1.简介:
Spring 是非常流行和成功的 Java 应用开发框架,Spring Security 正是 Spring 家族中的成员。Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。
1.1 特性:
- 支持对身份认证和访问鉴权的自定义扩展
- 防止会话固定、点击劫持、跨站点请求伪造等攻击
- Servlet API 集成
- 与 Spring Web MVC 的可选集
Spring Security的核心是提供认证(Authentication)、授权(Authorization)和攻击防护。
1.2 认证(Authentication)
身份认证,指验证用户是否为使用系统的合法主体,就是说用户能否访问该系统。
Spring Security支持的认证方式有:用户名和密码、OAuth2.0登录、SAML2.0登录、中央认证服务器(CAS)、记住我、JAAS身份认证、OpenID、预身份验证方案、X509认证
1.3 授权(Authorization)
身份鉴权,指验证某个用户是否具有权限使用系统的某个操作。
Spring Security支持的授权方案:基于过滤器授权、基于表达式访问控制、安全对象实现、方法安全、域对象安全(ACL)。
1.4 攻击防护
防止会话固定、点击劫持、跨站点请求伪造等攻击。(解决系统安全问题)
Spring Security支持的攻击防护有:CSRF、会话固定保护、安全请求头、HTTPS、HTTP防火墙
2 SpringSecurity 认证和授权流程
Spring Security是通过Filter来实现的,采用的是责任链的设计模式,它有一条很长的过滤器链,只有当前过滤器通过,才能进入下一个过滤器。
Spring Boot 自动装配通过WebSecurityConfiguration类,Spring容器中注入一个名为SpringSecurityFilterChain的Servlet过滤器,类型为FilterChainProxy。它实现了javax.servlet.Filter,因此外部的请求都会经过这个类。FilterChainProxy是一个代理,真正起作用的是FilterChainProxy中SecurityFilterChain所包含的各个Filter,同时,这些Filter都已经注入到Spring容器中,他们是Spring Security的核心,各有各的职责。但是他们并不直接处理用户的认证和授权,而是把他们交给了认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)和决策管理器(AccessDecisionManager)进行处理。

FilterChainProxy类图:

过滤器图:

除了默认过滤器,我们也可以自定义多个过滤器,通过configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中配置。认证的过程围绕图中过滤链的橙色部分(过滤器Filter),动态鉴权主要是围绕其绿色部分(拦截器Interceptor)。
内置的过滤器:
| 序号 | 名称 | 描述 |
| 1 | WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter | 根据请求封装获取WebAsyncManager,从WebAsyncManager获取/注册的安全上下文可调 用处理拦截器 |
| 2 | SecurityContextPersistenceFilter | SecurityContextPersistenceFilter主要是使用SecurityContextRepository在session中保存 或更新一个SecurityContext,并将SecurityContext给以后的过滤器使用,来为后续fifilter 建立所需的上下文。SecurityContext中存储了当前用户的认证以及权限信息。 |
