翻译:
Vlad和Nastya住在一个由𝑛房子和𝑛−1路组成的城市。从每一个房子,你只需要沿着路走就可以到达另一个。也就是说,城市是一棵树。
弗拉德住在索引为𝑥的房子里,娜斯提亚住在索引为𝑦的房子里。弗拉德决定去拜访娜斯提亚。然而,他想起他已经推迟了𝑘他必须在来纳斯提亚之前做的事情。要做𝑖-th的事情,他需要来𝑎𝑖-th的房子,事情可以按任何顺序进行。在1分钟内,他可以从一个房子走到另一个房子,如果他们有道路相连。
弗拉德不太喜欢走路,所以他很感兴趣的是他最少要在路上花多少分钟才能完成所有的事情,然后才能到达纳斯提亚。房子𝑎1,𝑎2,…,𝑎𝑘他可以按任何顺序访问。他可以多次访问任何房子(如果他想)。
输入
第一行输入包含一个整数𝑡(1≤𝑡≤104)—输入测试用例的数量。在每个测试用例之前都有一个空行。
每个测试用例的第一行分别包含两个整数𝑛和𝑘(1≤𝑘≤𝑛≤2⋅105)——房子和东西的数量。
每个测试用例的第二行包含两个整数𝑥和𝑦(1≤𝑥,𝑦≤𝑛)——分别是Vlad和Nastya居住的房子的指数。
每个测试用例的第三行包含𝑘整数𝑎1,𝑎2,…,𝑎𝑘(1≤𝑎𝑖≤𝑛)-房子Vlad需要来做的事情的指数。
以下的𝑛−1行包含城市的描述,每一行包含两个整数𝑣𝑗和𝑢𝑗(1≤𝑢𝑗,𝑣𝑗≤𝑛)——通过道路𝑗连接的房屋的指数。
保证所有案例𝑛的总和不超过2⋅105。
输出
输出𝑡行,每一行都包含输入的相应测试用例的答案。作为一个答案输出单个整数- Vlad在路上做所有事情和到达Nastya所需的最小分钟数。
例子
inputCopy
3.
3个1
1 3
2
1 3
1 2
6 4
3个5
1 6 2 1
1 3
3 4
3个5
5个6
5个2
6 - 2
3 - 2
5个3
1 3
3 4
3个5
5个6
5个2
outputCopy
3.
7
2
请注意
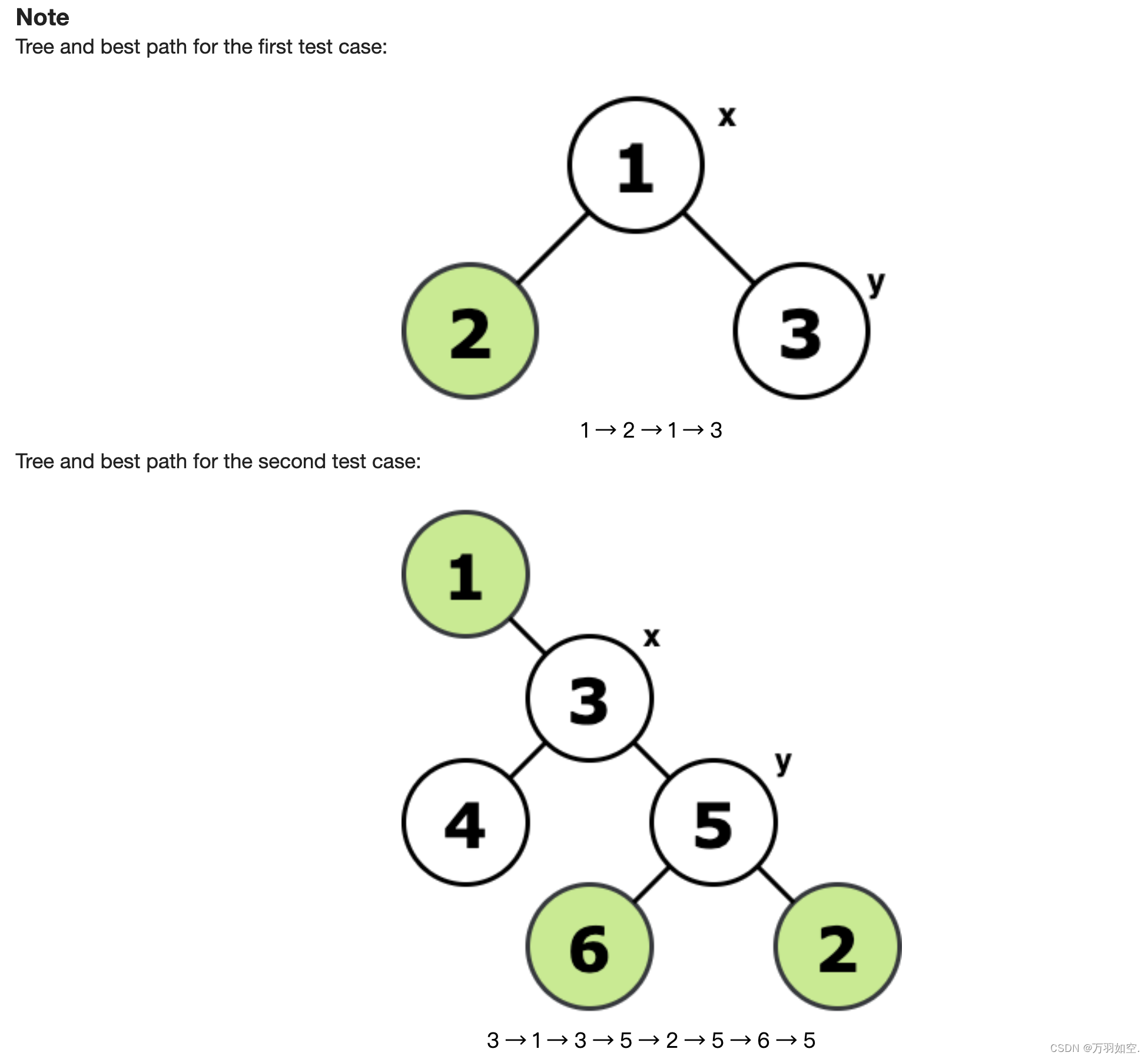
树和第一个测试用例的最佳路径:
1→2→1→3
树和第二个测试用例的最佳路径:
3→1→3→5→2→5→6→5
