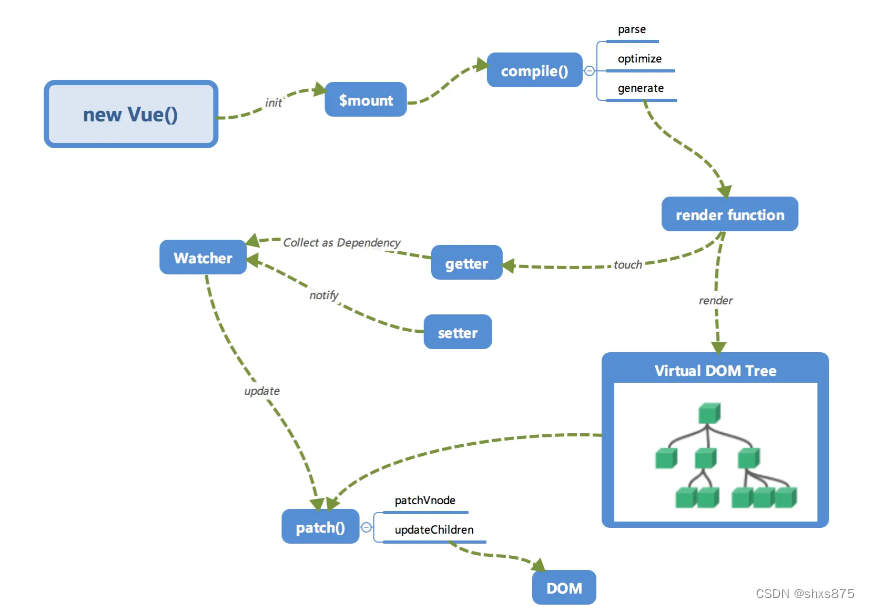
轮廓查找
- 1. 轮廓
- 2.轮廓查找
- 2.1 findContours()
- 2.2 drawContours()
- 2.3 contourArea()和arcLength()
- 2.4 多边形逼近与凸包
- approxPolyDP()
- convexHull()
- 2.5 外接矩形
- minAreaRect()
- boundingRect()
1. 轮廓
一个图像中具有相同颜色或强度(灰度图)的连续点所组成的集合,就是轮廓。轮廓可用于图形分析、物体的识别与检测等等。
2.轮廓查找
在图像中,为了防止轮廓边缘强弱不明显,需要先对图像进行二值化或Canny操作(一般改为黑底白字),画轮廓时会修改输入的图像。
2.1 findContours()
查找图形的轮廓
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, mode, ApproximationMode…)
contours:查找到所有轮廓的列表(点的集合)
hierarchy:层级,轮廓有无顺序
mode:(检测方式)
- RETR_EXTERNAL = 0 :表示只检测外部轮廓(红色为轮廓)

- RETR_LIST = 1 :检测的轮廓不建立等级关系,从里到外、从右到左,一层一层的编号,返回的列表也是按这个顺序排列的

- RETR_CCOMP = 2 :每层最多两级,从里到外、从右到左,单个图形,每两级为一层
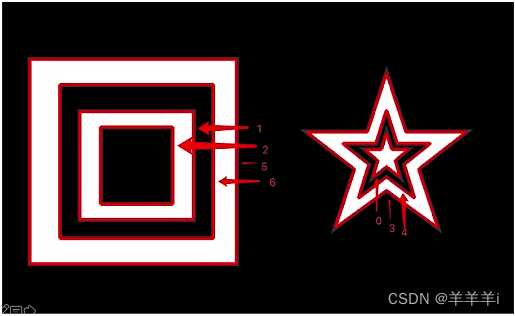
- RETR_TREE = 3 :按树形存储轮廓 ,从右到左,从外到里,一个图形一个图像的来,符合正常逻辑
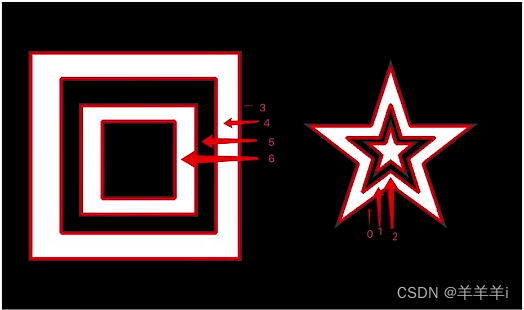
ApproximationMode:(逼近方式) - CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:保存所有轮廓上的点
- CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:只保存角点
2.2 drawContours()
根据获得到的坐标点(contours)绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, contourIdx, color, thickness…)
img:需要画轮廓的图像
contours:轮廓的点集
contourldx:-1表示绘制所有轮廓 0~n
color:颜色(255,255,255)
thinckness:线宽,-1是全部填充,1~n
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('./image/contours1.png')
# 转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 二值化,使轮廓更明显
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 获得轮廓列表
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 画全部的轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)
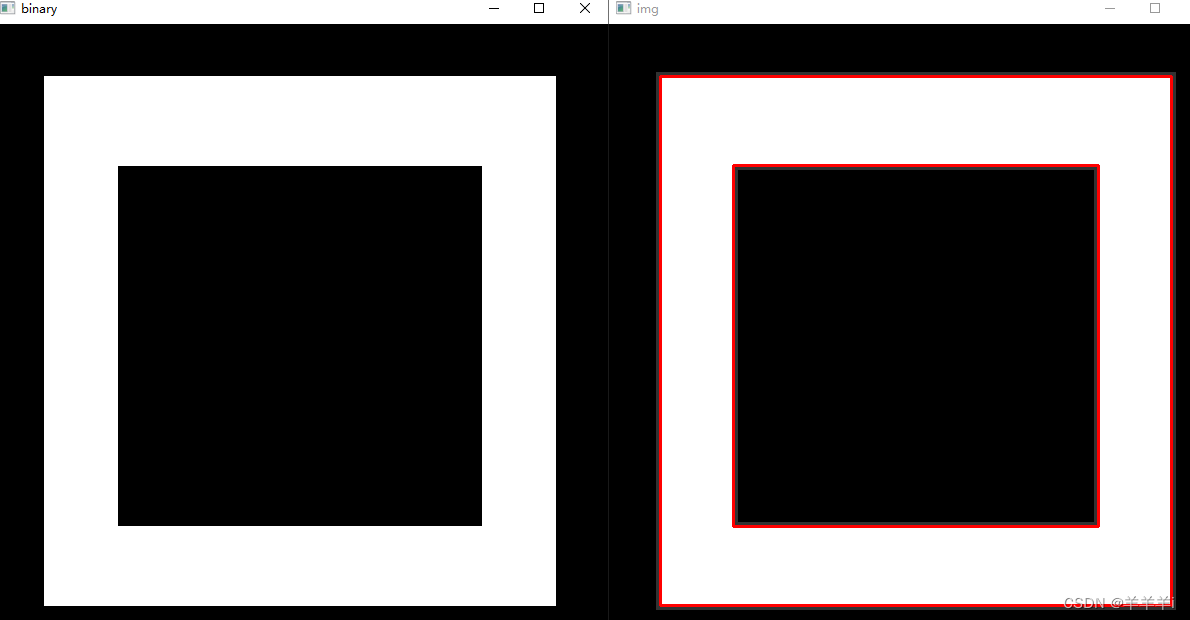
2.3 contourArea()和arcLength()
求轮廓的面积和周长
cv2.contourArea(contour)
contour:点集(轮廓)
cv2.arcLength(curve, closed)
curve:点集(轮廓)
closed:True/False是否是封闭的轮廓
# 计算面积
area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
print('面积 = %d' % area)
# 计算周长
len = cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True)
print('周长 = %d' % len)
2.4 多边形逼近与凸包
多边形逼近就是按照画多边形的方式画出图形的轮廓,而凸包只需画出大概轮廓即可。左图为多边形逼近,右图为凸包。

