一、前言
看了例子之后后续需要更加深入学习或者更多理解其他API的话,建议看官方文档。hutool项目是中国人维护的,有中文文档,阅读起来很方便。apache poi比较底层一点,可以更加自由去二次开发自己所需的功能。
hutool官方文档
hutool官方gitee
apache poi官方文档
二、基于hutool poi 实现导出excel文件到本地
有两种写法,可以一开始就为ExcelWriter 指定要写的文件,另一种是等到要flush的时候再指定对应文件的输出流。两种写法都能实现,不过第二种写法会显得更灵活一点,可以到后面再慢慢决定要输出到哪个文件。
具体实现逻辑
import cn.hutool.poi.excel.ExcelUtil;
import cn.hutool.poi.excel.ExcelWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PoiTest {
private int age;
private String name;
public PoiTest() {
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public PoiTest(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
PoiTest poiTest = (PoiTest) o;
return age == poiTest.age && Objects.equals(name, poiTest.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PoiTest{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
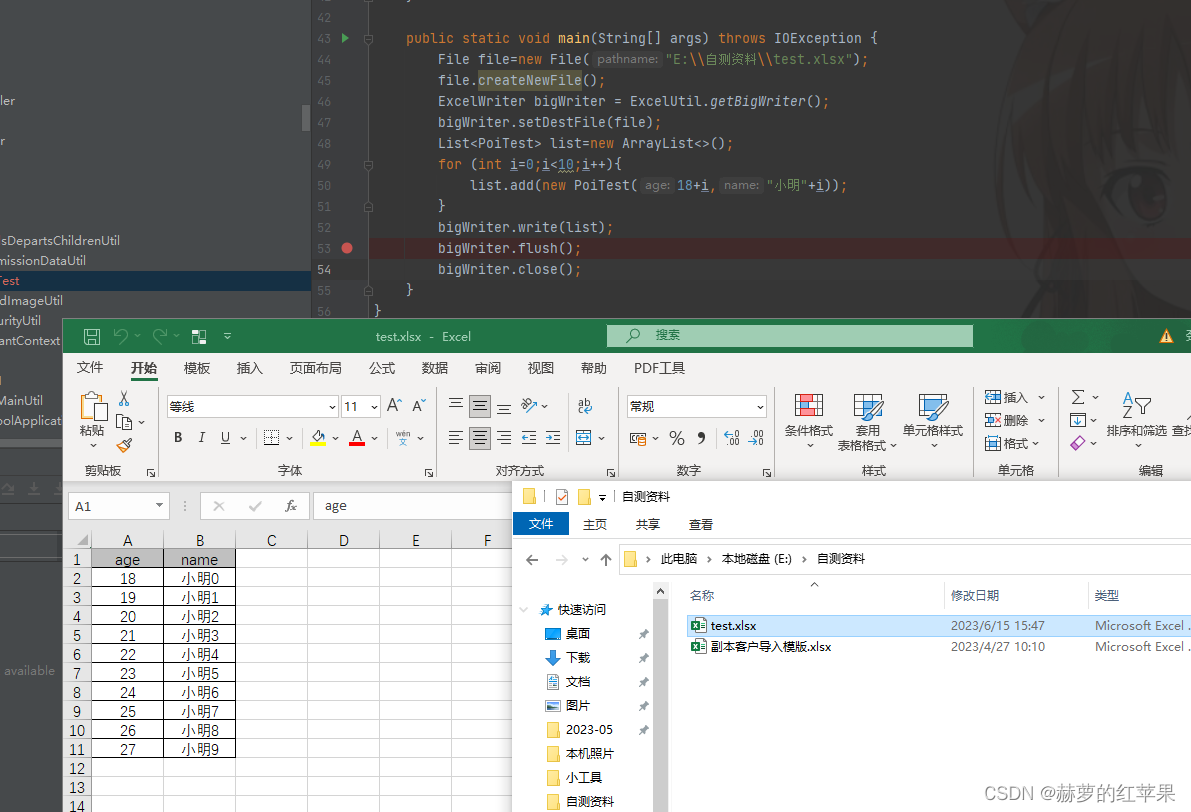
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//方式一
File file=new File("E:\\自测资料\\test.xlsx");
file.createNewFile();
ExcelWriter bigWriter = ExcelUtil.getBigWriter();
bigWriter.setDestFile(file);
List<PoiTest> list=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
list.add(new PoiTest(18+i,"小明"+i));
}
//将数据写入到ExcelWriter的workbook中
bigWriter.write(list);
//将数据写入excel表
bigWriter.flush();
//关闭资源
bigWriter.close();
// //方式二
// ExcelWriter bigWriter = ExcelUtil.getBigWriter();
// List<PoiTest> list=new ArrayList<>();
// for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
// list.add(new PoiTest(18+i,"小明"+i));
// }
// bigWriter.write(list);
//
// File file=new File("E:\\自测资料\\test.xlsx");
// file.createNewFile();
// OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream(file);
// bigWriter.flush(outputStream);
// bigWriter.close();
}
}
运行结果
三、基于hutool poi 实现从本地导入excel文件并转成对象列表
导入可以用map,list,对象来存储一行记录,推荐使用对象,方便后期使用。
具体实现逻辑
import cn.hutool.poi.excel.ExcelReader;
import cn.hutool.poi.excel.ExcelUtil;
