算法模板(3):搜索(6):做题积累
一、DFS
1. 1113. 红与黑
有一间长方形的房子,地上铺了红色、黑色两种颜色的正方形瓷砖。你站在其中一块黑色的瓷砖上,只能向相邻(上下左右四个方向)的黑色瓷砖移动。请写一个程序,计算你总共能够到达多少块黑色的瓷砖。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 25;
char mz[maxn][maxn];
int N, M, sx, sy, tx, ty, dx[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 }, dy[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
bool vis[maxn][maxn];
int dfs(int x, int y) {
int cnt = 1;
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M) continue;
if (vis[nx][ny] || mz[nx][ny] != '.') continue;
cnt += dfs(nx, ny);
}
return cnt;
}
int main() {
while (cin >> M >> N && N) {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> mz[i];
}
int sx, sy;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (mz[i][j] == '@') {
sx = i, sy = j;
break;
}
}
}
cout << dfs(sx, sy) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2. Tempter of the Bone
- 给一个迷宫地图,问是否存在一条从起点到终点的长度为 T 的简单路径. ( 1 ≤ N , M ≤ 7 , T ≤ 50 ) . (1 \le N, M \le 7, T \le 50). (1≤N,M≤7,T≤50).
- 要提到一个奇偶性剪枝的问题。如果要想到达终点,无论选择什么样子的简单路径,其路径长度奇偶性总是一样的。
- 这道题用深搜就可以写,宽搜似乎时不可以的。而深搜可以遍历出剪枝后的每一种可行的方案。
- 剪枝的方式有很多,最重要的还是用好vis数组做回溯法,以及刚才提到的奇偶性剪枝。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char g[10][10];
bool vis[10][10];
int N, M, t, sx, sy, gx, gy;
int dx[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 }, dy[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
bool dfs(int x, int y, int total) {
if (total > t) return false;
if (total == t && g[x][y] == 'D') return true;
//奇偶性剪枝(可行性剪枝)
if (abs(t - total - abs(x - gx) - abs(y - gy)) & 1) return false;
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M) continue;
if (g[nx][ny] == 'X' || vis[nx][ny]) continue;
if (dfs(nx, ny, total + 1)) return true;
}
vis[x][y] = false;
return false;
}
int main() {
while (cin >> N >> M >> t, N) {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
int block = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) cin >> g[i];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (g[i][j] == 'S') sx = i, sy = j;
else if (g[i][j] == 'D') gx = i, gy = j;
else if (g[i][j] == 'X') block++;
}
}
if (N * M - block < t || abs(abs(sx - gx) + abs(sy - gy) - t) & 1) printf("NO\n");
else if (dfs(sx, sy, 0)) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. 1116. 马走日
- 题意:马在中国象棋以日字形规则移动。请编写一段程序,给定 n ∗ m n*m n∗m 大小的棋盘,以及马的初始位置 ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y),要求不能重复经过棋盘上的同一个点,计算马可以有多少途径遍历棋盘上的所有点。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int N, M, sx, sy, ans;
int dy[] = { -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2 }, dx[] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
bool vis[15][15];
void dfs(int x, int y, int cnt) {
if (cnt == N * M) {
ans++;
return;
}
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M) continue;
if (vis[nx][ny]) continue;
dfs(nx, ny, cnt + 1);
}
vis[x][y] = false;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &N, &M, &sx, &sy);
ans = 0;
dfs(sx, sy, 1);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
4. 1117. 单词接龙
- 题意:单词接龙是一个与我们经常玩的成语接龙相类似的游戏。现在我们已知一组单词,且给定一个开头的字母,要求出以这个字母开头的最长的“龙”,每个单词最多被使用两次。在两个单词相连时,其重合部分合为一部分,例如 beast 和 astonish ,如果接成一条龙则变为 beastonish。我们可以任意选择重合部分的长度,但其长度必须大于等于1,且严格小于两个串的长度,例如 at 和 atide 间不能相连。
- 给定单词开头字母,求拼成的单词长度最长的方案.
