Win10安装:
win10下安装 RabbitMQ_柚几哥哥的博客-CSDN博客
Linux安装:
Linux下载安装 RabbitMQ_柚几哥哥的博客-CSDN博客
一、基础使用
1、导入依赖
<!--RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2、配置application.yml
spring:
#RabbitMQ
rabbitmq:
#服务器地址
host: 192.168.10.100
#用户名
username: guest
#密码
password: guest
#虚拟主机
virtual-host: /
#端口
port: 5672
listener:
simple:
#消费者最小数量
concurrency: 10
#消费者最大数量
max-concurrency: 10
#限制消费者每次只处理一条消息,处理完再继续下一条消息
prefetch: 1
#启动时是否默认启动容器,默认true
auto-startup: true
#被拒绝时重新进入队列
default-requeue-rejected: true
template:
retry:
#发布重试,默认false
enabled: true
#重试时间 默认1000ms
initial-interval: 1000
#重试最大次数,默认3次
max-attempts: 3
#重试最大间隔时间,默认10000ms
max-interval: 10000
#重试间隔的乘数。比如配2.0 第一次等10s,第二次等20s,第三次等40s
multiplier: 1.03、编写配置类RabbitMQConfig.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
@Bean
public Queue queue(){
return new Queue("queue",true);
}
}4、编写发送者MQSender.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(Object msg) {
log.info("发送消息:"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("queue", msg);
}
}5、编写接收者MQReceiver.java
/**
* @author zyw
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue")
public void receive(Object msg) {
log.info("接受消息:" + msg);
}
}6、编写测试接口UserController.java
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq")
@ResponseBody
public void mq() {
mqSender.send("Hello");
}7、结果

二、RabbitMQ交换机
Fanout模式
不处理路由键,只需要简单的将队里绑定到交换机上
发送到交换机的消息都会被转发到与该交换机绑定的所有队列上
Fanout
交换机转发消息是最快的
1、RabbitMQConfig.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
private static final String QUEUE01 = "queue_fanout01";
private static final String QUEUE02 = "queue_fanout02";
private static final String EXCHANGE = "fanoutExchange";
@Bean
public Queue queue01(){
return new Queue(QUEUE01);
}
@Bean
public Queue queue02(){
return new Queue(QUEUE02);
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange(EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding01(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue01()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding binding02(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue02()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}2、MQSender.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(Object msg) {
log.info("发送消息:"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","",msg);
}
}3、MQReceiver.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_fanout01")
public void receive01(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE01接受消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_fanout02")
public void receive02(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE02接受消息:" + msg);
}
}4、UserController.java
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/fanout")
@ResponseBody
public void mq() {
mqSender.send("Hello");
}5、测试
调用 mq/direct01 接口,消息经由交换机转发到绑定该交换机的所有队列

Direct模式
所有发送到
Direct Exchange
的消息被转发到
RouteKey
中指定的
Queue
注意:
Direct
模式可以使用
RabbitMQ
自带的
Exchange
:
default Exchange,
所以不需要将
Exchange
进行任何绑定
(binding)
操作,消息传递时,
RouteKey
必须完全匹配才会被队列接收,否
则该消息会被抛弃。
重点:
routing key
与队列
queues
的
key
保持一致,即可以路由到对应的
queue
中。
1、RabbitMQConfig.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
private static final String QUEUE01 = "queue_direct01";
private static final String QUEUE02 = "queue_direct02";
private static final String EXCHANGE = "directExchange";
private static final String ROUTINGKEY01 = "queue.red";
private static final String ROUTINGKEY02 = "queue.green";
@Bean
public Queue queue01(){
return new Queue(QUEUE01);
}
@Bean
public Queue queue02(){
return new Queue(QUEUE02);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange(EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding01(){
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue01()).to(directExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY01);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding02(){
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue02()).to(directExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY02);
}
}2、MQSender.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send01(Object msg) {
log.info("发送red消息:"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","queue.red",msg);
}
public void send02(Object msg) {
log.info("发送green消息:"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","queue.green",msg);
}
}3、MQReceiver.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_direct01")
public void receive01(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE01接受消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_direct02")
public void receive02(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE02接受消息:" + msg);
}
}4、UserController.java
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/direct01")
@ResponseBody
public void mq01() {
mqSender.send01("Hello,Red");
}
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/direct02")
@ResponseBody
public void mq02() {
mqSender.send02("Hello,Green");
}5、测试
调用
mq/direct01
接口,消息经由交换机绑定的
queue.red
RoutingKey
转发到
queue_direct01
队
列