| 3 | HeaderWriterFilter | 向请求的Header中添加相应的信息,可在http标签内部使用security:headers来控制 |
| 4 | CsrfFilter | csrf又称跨域请求伪造,SpringSecurity会对所有post请求验证是否包含系统生成的csrf的 token信息,如果不包含,则报错。起到防止csrf攻击的效果。 |
| 5 | LogoutFilter | 匹配URL为/logout的请求,实现用户退出,清除认证信息。 |
| 6 | UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter | 认证过滤器,表单认证操作全靠这个过滤器,默认匹配URL为/login且必须为POST请求 |
| 7 | DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter | 如果没有在配置文件中指定认证页面,则由该过滤器生成一个默认认证页面。 |
| 8 | DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter | 由此过滤器可以生产一个默认的退出登录页面 |
| 9 | BasicAuthenticationFilter | 此过滤器会自动解析HTTP请求中头部名字为Authentication,且以Basic开头的头信息 |
| 10 | RequestCacheAwareFilter | 通过HttpSessionRequestCache内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存 HttpServletRequest |
| 11 | SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter | 针对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的API |
| 12 | AnonymousAuthenticationFilter | 当SecurityContextHolder中认证信息为空,则会创建一个匿名用户存入到 SecurityContextHolder中。spring security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程, 只不过是一个匿名的身份。 |
| 13 | SessionManagementFilter | securityContextRepository限制同一用户开启多个会话的数量 |
| 14 | ExceptionTranslationFilter | 异常转换过滤器位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个链路中出现的异 常 |
| 15 | FilterSecurityInterceptor | 授权过滤器,获取所配置资源访问的授权信息,根据SecurityContextHolder中存储的用户信息来决定其 是否有权限。 |
2.1 认证流程
Spring Security有两种认证方式,一种是 HttpBasic认证和表单认证。
- HttpBasic登录验证模式是Spring Security实现登录验证最简单的一种方式,也可以说是最简陋 的一种方式。它的目的并不是保障登录验证的绝对安全,而是提供一种“防君子不防小人”的登录验证。
- 表单认证就是通过登录界面,将用户名密码通过表单的形式发送到服务器上。
- spring security 5.x以下默认是HttpBasic认证,以上默认是表单认证。
具体流程:
- 用户提交用户名、密码被SecurityFilterChain中的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器获取到,封装为请求Authentication,通常情况下是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken这个实现类。