- n ≤ 20. n \le 20. n≤20.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 25;
int g[maxn][maxn], N, ans = 0, used[maxn];
string words[maxn], head;
void dfs(string dragon, int last) {
ans = max((int)dragon.size(), ans);
used[last]++;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (g[last][i] && used[i] < 2) {
dfs(dragon + words[i].substr(g[last][i]), i);
}
}
used[last]--;
}
int main() {
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> words[i];
}
cin >> head;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
string& s1 = words[i], & s2 = words[j];
for (int k = 1; k < min(s1.size(), s2.size()); k++) {
if (s1.substr(s1.size() - k, k) == s2.substr(0, k)) {
g[i][j] = k;
break;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (words[i][0] == head[0]){
dfs(head + words[i].substr(1), 0);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
5. 1118. 分成互质组
- 题意:给定 n n n 个正整数,将它们分组,使得每组中任意两个数互质。至少要分成多少个组?
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 15;
//group存放的是数字的下标
int group[maxn][maxn], p[maxn], N, ans = 10;
bool vis[maxn];
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
bool check(int g[], int gc, int idx) {
for (int i = 0; i < gc; i++) {
if (gcd(p[g[i]], p[idx]) > 1) return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int g, int gc, int tc, int start) {
if (g >= ans) return;
if (tc == N) {
ans = g;
return;
}
bool flag = true;
for (int i = start; i < N; i++) {
if (!vis[i] && check(group[g], gc, i)) {
flag = false;
vis[i] = true;
group[g][gc] = i;
dfs(g, gc + 1, tc + 1, i + 1);
vis[i] = false;
}
}
if (flag) dfs(g + 1, 0, tc, 0);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) scanf("%d", &p[i]);
dfs(1, 0, 0, 0);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
6. 167. 木棒
- 优化搜索顺序:从大到小枚举
- 如果当前木棒加入到当前棒中失败了,就略过后面所有与之等长的木棒。
- 如果当前木棒无法放到第一根木棒或是最后一根木棒的位置,则一定失败。这个可以用反证法去证明。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 70;
int w[maxn], N, length, sum;
bool vis[maxn];
bool dfs(int u, int s, int start) {
if (length * u == sum) return true;
if (s == length) return dfs(u + 1, 0, 0);
for (int i = start; i < N; i++) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
if (s + w[i] > length) continue;
vis[i] = true;
if (dfs(u, s + w[i], i + 1)) return true;
vis[i] = false;
if (s == 0) return false;
if (s + w[i] == length) return false;
int j = i;
while (j < N && w[i] == w[j]) j++;
i = j - 1; //注意这里,因为马上要i++了,千万别写成i = j。
}
return false;
}
int main() {
while (cin >> N, N) {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
//注意,当一个length行不通的时候,vis都会被回溯成false的。
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> w[i];
sum += w[i];
}
sort(w, w + N, greater<int>());
for (length = 1; ; length++) {
if (sum % length == 0 && dfs(0, 0, 0)) {
cout << length << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
7. 181. 回转游戏
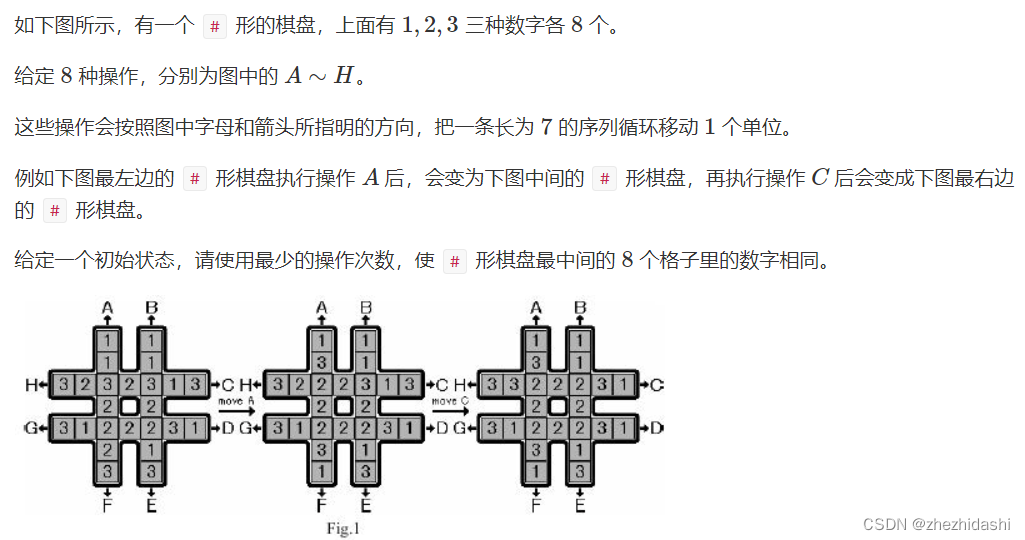
- 对节点编号,再对操作编号

#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int op[8][7]{
{0, 2, 6, 11, 15, 20, 22},
{1, 3, 8, 12, 17, 21, 23},
{10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4},
{19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13},
{23, 21, 17, 12, 8, 3, 1},
{22, 20, 15, 11, 6, 2, 0},
{13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19},
