文章目录
- Overview
- 1 Intro
- LTL任务分解
- STL任务分解
- 本文工作
- Background and Problem Definition
- STL
- Agent
- 假设与问题
- 方法
- An STL Rewriting System
- Rewriting System
- Formula Rewrite DAG
- Decomposing STL
- 智能体编队
- 任务分解
- 最优分解
- Exploring the Formula Rewrite DAG
- 心得体会
多智能体 STL任务分解
[1] K. Leahy, M. Mann, and C.-I. Vasile, “Rewrite-Based Decomposition of Signal Temporal Logic Specifications,” in NASA Formal Methods, K. Y. Rozier and S. Chaudhuri, Eds., in Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023, pp. 224–240. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-33170-1_14.
Overview
- 用rewriting system将STL公式分解以解决中心计算计算量太大的问题
- 同时给智能体分组
- 证明分解算法的收敛性
- 提出一个分解的评价指标并给出最佳分解的评价方式
1 Intro
LTL任务分解
[2,7,21,23]
STL任务分解
[6] Charitidou, M., Dimarogonas, D.V.: Signal temporal logic task decomposition via convex optimization. IEEE Contr. Syst. Lett. 6 , 1238–1243 (2021)
- 已知智能体的分组情况
[14] Leahy, K., Jones, A., Vasile, C.I.: Fast decomposition of temporal logic specifications for heterogeneous teams. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7 (2), 2297–2304 (2022)
- abstract reduction system,只能处理特定形式的STL
[22] Sun, D., Chen, J., Mitra, S., Fan, C.: Multi-agent motion planning from signal temporal logic specifications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7 (2), 3451–3458 (2022)
- 将任务分解给每一个机器人,不考虑编队
- 主要探究的是控制综合的问题
本文工作
- 公式分解 + 机器人编队 (分两阶段完成)
- 提供了分解式的正则形式以及量化了分解上限
- 基于优化方法在DAG上选择最佳分解和编队
Background and Problem Definition
STL
文章分层定义了predicate和conjugate,如下所示
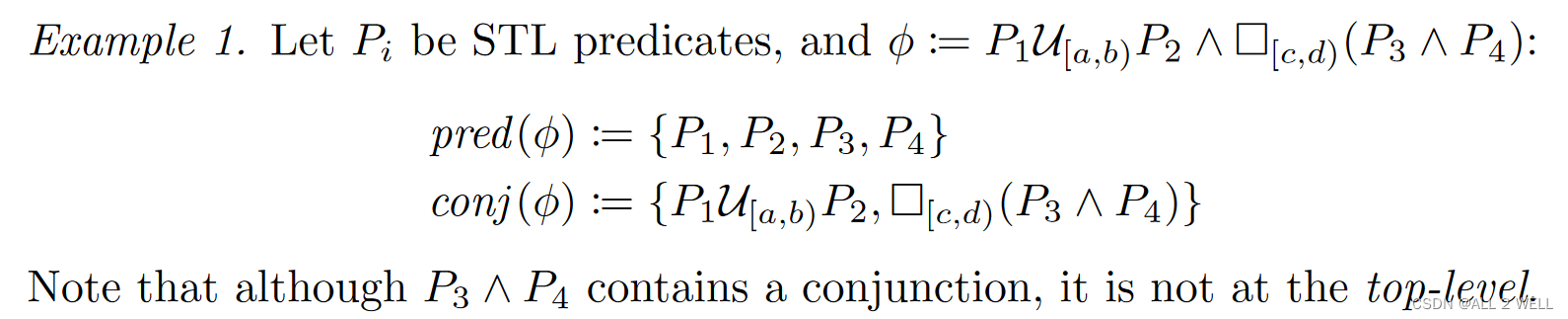
虽然文章说不约束STL的形式,但是这个定义一出来看上去是只接受一层时序嵌套和布尔运算的组合
Agent
-
智能体定义为一个状态和状态上界(element-wise)的元组 A = ( x ( t ) , u ) A=(x(t),u) A=(x(t),u)
-
u u u: x ( t ) x(t) x(t)有一个恒定的上界,假定是已知的
-
An agent “services” a predicate: 一个智能体的动作对该predicate是否满足有影响
-
equivalence class g u g_u gu: 具有相同 u u u的智能体被看做为同一类型
-
Robustness upper bound ρ u b \rho_{ub} ρub: 所有机器人鲁棒度能够达到的最大值之和
