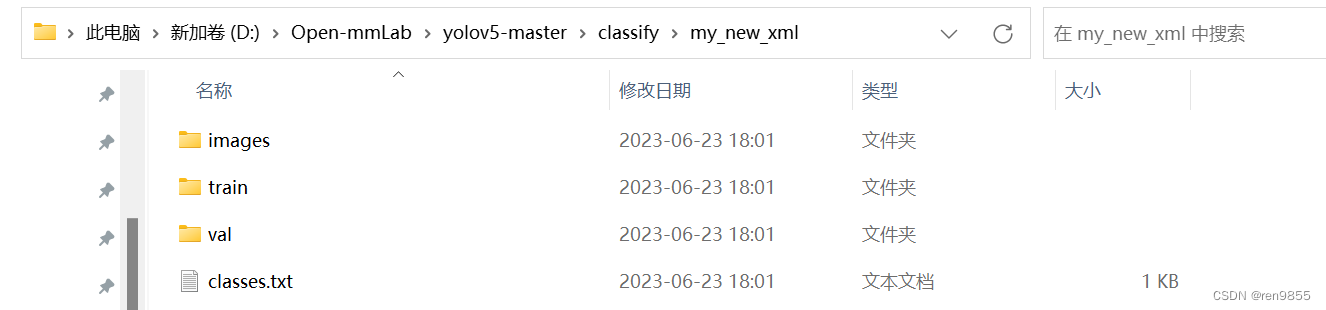
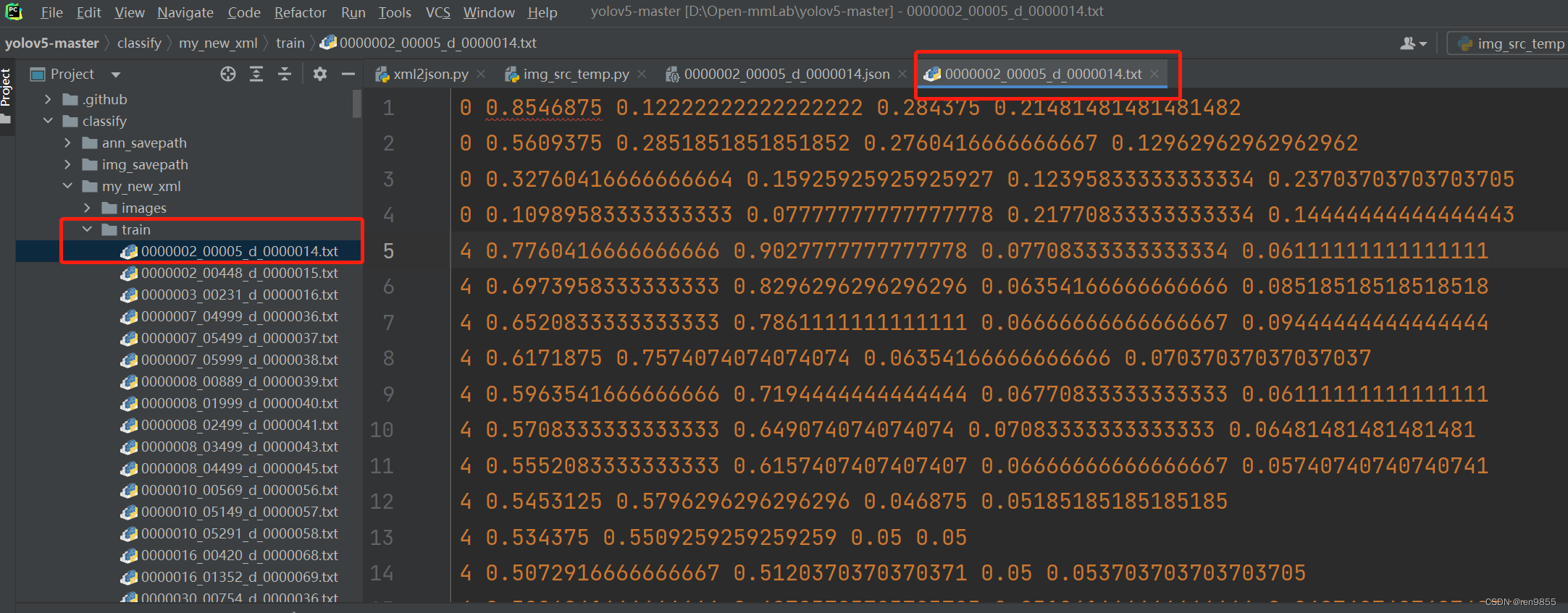

注意:json文件的imagePath路径是图片的路径
import os
import json
##这个文件是把转换后的json文件的img路径替换为自己想要的路径
# 输入、输出文件夹路径和待添加的路径
input_folder = "D:\\Open-mmLab\\yolov5-master\\classify\\my_xml"
output_folder = "D:\\Open-mmLab\\yolov5-master\\classify\\ann_savepath"
prefix = "D:\\Open-mmLab\\yolov5-master\\classify\\img_savepath\\"
# 如果输出文件夹不存在,创建它
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