{4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
};
int opposite[8] = { 5, 4, 7, 6, 1, 0, 3, 2 };
int center[8] = { 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17 };
int q[24], path[100];
int f() {
int sum[4] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) sum[q[center[i]]]++;
int s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) s = max(s, sum[i]);
return 8 - s;
}
void operate(int id) {
int head = q[op[id][0]];
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) q[op[id][i]] = q[op[id][i + 1]];
q[op[id][6]] = head;
}
bool dfs(int depth, int max_depth, int last) {
if (depth + f() > max_depth) return false;
if (f() == 0) return true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if (opposite[i] != last) {
operate(i);
path[depth] = i;
if (dfs(depth + 1, max_depth, i)) return true;
operate(opposite[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &q[0]) && q[0]) {
for (int i = 1; i < 24; i++) scanf("%d", &q[i]);
int depth = 0;
while (!dfs(0, depth, -1)) depth++;
if (!depth) printf("No moves needed\n");
else {
//再次提醒!! 一定要小心这个输出,循环到 depth - 1 就行!
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) printf("%c", path[i] + 'A');
printf("\n");
}
printf("%d\n", q[center[1]]);
}
return 0;
}
二、BFS
1. 八数码
- 这个题其实没什么的,属于bfs第二种类型(第一种是在地图上行走,这种是改变地图本身)。其实挺简单的。
- 状态的记录,用字符串记录就很好。然后用unordered_map储存距离。
queue<string> que;
unordered_map<string, int> d;
int dx[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 }, dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
string st, ed("12345678x");
int bfs() {
d[st] = 0;
que.push(st);
while (que.size()) {
auto s = que.front(); que.pop();
int dis = d[s];
if (s == ed) return dis;
int k = s.find('x');
int x = k / 3, y = k % 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= 3 || ny < 0 || ny >= 3) continue;
swap(s[x * 3 + y], s[nx * 3 + ny]);
if (!d.count(s)) {
d[s] = dis + 1;
que.push(s);
}
swap(s[nx * 3 + ny], s[x * 3 + y]);
}
}
return -1;
}
2. 1107. 魔板
- 这道题和八数码是一个样子。不过看清输入的是什么。
- 答案要求输出字典序最小的操作。实际上只需按照ABC操作的顺序进行操作,得到的路径字典序一定最小。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
queue<string> que;
unordered_map<string, int> d;
map<string, pair<string, char> > pre;
int dx[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 }, dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
string st("12345678"), ed;
int bfs() {
d[st] = 0;
que.push(st);
pre[st].first = "-1";
while (que.size()) {
auto s = que.front(); que.pop();
if (s == ed) return d[s];
string t = s;
swap(t[0], t[7]), swap(t[1], t[6]), swap(t[2], t[5]), swap(t[3], t[4]);
if (!d.count(t)) {
d[t] = d[s] + 1;
que.push(t);
pre[t] = make_pair(s, 'A');
}
t = s;
swap(t[3], t[2]), swap(t[2], t[1]), swap(t[1], t[0]);
swap(t[4], t[5]), swap(t[5], t[6]), swap(t[6], t[7]);
if (!d.count(t)) {
d[t] = d[s] + 1;
que.push(t);
pre[t] = make_pair(s, 'B');
}
t = s;
char c = t[1];
t[1] = t[6], t[6] = t[5], t[5] = t[2], t[2] = c;
if (!d.count(t)) {
d[t] = d[s] + 1;
que.push(t);
pre[t] = make_pair(s, 'C');
}
}
}
int main() {
char c;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
cin >> c;
ed += c;
}
int ans = bfs();
string path;
for (auto p = pre[ed]; p.first != "-1"; p = pre[p.first]) path += p.second;
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