import cn.hutool.poi.excel.ExcelWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class PoiTest {
private int age;
private String name;
public PoiTest() {
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public PoiTest(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
PoiTest poiTest = (PoiTest) o;
return age == poiTest.age && Objects.equals(name, poiTest.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PoiTest{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//方式一
File file=new File("E:\\自测资料\\test.xlsx");
ExcelReader reader = ExcelUtil.getReader(file);
//list中的每个map对应excel表中的一行记录,excel表第一行(字段名)当作key,value就是行记录对应列的值
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = reader.readAll();
for(Map map:maps){
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for(String key:set){
System.out.println(key+"-->"+map.get(key));
}
System.out.println("-----------");
}
reader.close();
//方式二
// //list返回,内部的list,每一个list代表一行记录,第一行记录可以当作表头。
// List<List<Object>> read = reader.read();
// for(List list:read){
// for (Object o:list){
// System.out.println(o);
// }
// System.out.println("-----");
// }
// reader.close();
//方式三
// //根据表头名和实体对象字段名来匹配记录,并返回实体列表
// File file=new File("E:\\自测资料\\test.xlsx");
// ExcelReader reader = ExcelUtil.getReader(file);
// /**
// * 第一个参数是表头所在行;第二个参数是读取数据开始行,会自动过滤掉表头行;第三个参数是实体类
// * 如果行记录所有列都为空,则会跳过该行记录,不创建对象。只要有一个列是不为空的,就会创建对象
// **/
// List<PoiTest> read = reader.read(0, 0, PoiTest.class);
// reader.close();
// for(PoiTest poiTest:read){
// System.out.println(poiTest);
// }
}
}
运行结果
map方式返回结果
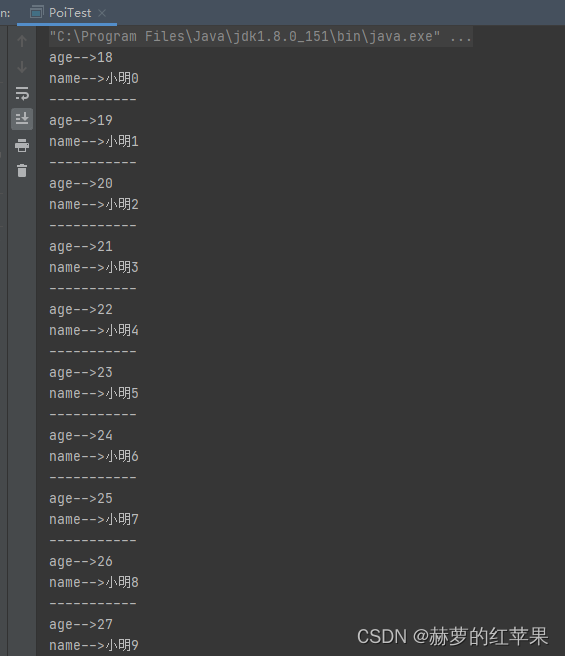
list方式返回结果:(excel中只要行记录存在,那么空的列会保存为空字符串)
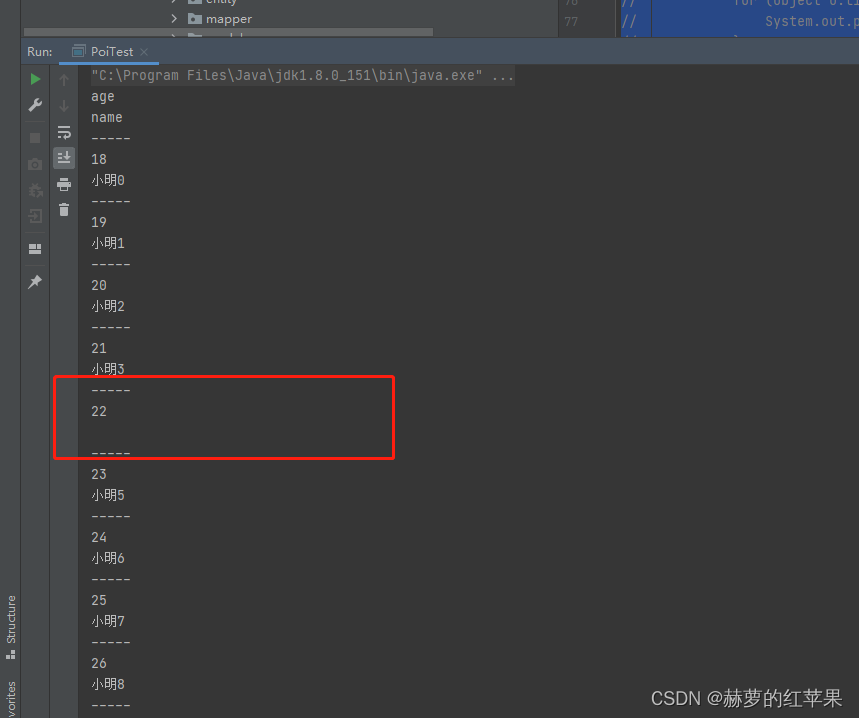
对象列表方式返回结果:

四、基于apache poi实现根据传入的类将excel的输入流解析成类对象(必学***)
这个就是我们日常使用的excel上传功能,因此非常有必要掌握。
一开始就想过可以通过传入类名,结合反射机制来创建对象,还可以获取对象的字段并赋值,实际上思路也确实大概这样。我从chat-gpt拿到了一个解析excel输入流的demo,不过这个demo并没有把excel表第一行当作表头;因此,我在这个基础上做了一些修改,实现了解析excel文件输入流成对象的工具类方法。(tips:支持的数据类型只能是比较基础的类型,不能是复杂的对象,复杂对象先json字符串接收,后面再自己转)
