目录
- pandas统计分析基础
- 1. Series数据
- 2.文件读取
- csv文件
- Excel文件
- 3.DataFrame
- 连接数据库
- 读取数据库
- 存入数据库
- DataFrame的属性
- 访问DataFrame中的数据
- 【实例1】info详细信息和describe描述统计分析
- 【实例2】 排序
- 【实例3】 布尔索引,条件索引
- 【案例】修改数据
- 3.描述分析DataFrame
- 【实例】获取最大值位置
- 【实例】字符串分割,转换成列表,电影数据
pandas统计分析基础
# 设置显示的最大列、宽等参数,消掉打印不完全中间的省略号
# pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.width', 1000)#加了这一行那表格的一行就不会分段出现了
# pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 1000)
# pd.set_option('display.height', 1000)
#显示所有列
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
#显示所有行
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
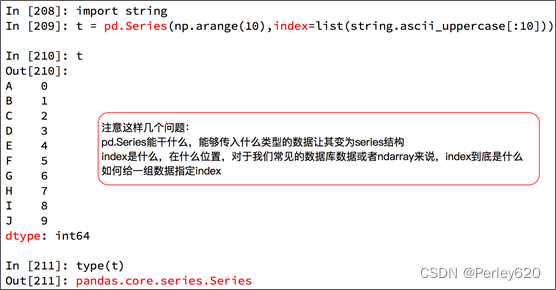
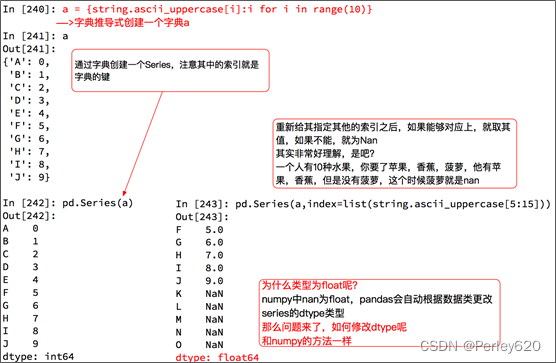
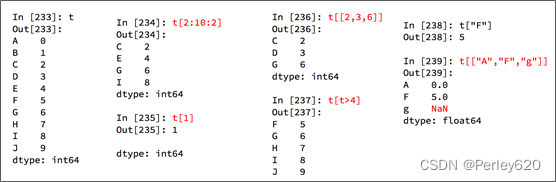
- Series 一维,带标签数组
- DataFrame 二维,Series容器
1. Series数据


2.文件读取
read_table已弃用,请改用read_csv
csv文件
CSV:Comma-Separated Value,逗号分隔值文件
显示:表格状态
源文件:换行和逗号分隔行列的格式化文本,每一行的数据表示一条记录
由于csv便于展示,读取和写入,所以很多地方也是用csv的格式存储和传输中小型的数据,为了方便教学,我们会经常操作csv格式的文件,但是操作数据库中的数据也是很容易的实现的
order=pd.read_csv('F:\python\meal_order_info.csv',sep = ',',encoding = 'gbk')
#encoding为文件编码格式,UTF-8,UTF-16,GBK,GB2312,GB18030
order.to_csv('F:\python\meal_o.csv',sep = ';',index = False)
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./dogNames2.csv")#同一目录下
print(df)
Excel文件
user = pd.read_excel('users.xlsx')## 读取user.xlsx文件
user.to_excel('F:\python\pd.xlsx')##存excel文件
import pandas as pd
userInfo = pd.read_excel('users.xlsx',sheet_name = 'users1')#文件路径直接为名字
print('客户信息表的长度为:',len(userInfo))
3.DataFrame