cout << ans << endl;
if (path != "") cout << path << endl;
return 0;
}
3. 1106. 山峰和山谷

- 对于给定的地图,求出山峰和山谷的数量。我的思路是找出数字相同的连通块。然后边找连通块,边检测是否连通块是山峰或是说山谷。
- 这个地方要小心判断 while 中判断 vis 的位置。因为要判断八个方向的块儿的高低,因此判断 vis 的位置要放到推入 que 的前面。
void bfs(int x, int y) {
int num = g[x][y];
que.push({ x, y });
vis[x][y] = true;
bool is_peak = true, is_valley = true;
while (que.size()) {
auto p = que.front(); que.pop();
int x = p.first, y = p.second;
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
int nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy;
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N) continue;
if (g[nx][ny] > num) is_peak = false;
else if (g[nx][ny] < num) is_valley = false;
else if(!vis[nx][ny]){
vis[nx][ny] = true;
que.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
}
}
if (is_peak) peak++;
if (is_valley) valley++;
}
void solve() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) bfs(i, j);
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", peak, valley);
}
4. 1098. 城堡问题
-
第一行包含两个整数 m 和 n,分别表示城堡南北方向的长度和东西方向的长度。接下来 m 行,每行包含 n 个整数,每个整数都表示平面图对应位置的方块的墙的特征。每个方块中墙的特征由数字 P 来描述,我们用1表示西墙,2表示北墙,4表示东墙,8表示南墙,P 为该方块包含墙的数字之和。例如,如果一个方块的 P 为3,则 3 = 1 + 2,该方块包含西墙和北墙。城堡的内墙被计算两次,方块(1,1)的南墙同时也是方块(2,1)的北墙。
-
这道题给出每个小块儿的东西南北是否有墙,然后问房间数量和房间的最大面积。1表示西墙,2表示北墙,4表示东墙,8表示南墙。
-
我们知道,一系列2的幂通过相加可以得到任何正整数。这是因为: 2 0 = 1 ( 2 ) 2^0 = 1_{(2)} 20=1(2), 2 1 = 1 0 ( 2 ) 2^1 = 10_{(2)} 21=10(2), 2 2 = 10 0 ( 2 ) 2^2 = 100_{(2)} 22=100(2)。因此二进制的每一位数字0或是1都可以通过相加得到。反之,给一个数字,我们可以通过右移并和1按位与可知有哪几个2的幂相加的得到的。
-
想到这一点,这道题就很好写了。不过有一点要注意,那个dx, dy四个方向的顺序就得和墙的标号顺序一样了。
-
这道题保留的意义其实是掌握如何把一个数拆成一系列2的幂之和
int N, M;
int g[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn][maxn];
typedef pair<int, int> P;
queue<P> que;
int dx[] = {0, -1, 0, 1}, dy[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int bfs(int x, int y) {
int cnt = 0;
que.push({ x, y });
vis[x][y] = true;
while (que.size()) {
auto p = que.front(); que.pop();
cnt++;
int x = p.first, y = p.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (g[x][y] >> i & 1) continue;
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M || vis[nx][ny]) continue;
vis[nx][ny] = true;
que.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
return cnt;
}
void solve() {
int cnt = 0, max_size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
max_size = max(max_size, bfs(i, j));
cnt++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n%d\n", cnt, max_size);
}
5. 179. 八数码
-
用 A* 算法
-
逆序对个数是奇数一定无解,个数是偶数一定有解。
-
估价函数:当前状态中每个数与他的目标位置曼哈顿距离之和。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, string> P;
int f(string s) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == 'x') continue;
int num = s[i] - '1';
int sx = num / 3, sy = num % 3, tx = i / 3, ty = i % 3;
res += abs(sx - tx) + abs(sy - ty);
}
return res;
}
string bfs(string start) {
char op[10] = "udlr";
string end = "12345678x";
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 }, dy[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> que;
unordered_map<string, int> d;
unordered_map<string, pair<char, string>> pre;
que.push(P(f(start), start));
d[start] = 0;
while (que.size()) {
auto p = que.top(); que.pop();
string state = p.second; int dis = p.first;
if (state == end) break;
