视觉SLAM十四讲----ch8的实践操作及避坑
- 0.实践前小知识介绍
- 1. 实践操作前的准备工作
- 2. 实践过程
- 2.1 LK光流
- 2.2 直接法
- 3. 遇到的问题及解决办法
- 3.1 编译时遇到的问题
0.实践前小知识介绍
里程计的历史渊源是什么?
里程计是一种用来测量车辆或机器人行驶距离的装置,它通常通过检测车辆轮子或机器人轮子的旋转来进行测量。里程计的历史可以追溯到17世纪早期,当时人们开始使用机械装置来测量车辆行驶的距离。这些装置通常使用一个机械计数器,它们可以在车轮旋转的过程中记录里程数。18世纪末期,发明家托马斯·戈德史密斯发明了一种称为“奥多米特”的装置,它使用一个机械计数器来记录马车或自行车行驶的里程。这个装置被认为是现代里程计的早期形式。
随着时间的推移,里程计逐渐发展成为电子化和计算机化的设备。现代车辆和机器人通常使用激光或红外线传感器来测量轮子的旋转,并将数据传输到计算机或控制系统中。总的来说,里程计的历史经历了从机械装置到电子化和计算机化的过程。
1. 实践操作前的准备工作
- 在终端中进入ch8文件夹下,顺序执行以下命令进行编译。
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
//注意,j8还是其他主要看自己的电脑情况
make -j8
- 在build文件中进行运行。
注意: 在make之前,尽量将文件中的获取图片的路径都更改以下,否则后期运行有问题还得再更改,再make。
2. 实践过程
2.1 LK光流
代码:
//
// Created by Xiang on 2017/12/19.
//
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <chrono>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
//添加头文件
#include <opencv2/imgproc/types_c.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
string file_1 = "/home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch8/LK1.png"; // first image
string file_2 = "/home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch8/LK2.png"; // second image
/// Optical flow tracker and interface
class OpticalFlowTracker {
public:
OpticalFlowTracker(
const Mat &img1_,
const Mat &img2_,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1_,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2_,
vector<bool> &success_,
bool inverse_ = true, bool has_initial_ = false) :
img1(img1_), img2(img2_), kp1(kp1_), kp2(kp2_), success(success_), inverse(inverse_),
has_initial(has_initial_) {}
void calculateOpticalFlow(const Range &range);
private:
const Mat &img1;
const Mat &img2;
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1;
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2;
vector<bool> &success;
bool inverse = true;
bool has_initial = false;
};
/**
* single level optical flow
* @param [in] img1 the first image
* @param [in] img2 the second image
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [in|out] kp2 keypoints in img2, if empty, use initial guess in kp1
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse use inverse formulation?
*/
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse = false,
bool has_initial_guess = false
);
/**
* multi level optical flow, scale of pyramid is set to 2 by default
* the image pyramid will be create inside the function
* @param [in] img1 the first pyramid
* @param [in] img2 the second pyramid
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [out] kp2 keypoints in img2
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse set true to enable inverse formulation
*/
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse = false
);
/**
* get a gray scale value from reference image (bi-linear interpolated)
* @param img
* @param x
* @param y
* @return the interpolated value of this pixel
*/
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
// boundary check
if (x < 0) x = 0;
if (y < 0) y = 0;
if (x >= img.cols - 1) x = img.cols - 2;
if (y >= img.rows - 1) y = img.rows - 2;
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
int x_a1 = std::min(img.cols - 1, int(x) + 1);
int y_a1 = std::min(img.rows - 1, int(y) + 1);
return (1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * img.at<uchar>(y, x)
+ xx * (1 - yy) * img.at<uchar>(y, x_a1)
+ (1 - xx) * yy * img.at<uchar>(y_a1, x)
+ xx * yy * img.at<uchar>(y_a1, x_a1);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// images, note they are CV_8UC1, not CV_8UC3
Mat img1 = imread(file_1, 0);
Mat img2 = imread(file_2, 0);
// key points, using GFTT here.