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)),index=list("abc"),columns=list("wxyz"))
print(df)
连接数据库
SQL问题解决:
https://www.cnblogs.com/liuzengzhi/p/11704069.html
https://blog.csdn.net/rnzhiw/article/details/84307694
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_30709809/article/details/95542057
SQL文件导入mysql中:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37887248/article/details/80897230
show databases;
use testdb;
source F:/data/meal_order_detail3.sql
show tables;
数据库产品名+连接工具名://用户名:密码@数据库IP地址:数据库端口号/数据库名称?charset=数据库数据编码
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
## 创建一个mysql连接器,用户名为root,密码为1234
## 地址为127.0.0.1,数据库名称为testdb,编码为utf-8
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:1234@127.0.0.1:\
3306/testdb?charset=utf8')
print(engine)
读取数据库
## 使用read_sql_query查看tesdb中的数据表数目
formlist = pd.read_sql_query('show tables', con = engine)
## 使用read_sql_table读取订单详情表
detail1 = pd.read_sql_table('meal_order_detail1',con = engine)
## 使用read_sql读取订单详情表
detail2 = pd.read_sql('select * from meal_order_detail2',con = engine)
detail3 = pd.read_sql('meal_order_detail3',con = engine)
存入数据库
## 使用to_sql存储orderData
detail1.to_sql('test1',con = engine,index = False,if_exists = 'replace')
DataFrame的属性

detail= pd.read_sql_table('meal_order_detail1',con = engine)
print(detail.index) #订单详情表的索引
print(detail.values) #订单详情表的所有值
print(detail.columns) #订单详情表的列名
print(detail.dtypes) #订单详情表的数据类型'\n',
print(detail.size) ## 查看元素个数
print(detail.ndim) ## 查看DataFrame的维度数
print(detail.shape) ## 查看DataFrame的形状
print(detail.T.shape) ##订单详情表转置
访问DataFrame中的数据
order_id = detail['order_id'] #访问一列数据
dishes_name5 = detail['dishes_name'][:5]#前5个元素
orderDish = detail[['order_id','dishes_name']][:5]#order_id和dishes_name前5个元素
order5 = detail[:][1:6] #1-6行元素
detail.head() #订单详情表中前五个元素
detail.tail() #订单详情表中后五个元素
【实例1】info详细信息和describe描述统计分析
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)),index=list("abc"),columns=list("wxyz"))
print(df)
d1={"name":["xiaomin","xiaohong"],"age":[12,13],"tel":[100,120]}
d2=pd.DataFrame(d1)
print(d2.info(2))
print(df.describe())
【实例2】 排序
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./dogNames2.csv")
print(df.head())
print(df.info())
#dataFrame中排序的方法
df=df.sort_values(by="Count_AnimalName",ascending=False)
print(df.head(10))
df.loc 通过标签索引行数据
df.iloc 通过位置获取行数据

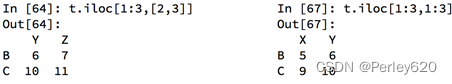
赋值更改数据的过程:

【实例3】 布尔索引,条件索引
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./dogNames2.csv")
#dataFrame中排序的方法
df=df.sort_values(by="Count_AnimalName",ascending=False)
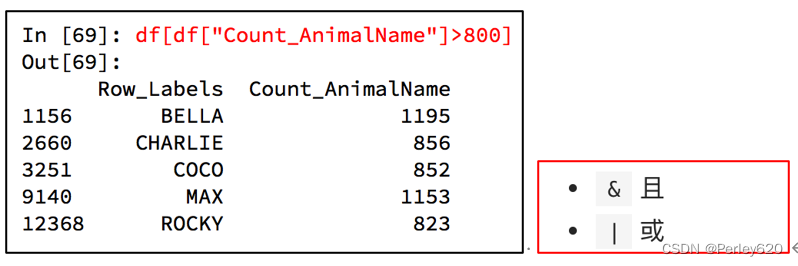
#次数超过800的狗的名字
a=df[df["Count_AnimalName"]>800]
#使用次数超过700并且名字的字符串的长度大于4的狗
b=df[(df["Row_Labels"].str.len()>4)&(df["Count_AnimalName"]>700)]
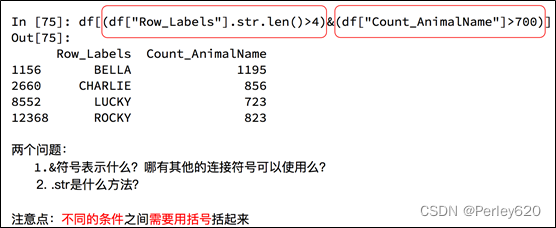
【其他】字符串常用方法,切片

