目录:导读
- 前言
- 一、Python编程入门到精通
- 二、接口自动化项目实战
- 三、Web自动化项目实战
- 四、App自动化项目实战
- 五、一线大厂简历
- 六、测试开发DevOps体系
- 七、常用自动化测试工具
- 八、JMeter性能测试
- 九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
前言
第一种:通过yaml文件获取数据(一维列表)
data.yaml文件内容如下:
- '软件测试'
- '单元测试'
- '自动化测试'
- '性能测试'
- '测试开发'
- '测试架构师'
测试用例内容如下:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('data', yaml.load(open('data.yml', 'r')))
def test_ddt(data):
url='https://www.baidu.com/search/query?key='
header = {'Accept': "application/json",
'Content-Type': "application/json; charset=utf-8",
'Accept-Encoding': "gzip, deflate, br"}
res=requests.get(url+data, header)
assert res.status_code==200
第二种:通过yaml文件获取数据(二维列表)
data.yaml文件内容如下:
#用例1
-
api_name: page_title
url: http://www.baidu.com/
header = {'Accept': "application/json",
'Content-Type': "application/json; charset=utf-8",
'Accept-Encoding': "gzip, deflate, br"}
data: {
"status_code": 200
}
#用例2
-
api_name: searching
url: http://www.baidu.com/
header = {'Accept': "application/json",
'Content-Type': "application/json; charset=utf-8",
'Accept-Encoding': "gzip, deflate, br"}
data: {
"status_code": 200
}
#用例3
-
api_name: login
url: http://www.baidu.com/
header = {'Accept': "application/json",
'Content-Type': "application/json; charset=utf-8",
'Accept-Encoding': "gzip, deflate, br"}
data: {
"status_code": 200
}
测试用例内容如下:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('data', yaml.load(open('data.yml', 'r')))
def test_ddt(data):
api_name = data['api_name']
url=data['url']
header = data['header']
res=requests.get(url + api_name, header)