vector<KeyPoint> kp1;
Ptr<GFTTDetector> detector = GFTTDetector::create(500, 0.01, 20); // maximum 500 keypoints
detector->detect(img1, kp1);
// now lets track these key points in the second image
// first use single level LK in the validation picture
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_single;
vector<bool> success_single;
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_single, success_single);
// then test multi-level LK
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_multi;
vector<bool> success_multi;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowMultiLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_multi, success_multi, true);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by gauss-newton: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// use opencv's flow for validation
vector<Point2f> pt1, pt2;
for (auto &kp: kp1) pt1.push_back(kp.pt);
vector<uchar> status;
vector<float> error;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(img1, img2, pt1, pt2, status, error);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by opencv: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// plot the differences of those functions
Mat img2_single;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_single, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_single.size(); i++) {
if (success_single[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_single, kp2_single[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_single, kp1[i].pt, kp2_single[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_multi;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_multi, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_multi.size(); i++) {
if (success_multi[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_multi, kp2_multi[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_multi, kp1[i].pt, kp2_multi[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_CV;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_CV, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < pt2.size(); i++) {
if (status[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_CV, pt2[i], 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_CV, pt1[i], pt2[i], cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
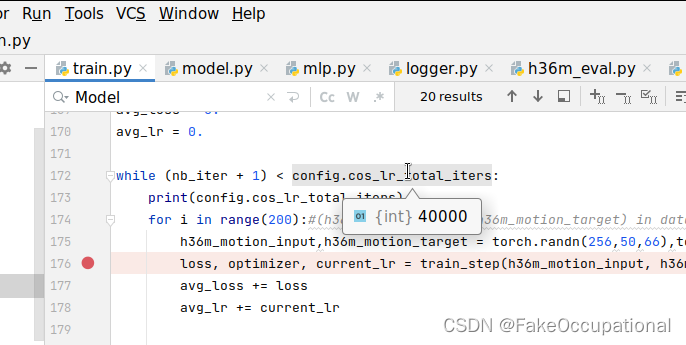
}
}
cv::imshow("tracked single level", img2_single);
cv::imshow("tracked multi level", img2_multi);
cv::imshow("tracked by opencv", img2_CV);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse, bool has_initial) {
kp2.resize(kp1.size());
success.resize(kp1.size());
OpticalFlowTracker tracker(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, success, inverse, has_initial);
parallel_for_(Range(0, kp1.size()),
std::bind(&OpticalFlowTracker::calculateOpticalFlow, &tracker, placeholders::_1));
}
void OpticalFlowTracker::calculateOpticalFlow(const Range &range) {
// parameters
int half_patch_size = 4;
int iterations = 10;
for (size_t i = range.start; i < range.end; i++) {
auto kp = kp1[i];
double dx = 0, dy = 0; // dx,dy need to be estimated
if (has_initial) {
dx = kp2[i].pt.x - kp.pt.x;
dy = kp2[i].pt.y - kp.pt.y;
}
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
bool succ = true; // indicate if this point succeeded
// Gauss-Newton iterations
Eigen::Matrix2d H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero(); // hessian
Eigen::Vector2d b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero(); // bias
Eigen::Vector2d J; // jacobian
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