#单列切片
dishes_name1 = detail.loc[:,'dishes_name']
dishes_name2 = detail.iloc[:,3]
#多列切片
orderDish1 = detail.loc[:,['order_id','dishes_name']]
orderDish2 = detail.iloc[:,[1,3]]
#花式切片
#列名为order_id和dishes_name的行名为3的数据
print(detail.loc[3,['order_id','dishes_name']])
#列名为order_id和dishes_name行名为2,3,4,5,6的数据
print(detail.loc[2:6,['order_id','dishes_name']])
#列位置为1和3行位置为3的数据
print(detail.iloc[3,[1,3]])
#列位置为1和3行位置为2,3,4,5,6的数据
print(detail.iloc[2:6,[1,3]])
#条件切片
#detail中order_id为458的dishes_name
print(detail.loc[detail['order_id']=='458',['order_id','dishes_name']])
#detail中order_id为458的第1,5列数据为
print(detail.iloc[(detail['order_id']=='458').values,[1,5]])
【案例】修改数据
#修改
##将order_id为458的,变换为45800
detail.loc[detail['order_id']=='458','order_id'] = '45800'
#增加
detail['payment'] = detail['counts']*detail['amounts'] #增加非定值
detail['pay_way'] = '现金支付' #增加定值
#删除
detail.drop(labels = 'pay_way',axis = 1,inplace = True) #删除列
detail.drop(labels = range(1,11),axis = 0,inplace = True) #删除行
3.描述分析DataFrame
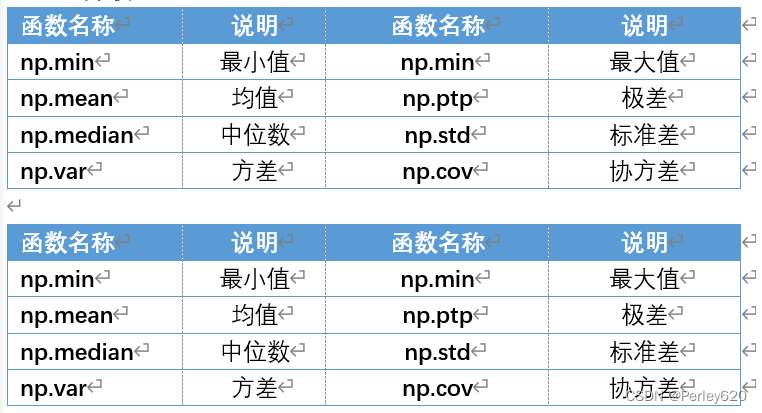

【实例】获取最大值位置
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./IMDB-Movie-Data.csv")
print(df.info())
b=df["Rating"].argmax()
#获取最大值的位置
print(b)
【实例】字符串分割,转换成列表,电影数据
按照字符串类型“/”分隔,并转换成列表