动态代理太酷啦!!!
实体类对象(也就是要解析成的对象)
package com.yumoxuan.pojo;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private Date birthday;
private double high;
public Person() {
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public double getHigh() {
return high;
}
public void setHigh(double high) {
this.high = high;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age &&
Double.compare(person.high, high) == 0 &&
Objects.equals(name, person.name) &&
Objects.equals(birthday, person.birthday);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name, birthday, high);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
", high=" + high +
'}';
}
}
具体实现逻辑
import com.yumoxuan.pojo.Person;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ExcelParser {
public static <T> List<T> parseExcelFile(InputStream inputStream, Class<T> clazz) {
List<T> objectList = new ArrayList<>();
try (Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream)) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); // Assuming the data is in the first sheet
// Get the field names from the class
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
List<String> objectFieldNameList= Arrays.stream(fields).map(o->o.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
//获取excel第一行作为对象的字段名
List<String> excelFieldNameList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean firstRow = true;
// Iterate over rows in the sheet
for (Row row : sheet) {
T object = clazz.newInstance(); // Create an instance of the class
// Map cell values to object fields
int i = 0;
for (Cell cell : row) {
if (firstRow) {
//获取excel表的第一行作为字段名
excelFieldNameList.add(cell.getStringCellValue());
continue;
}
if(!objectFieldNameList.contains(excelFieldNameList.get(i))){
//过滤excel中存在,但类中不存在的字段
continue;
}