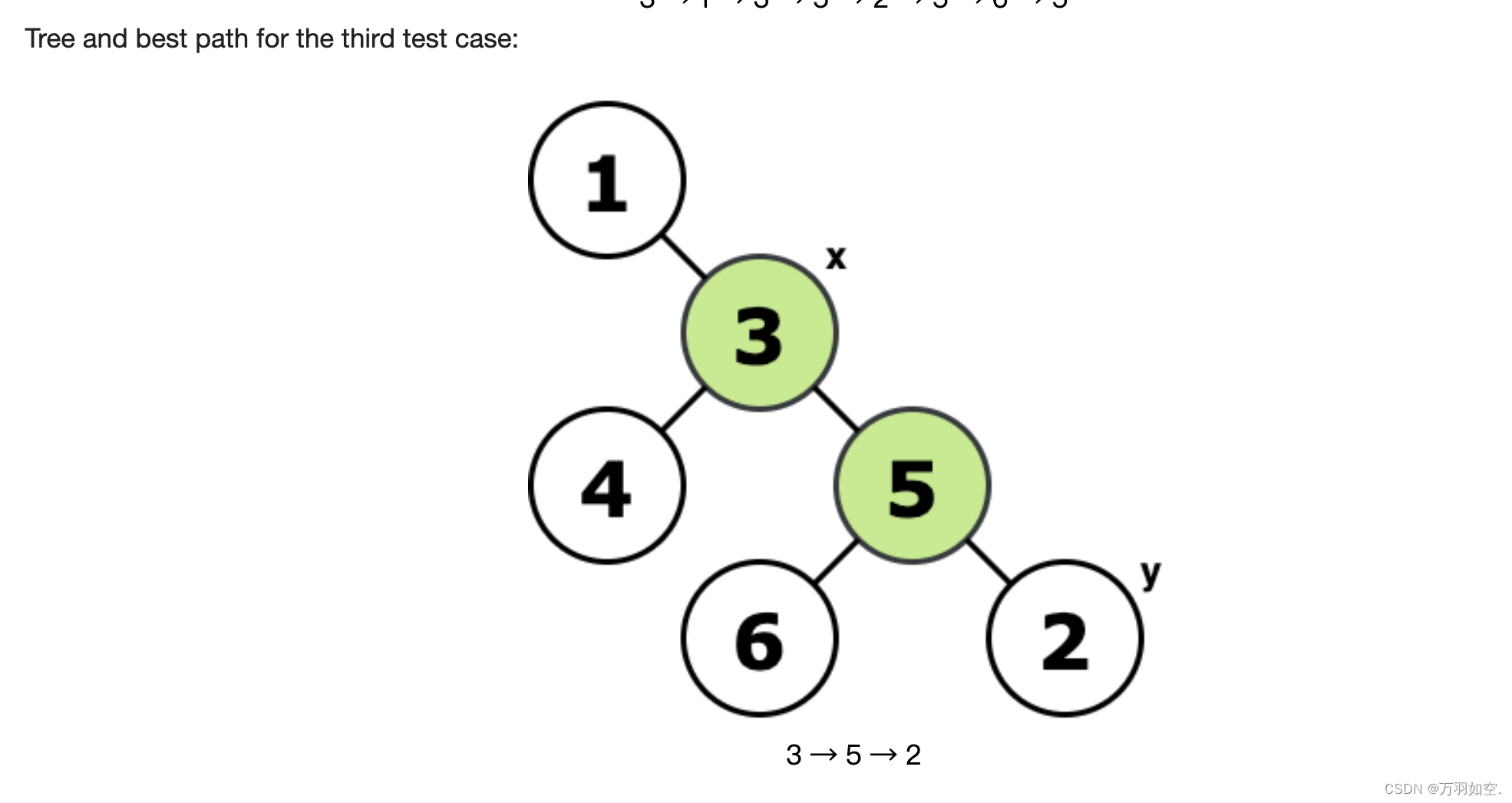
树和第三个测试用例的最佳路径:
3→5→2
思路:x——>y,要先经过k个点。是道结论题,如果k中有点在x——>y的路径上,就只需要跑一次,不需要回头,如果点不在x——>y的路径上,就需要回头跑两次。画下图,大概就可以理解了。然后我们直接建树+标记+dfs,最后根据每个路径跑一次还是两次,进行加和即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
#include<stack>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,t;
inline __int128 read(){
__int128 x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
if(ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x < 0){
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x > 9)
print(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
vector<int>q[200005];
//int a[200005];
bool fir[200005];
bool sec[200005];
int k,cx,cy,ww,qq;
void dfs(int now,int fa){
for (int i =0; i<q[now].size(); i++) {
if (q[now][i]==fa) {
continue;
}
dfs(q[now][i], now);
if (fir[q[now][i]]) {
fir[now]=true;
}else if (sec[q[now][i]]){
sec[now]=true;
}
}
}
void solv(){
cin>>n>>k>>cx>>cy;
for (int i =0; i<=n; i++) {
fir[i]=sec[i]=false;
q[i].clear();
}
fir[cy]=true;
for (int i =1; i<=k; i++) {
cin>>ww;
sec[ww]=true;
}
ll ans=0;
for (int i =1; i<n; i++) {
cin>>qq>>ww;
q[qq].push_back(ww);
q[ww].push_back(qq);
}
dfs(cx, cx);
// for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
// if (fir[i]) {
// printf("%d ",i);
// }
//
// }
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
if (i==cx) {
continue;
}
if (fir[i]) {
ans++;
}
else if(sec[i])
ans+=2;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
solv();
}
return 0;
}
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM交通事故记录信息管理系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5ea282dbacd44ea886358f608263a82c.png)



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django数字乡村基础治理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7f73ea90c4ae4a5189ea857db15598d9.png)