- 然后过滤器将Authentication提交至认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)进行认证,它的实现类是ProviderManager。
- 认证成功后, AuthenticationManager 身份管理器返回一个被填充满了信息的(包括上面提到的权限信息,身份信息,细节信息,但密码通常会被移除)Authentication 实例。
- SecurityContextHolder 安全上下文容器将第3步填充了信息的 Authentication,通过 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(…)方法,设置到其中。

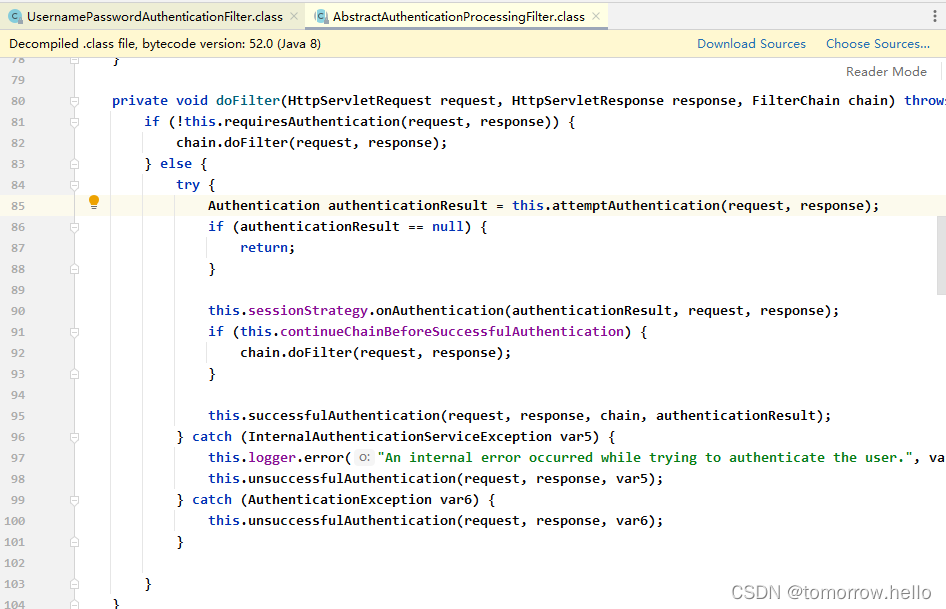
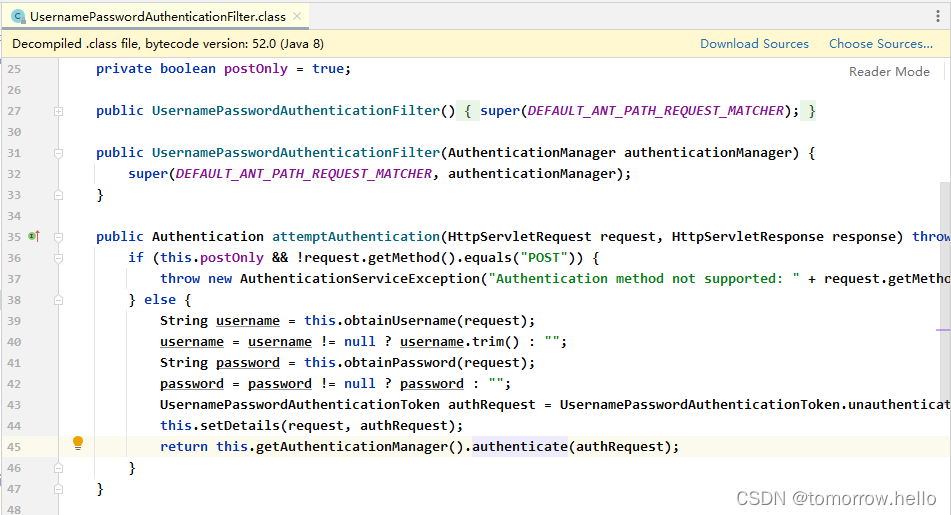
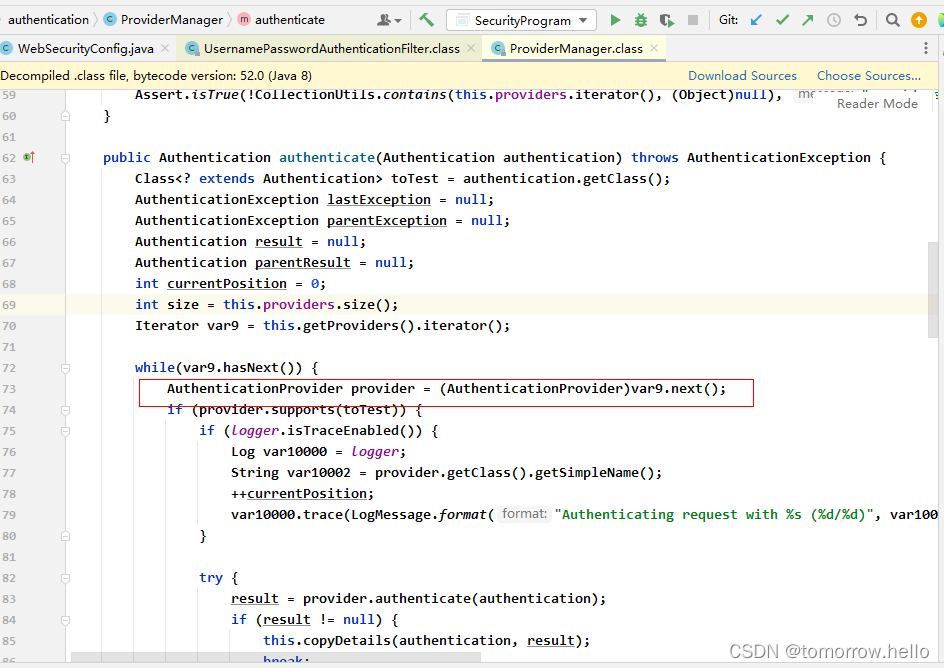
2.1.1 HttpBasic认证
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/hello", "/loginalert", "/mylogin").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/helloadmin").hasRole("admin")
.antMatchers("/hellouser").hasAuthority("query")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().httpBasic();
}2.1.2 表单认证
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/hello", "/loginalert", "/mylogin").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/helloadmin").hasRole("admin")
.antMatchers("/hellouser").hasAuthority("query")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin().loginPage("/mylogin.html")
.usernameParameter("uname").passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.failureHandler((request, response, exception) -> {
String message = "login fail:" + exception.getMessage();
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().write("<script>alert('" + message + "');window.location.href='/mylogin.html'</script>");
}).successHandler(((request, response, authentication) -> {
String message = "login success:" + authentication.getName();
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().write("<script>alert('" + message + "');window.location.href='/index'</script>");
}));
