文章目录
- 前提条件
- 一、常用查询
- 1. SELECT(显示查询)
- 2. DISTINCT(不重复查询)
- 3. WHERE(有条件查询)
- 4. AND/OR(且/或)
- 5. IN (显示已知值的字段)
- 6. BETWEEN(显示两个值范围内的字段)
- 7. 通配符的使用
- LIKE (匹配关键字查询)
- 8. ORDER BY (按关键字排序)
- 二、常用函数
- 1. 数学函数
- 2. 聚合函数
- 3. 字符串函数
- 三、查询与函数
- 1. GROUP BY(汇总分组)
- 2. HAVING (过滤返回值)
- 3. 别名(字段别名 表格别名)
- 4. 子查询
- 5. EXISTS(类查询)
- 总结
- 1. sql 语句中 HAVING 的用法
前提条件
location表格创建
use class;
create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20));
insert into location values('East','Boston');
insert into location values('East','New York');
insert into location values('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values('West','Houston');
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-M8A30HhZ-1687255797624)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620140331268.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/29b744a89e4745b7b2c31f9e94010eb8.png#pic_center)
store_info表格创建
create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05');
insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08');
insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-76Uc2W4D-1687255797625)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620140459620.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/402fdd144c2642ee9eacc3893a2a8ef2.png#pic_center)
一、常用查询
1. SELECT(显示查询)
显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名";
例如
select Store_name from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-swNPEhYH-1687255797625)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620140533955.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6634b8a2818a41559a1430a5d91230bd.png#pic_center)
2. DISTINCT(不重复查询)
不显示重复的数据记录
SELECT DISTINCT "字段" FROM "表名";
例如
select distinct Store_Name from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TB8ttezc-1687255797626)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620140550840.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4d16d464c43b4022a83791cdc1add083.png#pic_center)
3. WHERE(有条件查询)
按照条件进行查询
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "条件";
例如
select distinct Store_Name from store_info where Sales > 1000;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MDvqQTZW-1687255797626)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141321876.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8bf8e25d43e54f7e9248fb401c9e8b6c.png#pic_center)
4. AND/OR(且/或)
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "条件1" {[AND|OR] "条件2"} + ;
例如
select Store_Name from store_info where Sales > 1000 OR ( Sales < 500 and Sales > 200 );
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-61Kt25MA-1687255797627)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141404552.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b9ea8b250e1941028308ef36a139da24.png#pic_center)
5. IN (显示已知值的字段)
在已知的字段数据取值范围内取值
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" IN ('值1', '值2', ...);
例如
select * from store_info where Store_Name in ('Los Angeles', 'Houston');
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2JnfgOtj-1687255797627)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141429181.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1080613594564477b9cf5b2c4ffbce9c.png#pic_center)
6. BETWEEN(显示两个值范围内的字段)
在两个字段数据值之间取值,包含两边字段的数据
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" BETWEEN '值1' AND '值2';
例如
select * from store_info where Date between '2020-12-06' and '2020-12-10';
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-iOdqgdiw-1687255797628)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141538394.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b4770cf0a44f4cbf8ac48393cd4f38dc.png#pic_center)
7. 通配符的使用
通常通配符都是与like配合使用的
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符
'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
LIKE (匹配关键字查询)
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" LIKE {模式};
例如
select * from store_info where Store_Name like '%os%';
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-nqItwmTs-1687255797628)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141620857.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fe241bb4536a4e5598c31ae0605ccd3d.png#pic_center)
8. ORDER BY (按关键字排序)
SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" [WHERE “条件”] ORDER BY "字段" [ASC, DESC];
#ASC 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#DESC 是按降序方式进行排序。
例如
select Store_Name,Sales,Date from store_info order by Sales DESC;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AnAOrwut-1687255797628)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141645511.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e90ec8bbb00041559c9f4bfd78b51da9.png#pic_center)
二、常用函数
1. 数学函数
| 关键字 | 含义 |
|---|---|
abs(x) | 返回 x 的绝对值 |
rand() | 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 |
mod(x,y) | 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数 |
power(x,y) | 返回 x 的 y 次方 |
round(x) | 返回离 x 最近的整数 |
round(x,y) | 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值 |