if (inverse == false) {
H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero();
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
} else {
// only reset b
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
}
cost = 0;
// compute cost and jacobian
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x < half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y < half_patch_size; y++) {
double error = GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + x + dx, kp.pt.y + y + dy);; // Jacobian
if (inverse == false) {
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x + 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x - 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y - 1))
);
} else if (iter == 0) {
// in inverse mode, J keeps same for all iterations
// NOTE this J does not change when dx, dy is updated, so we can store it and only compute error
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x + 1, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x - 1, kp.pt.y + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y - 1))
);
}
// compute H, b and set cost;
b += -error * J;
cost += error * error;
if (inverse == false || iter == 0) {
// also update H
H += J * J.transpose();
}
}
// compute update
Eigen::Vector2d update = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (std::isnan(update[0])) {
// sometimes occurred when we have a black or white patch and H is irreversible
cout << "update is nan" << endl;
succ = false;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost > lastCost) {
break;
}
// update dx, dy
dx += update[0];
dy += update[1];
lastCost = cost;
succ = true;
if (update.norm() < 1e-2) {
// converge
break;
}
}
success[i] = succ;
// set kp2
kp2[i].pt = kp.pt + Point2f(dx, dy);
}
}
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse) {
// parameters
int pyramids = 4;
double pyramid_scale = 0.5;
double scales[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125};
// create pyramids
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
vector<Mat> pyr1, pyr2; // image pyramids
for (int i = 0; i < pyramids; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pyr1.push_back(img1);
pyr2.push_back(img2);
} else {
Mat img1_pyr, img2_pyr;
cv::resize(pyr1[i - 1], img1_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr1[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr1[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
cv::resize(pyr2[i - 1], img2_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr2[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr2[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
pyr1.push_back(img1_pyr);
pyr2.push_back(img2_pyr);
}
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "build pyramid time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// coarse-to-fine LK tracking in pyramids
vector<KeyPoint> kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr;
for (auto &kp:kp1) {
auto kp_top = kp;
kp_top.pt *= scales[pyramids - 1];
kp1_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
kp2_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
}
for (int level = pyramids - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
// from coarse to fine
success.clear();
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(pyr1[level], pyr2[level], kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr, success, inverse, true);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "track pyr " << level << " cost time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