# 遍历输入文件夹中的json文件
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# 判断是否为json文件
if filename.endswith(".json"):
# 读取json文件内容
input_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
with open(input_path, "r") as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 修改imagePath字段值
image_path = prefix + filename[:-5] + ".jpg" # 构造新的imagePath路径
data["imagePath"] = image_path
# 保存修改后的内容到输出文件夹
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, filename)
with open(output_path, "w") as f:
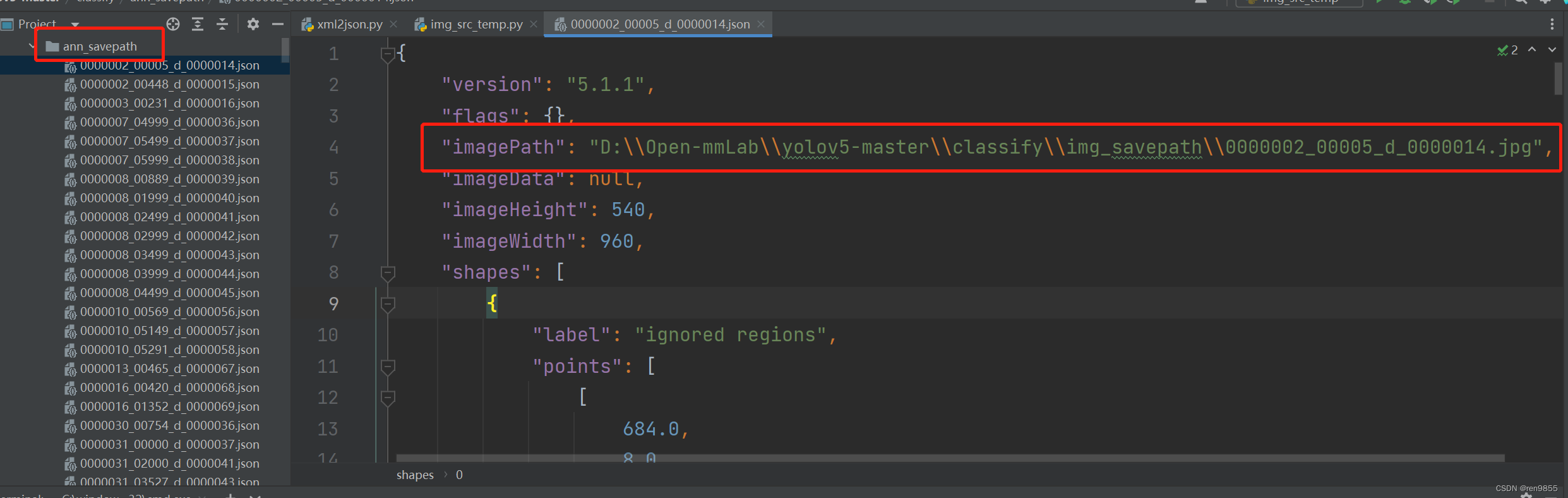
json.dump(data, f, indent=4)
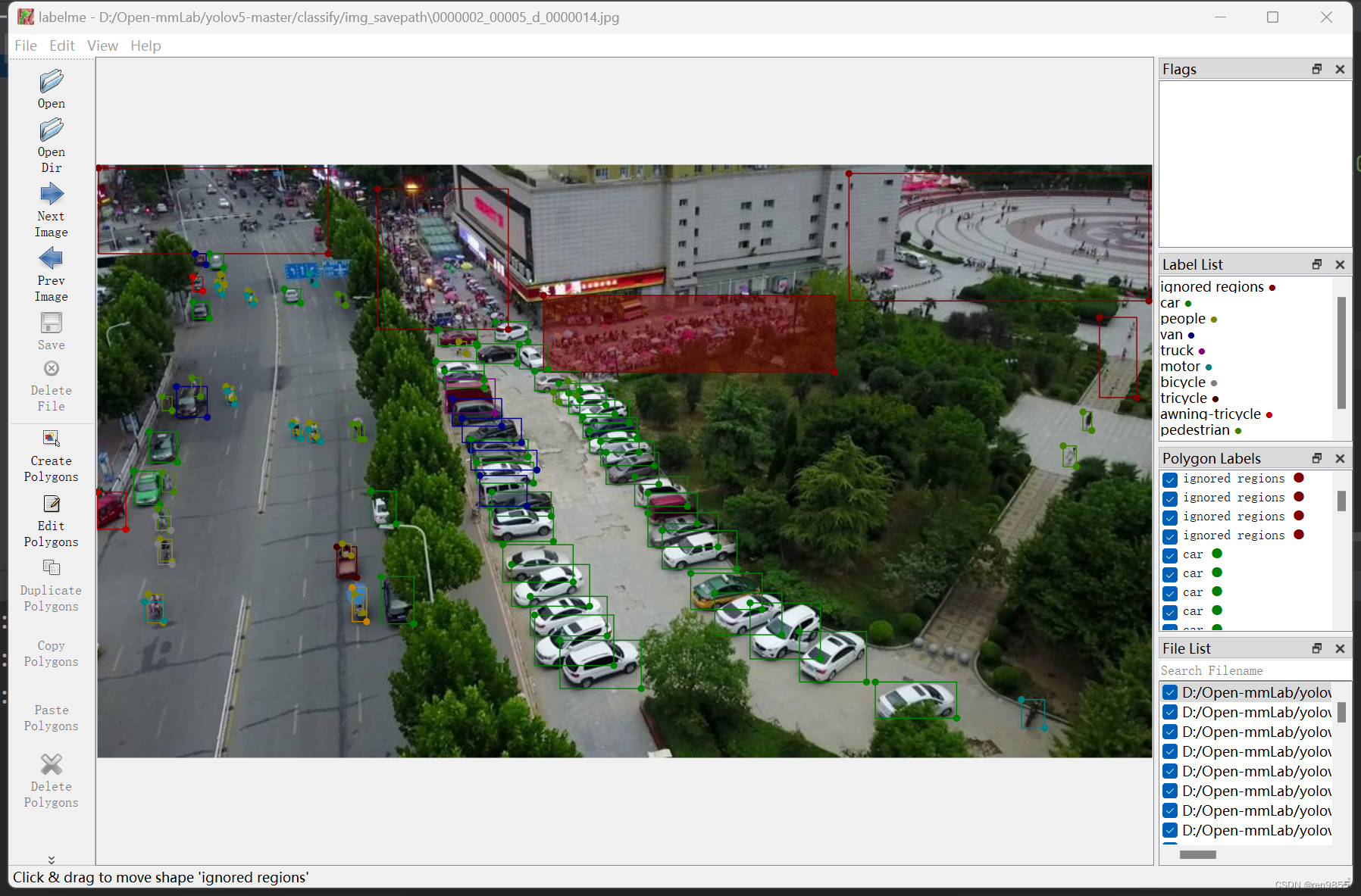
可以看到ImgPath的路径已经改变了
打开labelme
打开存放图片的文件夹
**file,change output dir **
可以看到标注已经出来了


![[BPU部署教程] 万字长文!通透解读模型部署端到端大流程——以终为始,以行为知](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/88981d2ca8354d5c9430b1f2d7dfdcf0.png)