1.二叉搜索树最小差值
二叉搜索树中序遍历得到有序的数字序列,记录前一个节点
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
//左中右的遍历顺序
//左
traversal(root.left);
//中
if(pre!=null){
result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
}
pre = root;
//右
traversal(root.right);
}
}2.二叉搜索树中的众数
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
(1)暴力法
需要用到关于Map和List的一些函数
class Solution {
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
// 获得频率 Map
searchBST(root, map);
List<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> mapList = map.entrySet().stream()
.sorted((c1, c2) -> c2.getValue().compareTo(c1.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.add(mapList.get(0).getKey());
// 把频率最高的加入 list
for (int i = 1; i < mapList.size(); i++) {
if (mapList.get(i).getValue() == mapList.get(i - 1).getValue()) {
list.add(mapList.get(i).getKey());
} else {
break;
}
}
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
void searchBST(TreeNode curr, Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
if (curr == null) return;
map.put(curr.val, map.getOrDefault(curr.val, 0) + 1);
searchBST(curr.left, map);
searchBST(curr.right, map);
}
}(95条消息) map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);用来统计数字出现的次数:_天才小熊猫啊的博客-CSDN博客
Map.getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue);
如果在Map中存在key,则返回key所对应的的value。
如果在Map中不存在key,则返回默认值。
例如:
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
表示:
value默认从1开始,每次操作后num对应的value值加1
ArrayList用stream流转化为int数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int[] arr = list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
由于Map中存放的元素均为键值对,故每一个键值对必然存在一个映射关系。
Map中采用Entry内部类来表示一个映射项,映射项包含Key和Value (我们总说键值对键值对, 每一个键值对也就是一个Entry)。Map.Entry里面包含getKey()和getValue()方法
Map按value排序,在Collectors.toList()方法中使用lambda表达式将Map转换为List
List<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> mapList = map.entrySet()
. stream()
.sorted((c1, c2) -> c2.getValue().compareTo(c1.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
(2)针对二叉搜索树的方法
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> resList;
int maxCount;
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
int[] res = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); i++) {
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void findMode1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) { //为空,直接return
return;
}
findMode1(root.left); //左
//中
int rootValue = root.val;
// 计数
if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val) {
count = 1; //count更新为1
} else {
count++; //记录该数出现的次数
}
// 更新结果以及maxCount
if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(rootValue);
maxCount = count;
} else if (count == maxCount) { //不止一个众数
resList.add(rootValue);
}
pre = root; //赋值pre
//右
findMode1(root.right);
}
}3.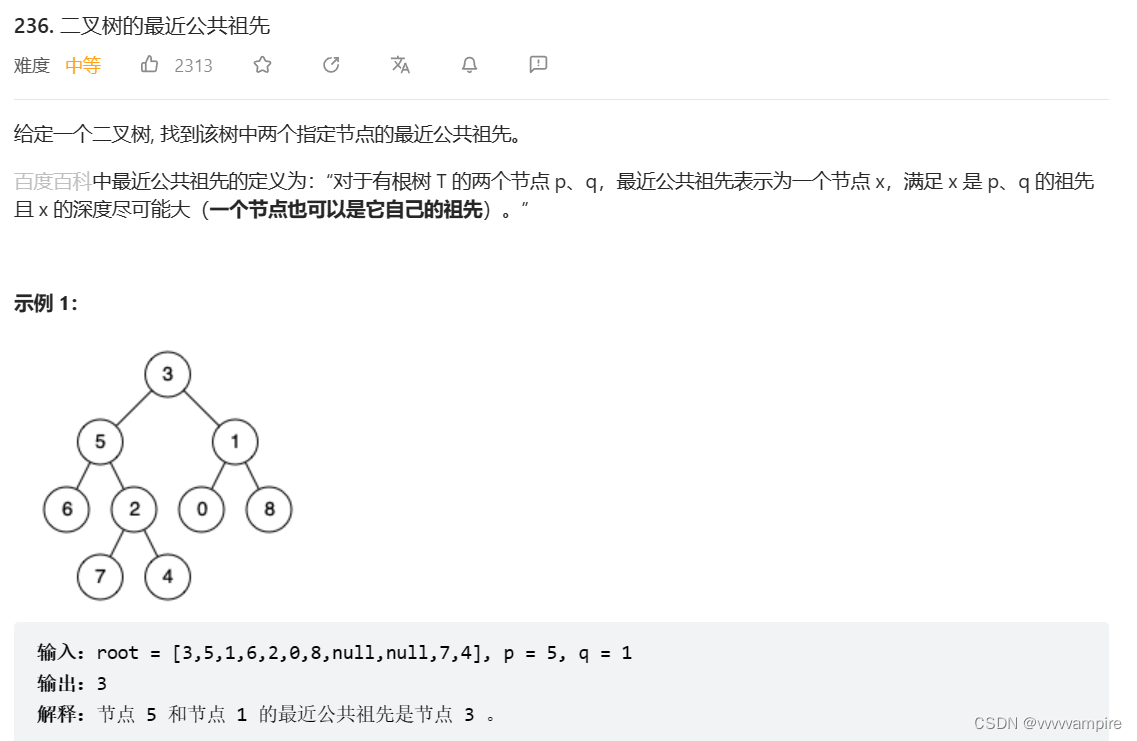
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
使用后序遍历实现,因为最终处理中节点
(1)只要出现p和q就往上返回到他们的公共父节点
(2)p是q的父节点(或相反)——已经包括在情况1中了
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { // 递归结束条件
return root;
}
// 后序遍历
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null && right == null) { // 若未找到节点 p 或 q
return null;
}else if(left == null && right != null) { // 若找到一个节点
return right;
}else if(left != null && right == null) { // 若找到一个节点
return left;
}else { // 若找到两个节点
return root;
}
}
}