if (level > 0) {
for (auto &kp: kp1_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
for (auto &kp: kp2_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
}
}
for (auto &kp: kp2_pyr)
kp2.push_back(kp);
}
在build中执行语句:
./optical_flow
运行结果:
运行后展示使用opencv、单层、多层的追踪
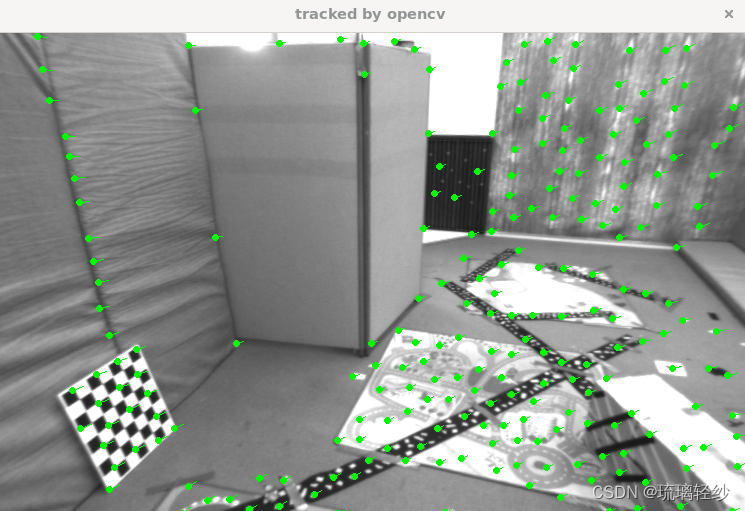
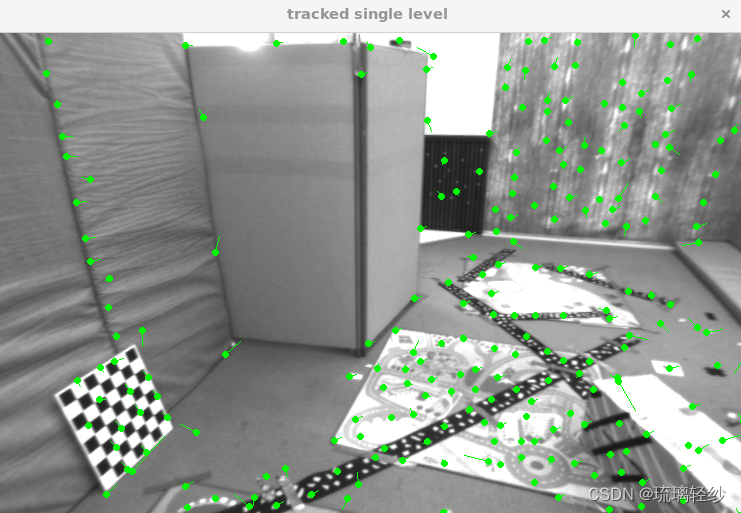
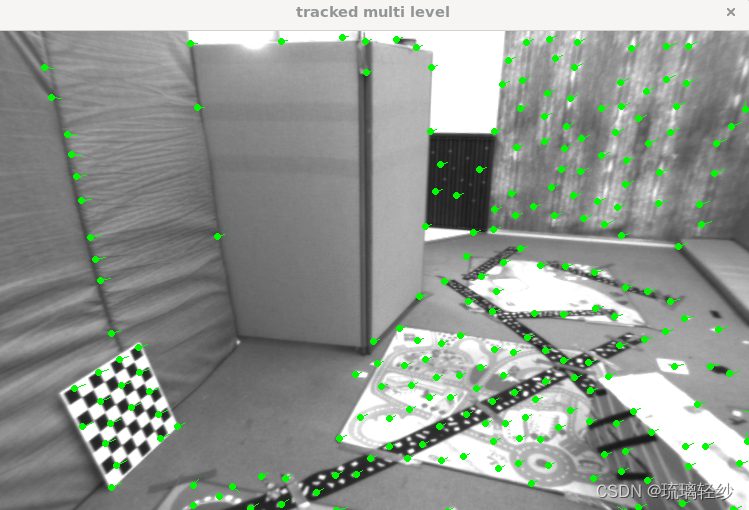
同时终端输出:
build pyramid time: 0.0072683
track pyr 3 cost time: 0.0004321
track pyr 2 cost time: 0.0002794
track pyr 1 cost time: 0.0002624
track pyr 0 cost time: 0.0003014
optical flow by gauss-newton: 0.0087955
optical flow by opencv: 0.0054821
2.2 直接法
代码:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
//添加头文件
#include <opencv2/imgproc/types_c.h>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector2d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector2d>> VecVector2d;
// Camera intrinsics
double fx = 718.856, fy = 718.856, cx = 607.1928, cy = 185.2157;
// baseline
double baseline = 0.573;
// paths
string left_file = "/home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch8/left.png";
string disparity_file = "/home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch8/disparity.png";
boost::format fmt_others("/home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch8/%06d.png"); // other files
// useful typedefs
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> Matrix6d;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> Matrix26d;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
/// class for accumulator jacobians in parallel
class JacobianAccumulator {
public:
JacobianAccumulator(
const cv::Mat &img1_,
const cv::Mat &img2_,
const VecVector2d &px_ref_,
const vector<double> depth_ref_,
Sophus::SE3d &T21_) :
img1(img1_), img2(img2_), px_ref(px_ref_), depth_ref(depth_ref_), T21(T21_) {
projection = VecVector2d(px_ref.size(), Eigen::Vector2d(0, 0));
}
/// accumulate jacobians in a range
void accumulate_jacobian(const cv::Range &range);
/// get hessian matrix
Matrix6d hessian() const { return H; }
/// get bias
Vector6d bias() const { return b; }
/// get total cost
double cost_func() const { return cost; }
/// get projected points
VecVector2d projected_points() const { return projection; }
/// reset h, b, cost to zero
void reset() {
H = Matrix6d::Zero();
b = Vector6d::Zero();
cost = 0;
}
private:
const cv::Mat &img1;
const cv::Mat &img2;
const VecVector2d &px_ref;
const vector<double> depth_ref;
Sophus::SE3d &T21;
VecVector2d projection; // projected points
std::mutex hessian_mutex;
Matrix6d H = Matrix6d::Zero();
Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();
double cost = 0;
};
/**
* pose estimation using direct method
* @param img1
* @param img2
* @param px_ref
* @param depth_ref
* @param T21
*/
void DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21
);
/**
* pose estimation using direct method
* @param img1
* @param img2
* @param px_ref
* @param depth_ref
* @param T21
*/
void DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21
);
// bilinear interpolation
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
// boundary check
if (x < 0) x = 0;
if (y < 0) y = 0;
if (x >= img.cols) x = img.cols - 1;
if (y >= img.rows) y = img.rows - 1;
uchar *data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
cv::Mat left_img = cv::imread(left_file, 0);
cv::Mat disparity_img = cv::imread(disparity_file, 0);
// let's randomly pick pixels in the first image and generate some 3d points in the first image's frame