sqrt(x) | 返回 x 的平方根 |
truncate(x,y) | 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 |
ceil(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
floor(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
greatest(x1,x2...) | 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值 |
least(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值 |
select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89);
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6cesclfZ-1687255797629)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141747900.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d4138f2fa1134ed69e3b42b4179b7ab0.png#pic_center)
select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-V04tfNVS-1687255797629)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620141808995.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/01c1cff42d6a43f8984d2aa24ec27bfb.png#pic_center)
#求一组数据最大值
create table t1 (id1 int, id2 int, id3 int, id4 int);
insert into t1 values (10, 50, 30, 20);
select * from t1;
select greatest(id1,id2,id3,id4) from t1;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9m8oGZmf-1687255797630)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620142853498.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a6ca65f379884c7592404a1e94eb1633.png#pic_center)
#求1000以内的随机整数
select round(rand() * 1000);
select truncate(rand() * 1000,0);
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dcxEJv40-1687255797630)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620142922318.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/88a5785d22ce486e830318300b9f24f8.png#pic_center)
2. 聚合函数
| 关键字 | 含义 |
|---|---|
avg() | 返回指定列的平均值 |
count() | 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数 |
min() | 返回指定列的最小值 |
max() | 返回指定列的最大值 |
sum(x) | 返回指定列的所有值之和 |
#求平均值
select avg(Sales) from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aft7VI8S-1687255797630)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620142952378.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d88c9847e69d408ca869c7f93ada16d0.png#pic_center)
#求表中城市数量
select count(Store_Name) from store_info where Store_Name is NOT NULL;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uV07qn1a-1687255797631)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143001063.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c664d1ce247149a0bfbfdc87105fbe43.png#pic_center)
#统计数量,进行去重
select count(DISTINCT Store_Name) from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uQFEyunh-1687255797631)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143007782.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3c46fefb94574d9f8594f7aaa9d65840.png#pic_center)
#统计字段中最大值
select max(Sales) from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ooZPNcCv-1687255797631)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143050512.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5a93ad9a32b740879ea38ba361581ad7.png#pic_center)
#统计字段中最小值
select min(Sales) from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-enURmoPY-1687255797631)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143058997.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4cda6a1602bc40a49641be58483c6240.png#pic_center)
#统计字段中的总和
select sum(Sales) from store_info;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Q5rRmw9P-1687255797632)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143104492.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a0b83447f04f42c5a3290b1ced4d138f.png#pic_center)
3. 字符串函数
| 关键字 | 含义 |
|---|---|
trim() | 返回去除指定格式的值 |
concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
substr(x,y) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 |
substr(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串 |
length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
replace(x,y,z) | 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
#输出指定一个字段中某一部分
#命令行
i='123456789'
echo ${i:3:4}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jLr7i60P-1687255797632)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620145401175.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d06f0dc49fc94fc59da36359568f5d79.png#pic_center)
#字段替换
#命令行操作
i='123456789'
echo $i | tr '456' 'abc'
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6lMes6ye-1687255797632)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620145306764.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/365c375944944dc683dd38ca26022bfa.png#pic_center)
#大小写字母替换
#命令行操作
echo abc123xyz | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EfDv9jRu-1687255797633)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620145349286.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/670ea0226064475ebf7271bdd4b5ac2e.png#pic_center)
#字段拼接
select concat(Region, Store_Name) from location where Store_Name = 'Boston';
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-n4yj5WC3-1687255797633)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143346203.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/87e24150fe694206b48de7c82b75f52e.png#pic_center)
