今天端午,祝各位端午安康!
今天来说说模板匹配这个专题。
模板匹配(Template Matching)是一种图像处理技术,用于在一幅图像上查找与另一幅模板图像相同的区域。模板图像和待匹配图像的大小相同。模板匹配的目的是在待检测图像中找到与模板图像最匹配的区域。
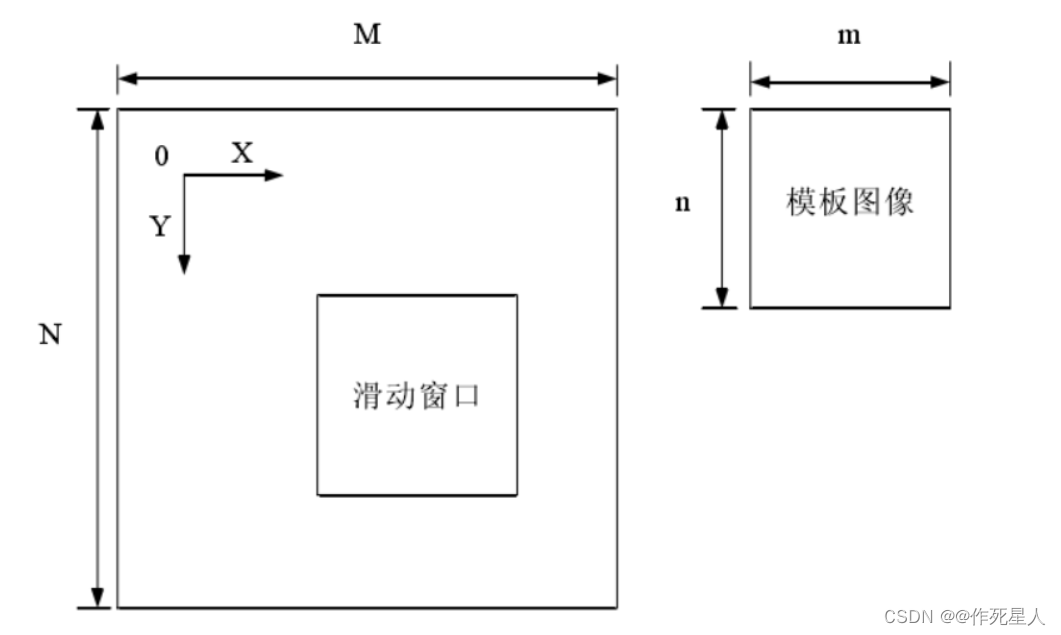
在机器视觉中,模板匹配有以下应用:
- 目标定位:模板匹配可用来定位目标在图像中的位置。这可以帮助确定目标在图像中的尺寸、形状、位置等信息。
- 目标识别:模板匹配可用于识别不同的物体、人脸或其他特征,从而实现目标识别。
- 物体跟踪:模板匹配可用于跟踪移动物体,检测目标在图像中的变化,从而实现物体跟踪。
- 光学字符识别(OCR):模板匹配可用于检测待识别的文本区域,从而实现光学字符识别。
文章目录
- 1. 均值漂移(Mean Shift):
- 2. 最大值匹配(Maximum Mean Square Error,MMSE):
- 3. 直方图匹配(Histogram Matching):
- 4. Brute Force Matching(暴力匹配):
总之,模板匹配通常用于在一个图像中定位另一个图像的区域。常见的模板匹配方法有以下几种:
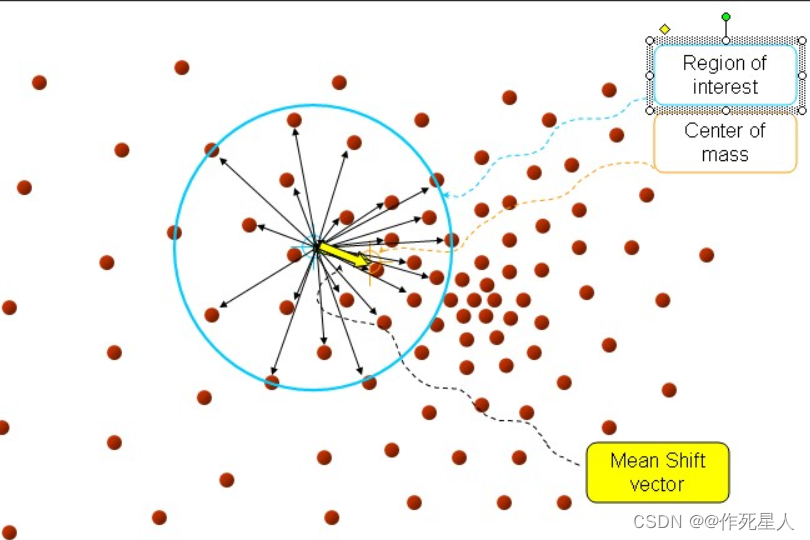
1. 均值漂移(Mean Shift):
均值漂移是一种基于局部极值的模板匹配方法。通过在搜索窗口中逐点计算梯度直方图,均值漂移会沿着梯度方向搜索,直到找到最大值。梯度直方图的峰值位置即为匹配的区域。
Python 实现:matplotlib 和 numpy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
template = np.zeros((100, 100, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 缩放模板
template = np.moveaxis(template, 1, 0)
template = np.moveaxis(template, 2, 0)
# 在图像上进行模板匹配
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = template.min(0), template.min(1), template.max(0), template.max(1)
def mean_shift(img, pattern, x, y, w, h):
"""
在img图像上进行均值漂移
:param img:
:param pattern:
:param x:
:param y:
:param w:
:param h:
:return:
"""
diff = pattern - img
diff = diff.reshape(w, h)
diff = diff.T
diff = diff[np.abs(diff).argmax(1)]
return img + diff / (w * h)
img = mean_shift(img, template, x_min, y_min, 100, 100)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
用halcon实现
dev_update_off ()
dev_close_window ()
read_image (Image, 'your_image_file')
get_image_size (Image, Width, Height)
dev_open_window_fit_image (Image, 0, 0, Width, Height, WindowHandle)
dev_set_draw ('margin')
dev_set_color ('blue')
set_display_font (WindowHandle, 16, 'mono', 'true', 'false')
MeanShift (Image, Region, 5, 'blue')
dev_display (Region)
disp_continue_message (WindowHandle, 'black', 'true')
stop ()
2. 最大值匹配(Maximum Mean Square Error,MMSE):
最大值匹配是一种在图像中查找模板的方法,它将搜索窗口划分为多个相等的区域,并在每个区域内计算模板与区域内像素的差异。当差值的平方和最小时,找到最佳匹配区域。
Python 实现:numpy
import numpy as np