int id = state.find('x');
int x = id / 3, y = id % 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= 3 || ny < 0 || ny >= 3) continue;
string t = state;
swap(t[nx * 3 + ny], t[x * 3 + y]);
if (!d.count(t) || d[t] > d[state] + 1) {
d[t] = d[state] + 1;
que.push(P(f(t) + d[t], t));
pre[t] = make_pair(op[i], state);
}
}
}
string path, now = end;
while (now != start) {
path += pre[now].first;
now = pre[now].second;
}
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
return path;
}
int main() {
char c;
string start, nums;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
cin >> c;
start += c;
if (c != 'x') nums += c;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt & 1) cout << "unsolvable\n";
else cout << bfs(start) << endl;
return 0;
}
三、图论
1.1126. 最小花费
- 题意:给定这些人之间转账时需要从转账金额里扣除百分之几的手续费,请问 A 最少需要多少钱使得转账后 B 收到 100 元。
- 注意,这道题求的是乘积最大值。因为这个边权都是在0到1之间,越乘越小,因此也不怕有环的情况了。直接乘就行。大雪菜是从取对数的角度来考虑的(小心取对数后变成负数)。
- 但是,求最大值需要注意两点:优先队列的声明,要改一下;另外在判断时也要改成 d [ v ] < d [ u ] ∗ w [ i ] d[v] < d[u] * w[i] d[v]<d[u]∗w[i]。
double bfs() {
d[A] = 1;
priority_queue<P> que;
que.push({ 1, A });
while (que.size()) {
auto p = que.top(); que.pop();
int u = p.second; double dist = p.first;
if (vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (d[v] < d[u] * w[i]) {
d[v] = d[u] * w[i];
que.push({ d[v], v });
}
}
}
return 100.0 / d[B];
}
2.340. 通信线路
- 农产主可以指定一条从 1 号基站到 N 号基站的路径,并指定路径上不超过 K 条电缆,由电话公司免费提供升级服务。农场主只需要支付在该路径上剩余的电缆中,升级价格最贵的那条电缆的花费即可。
- 最小化最大值,二分法选出x。关键是如何选路的问题。我们要找的是从 1 1 1~ N N N 最少经过几条不超过x的边。这道题用 b f s bfs bfs 就可以了,最短路倒是不行(因为最短路每次选的路径都是一样的)。
- 不过,这里的用 q u e u e queue queue 来 b f s bfs bfs 是不可以的。因为这个只适用于边的长度是1的情况。这道题,可以边权大于 x 的记为1,不超过x的记为0。有0有1的话可以用双端队列 b f s bfs bfs。下面是 AC 代码。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1010, maxm = 200010, INF = 1e9;
int h[maxn], e[maxm], ne[maxm], idx, w[maxm], N, M, K, d[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
bool bfs(int x) {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
fill(d, d + maxn, INF);
d[1] = 0;
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_back(1);
while (dq.size()) {
int u = dq.front(); dq.pop_front();
if (u == N) break;
if (vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
int cost = (w[i] > x);
if (d[v] >= d[u] + cost) {
d[v] = d[u] + cost;
if (cost) dq.push_back(v);
else dq.push_front(v);
}
}
}
return d[N] <= K;
}
int main() {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d%d%d", &N, &M, &K);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
int lb = -1, ub = 1000010;
while (ub - lb > 1) {
int mid = (lb + ub) / 2;
if (bfs(mid)) ub = mid;
else lb = mid;
}
if (ub > 1000000) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n", ub);
return 0;
}
01分数规划
指的是在图论里面,一堆值之和与另一堆值之和的比值最大,这一般称为01分数规划问题,通常可以用二分去写。
3. 361. 观光奶牛
-
给定一张 L L L 个点、 P P P 条边的有向图,每个点都有一个权值 f [ i ] f[i] f[i],每条边都有一个权值 t [ i ] t[i] t[i]。求图中的一个环,使 “环上各点的权值之和 ”除以“ 环上各边的权值之和” 最大。输出这个最大值。
-
其实,每条边的权重转化为 $ f[i] - mid * w[i]$ 了。然后再看看有没有正环。有正环的话,最大值会一直更新下去。
-
保留两位小数,循环跳出条件可以是 u b − l b > 1 e − 4 ub - lb > 1e-4 ub−lb>1e−4 .循环 100 次的话会超时。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1010, maxm = 5010;
int h[maxn], w[maxm], ver[maxn], e[maxm], ne[maxm], idx;
int N, M, cnt[maxn];