cv::RNG rng;
int nPoints = 2000;
int boarder = 20;
VecVector2d pixels_ref;
vector<double> depth_ref;
// generate pixels in ref and load depth data
for (int i = 0; i < nPoints; i++) {
int x = rng.uniform(boarder, left_img.cols - boarder); // don't pick pixels close to boarder
int y = rng.uniform(boarder, left_img.rows - boarder); // don't pick pixels close to boarder
int disparity = disparity_img.at<uchar>(y, x);
double depth = fx * baseline / disparity; // you know this is disparity to depth
depth_ref.push_back(depth);
pixels_ref.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(x, y));
}
// estimates 01~05.png's pose using this information
Sophus::SE3d T_cur_ref;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) { // 1~10
cv::Mat img = cv::imread((fmt_others % i).str(), 0);
// try single layer by uncomment this line
// DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(left_img, img, pixels_ref, depth_ref, T_cur_ref);
DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(left_img, img, pixels_ref, depth_ref, T_cur_ref);
}
return 0;
}
void DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21) {
const int iterations = 10;
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
auto t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
JacobianAccumulator jaco_accu(img1, img2, px_ref, depth_ref, T21);
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
jaco_accu.reset();
cv::parallel_for_(cv::Range(0, px_ref.size()),
std::bind(&JacobianAccumulator::accumulate_jacobian, &jaco_accu, std::placeholders::_1));
Matrix6d H = jaco_accu.hessian();
Vector6d b = jaco_accu.bias();
// solve update and put it into estimation
Vector6d update = H.ldlt().solve(b);;
T21 = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update) * T21;
cost = jaco_accu.cost_func();
if (std::isnan(update[0])) {
// sometimes occurred when we have a black or white patch and H is irreversible
cout << "update is nan" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost > lastCost) {
cout << "cost increased: " << cost << ", " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
if (update.norm() < 1e-3) {
// converge
break;
}
lastCost = cost;
cout << "iteration: " << iter << ", cost: " << cost << endl;
}
cout << "T21 = \n" << T21.matrix() << endl;
auto t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "direct method for single layer: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// plot the projected pixels here
cv::Mat img2_show;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_show, CV_GRAY2BGR);
VecVector2d projection = jaco_accu.projected_points();
for (size_t i = 0; i < px_ref.size(); ++i) {
auto p_ref = px_ref[i];
auto p_cur = projection[i];
if (p_cur[0] > 0 && p_cur[1] > 0) {
cv::circle(img2_show, cv::Point2f(p_cur[0], p_cur[1]), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_show, cv::Point2f(p_ref[0], p_ref[1]), cv::Point2f(p_cur[0], p_cur[1]),
cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
cv::imshow("current", img2_show);
cv::waitKey();
}
void JacobianAccumulator::accumulate_jacobian(const cv::Range &range) {
// parameters
const int half_patch_size = 1;
int cnt_good = 0;
Matrix6d hessian = Matrix6d::Zero();
Vector6d bias = Vector6d::Zero();
double cost_tmp = 0;
for (size_t i = range.start; i < range.end; i++) {
// compute the projection in the second image
Eigen::Vector3d point_ref =
depth_ref[i] * Eigen::Vector3d((px_ref[i][0] - cx) / fx, (px_ref[i][1] - cy) / fy, 1);
Eigen::Vector3d point_cur = T21 * point_ref;
if (point_cur[2] < 0) // depth invalid