#如sql_mode开启开启了PIPES_AS_CONCAT,"||"视为字符串的连接操作符而非或运算符,
#和字符串的拼接函数Concat相类似,这和Oracle数据库使用方法一样的
select Region || ' ' || Store_Name from location where Store_Name = 'Boston';
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-izpkQijY-1687255797634)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143450953.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/74b762ad7387430a99c9c4810130085b.png#pic_center)
select substr(Store_Name,5) from location where Store_Name = 'Los Angeles';
select substr(Store_Name,3,4) from location where Store_Name = 'New York';
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CMzpF4bD-1687255797634)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143659443.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/130d559285cd4c31bc0ff7c369f44391.png#pic_center)
SELECT TRIM ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] FROM ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 LEADING (起头), TRAILING (结尾), BOTH (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
例如
select trim(leading 'New ' from 'New York');
select trim(leading 'Los' from (select store_name from location where store_name = 'Los Angeles'));
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9xevhfWr-1687255797634)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144436274.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b8c0ab047e5f4103abc75b1ec27b8535.png#pic_center)
select replace(Region, 'ast', 'astern')from location;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-cHBnmPll-1687255797635)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620143841232.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/02c74584687740c9a2fe4f398eca7277.png#pic_center)
三、查询与函数
1. GROUP BY(汇总分组)
对GROUP BY后面的栏位的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的。
GROUP BY有一个原则,就是 SELECT 后面的所有列中,没有使用聚合函数的列,必须出现在GROUP BY后面。
SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表名" GROUP BY "字段1";
例如
#对分组的总和进行降序排序
select Store_Name,sum(Sales) from store_info group by Store_Name order by sales desc;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QgzP10x4-1687255797635)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144452549.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d2c613673c754373b42a6adab49e6bc6.png#pic_center)
2. HAVING (过滤返回值)
用来过滤由 GROUP BY 语句返回的记录集,通常与 GROUP BY 语句联合使用。
HAVING 语句的存在弥补了 WHERE 关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表格名" GROUP BY "字段1" HAVING (函数条件);
例如
select Store_Name, SUM(Sales) from store_info group by Store_Name having SUM(Sales) > 1500;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-laBozDPj-1687255797636)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144613694.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4e297ebbee7c47cc814fb9e3ada32910.png#pic_center)
3. 别名(字段别名 表格别名)
SELECT "表格別名"."字段1" [AS] "字段別名" FROM "表格名" [AS] "表格別名";
例如
select A.Store_Name Store, SUM(A.Sales) "Total Sales" from store_info A group by A.Store_Name;
select Store_Name,sum(Sales) as "Total Sales" from store_info group by Store_Name;
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yQefuTDH-1687255797636)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144639200.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cac6031836744d20a41bf13ed37f18cf.png#pic_center)
4. 子查询
连接表格,在WHERE 子句或 HAVING 子句中插入另一个 SQL 语句
SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE "字段2" [比较运算符] #外查询
(SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件"); #内查询
#内查询优先级高于外查询
#可以是符号的运算符,例如 =、>、<、>=、<= ;也可以是文字的运算符,例如 LIKE、IN、BETWEEN
例如
#查询两个表交集的城市
select * from location where store_name in (select store_name from store_info);
#查询在location表中西部城市的销售总和
select sum(sales) from store_info where store_name in (select store_name from location where region = 'West');
#通过多表查询,查询两个表中有交集的值
select sum(A.Sales) from store_info A where A.Store_Name in (select Store_Name from location B where B.Store_Name = A.Store_Name);
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Cp4Sh4fA-1687255797636)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144740036.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/10637f52f5ed495d8560aafcd3f3f507.png#pic_center)
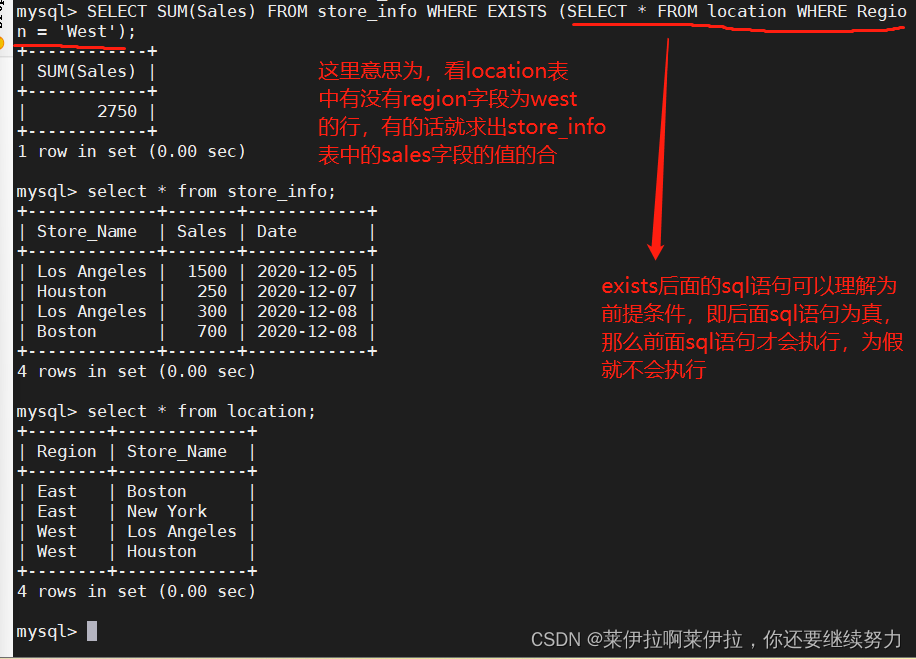
5. EXISTS(类查询)
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果,类似布尔值是否为真。
如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句。若是没有的话,那整个 SQL 语句就不会产生任何结果。
SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件");
例如
#判断是否有西部城市,有的话就计算销售和
,如果没有就输出NULL
select SUM(Sales) from store_info where exists (select * from location where Region = 'West');
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uIGixYUA-1687255797637)(C:\Users\86138\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230620144806324.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f22da998d73f472d93af41fd37f10340.png#pic_center)
总结
1. sql 语句中 HAVING 的用法
having 对 group by 分组后的结果根据条件进行过滤筛选。