double d[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
bool C(double x) {
queue<int> que;
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
que.push(i);
vis[i] = true;
}
while (que.size()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (d[v] < d[u] + ver[v] - x * w[i]) {
d[v] = d[u] + ver[v] - x * w[i];
cnt[v] = cnt[u] + 1;
if (cnt[v] >= N) return true;
if (!vis[v]) {
que.push(v);
vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) scanf("%d", &ver[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
double lb = 0, ub = 1000;
while(ub - lb > 1e-4) {
double mid = (lb + ub) / 2;
if (C(mid)) lb = mid;
else ub = mid;
}
printf("%.2f\n", lb);
return 0;
}
4. 1165. 单词环
-
我们有 n 个字符串,每个字符串都是由 a∼z 的小写英文字母组成的。如果字符串 A 的结尾两个字符刚好与字符串 B 的开头两个字符相匹配,那么我们称 A 与 B 能够相连(注意:A 能与 B 相连不代表 B 能与 A 相连)。我们希望从给定的字符串中找出一些,使得它们首尾相连形成一个环串(一个串首尾相连也算),我们想要使这个环串的平均长度最大。
-
当入队次数大于2N的时候往往就是因为环的存在。当然不一定是2N,可能是一个更大的数字,比如10000之类的。
-
数组越界的话,报错还可能是TLE,神奇的编译器。
-
经验表明,当图中有负环的时候,直接把队列换成栈,往往可以迅速找到负环。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 700, maxm = 100010;
int h[maxn], w[maxm], e[maxm], ne[maxm], idx;
char edge[1010];
bool vis[maxn];
int N, M;
double d[maxn];
map<string, int> id;
void init() {
string ver("__");
for (int i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
for (int j = 'a'; j <= 'z'; j++) {
ver[0] = i, ver[1] = j;
id[ver] = N++;
}
}
}
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
bool C(double x) {
queue<int> que;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
que.push(i);
vis[i] = true;
}
int cnt = 0;
while (que.size()) {
if (++cnt > 10000) return true;
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (d[v] < d[u] + w[i] - x) {
d[v] = d[u] + w[i] - x;
if (!vis[v]) {
que.push(v);
vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
init();
string st("__"), ed("__");
while (scanf("%d", &M) && M) {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
scanf("%s", edge);
int len = strlen(edge);
if (len < 2) continue;
st[0] = edge[0], st[1] = edge[1];
ed[0] = edge[len - 2], ed[1] = edge[len - 1];
int a = id[st], b = id[ed];
add(a, b, len);
}
double lb = 0, ub = 1000;
while (ub - lb > 1e-6) {
double mid = (lb + ub) / 2;
if (C(mid)) lb = mid;
else ub = mid;
}
if(fabs(lb) < 1e-3) printf("No solution\n");
else printf("%f\n", lb);
}
return 0;
}
5. 1125. 牛的旅行
-
给一些牧场以及每个牧场中的点的坐标,现在找出一条连接两个不同牧场的路径,使得连上这条路径后,所有牧场(生成的新牧场和原有牧场)中直径最大的牧场的直径尽可能+小。
-
其实,最大直径一定是两种可能性,一个是最远两点距离,另一个是新生成的。而你任意连接两个点,生成的直径一定是两点间的距离,以及之前分别与这两个点相离最远的两个点的距离三者之和。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 160;
const double INF = 1e9, EPS = 1e-3;
int N;
double x[maxn], y[maxn], d[maxn][maxn], max_d[maxn], ans = INF;
char g[maxn][maxn];
bool equal(double x, double y) {
return fabs(x - y) <= EPS;
}
double dis(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
}
void floyd() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) fill(d[i], d[i] + N, INF);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
d[i][i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (g[i][j] == '1') d[i][j] = d[j][i] = dis(x[i], y[i], x[j], y[j]);
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!equal(d[i][j], INF)) max_d[i] = max(max_d[i], d[i][j]);
}
}
}
void solve() {
