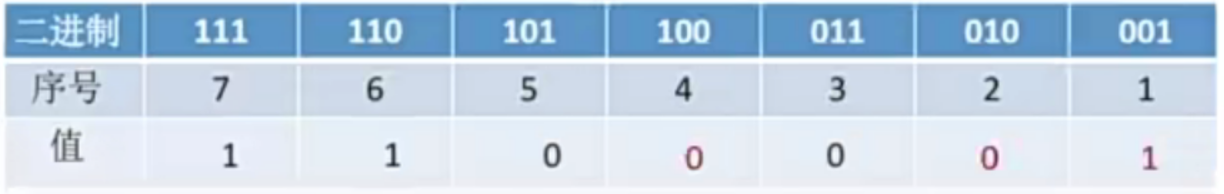
比较含退格的字符串
给定 s 和 t 两个字符串,当它们分别被输入到空白的文本编辑器后,如果两者相等,返回 true 。# 代表退格字符。
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String S, String T) {
int S_Len = S.length(), T_Len = T.length();
char[] S_arr = S.toCharArray(), T_arr = T.toCharArray();
int skipS = 0, skipT = 0;
for (int i = S_Len - 1, j = T_Len - 1; i >= 0 || j >= 0; i--, j--) {
while (i >= 0) {
if (S_arr[i] == '#') {
skipS++;
i--;
} else if (skipS > 0) {
// 遇到字符, 但由于需要回退, 所以还需要前移1位
skipS--;
i--;
} else {
// 遇到字符, 且不能回退了, 所以需要比对这个字符是否与T对应位置上的字符相等
break;
}
}
while (j >= 0) {
if (T_arr[j] == '#') {
skipT++;
j--;
} else if (skipT > 0) {
skipT--;
j--;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (S_arr[i] != T_arr[j]) return false;
} else if (i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
// 有其中一方已经遍历完整个字符串, 但另外一方没有遍历完整个字符串, 直接返回false
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}有序数组的平方
输入:nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10]
输出:[0,1,9,16,100]
解释:平方后,数组变为 [16,1,0,9,100]
排序后,数组变为 [0,1,9,16,100]
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int right = nums.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int index = result.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
result[index--] = nums[left] * nums[left];
++left;
} else {
result[index--] = nums[right] * nums[right];
--right;
}
}
return result;
}
}76. 最小覆盖子串
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" 输出:"BANC"
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (t.length() > s.length()) {
return "";
}
Map<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();// 统计所需字符及其数量
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
need.put(t.charAt(i), need.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);
}
Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();// 统计窗口内的字符及其数量
int valid = 0;// 满足条件的字符数
int l = 0, r = 0;
int min_LEN = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min_LEFT = 0;//记录最小窗口的长度和开始位置
while (r < s.length()) {
// 扩大右边界
char ch = s.charAt(r);
r++;
window.put(ch, window.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
if (window.get(ch).equals(need.get(ch))) {
valid++;
}
// 满足条件时缩小窗口
while (valid == need.size()) {
// 记录当前窗口
if (r - l < min_LEN) {
min_LEN = r - l;
min_LEFT = l;
}
// 缩小左边界
char c = s.charAt(l);
if (window.get(c).equals(need.get(c))) {
valid--;
}
window.put(c, window.get(c) - 1);
l++;
}
}
return min_LEN == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(min_LEFT, min_LEFT + min_LEN);
}
}438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
输入: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
输出: [0,6]
解释:
起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "cba", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。
起始索引等于 6 的子串是 "bac", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
int sLen = s.length();
int pLen = p.length();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] sBuc = new int[26]; //待处理词频桶
int[] pBuc = new int[26]; //目标词频桶
for(int i = 0; i < pLen; i++){ //统计目标词频
pBuc[p.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
int l = 0; //左窗口
for(int r = 0; r < sLen; r++){ //右窗口
sBuc[s.charAt(r) - 'a']++; //记录待处理词频桶
if(r - l + 1 > pLen){ //当窗口长度超过目标字符串长度
sBuc[s.charAt(l++) - 'a']--; //左窗口向右移动, 同时清空刚才左窗口加入到待处理词频桶的字符
}
if(Arrays.equals(sBuc, pBuc)){ //如果待处理词频桶和左窗口词频桶内容一样
res.add(l); //记录左窗口
}
}
return res;
}
}字母异位词分组
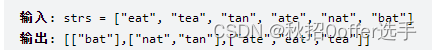
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
HashMap<String,Integer> hm=new HashMap();
List<List<String>> list=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<strs.length;i++){
String tmp=strs[i];
Arrays.sort(tmp);
if(hm.containsKey(tmp)){
int index=hm.get(tmp);
list.get(index).add(strs[i]);
}else{
List<String> list1=new ArrayList();
list1.add(strs[i]);
list.add(list1);
}
}
return list;
}
}454. 四数相加 II
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int temp;
int res = 0;
//统计两个数组中的元素之和,同时统计出现的次数,放入map
for (int i : nums1) {
for (int j : nums2) {
temp = i + j;
if (map.containsKey(temp)) {
map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
} else {
map.put(temp, 1);
}
}
}
//统计剩余的两个元素的和,在map中找是否存在相加为0的情况,同时记录次数
for (int i : nums3) {
for (int j : nums4) {
temp = i + j;
if (map.containsKey(0 - temp)) {
res += map.get(0 - temp);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}18. 四数之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 去重
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > target) {
right--;
… }
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计数字乡村基础治理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6a451369471d4ce4a5278f2ea0b7a121.png)

![[Mysql]数据库约束](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/045859dcb98a426c9dbb10fdce5ece20.png)