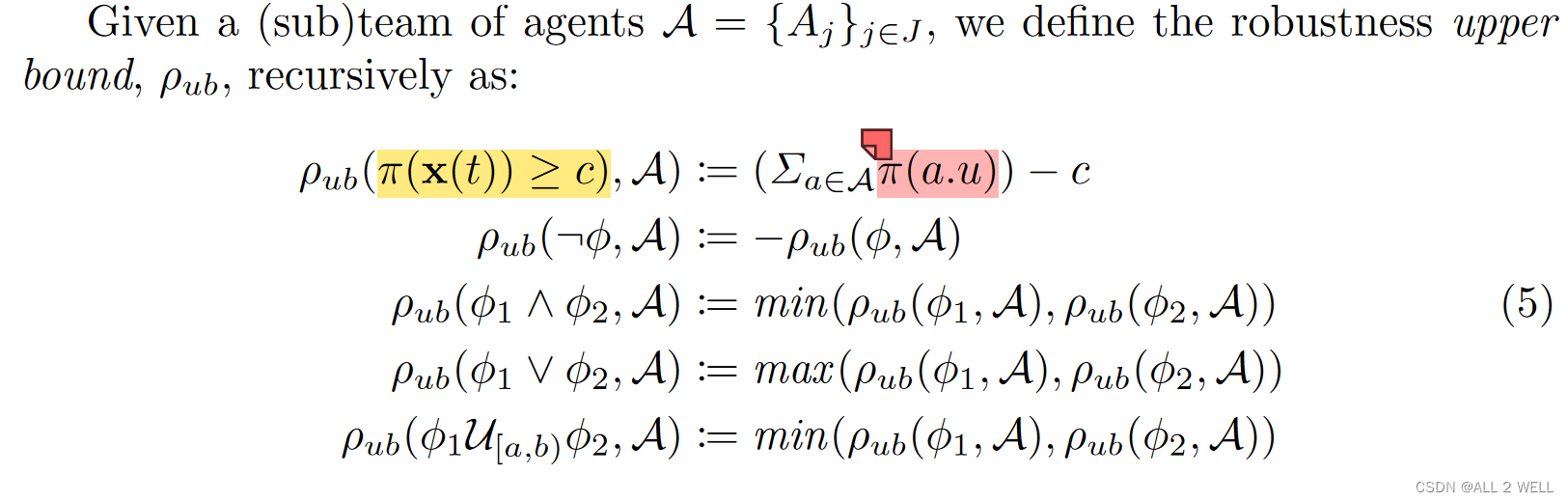
- 上面公式定义的很奇怪,感觉像是括号打错了,正确的应该是 ρ u b ( π ( x ( t ) ≥ c ) , A ) : = ∑ a ∈ A ( π ( a . u ) − c ) \rho_{ub}(\pi(x(t)\geq c),\mathcal{A}):=\sum_{a\in\mathcal{A}}(\pi(a.u)-c) ρub(π(x(t)≥c),A):=a∈A∑(π(a.u)−c)
- 如果 ρ u b \rho_{ub} ρub为负,则不存在满足此公式的控制律
假设与问题
- 假定 S y n t h ( J , ϕ ) Synth(J,\phi) Synth(J,ϕ)是一个已知的函数,输出一个控制律,使得智能体集群 J J J满足公式 ϕ \phi ϕ
- 由于目前没有方法能够在求解控制律之前就得出问题是否可行,因此本文将robustness upper bound作为存在可行解的一个必要条件

- 即得到智能体的编队方式 R R R以及每一队所对应的公式 ϕ r \phi_r ϕr
- 为了使分解有意义,接下来假设原控制综合问题是有可行解的
方法
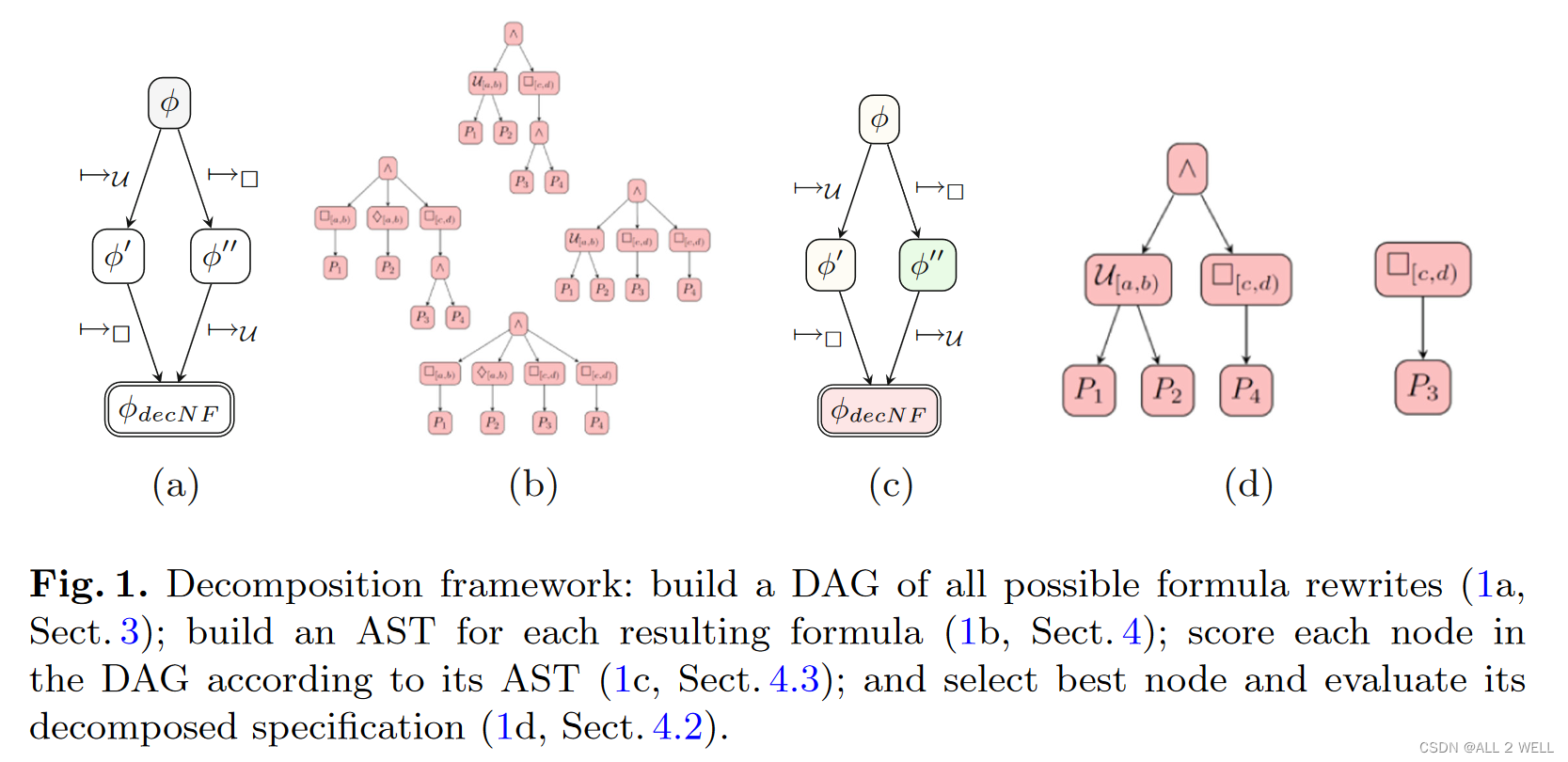
大致步骤如下:
- 先将原公式转化为更容易分解的形式(很多种)
- 为每种变形构建抽象语法树(AST, abstract syntax tree)
- 给所有变形打分
- 选择最好的结点,完成公式的分解
- 根据公式完成智能体编队
An STL Rewriting System
这里完成上面步骤中的第一步:将原公式转化为更容易分解的形式
Rewriting System
最顶层为合取 ∧ \land ∧组合为的公式是最容易分解的, ∧ \land ∧下的子公式没有逻辑关联性(都满足就好了),因此这里想了一个方法将所有的公式都改成顶层连接词为 ∧ \land ∧的形式。
为了保证分解后的问题与原问题的统一性,必须保证改写后的公式比原公式更加严格。
因此文章提出下面3中加入顶层
∧
\land
∧的方法:
→
□
,
→