approxPolyDP()
多边形逼近轮廓
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(curve, epsilon, closed)
curve:点集(轮廓)
epsilon:精度(越小越逼近)
closed:是否是闭合的轮廓True/False
返回值approx是一个列表
import cv2
import numpy as np
def drawShape(src, points):
i = 0
while i<len(points):
if i == len(points)-1:
x1, y1 = points[i][0]
x2, y2 = points[0][0]
cv2.line(src, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
else:
x1, y1 = points[i][0]
x2, y2 = points[i+1][0]
cv2.line(src, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
i = i+1
img = cv2.imread('./image/hand.png')
# 转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 二值化,使轮廓更明显
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 获得轮廓列表
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 多边形逼近法
e = 5
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0], e, True)
drawShape(img, approx)
print(approx[0][0])
cv2.imshow('img_5', img)
# cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)
分别是精度为20,精度为5的逼近图像

convexHull()
凸包
hull = cv2.convexHull(points, clockwise, …)
points:轮廓
clockwose:是否顺时针绘制True/False
返回值同样是一个列表
import cv2
import numpy as np
def drawShape(src, points):
i = 0
while i<len(points):
if i == len(points)-1:
x1, y1 = points[i][0]
x2, y2 = points[0][0]
cv2.line(src, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
else:
x1, y1 = points[i][0]
x2, y2 = points[i+1][0]
cv2.line(src, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
i = i+1
img = cv2.imread('./image/hand.png')
# 转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 二值化,使轮廓更明显
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 获得轮廓列表
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 凸包
hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
drawShape(img, hull)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)

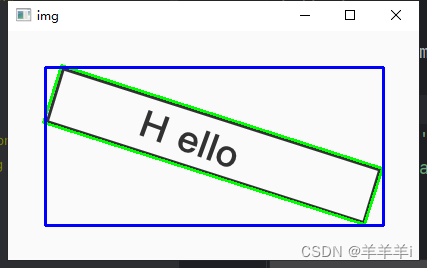
2.5 外接矩形
分为最大外接矩形和最小外接矩形,如下图所示。
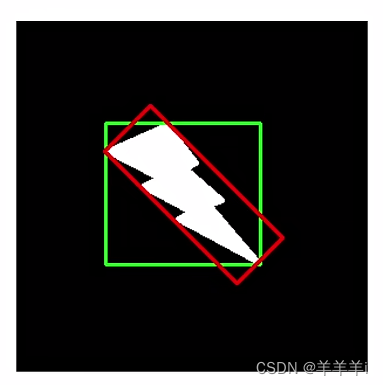
minAreaRect()
最小外接矩形
RotatedRect = cv2.minAreaRect(points)
points:点集(轮廓)
返回值:矩形中心点坐标,宽高,旋转角度
boundingRect()
最大外接矩形
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(array)
array:点集(轮廓)
返回值是矩形的列表:(x,y是起始坐标,w是宽度,h是高度)
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('./image/hello.jpeg')
# 转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 二值化,使轮廓更明显
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 获得轮廓列表
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 获取最小外接矩阵,中心点坐标,宽高,旋转角度
r = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[1])
# 获取矩形四个顶点,浮点型
box = cv2.boxPoints(r)
# 取整
box = np.intp(box)
# 画轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, [box], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 获取最大外接矩形
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[1])
# 画矩形
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h),(255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)