1、查看运行中的容器:docker ps

2、进入容器:docker exec -it my_rstudio /bin/bash
![]()
3、安装工具:apt-get install

4、查看权限配置文件:cat /etc/sudo
![]()
5、查看确认用户(rstudio):cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f1
root: 系统管理员用户,拥有最高权限,可以执行任何操作。
daemon: 系统守护进程用户,用于后台运行的系统服务。
bin: 系统基本命令的拥有者,这些命令通常用于系统启动和维护。
sys: 系统拥有者,用于执行系统级任务。
sync: 同步用户,用于将文件系统缓存中的数据同步到磁盘中。
games: 用于游戏程序的运行。
man: 用于查看系统帮助文档。
lp: 打印用户,用于打印操作。
mail: 邮件用户,用于邮件传输和处理。
news: 新闻用户,用于新闻组传输和处理。
uucp: Unix to Unix Copy 用户,用于远程文件传输。
proxy: 代理用户,用于网络代理服务。
www-data: Web 服务器用户,用于运行 Web 服务器。
backup: 备份用户,用于执行系统备份任务。
list: 系统邮件列表用户。
irc: Internet Relay Chat(IRC)用户,用于聊天服务。
gnats: GNU bug跟踪系统用户。
nobody: 匿名用户,用于执行无特权的任务。
_apt: apt 软件包管理系统用户。
rstudio-server: RStudio Server 用户,用于运行 RStudio 服务器。
rstudio: RStudio 用户,用于登录和运行 RStudio。5:修改权限,添加用户:vi /etc/sudoers
增加:rstudio ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root.
#
# Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of
# directly modifying this file.
#
# See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file.
#
Defaults env_reset
Defaults mail_badpass
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
Defaults use_pty
# This preserves proxy settings from user environments of root
# equivalent users (group sudo)
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "http_proxy https_proxy ftp_proxy all_proxy no_proxy"
# This allows running arbitrary commands, but so does ALL, and it means
# different sudoers have their choice of editor respected.
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "EDITOR"
# Completely harmless preservation of a user preference.
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "GREP_COLOR"
# While you shouldn't normally run git as root, you need to with etckeeper
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "GIT_AUTHOR_* GIT_COMMITTER_*"
# Per-user preferences; root won't have sensible values for them.
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "EMAIL DEBEMAIL DEBFULLNAME"
# "sudo scp" or "sudo rsync" should be able to use your SSH agent.
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "SSH_AGENT_PID SSH_AUTH_SOCK"
# Ditto for GPG agent
#Defaults:%sudo env_keep += "GPG_AGENT_INFO"
# Host alias specification
# User alias specification
# Cmnd alias specification
# User privilege specification
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
rstudio ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# Members of the admin group may gain root privileges
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# See sudoers(5) for more information on "@include" directives:
@includedir /etc/sudoers.d这是 /etc/sudoers 文件的示例内容。该文件用于配置 sudo 命令的访问权限。下面是对该文件内容的解释:
Defaults行定义了一些默认设置,例如重置环境变量、发送邮件通知等。Defaults secure_path定义了sudo命令可以搜索执行程序的路径。root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL表示超级用户root具有在任何主机、以任何用户身份执行任何命令的权限。rstudio ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL表示用户rstudio具有在任何主机、以任何用户身份执行任何命令的权限。%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL表示admin用户组的成员可以获得完全的root权限。%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL表示sudo用户组的成员可以以任何用户身份在任何主机上执行任何命令。
此外,文件的最后一行 @includedir /etc/sudoers.d 表示可以在 /etc/sudoers.d 目录中包含其他文件来进行进一步的权限配置。这种做法可以将不同权限的配置分开,便于管理。
请注意,根据注释提示,应该使用 visudo 命令来编辑 /etc/sudoers 文件,而不是直接修改它。这样可以确保语法正确,并避免意外破坏系统。
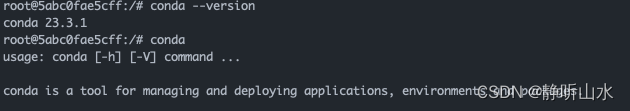
6、下载miniconda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-aarch64.sh
![]()
7、指定目录安装:/opt/conda
sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-aarch64.sh -b -p /opt/conda
8、添加conda到系统的环境变量中
编辑/etc/profile文件,并在文件末尾添加行:export PATH="/opt/conda/bin:$PATH"
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shell (sh(1))
# and Bourne compatible shells (bash(1), ksh(1), ash(1), ...).
if [ "${PS1-}" ]; then
if [ "${BASH-}" ] && [ "$BASH" != "/bin/sh" ]; then
# The file bash.bashrc already sets the default PS1.
# PS1='\h:\w\$ '
if [ -f /etc/bash.bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bash.bashrc
fi
else
if [ "$(id -u)" -eq 0 ]; then
PS1='# '
else
PS1='$ '
fi
fi
fi
if [ -d /etc/profile.d ]; then
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r $i ]; then
. $i
fi
done
unset i
fi
export PATH="/opt/conda/bin:$PATH"运行命令以使更改生效:source /etc/profile