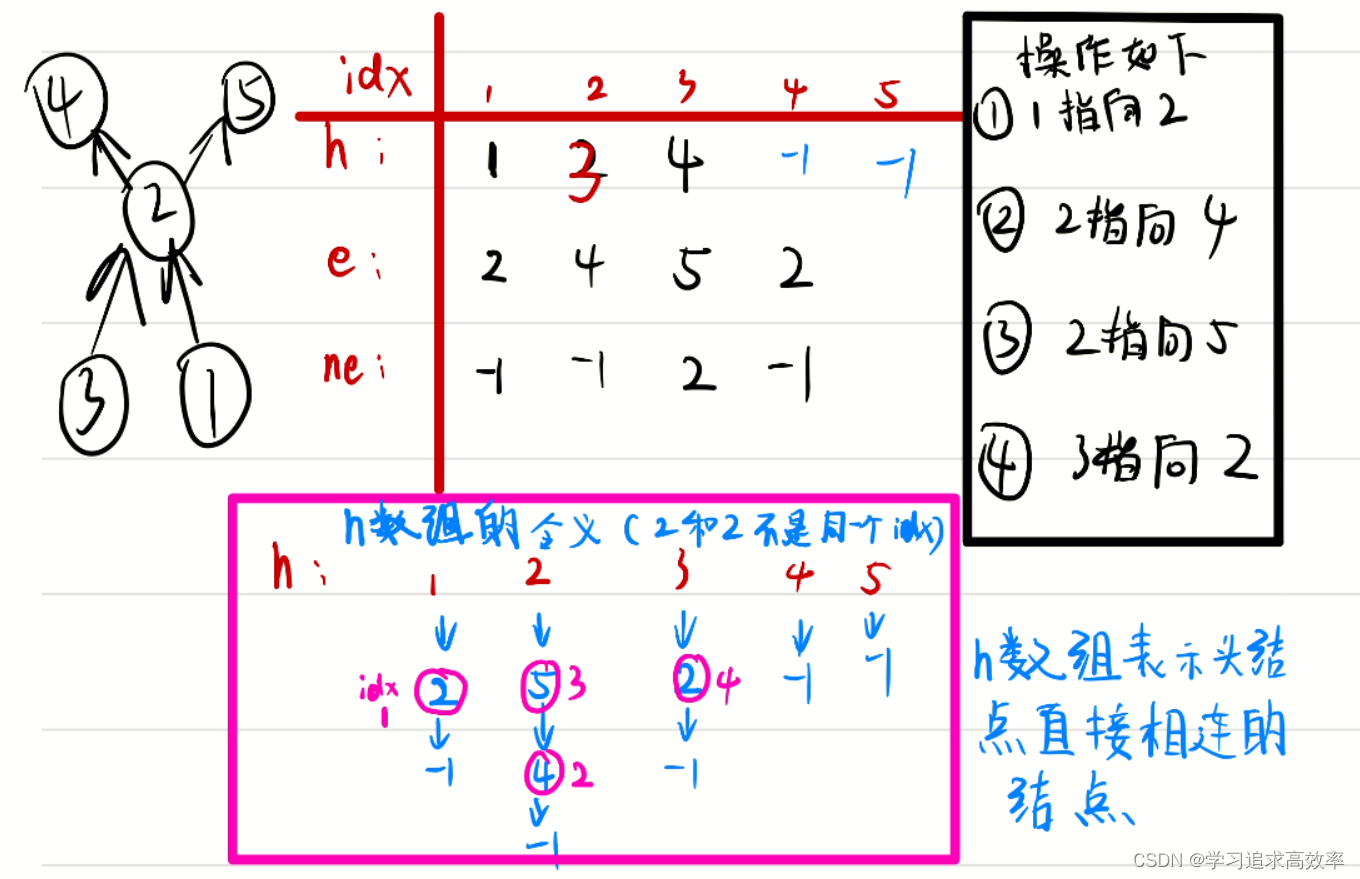
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,其中的值均为非负整数,代表二维高度图每个单元的高度,请计算图中形状最多能接多少体积的雨水。
示例 1:

输入: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] 输出: 4 解释: 下雨后,雨水将会被上图蓝色的方块中。总的接雨水量为1+2+1=4。
示例 2:
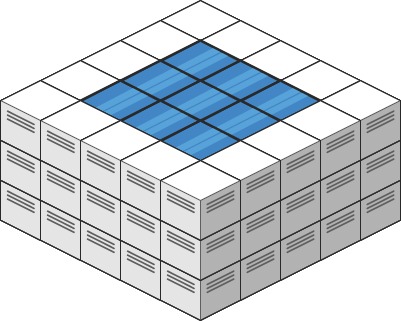
输入: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]] 输出: 10
提示:
m == heightMap.lengthn == heightMap[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 104
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap)
{
//1.把外围的点放到优先队列,优先队列把最小优先出队
//2.每天点都要四个方面都要访问
typedef pair<int, int> qp;
priority_queue<qp, vector<qp>, greater<qp> >que;//从小到大排序
vector<int> direction = { -1,0,1,0,-1 };//左、上、右、下
int row = heightMap.size();
int col = heightMap[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>>visitedVec(row, vector<bool>(col, false));
//
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (true == visitedVec[i][j])
{
continue;
}
if (i == 0 || i == row - 1 || j == 0 || j == col - 1)//外围点保存
{
que.push(qp{ heightMap[i][j],i*col + j });
visitedVec[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
int result = 0;
while (!que.empty())
{
qp top =que.top();
que.pop();
int nx = top.second / col;
int ny = top.second % col;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = nx+direction[k];
int y = ny+direction[k + 1];
if (x == 0 || x == row - 1 || y == 0 || y == col - 1)//外围
{
continue;
}
if (x<0 || x> row - 1 || y<0 || y>col - 1)//超出范围
{
continue;
}
if (visitedVec[x][y] == true)
{
continue;
}
if (heightMap[x][y]>top.first)
{
que.push(qp{ heightMap[x][y],x*col + y });
visitedVec[x][y] = true;
}
else
{
result += top.first - heightMap[x][y];
heightMap[x][y] = top.first;
que.push(qp{ heightMap[x][y],x*col + y });
visitedVec[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
return result;
}