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(((request, response, accessDeniedException) -> {
String message = "access fail:" + accessDeniedException.getMessage();
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().write("<script>alert('" + message + "');window.location.href='/index'</script>");
}));
}2.2 授权流程
授权是在用户认证通过后,对访问资源的权限进行检查的过程。Spring Security可以通过http.authorizeRequests()对web请求进行授权保护。Spring Security使用标准Filter建立了对web请求的拦截,最终实现对资源的授权访问。

- 拦截请求,已认证用户访问受保护的web资源将被SecurityFilterChain中(实现类为DefaultSecurityFilterChain)的 FilterSecurityInterceptor 的子类拦截。
- 获取资源访问策略,FilterSecurityInterceptor会从 SecurityMetadataSource的子类DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 获取要访问当前资源所需要的权限Collection 。SecurityMetadataSource其实就是读取访问策略的抽象,而读取的内容,其实就是我们配置的访问规则,读取访问策略如
- 最后,FilterSecurityInterceptor会调用 AccessDecisionManager 进行授权决策,若决策通过,则允许访问资源,否则将禁止访问。
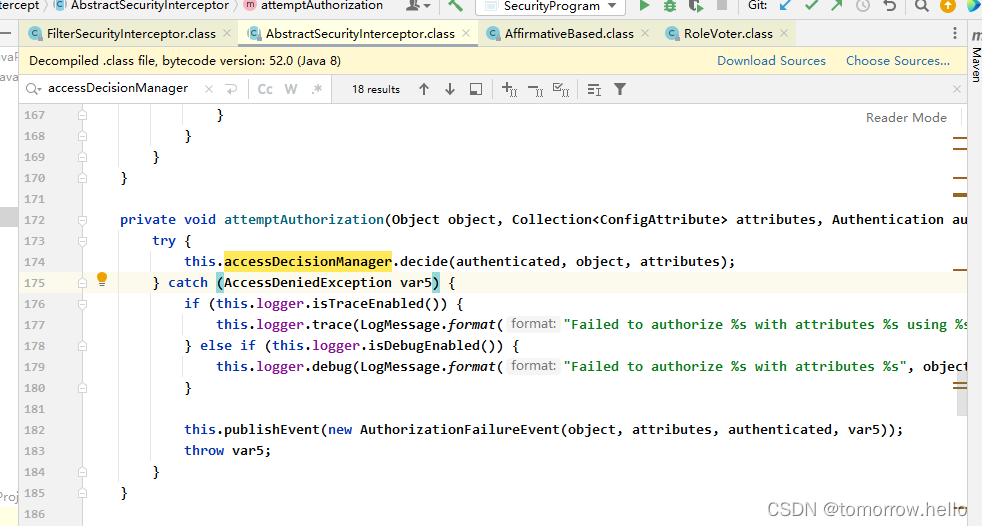
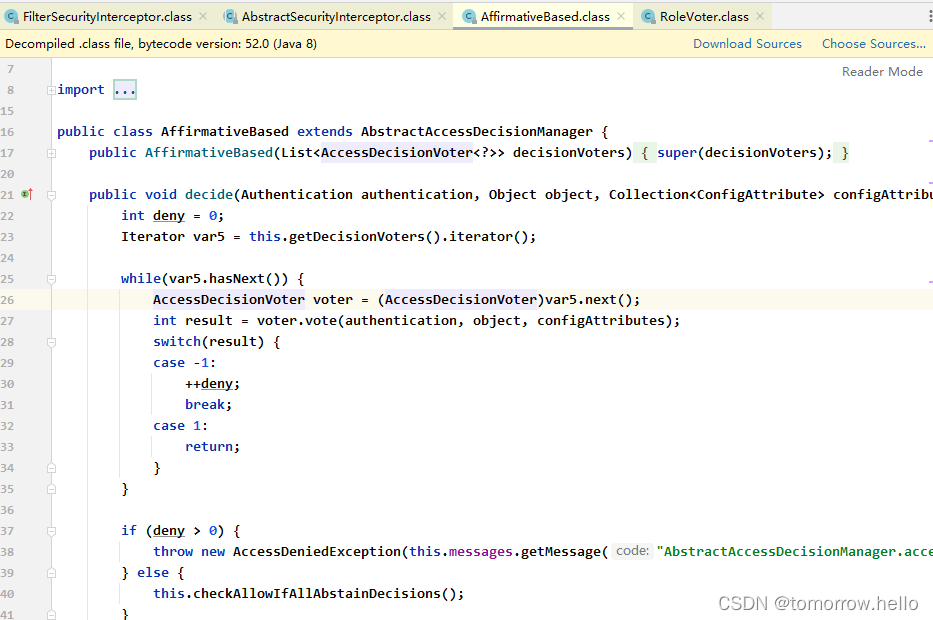
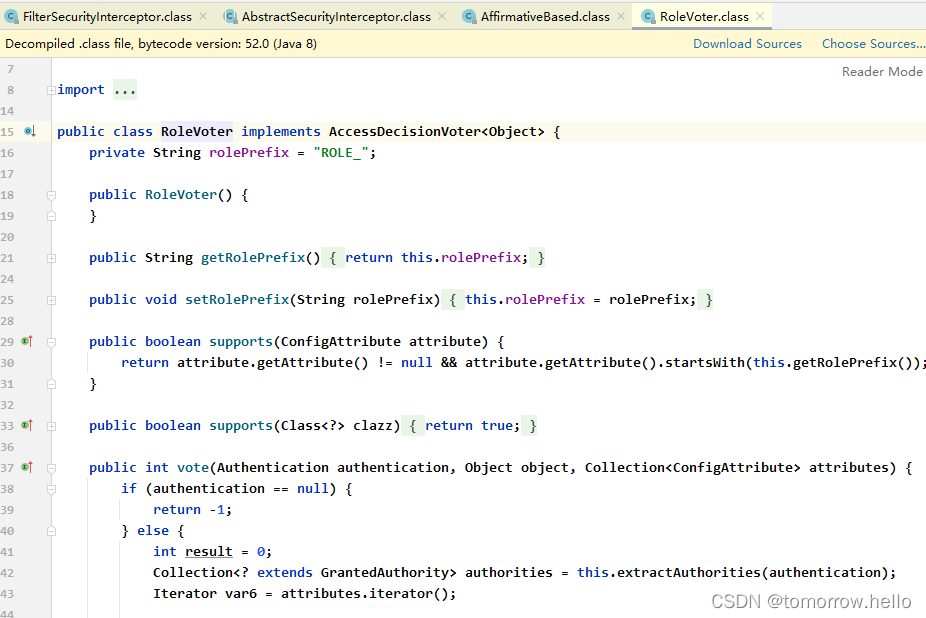
2.2.1 权限配置
权限配置有两种方式一种在SecurityFilterChain中配置,另一种在接口上增加注解。
权限表达式(方法):
- hasRole(role):当前用户是否具备指定角色
- hasAnyRole(role …):当前用户是否具备指定角色中的任意一个
- hasAuthority(authority):当前用户是否具备指定的权限
- hasAnyAuthority(authority …):当前用户是否具备指定的权限任意一个
- principal:当前登录主体
- authentication:context中authentication对象
- permitAll():允许所有请求
- denyAll():拒绝所有请求
- isAnonymous():当前用户是否是一个匿名用户
1. SecurityFilterChain配置
.antMatchers("/toUserAdd").hasAnyRole("admin");
.antMatchers("/toUserAdd").hasRole("admin");
.antMatchers("/toUserEdit").hasAuthority("edit")
.antMatchers("/toUserEdit").hasAnyAuthority("edit")
2.注解方式
- @PostAuthorize:在目标方法执行之后进行权限校验
- @PostFilter:在目标方法执行之后对方法的返回结果进行过滤
- @PreAuthorize:在目标方法执行之前进行权限校验。
- @PreFilter:在目标方法执行之前对方法参数进行过滤。
- @Secured:访问目标方法必须具备相应的角色
- @DenyAll:拒绝所有访问
- @PermitAll: 允许所有访问
- @RolesAlowed:访问目标方法必须具有的角色