floyd();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (equal(d[i][j], INF)) {
ans = min(ans, max_d[i] + max_d[j] + dis(x[i], y[i], x[j], y[j]));
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
ans = max(max_d[i], ans);
}
printf("%.6f\n", ans);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x[i], &y[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%s", g[i]);
}
solve();
return 0;
}
6. 传递闭包
343. 排序
-
给定 n 个变量和 m 个不等式。其中 n 小于等于 26,变量分别用前 n 的大写英文字母表示。不等式之间具有传递性,即若 A>B 且 B>C,则 A>C。请从前往后遍历每对关系,每次遍历时判断:(1)如果能够确定全部关系且无矛盾,则结束循环,输出确定的次序;(2)如果发生矛盾,则结束循环,输出有矛盾;(3)如果循环结束时没有发生上述两种情况,则输出无定解。
-
我们把 d [ i , j ] = 0 d[i, j] = 0 d[i,j]=0 当且仅当 i > j i > j i>j, d [ i , j ] = 1 d[i, j] = 1 d[i,j]=1 当且仅当 i < j i < j i<j。求完传递闭包,三种关系的判断:
- 矛盾:d[i, i] = 1;
- 唯一确定:d[i, j] 与 d[j, i] (i != j) 有且只有一个是1。
- 若前两种情况都不满足,那么就是顺序不惟一。
- 原题目说的几次迭代,其实就是需要几个不等式就可以确定出前两种情况中的一种。而且还有一个地方,就是说一旦确定关系或是一旦出现矛盾,就立刻结束判断,不管后面给的关系如何如何。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, maxn = 35;
int g[maxn][maxn], d[maxn][maxn], N, M, type, t;
bool vis[maxn];
void floyd() {
memcpy(d, g, sizeof g);
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
d[i][j] |= d[i][k] && d[k][j];
}
}
}
}
int check() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (d[i][i]) return 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (!d[i][j] && !d[j][i]) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
char get_min() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
bool flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!vis[j] && d[j][i]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
vis[i] = true;
return 'A' + i;
}
}
}
int main() {
while (cin >> N >> M && N) {
memset(g, 0, sizeof g);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
type = 0;
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cin >> s;
int a = s[0] - 'A', b = s[2] - 'A';
if (!type) {
g[a][b] = 1;
floyd();
type = check();
if (type) t = i + 1;
}
}
if (!type) printf("Sorted sequence cannot be determined.\n");
else if (type == 2) printf("Inconsistency found after %d relations.\n", t);
else {
printf("Sorted sequence determined after %d relations: ", t);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("%c", get_min());
}
printf(".\n");
}
}
}
传递闭包优化
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, maxn = 35;
int d[maxn][maxn], N, M, type, t;
bool vis[maxn];
int check() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (d[i][i]) return 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (!d[i][j] && !d[j][i]) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
char get_min() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
bool flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!vis[j] && d[j][i]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
vis[i] = true;
return 'A' + i;
}
}
}
int main() {
while (cin >> N >> M && N) {
memset(d, 0, sizeof d);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
type = 0;
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cin >> s;
int a = s[0] - 'A', b = s[2] - 'A';
if (!type) {
d[a][b] = 1;
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++) {
if (d[x][a]) d[x][b] = 1;
if (d[b][x]) d[a][x] = 1;
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++) {
if (d[x][a] && d[b][y]) {
d[x][y] = 1;