continue;
float u = fx * point_cur[0] / point_cur[2] + cx, v = fy * point_cur[1] / point_cur[2] + cy;
if (u < half_patch_size || u > img2.cols - half_patch_size || v < half_patch_size ||
v > img2.rows - half_patch_size)
continue;
projection[i] = Eigen::Vector2d(u, v);
double X = point_cur[0], Y = point_cur[1], Z = point_cur[2],
Z2 = Z * Z, Z_inv = 1.0 / Z, Z2_inv = Z_inv * Z_inv;
cnt_good++;
// and compute error and jacobian
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x <= half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y <= half_patch_size; y++) {
double error = GetPixelValue(img1, px_ref[i][0] + x, px_ref[i][1] + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v + y);
Matrix26d J_pixel_xi;
Eigen::Vector2d J_img_pixel;
J_pixel_xi(0, 0) = fx * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 1) = 0;
J_pixel_xi(0, 2) = -fx * X * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 3) = -fx * X * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 4) = fx + fx * X * X * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 5) = -fx * Y * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 0) = 0;
J_pixel_xi(1, 1) = fy * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 2) = -fy * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 3) = -fy - fy * Y * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 4) = fy * X * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 5) = fy * X * Z_inv;
J_img_pixel = Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, u + 1 + x, v + y) - GetPixelValue(img2, u - 1 + x, v + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v + 1 + y) - GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v - 1 + y))
);
// total jacobian
Vector6d J = -1.0 * (J_img_pixel.transpose() * J_pixel_xi).transpose();
hessian += J * J.transpose();
bias += -error * J;
cost_tmp += error * error;
}
}
if (cnt_good) {
// set hessian, bias and cost
unique_lock<mutex> lck(hessian_mutex);
H += hessian;
b += bias;
cost += cost_tmp / cnt_good;
}
}
void DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21) {
// parameters
int pyramids = 4;
double pyramid_scale = 0.5;
double scales[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125};
// create pyramids
vector<cv::Mat> pyr1, pyr2; // image pyramids
for (int i = 0; i < pyramids; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pyr1.push_back(img1);
pyr2.push_back(img2);
} else {
cv::Mat img1_pyr, img2_pyr;
cv::resize(pyr1[i - 1], img1_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr1[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr1[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
cv::resize(pyr2[i - 1], img2_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr2[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr2[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
pyr1.push_back(img1_pyr);
pyr2.push_back(img2_pyr);
}
}
double fxG = fx, fyG = fy, cxG = cx, cyG = cy; // backup the old values
for (int level = pyramids - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
VecVector2d px_ref_pyr; // set the keypoints in this pyramid level
for (auto &px: px_ref) {
px_ref_pyr.push_back(scales[level] * px);
}
// scale fx, fy, cx, cy in different pyramid levels
fx = fxG * scales[level];
fy = fyG * scales[level];
cx = cxG * scales[level];
cy = cyG * scales[level];
DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(pyr1[level], pyr2[level], px_ref_pyr, depth_ref, T21);
}
}
在build中执行语句: ./direct_method
运行结果:
运行结果图可以看出追踪流,需要不停的对窗口关闭,可以看出来其变化。