public class UserService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and authentication.name=='lglbc'")
public String hello2() {
return "hello";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and authentication.name==#name")
public String hello3(String name) {
return "hello";
}
@PreFilter(value = "filterObject.id%2!=0",filterTarget = "users")
public void addUsers(List<User> users, Integer other) {
System.out.println("users = " + JSON.toJSONString(users));
}
@PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0")
public List<User> getAll() {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
users.add(new User(i, "lglbc_:" + i));
}
return users;
}
@Secured({"ROLE_ADMIN","ROLE_USER"})
public User getUserByUsername(String username) {
return new User(99, username);
}
@DenyAll
public String denyAll() {
return "DenyAll";
}
@PermitAll
public String permitAll() {
return "PermitAll";
}
@RolesAllowed({"ADMIN","USER"})
public String rolesAllowed() {
return "RolesAllowed";
}
}2.2.2 hasRole 和hasAuthority 区别

通过原来分析,hasRole 的处理逻辑和 hasAuthority 似乎是一样的,只是hasRole 这里会自动给传入的字符串前缀(默认是ROLE_ ),使用 hasAuthority 更具有一致性,不用考虑要不要加 ROLE_ 前缀,在UserDetailsService类的loadUserByUsername中查询权限,也不需要手动增加。在SecurityExpressionRoot 类中hasAuthority 和 hasRole 最终都是调用了 hasAnyAuthorityName 方法。
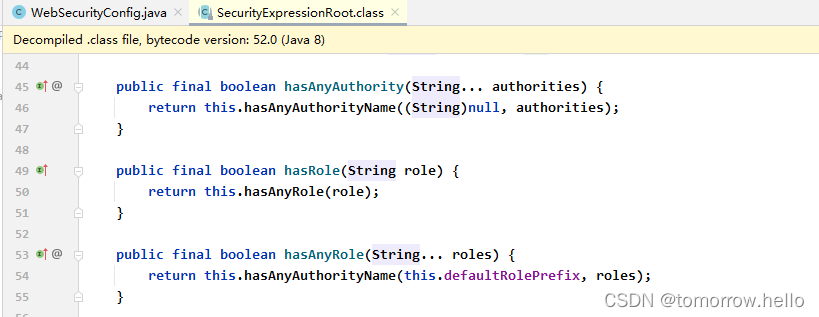
3.异常处理
异常处理设计到两个 Handler 进行处理 ,一个是处理认证异常的Handler处理器 AuthenticationEntryPoint,一个是授权异常的Handler处理器 AccessDeniedHandler。异常类主要分为两大类:AuthenticationException认证异常和AccessDeniedException授权异常。
AuthenticationException异常:
| 异常类型 | 备注 |
| AuthenticationException | 认证异常的父类,抽象类 |
| BadCredentialsException | 登录凭证(密码)异常 |
| InsufficientAuthenticationException | 登录凭证不够充分而抛出的异常 |
| SessionAuthenticationException | 会话并发管理时抛出的异常,例如会话总数超出最大限制数 |