⋄
,
→
U
\to_\square,\to_\diamond,\to_\mathcal{U}
→□,→⋄,→U

- 上面的split-finally和split-until对原公式的逻辑压缩得简直是大刀阔斧
- 文中还有两种合并,就是说很有道理但是又没有道理 😅
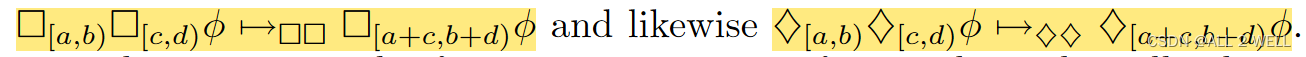
接下来就是一些比较长的数学证明,这里不细看了
- rewrite系统的终止条件:出现一个单调
φ
\varphi
φ,其中
φ
=
∑
i
=
1
n
∧
,
U
d
i
+
(
n
∧
,
U
+
1
)
n
U
\varphi=\sum_{i=1}^{n_{\land,\mathcal U}}d_i+(n_{\land,\mathcal U}+1)n_\mathcal{U}
φ=i=1∑n∧,Udi+(n∧,U+1)nU
- n ∧ , U n_{\land,\mathcal U} n∧,U是顶层连接词 ∧ \land ∧和 U \mathcal U U的数量
- d i d_i di是第 i i i个顶层连接词到AST根节点的距离
- monotone embedding into ( N , > ) (\mathbb N,>) (N,>)
- Confluence
Formula Rewrite DAG
G
:
=
<
Φ
,
E
>
G:=\left<\Phi,E\right>
G:=⟨Φ,E⟩ 表示公式的变化过程,结点为公式形态,边为重写规则,如下如所示
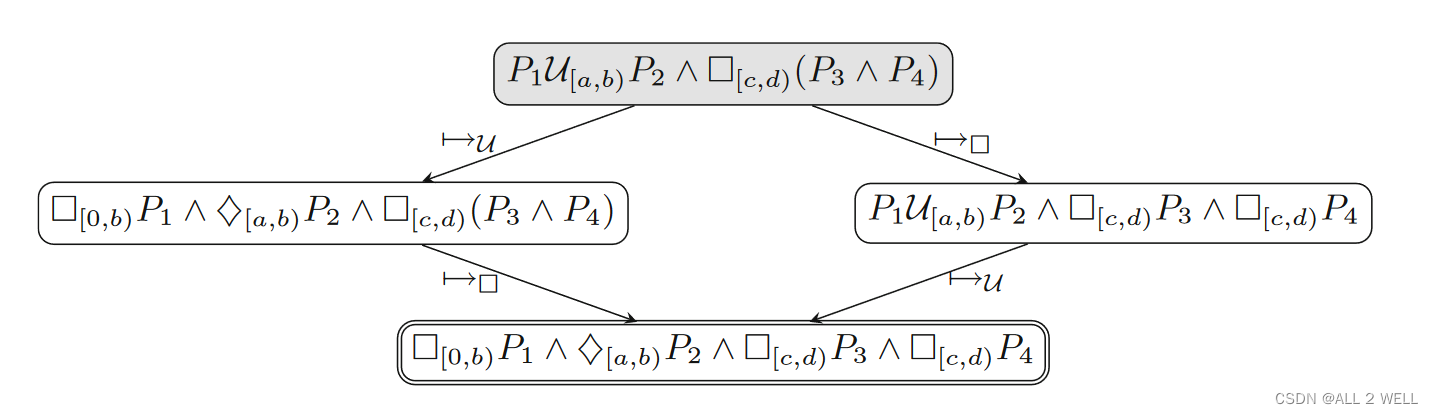
上面证明过DAG一定能够以有限图终止,上图最下方也展示了这个结果
Decomposing STL
这一部分做的是给上面的所有结点评分,以选出一个最佳的分解方法
智能体编队
一个将STL公式转化成智能体集合的函数:
α
:
c
o
n
j
(
ϕ
)
→
2
J
\alpha:conj(\phi)\to 2^J
α:conj(ϕ)→2J
任务分解
最优分解
Exploring the Formula Rewrite DAG
心得体会
- inference可以用来做分解