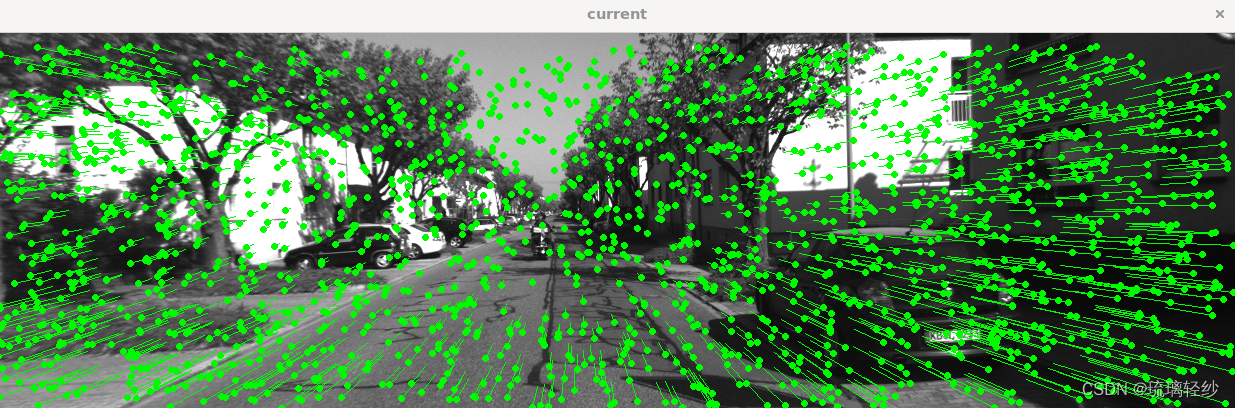

终端输出相应信息:
iteration: 0, cost: 1.59797e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 651716
iteration: 2, cost: 243255
iteration: 3, cost: 176884
cost increased: 183909, 176884
T21 =
0.999991 0.00245009 0.0033858 0.00303273
-0.00245906 0.999993 0.00264927 0.000424829
-0.00337929 -0.00265757 0.999991 -0.730917
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0016574
iteration: 0, cost: 186361
T21 =
0.999989 0.00302157 0.00347121 0.000762356
-0.00302936 0.999993 0.00224074 0.00666315
-0.00346442 -0.00225123 0.999991 -0.728227
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.002358
iteration: 0, cost: 247529
iteration: 1, cost: 229117
T21 =
0.999991 0.00251345 0.00346578 -0.00270253
-0.00252155 0.999994 0.00233534 0.00243076
-0.00345989 -0.00234406 0.999991 -0.734719
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00523089
iteration: 0, cost: 348441
T21 =
0.999991 0.00248082 0.00343389 -0.00373965
-0.00248836 0.999994 0.00219448 0.00304522
-0.00342843 -0.00220301 0.999992 -0.732343
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0012425
iteration: 0, cost: 1.315e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 906037
iteration: 2, cost: 603626
iteration: 3, cost: 399435
iteration: 4, cost: 280889
iteration: 5, cost: 237691
cost increased: 238395, 237691
T21 =
0.999971 0.000902974 0.00759567 0.00772499
-0.000938067 0.999989 0.00461783 0.00179863
-0.00759142 -0.00462482 0.99996 -1.46052
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0045787
iteration: 0, cost: 355480
iteration: 1, cost: 348267
cost increased: 348423, 348267
T21 =
0.999972 0.00120085 0.00742895 0.0085892
-0.00123022 0.999991 0.00395007 0.00531883
-0.00742414 -0.0039591 0.999965 -1.46883
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0009226
iteration: 0, cost: 443225
iteration: 1, cost: 435054
cost increased: 437537, 435054
T21 =
0.999971 0.000737127 0.00764046 -0.000242531
-0.000767091 0.999992 0.00391957 0.00279348
-0.00763751 -0.00392532 0.999963 -1.4818
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0009165
iteration: 0, cost: 501709
iteration: 1, cost: 463084
cost increased: 463953, 463084
T21 =
0.999971 0.000695392 0.00758989 -0.00249798
-0.000723685 0.999993 0.00372567 0.00395279
-0.00758725 -0.00373106 0.999964 -1.48132
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0008786
iteration: 0, cost: 1.37107e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.10683e+06
iteration: 2, cost: 921990
iteration: 3, cost: 794740
iteration: 4, cost: 601342
iteration: 5, cost: 559319
iteration: 6, cost: 394434
iteration: 7, cost: 363978
cost increased: 374118, 363978
T21 =
0.999945 0.00160897 0.0103684 0.0493737
-0.00166631 0.999983 0.00552457 0.0132374
-0.0103594 -0.00554155 0.999931 -2.18064
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0020563
iteration: 0, cost: 461649
iteration: 1, cost: 443603
iteration: 2, cost: 436513
iteration: 3, cost: 432080
iteration: 4, cost: 423494
cost increased: 431930, 423494
T21 =
0.999938 0.00146627 0.011054 0.0282033
-0.00152599 0.999984 0.0053958 0.00256267
-0.0110459 -0.00541233 0.999924 -2.21468
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0015141
iteration: 0, cost: 646880
iteration: 1, cost: 614318
iteration: 2, cost: 613113
cost increased: 620133, 613113
T21 =
0.999935 0.00152579 0.0112714 0.0183767
-0.00158773 0.999984 0.00548783 -0.00540064
-0.0112629 -0.00550537 0.999921 -2.23461
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0011636
iteration: 0, cost: 924370