| UsernameNotFoundException | 用户名不存在异常 |
| PreAuthenticatedCredentialsNotFoundException | 身份预认证失败异常 |
| ProviderNotFoundException | 未配置AuthenticationProvider 异常 |
| AuthenticationServiceException | 由于系统问题而无法处理认证请求异常。 |
| InternalAuthenticationServiceException | 由于系统问题而无法处理认证请求异常。和AuthenticationServiceException 不同之处在于,如果外部系统出错,则不会抛出该异常 |
| AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException | SecurityContext中不存在认证主体时抛出的异常 |
| NonceExpiredException | HTTP摘要认证时随机数过期异常 |
| RememberMeAuthenticationException | RememberMe认证异常 |
| CookieTheftException | RememberMe认证时Cookie 被盗窃异常 |
| InvalidCookieException | RememberMe认证时无效的Cookie异常 |
| AccountStatusException | 账户状态异常 |
| LockedException | 账户被锁定异常 |
| DisabledException | 账户被禁用异常 |
| CredentialsExpiredException | 登录凭证(密码)过期异常 |
| AccountExpiredException | 账户过期异常 |
AccessDeniedException异常:
| 异常类型 | 备注 |
| AccessDeniedException | 权限异常的父类 |
| AuthorizationServiceException | 由于系统问题而无法处理权限时抛出异常 |
| CsrfException | Csrf令牌异常 |
| MissingCsrfTokenException | Csrf令牌缺失异常 |
| InvalidCsrfTokenException | Csrf令牌无效异常 |
可以通过SecurityFilterChain进行配置
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(((request, response, accessDeniedException) -> {
String message = "access fail:" + accessDeniedException.getMessage();
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().write("<script>alert('" + message + "');window.location.href='/index'</script>");
}));
http.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint((request, response, authException) -> {
System.out.println("error:" + authException);
});
参考:
SpringBoot Security工作原理_springbootsecurity原理_StrangerIt的博客-CSDN博客
springSecurity源码之鉴权原理_凯歌的博客的博客-CSDN博客
SpringSecurity认证基本原理与认证2种方式_spring security 多种认证_程序小黑马的博客-CSDN博客