import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./IMDB-Movie-Data.csv")
print(df.info())
b=df["Rating"]
#获取平均分
rating_mean=b.mean()
#获取导演人数,字符串的处理
diector_num=len(df["Director"].unique())
diector_num2=len(set(df["Director"].tolist()))
#获取演员人数
temp_actor_list=df["Actors"].str.split(",").tolist()
#列表里的数据转换到一个数据里
actor_list1=[i for j in temp_actor_list for i in j ]
print(len(set(actor_list1)))
print(diector_num)
np.mean(detail['amounts']) #np求均值
detail['amounts'].mean() #pd求均值
detail[['counts','amounts']].describe()#描述性统计非空值数均值四分位数标准差
detail['dishes_name'].value_counts()[0:10] #频数统计结果前10
#单信息表dishes_name列转变数据类型为category类型
detail['dishes_name'] = detail['dishes_name'].astype('category')
#category类型描述统计结果,非空值数、类别数目、数目最多的类别、数目最多的类别数目
detail['dishes_name'].describe()
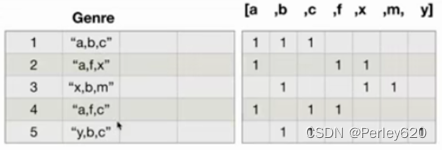
对于这一组电影数据,如果我们希望统计电影分类(genre)的情况,应该如何处理数据?
思路:
重新构造一个全为0的数组,列名为分类,如果某一条数据中分类出现过,就让0变为1
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
file_path = "./IMDB-Movie-Data.csv"
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df["Genre"].head(3))
#统计分类的列表
temp_list = df["Genre"].str.split(",").tolist() #[[],[],[]]
genre_list = list(set([i for j in temp_list for i in j]))
#构造全为0的数组
zeros_df = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0],len(genre_list))),columns=genre_list)
# print(zeros_df)
#给每个电影出现分类的位置赋值1
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
#zeros_df.loc[0,["Sci-fi","Mucical"]] = 1
zeros_df.loc[i,temp_list[i]] = 1
# print(zeros_df.head(3))
#统计每个分类的电影的数量和
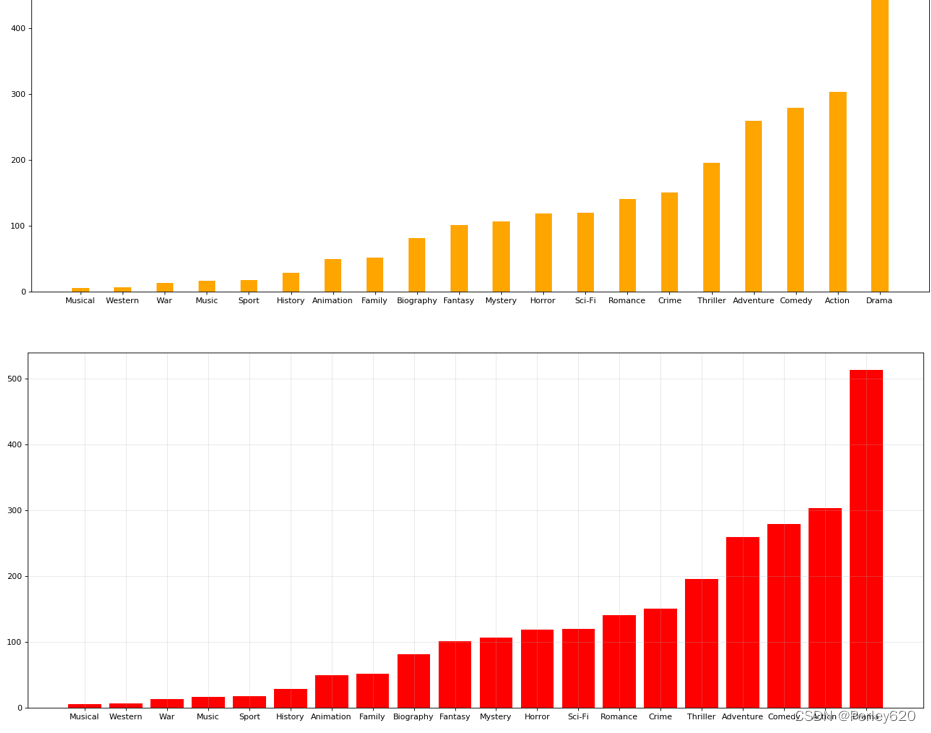
genre_count = zeros_df.sum(axis=0)
print(genre_count)
#排序
genre_count = genre_count.sort_values()
_x = genre_count.index
_y = genre_count.values
#画图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.bar(range(len(_x)),_y,width=0.4,color="orange")
plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x)
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 设置显示的最大列、宽等参数,消掉打印不完全中间的省略号
# pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.width', 1000)#加了这一行那表格的一行就不会分段出现了
# pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 1000)
# pd.set_option('display.height', 1000)
#显示所有列
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
#显示所有行
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
df=pd.read_csv("./IMDB-Movie-Data.csv")
#统计分类的列表
temp_list=df["Genre"].str.split(",").tolist()
gener_list=list(set([i for j in temp_list for i in j ]))
a=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((len(df["Genre"]),len(gener_list))),columns=gener_list)
for i in range(len(df["Genre"])):
a.loc[i,temp_list[i]]=1
genre_sum=a.sum(axis=0)
df=genre_sum.sort_values()
print(df)
a_=df.index
b_=df.values
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)#设置窗口大小
plt.bar(a_,b_,color="red")
plt.xticks(a_,rotation=0)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.show()