assert res.status_code ==data['data']['status_code']
第三种:通过yaml文件获取数据(@pytest.fixture)
@pytest.fixture()
def login(request):
name = request.param
print(f"== 账号是:{name} ==")
return name
data = ["pyy1", "polo"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("login", data, indirect=True)
def test_name(login):
print(f" 测试用例的登录账号是:{login} ")
@pytest.fixture()
def logins(request):
param = request.param
print(f"账号是:{param['username']},密码是:{param['pwd']}")
return param
data = [ {"username": "name1", "pwd": "pwd1"}, {"username": "name2", "pwd": "pwd2"} ]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("logins", data, indirect=True)
def test_name_pwd(logins):
print(f"账号是:{logins['username']},密码是:{logins['pwd']}")
# 多个fixture
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def input_user(request):
user = request.param
print("登录账户:%s" % user)
return user
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def input_psw(request):
psw = request.param
print("登录密码:%s" % psw)
return psw
data = [("name1", "pwd1"), ("name2", "pwd2")]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input_user,input_psw", data, indirect=True)
def test_more_fixture(input_user, input_psw):
print("fixture返回的内容:", input_user, input_psw)
name = ["name1", "name2"]
pwd = ["pwd1", "pwd2"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input_user", name, indirect=True)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input_psw", pwd, indirect=True)
def test_more_fixture(input_user, input_psw):
print("fixture返回的内容:", input_user, input_psw)
| 下面是我整理的2023年最全的软件测试工程师学习知识架构体系图 |