//注意,这里如果尝试获取类里面没有的字段,会抛异常,因此excel表结构最好协商定下来。当然有了上一步的判断,这个问题不会发生
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(excelFieldNameList.get(i));
//开启编辑权限
field.setAccessible(true);
Class<?> fieldType = field.getType();
// 这里只需要把可能的数据类型都加上就可以了;不过一般也就那么基本数据类型加上字符串
if (fieldType == String.class) {
field.set(object, cell.getStringCellValue());
} else if (fieldType == int.class || fieldType == Integer.class) {
field.set(object, (int) cell.getNumericCellValue());
} else if (fieldType == boolean.class || fieldType == Boolean.class) {
field.set(object, cell.getBooleanCellValue());
} else if (fieldType == double.class || fieldType == Double.class) {
field.set(object, cell.getNumericCellValue());
} else if (fieldType == float.class || fieldType == Float.class) {
field.set(object, (float) cell.getNumericCellValue());
} else if (fieldType == Date.class) {
field.set(object, cell.getDateCellValue());
} else {
//暂不支持的类型
}
i++;
//关闭编辑权限
field.setAccessible(false);
}
if (!firstRow) {
objectList.add(object);
}
firstRow = false;
}
} catch (IOException | ReflectiveOperationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return objectList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("F:\\JAVA\\test.xlsx");
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
List<Person> people = ExcelParser.parseExcelFile(inputStream, Person.class);
for (Person person : people) {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
}
excel文件路径及数据
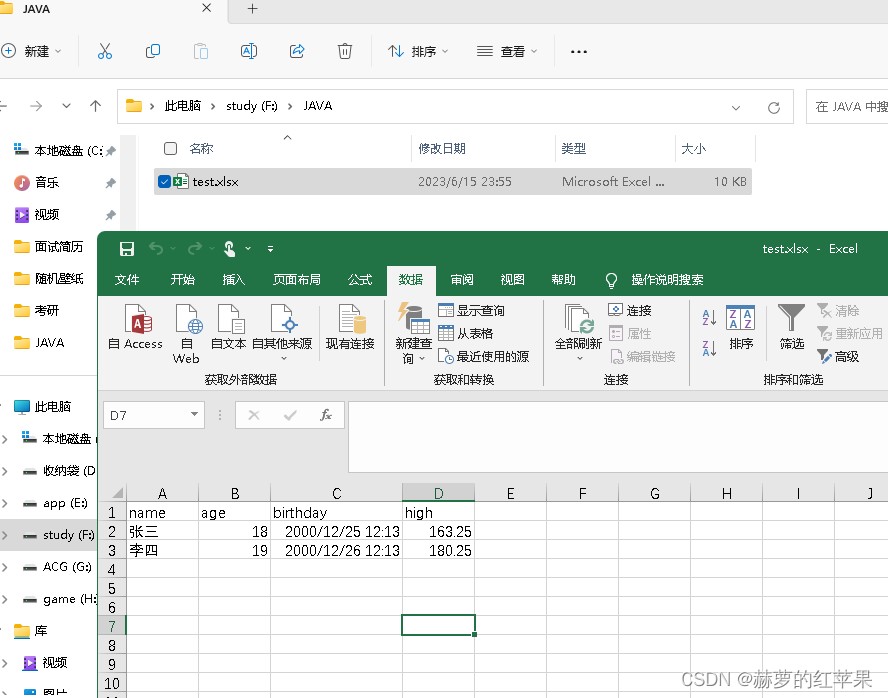
运行结果
Person{age=18, name=‘张三’, birthday=Mon Dec 25 12:13:00 CST 2000, high=163.25}
Person{age=19, name=‘李四’, birthday=Tue Dec 26 12:13:00 CST 2000, high=180.25}
学无止境,共勉。如果有帮到你,给我点个赞吧。
![【Java入门】-- Java基础详解之 [数组、冒泡排序]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ab4fbf404e044c9cabbdd8d7ab2329d7.png)




![[n00bzCTF 2023] CPR 全](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9984f416418e43e7837cde50f299679b.png)