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
template = np.zeros((100, 100, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 缩放模板
template = np.moveaxis(template, 1, 0)
template = np.moveaxis(template, 2, 0)
# 在图像上进行模板匹配
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = template.min(0), template.min(1), template.max(0), template.max(1)
def find_best_match(image, pattern):
"""
在图像image中找到最匹配的区域
:param image:
:param pattern:
:return:
"""
match_areas = np.zeros(image.shape[:2], dtype=np.int32)
for x_stride in range(0, image.shape[0], x_max):
for y_stride in range(0, image.shape[1], y_max):
match_area = ((x_max - x_min) * (y_max - y_min)) * (pattern == image[y_stride:y_stride + y_max, x_stride:x_stride + x_max])
match_areas[y_stride + x_stride // x_max, x_stride + y_stride // y_max] = match_area
best_match = np.argmax(match_areas)
return best_match
img = find_best_match(img, template)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
用halcon实现
dev_update_off ()
dev_close_window ()
read_image (Image, 'your_image_file')
dev_open_window_fit_image (Image, 0, 0, Width, Height, WindowHandle)
dev_set_draw ('margin')
dev_set_color ('red')
set_display_font (WindowHandle, 16, 'mono', 'true', 'false')
FindClosestPixel (Image, Region, [0 255 255], [0 255 255], 'max')
dev_display (Region)
disp_continue_message (WindowHandle, 'black', 'true')
stop ()
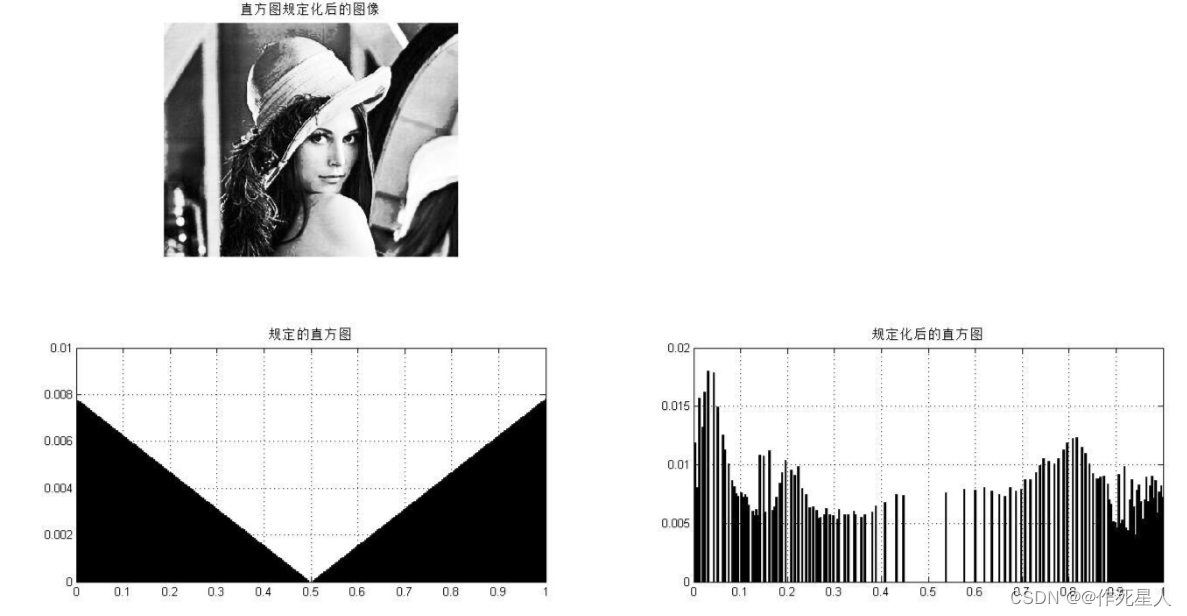
3. 直方图匹配(Histogram Matching):
直方图匹配是一种基于局部直方图的模板匹配方法。它会对搜索窗口中的像素进行局部直方图计算,并与模板的直方图进行比较。当局部直方图与模板直方图之间的相似度最大时,找到最佳匹配区域。
Python 实现:skimage
import numpy as np
from skimage import measure, draw
from skimage.morphology import expand_edges
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
template = np.zeros((100, 100, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 缩放模板
template = expand_edges(template, dim=2)
template = draw.rectangle(template, fill=0)
# 在图像上进行模板匹配
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = template.min(0), template.min(1), template.max(0), template.max(1)