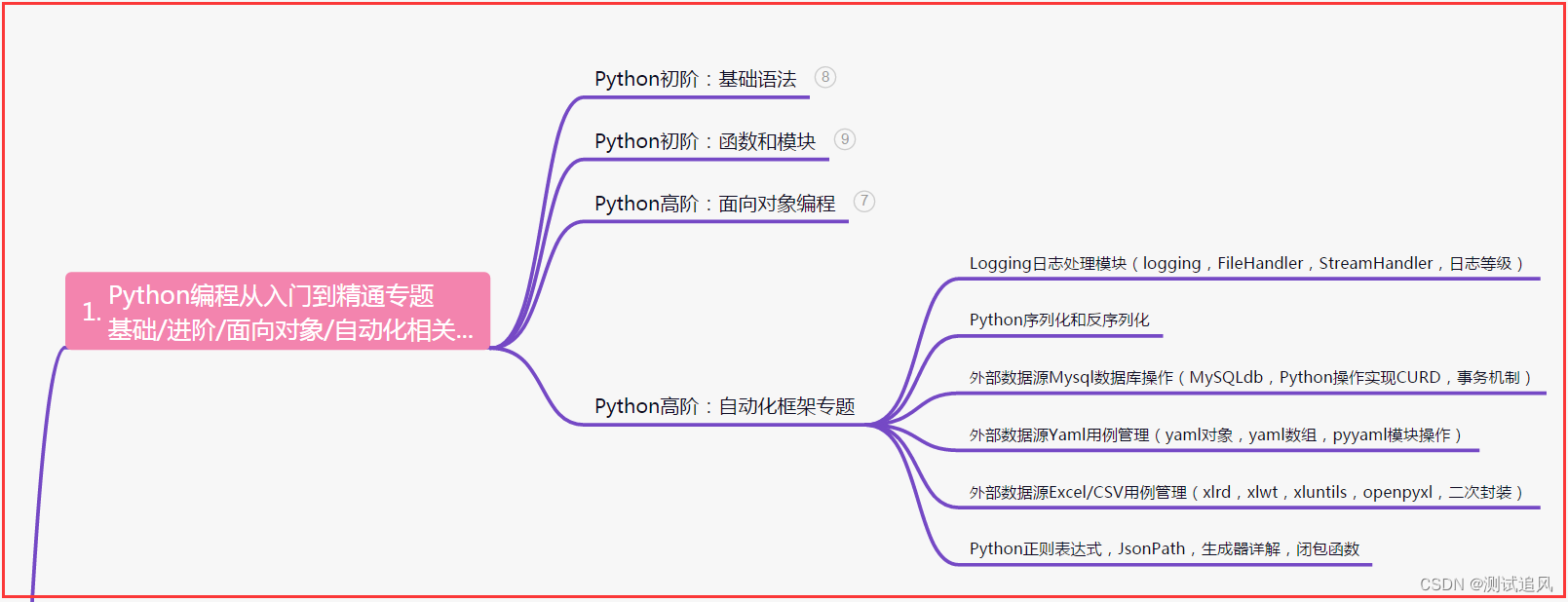
一、Python编程入门到精通
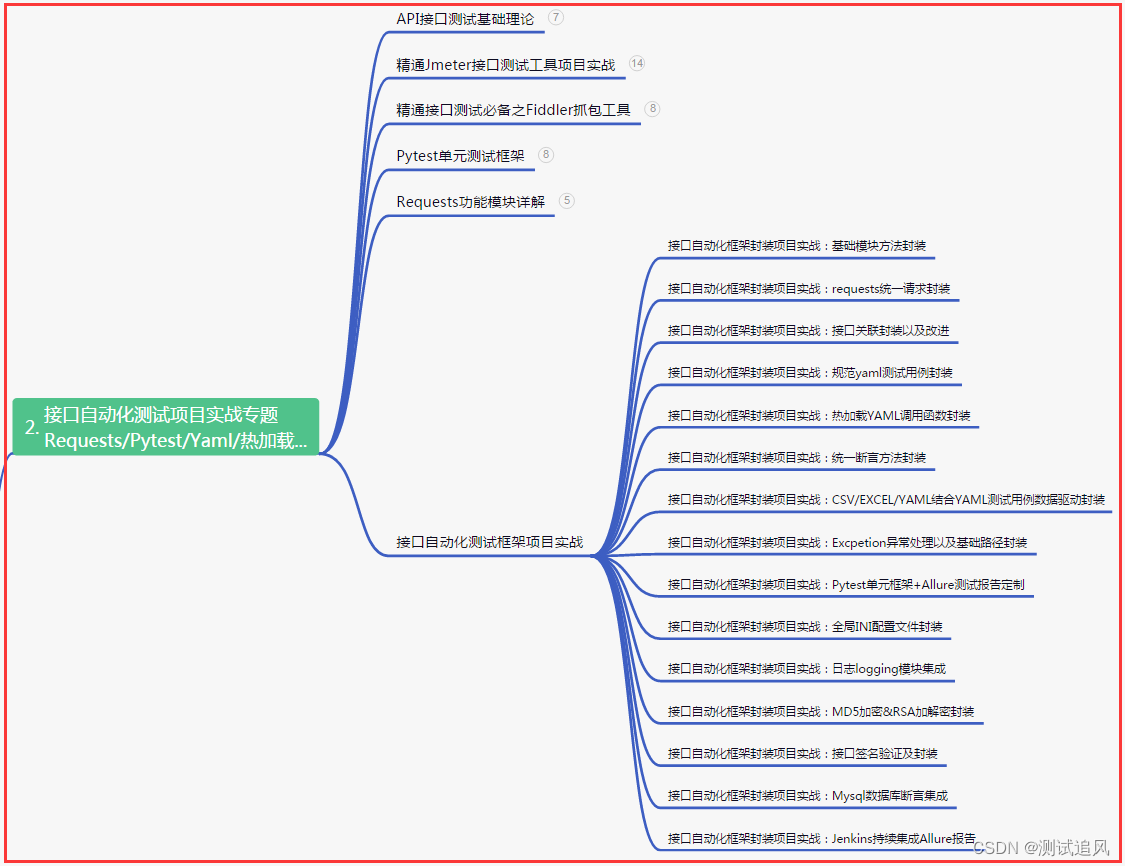
二、接口自动化项目实战
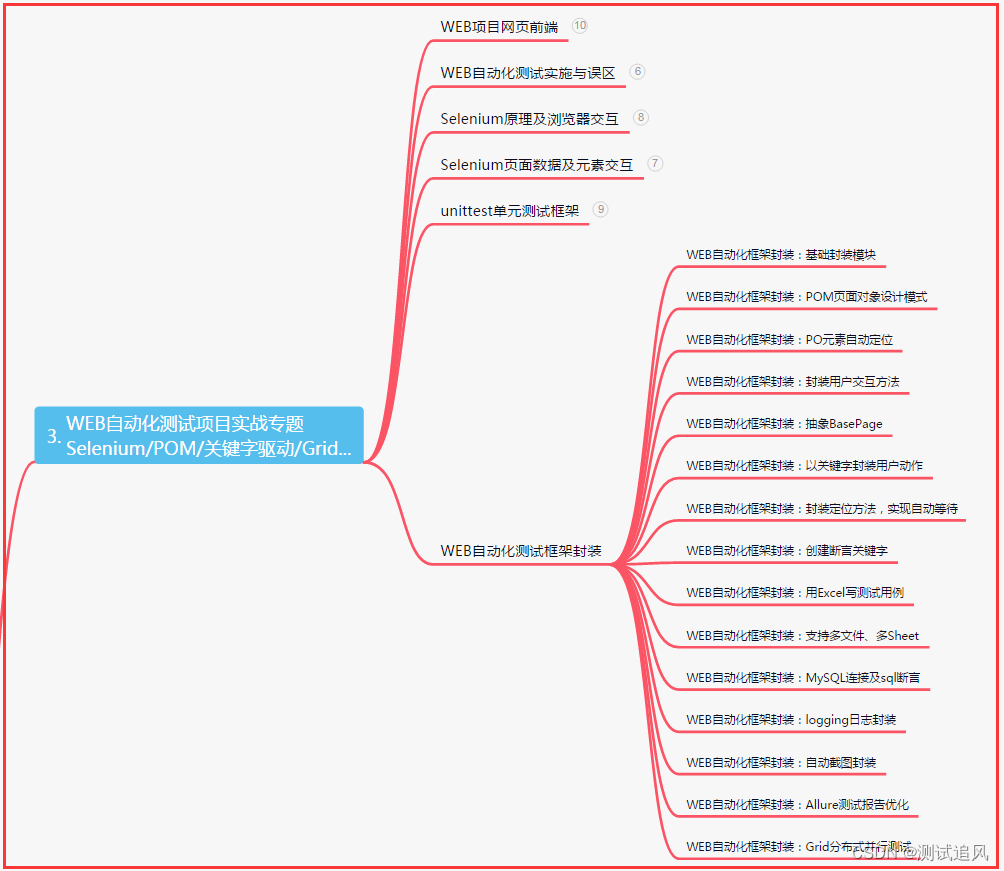
三、Web自动化项目实战
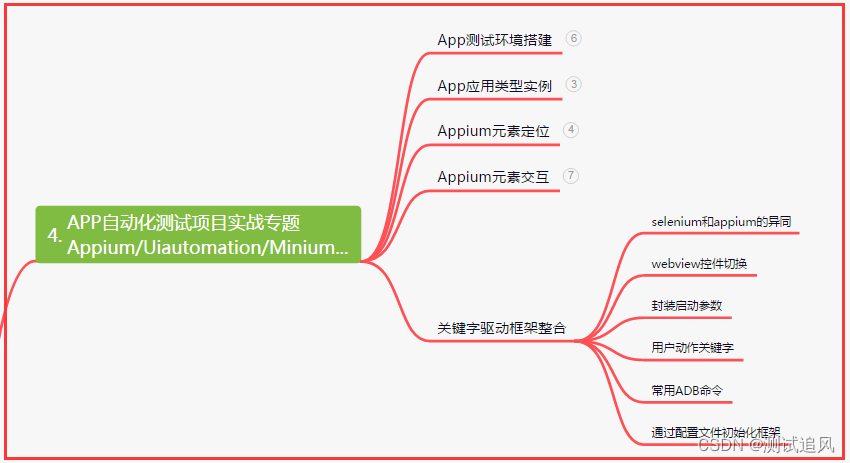
四、App自动化项目实战
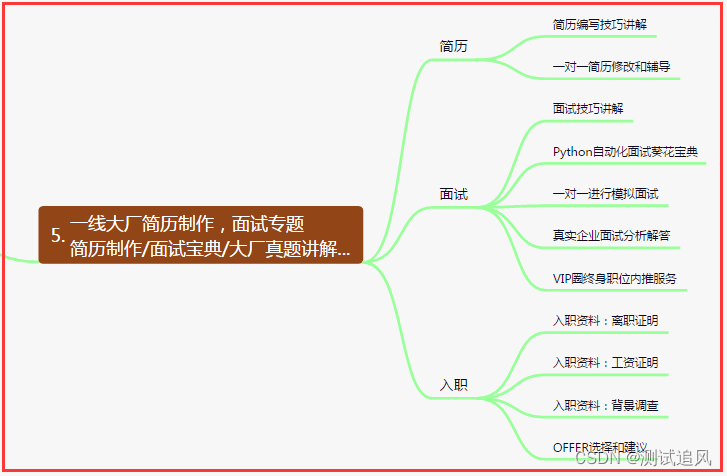
五、一线大厂简历
六、测试开发DevOps体系

七、常用自动化测试工具
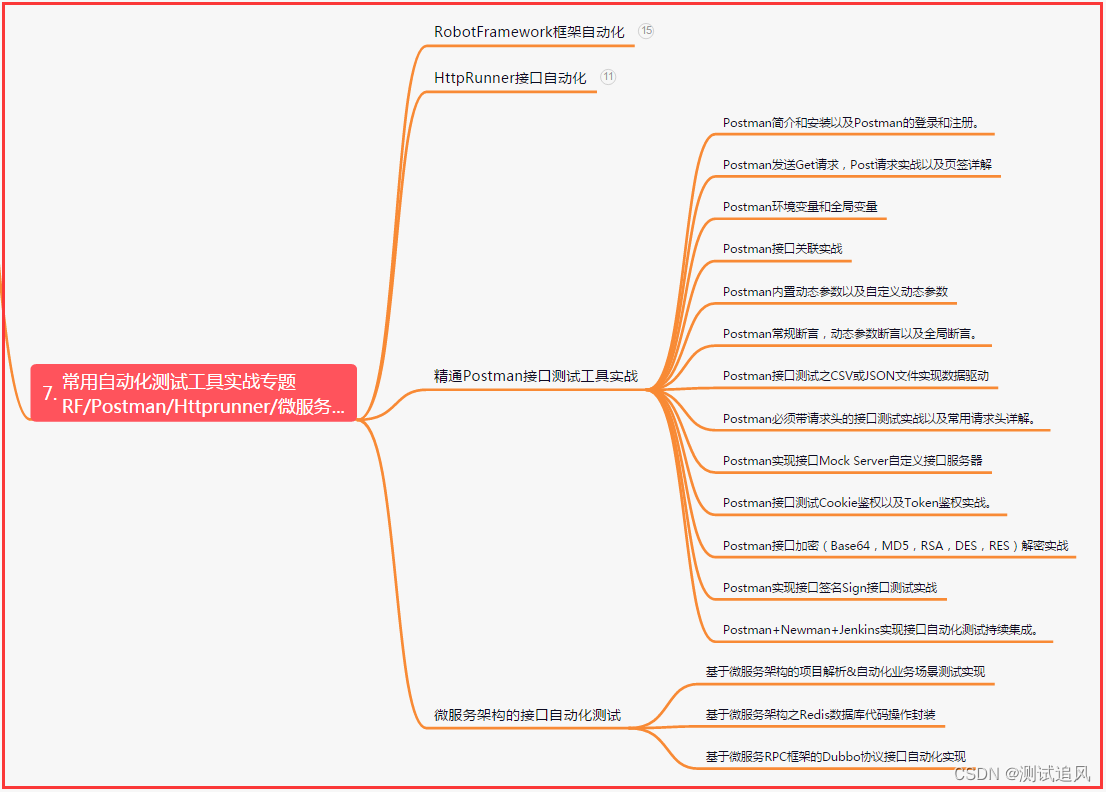
八、JMeter性能测试
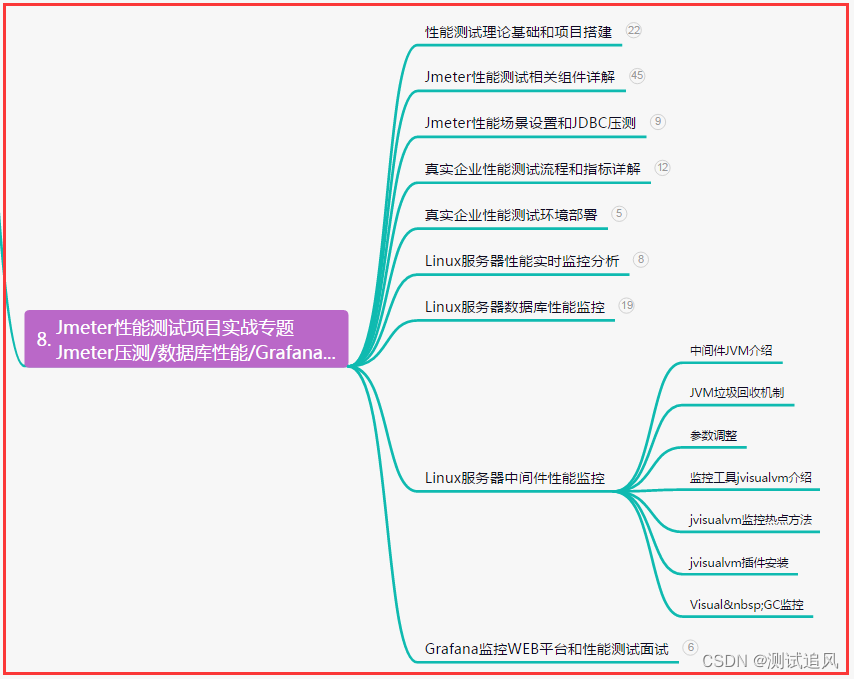
九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
只有拼搏,才有机会实现自己的梦想。不要轻易放弃,坚持到底才是胜利。付出总有回报,只要你能不断努力,成功就在不远处。让激情点燃你的人生,追求卓越,成为最好的自己!
每一天都是一个新的开始,把握机会、勇往直前;不要畏惧失败,它是成长的踏脚石;坚持自己的梦想,付出总有回报;相信自己,你能够超越自我,迎接更好的明天!
只有不停地前行,才能在生命中创造属于自己的精彩。不要被失败所吓倒,因为成功就在坚持和尝试的另一边等着你。每一次的奋斗都是对未来最好的投资,让我们勇往直前,不断超越自我!



![[Flutter]理解Widget-Key的作用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1769a8a74e424f4ebe059114f2106357.jpeg)