iteration: 1, cost: 828022
iteration: 2, cost: 821445
iteration: 3, cost: 803411
cost increased: 811368, 803411
T21 =
0.999934 0.00125001 0.0114068 0.00255272
-0.00131019 0.999985 0.00527034 -0.000605904
-0.0114001 -0.00528494 0.999921 -2.24055
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0015292
iteration: 0, cost: 1.43709e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.31501e+06
iteration: 2, cost: 1.06723e+06
iteration: 3, cost: 938977
iteration: 4, cost: 788005
iteration: 5, cost: 680776
iteration: 6, cost: 605861
iteration: 7, cost: 548408
iteration: 8, cost: 516721
iteration: 9, cost: 513621
T21 =
0.999872 -0.000312873 0.0159856 0.0259369
0.000197362 0.999974 0.00722705 -0.00480823
-0.0159874 -0.00722297 0.999846 -2.96617
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0048151
iteration: 0, cost: 640692
iteration: 1, cost: 616653
iteration: 2, cost: 610486
cost increased: 615297, 610486
T21 =
0.999864 -0.000319108 0.0164719 0.00993795
0.000208632 0.999977 0.00670821 -0.00627072
-0.0164737 -0.00670386 0.999842 -3.005
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0009756
iteration: 0, cost: 848724
iteration: 1, cost: 823518
iteration: 2, cost: 780844
cost increased: 802765, 780844
T21 =
0.999865 -0.000227727 0.0164536 0.0022434
0.000124997 0.99998 0.0062444 -0.00399514
-0.0164547 -0.00624149 0.999845 -3.01734
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0010828
iteration: 0, cost: 1.26838e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.16447e+06
cost increased: 1.19957e+06, 1.16447e+06
T21 =
0.999865 0.00017071 0.0164584 -0.00906366
-0.000267333 0.999983 0.00586871 0.000576184
-0.0164571 -0.00587231 0.999847 -3.02444
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0008361
iteration: 0, cost: 1.64476e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.49383e+06
iteration: 2, cost: 1.23318e+06
iteration: 3, cost: 950472
iteration: 4, cost: 794112
iteration: 5, cost: 686345
iteration: 6, cost: 671817
iteration: 7, cost: 659908
iteration: 8, cost: 652671
iteration: 9, cost: 605440
T21 =
0.999803 0.00057056 0.0198394 0.0427397
-0.000712283 0.999974 0.00713717 0.0136135
-0.0198348 -0.00714989 0.999778 -3.76444
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0088727
iteration: 0, cost: 983836
iteration: 1, cost: 948750
iteration: 2, cost: 945444
iteration: 3, cost: 895561
cost increased: 898341, 895561
T21 =
0.99978 0.000643056 0.0209471 0.000477452
-0.000787155 0.999976 0.00687165 0.00707341
-0.0209422 -0.00688663 0.999757 -3.83472
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0012023
iteration: 0, cost: 1.27161e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.22543e+06
iteration: 2, cost: 1.04807e+06
cost increased: 1.2001e+06, 1.04807e+06
T21 =
0.999777 0.00108579 0.0210816 -0.00872002
-0.00121752 0.99998 0.00623637 0.0124058
-0.0210744 -0.00626065 0.999758 -3.85459
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0010238
iteration: 0, cost: 1.67716e+06
iteration: 1, cost: 1.64927e+06
iteration: 2, cost: 1.63771e+06
cost increased: 1.64371e+06, 1.63771e+06
T21 =
0.999786 0.00136909 0.0206569 -0.00336234
-0.00149442 0.999981 0.0060529 0.00874311
-0.0206482 -0.00608247 0.999768 -3.86001
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.001018
3. 遇到的问题及解决办法
3.1 编译时遇到的问题
- 在make时出现的有关opencv的问题:
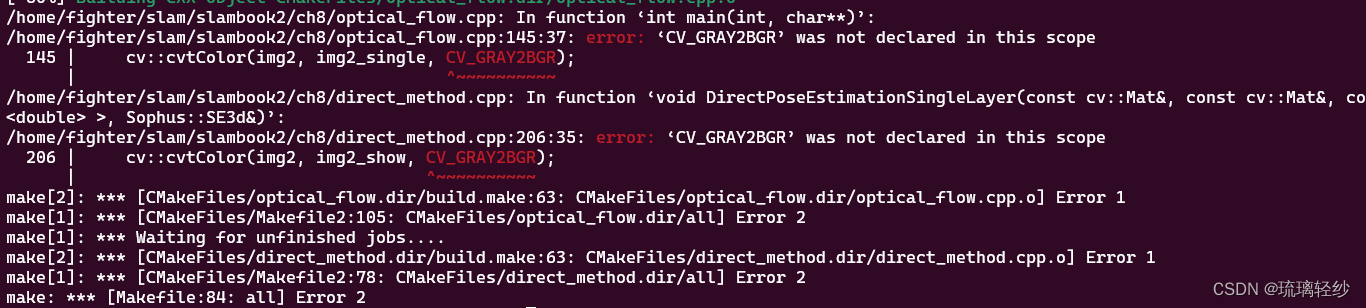
解决办法:按照之前的方法解决即可。查询链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44164791/article/details/131210608?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502