def histogram_match(image, pattern):
"""
在图像image中找到最匹配的区域
:param image:
:param pattern:
:return:
"""
match_areas = np.zeros(image.shape[:2], dtype=np.int32)
for x_stride in range(0, image.shape[0], x_max):
for y_stride in range(0, image.shape[1], y_max):
match_area = ((x_max - x_min) * (y_max - y_min)) * (pattern == image[y_stride:y_stride + y_max, x_stride:x_stride + x_max])
match_areas[y_stride + x_stride // x_max, x_stride + y_stride // y_max] = match_area
best_match = np.argmax(match_areas)
return best_match
img = histogram_match(img, template)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
用halcon实现
4. Brute Force Matching(暴力匹配):
Brute Force Matching(暴力匹配)是一种简单的模板匹配方法,它通过计算模板与图像中每个像素的匹配程度来找到最佳匹配。暴力匹配的性能取决于匹配方法和图像本身的质量。

Python 实现:opencv
import cv2
# 读取图像
img = cv2.imread('input.jpg')
template = cv2.imread('template.jpg')
# 缩放模板
template = cv2.resize(template, (img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
# 在图像上进行模板匹配
matches = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
# 计算匹配度
max_val, min_val, _, _ = cv2.minMaxLoc(matches)
# 找到最佳匹配区域
min_pt = min_val * img.shape[1]
max_pt = max_val * img.shape[1]
x_min = min_pt[0]
y_min = min_pt[1]
x_max = max_pt[0]
y_max = max_pt[1]
# 在图像上显示最佳匹配区域
cv2.rectangle(img, (x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 显示最佳匹配区域
cv2.imshow('Match Results', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
在实际应用中,根据图像的复杂程度、模板的大小和匹配方法的计算复杂度,可能需要选择合适的模板匹配方法。同时,为了提高匹配的准确性和鲁棒性,可以尝试使用多种匹配方法进行多次匹配,并从中选择最佳结果。
在计算机视觉中,模板匹配通常与其他计算机视觉技术(如特征提取和图像分割)一起使用,以实现更高级别的图像分析。以下是一些常见的计算机视觉应用:
- 目标跟踪:通过模板匹配找到目标物体在连续帧中的位置。这可以用于视频监控、智能交通系统等场景。
- 3D重建:通过在图像中找到匹配的区域,可以估计物体的3D形状。这对于虚拟现实、增强现实、机器人导航等领域非常有用。
- 图像分割:将图像分割成不同的区域,以便对每个区域进行特征提取、分类等操作。模板匹配可以帮助分割出感兴趣的物体或区域。
- 面部识别:在面部识别系统中,模板匹配可以用于检测和识别面部特征。这在安全监控、智能手机解锁等场景中有广泛应用。
- 物体识别:通过在图像中找到与模板相似的区域,可以实现物体识别。这对于自动驾驶、机器人视觉等领域非常有用。
- 运动分析:模板匹配可以用于分析运动物体在视频中的运动轨迹。这对于运动分析、视频监控等领域有重要作用。
- 光学字符识别(OCR):在OCR系统中,模板匹配可以帮助检测和定位文本区域。这对于自动文档处理、手写识别等应用场景非常有用。
为了实现这些应用,模板匹配通常与其他计算机视觉技术相结合,如特征提取、图像分割、机器学习等。模板匹配可以作为一种基本的技术,用于实现更复杂的计算机视觉任务。