调用
mq/direct02
接口,消息经由交换机绑定的
queue.green
RoutingKey
转发到
queue_direct02
队列

Topic模式
所有发送到
Topic Exchange
的消息被转发到所有管线
RouteKey
中指定
Topic
的
Queue
上
Exchange
将
RouteKey
和某
Topic
进行模糊匹配
,
此时队列需要绑定一个
Topic
对于
routing key
匹配模式定义规则举例如下
:
routing key
为一个句点号
.
分隔的字符串(我们将被句点号
.
分隔开的每一段独立的字符串称为
一个单词),如
“stock.usd.nyse”
、
“nyse.vmw”
、
“quick.orange.rabbit”
routing key
中可以存在两种特殊字符
*
与
#
,用于做模糊匹配,其中
*
用于匹配一个单词,
#
用
于匹配多个单词(可以是零个)
1、RabbitMQConfig.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
private static final String QUEUE01 = "queue_topic01";
private static final String QUEUE02 = "queue_topic02";
private static final String EXCHANGE = "topicExchange";
private static final String ROUTINGKEY01 = "#.queue.#";
private static final String ROUTINGKEY02 = "*.queue.#";
@Bean
public Queue queue01(){
return new Queue(QUEUE01);
}
@Bean
public Queue queue02(){
return new Queue(QUEUE02);
}
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding01(){
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue01()).to(topicExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY01);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding02(){
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue02()).to(topicExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY02);
}
}2、MQSender.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send01(Object msg) {
log.info("发送消息(被01队列接受):"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","queue.red.message",msg);
}
public void send02(Object msg) {
log.info("发送消息(被两个queue接受):"+msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","message.queue.green.abc",msg);
}
}3、MQReceiver.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_topic01")
public void receive01(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE01接受消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_topic02")
public void receive02(Object msg) {
log.info("QUEUE02接受消息:" + msg);
}
}4、UserController.java
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/topic01")
@ResponseBody
public void mq01() {
mqSender.send01("Hello,Red");
}
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/topic02")
@ResponseBody
public void mq02() {
mqSender.send02("Hello,Green");
}5、测试
调用 mq/topic01 接口,消息经由交换机绑定的 #.queue.# RoutingKey 转发到 queue_topic01 队列
调用
mq/topic02
接口,消息经由交换机绑定的
*.queue.#
和
#.queue.#
RoutingKey
转发到
queue_topic01
和
queue_topic02
队列

Headers模式
不依赖
routingkey
,使用发送消息时
basicProperties
对象中的
headers
匹配队列
headers
是一个键值对类型,键值对的值可以是任何类型
在队列绑定交换机时用
x-match
来指定,
all
代表定义的多个键值对都要满足,
any
则代表只要满足
一个可以了
1、RabbitMQConfig.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.HeadersExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
private static final String QUEUE01 = "queue_header01";
private static final String QUEUE02 = "queue_header02";
private static final String EXCHANGE = "headersExchange";
@Bean
public Queue queue01(){
return new Queue(QUEUE01);
}
@Bean
public Queue queue02(){
return new Queue(QUEUE02);
}
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersExchange(){
return new HeadersExchange(EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding01(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("color","red");
map.put("speed","low");
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue01()).to(headersExchange()).whereAny(map).match();
}
@Bean
public Binding binding02(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("color","red");
map.put("speed","fast");
return
BindingBuilder.bind(queue02()).to(headersExchange()).whereAll(map).match();
}
}2、MQSender.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send01(String msg) {
log.info("发送消息(被两个queue接受):" + msg);
MessageProperties properties = new MessageProperties();
properties.setHeader("color", "red");
properties.setHeader("speed", "fast");
Message message = new Message(msg.getBytes(), properties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("headersExchange", "", message);
}
public void send02(String msg) {
log.info("发送消息(被01队列接受):" + msg);
MessageProperties properties = new MessageProperties();
properties.setHeader("color", "red");
properties.setHeader("speed", "normal");
Message message = new Message(msg.getBytes(), properties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("headersExchange", "", message);
}
}3、MQReceiver.java
package com.xxxx.seckill.rabbitmq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhoubin
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_header01")
public void receive01(Message message) {
log.info("QUEUE01接受Message对象:" + message);
log.info("QUEUE01接受消息:" + new String(message.getBody()));
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_header02")
public void receive02(Message message) {
log.info("QUEUE02接受Message对象:" + message);
log.info("QUEUE02接受消息:" + new String(message.getBody()));
}
}4、UserController.java
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/header01")
@ResponseBody
public void mq01() {
mqSender.send01("Hello,header01");
}
/**
* 测试发送RabbitMQ消息
*/
@RequestMapping("/mq/header02")
@ResponseBody
public void mq02() {
mqSender.send02("Hello,header02");
}5、测试
queue_header01
设置
x-match
为
any
,
queue_header02
设置
x-match
为
all
。因此调用
mq/header01
接口,可以匹配两个队列
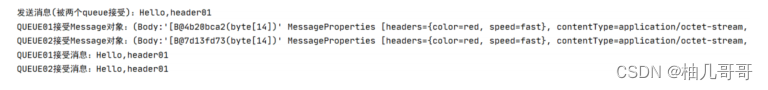
调用
mq/header02
接口,只能匹配
queue_header01
队列







![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计日常办公管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9aa1ede28d7e472cab8d2841c1b45ffe.png)