}
}
}
type = check();
if (type) t = i + 1;
}
}
if (!type) printf("Sorted sequence cannot be determined.\n");
else if (type == 2) printf("Inconsistency found after %d relations.\n", t);
else {
printf("Sorted sequence determined after %d relations: ", t);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("%c", get_min());
}
printf(".\n");
}
}
}
7. 差分约束
1. 393. 雇佣收银员
- 设 n u m [ i ] num[i] num[i] 表示第i时刻有 n u m [ i ] num[i] num[i] 个人会来, r [ i ] r[i] r[i] 表示第 i i i 时刻至少需要 r [ i ] r[i] r[i] 个人。 x i x_i xi表示在第i时刻招了 x i x_i xi个人,算出 x i x_i xi的前缀和 S i S_i Si,则有以下不等式:
- S i − S i − 1 < = n u m [ i ] S_{i} - S_{i-1}<=num[i] Si−Si−1<=num[i]
- S i > = S i − 1 S_i >= S_{i-1} Si>=Si−1
- S i − S i − 8 > = r [ i ] S_i-S_{i-8}>=r[i] Si−Si−8>=r[i], ( i > = 8 ) (i >=8) (i>=8)
- S i + S 24 − S i + 16 > = r [ i ] S_i+S_{24}-S_{i+16}>=r[i] Si+S24−Si+16>=r[i], ( 0 < = i < = 7 ) (0 <=i<=7) (0<=i<=7)
- 此时,前三个式子是正常的, 第四个式子有三个变量,那么可以从小到大枚举 S 24 S_{24} S24的值(我试试发现二分枚举并不可以),每次枚举都建一次图,直到枚举成功的时候算结束。但是,大雪菜说,再建两条边: S 24 > = S 0 + c , S 24 < = S 0 + c S_{24}>=S_0+c,S_{24}<=S_0+c S24>=S0+c,S24<=S0+c,其中c便是枚举的值。这两个式子表示 S 24 S_{24} S24是常量,当然还要把 S 0 S_0 S0初始化为 0 0 0,就是 d [ 0 ] = 0 d[0] = 0 d[0]=0。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 30, maxm = 200, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[maxn], ne[maxm], e[maxm], w[maxm], idx;
int r[maxn], num[maxn], N, d[maxn], cnt[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
void build(int s24) {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
idx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 24; i++) {
add(i, i - 1, -num[i]);
add(i - 1, i, 0);
if (i <= 7) {
add(i + 16, i, r[i] - s24);
}
else {
add(i - 8, i, r[i]);
}
}
add(0, 24, s24), add(24, 0, -s24);
}
bool C(int s24) {
build(s24);
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
fill(d, d + maxn, -INF);
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
d[0] = 0;
queue<int> que;
que.push(0);
while (que.size()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (d[v] < d[u] + w[i]) {
d[v] = d[u] + w[i];
cnt[v] = cnt[u] + 1;
if (cnt[v] >= 25) return false;
if (!vis[v]) {
que.push(v);
vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 24; i++) scanf("%d", &r[i]);
scanf("%d", &N);
memset(num, 0, sizeof num);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
num[++t]++;
}
int i = 0;
for (; i <= 1000; i++) {
if (C(i)) break;
}
if (i == 1001) printf("No Solution\n");
else printf("%d\n", i);
}
return 0;
}
2. 362. 区间
- 题意:给定 n n n 个区间 [ a i , b i ] [a_i,b_i] [ai,bi] 和 n n n 个整数 c i c_i ci。你需要构造一个整数集合 Z Z Z,使得 ∀ i ∈ [ 1 , n ] \forall i \in [1,n] ∀i∈[1,n], Z Z Z 中满足 a i ≤ x ≤ b i a_i \le x \le b_i ai≤x≤bi 的整数 x x x 不少于 c i c_i ci 个。这样的整数集合 Z Z Z 最少包含多少个数。输入格式:第一行包含整数 n n n。接下来 n n n 行,每行包含三个整数 a i , b i , c i a_i,b_i,c_i ai,bi,ci。 1 ≤ n ≤ 50000 1 \le n \le 50000 1≤n≤50000, 0 ≤ a i , b i ≤ 50000 0 \le a_i,b_i \le 50000 0≤ai,bi≤50000, 1 ≤ c i ≤ b i − a i + 1 1 \le c_i \le b_i-a_i+1 1≤ci≤bi−ai+1
- 我们希望把 0 0 0 号点做成一个超级源点,而 a a a 和 b b b 的最小值是 0 0 0,因此,把 a a a 和 b b b 都自增 1 1 1 之后再进行计算。
- 设 S i S_i Si 表示从 1 ∼ i 1\sim i 1∼i 中挑选的数字个数,那么有以下条件:
- S i ≥ S i − 1 S_i \ge S_{i-1} Si≥Si−1
- S i − S i − 1 ≤ 1 S_i-S_{i-1}\le 1 Si−Si−1≤1
- S b − S a − 1 ≥ c S_b-S_{a-1}\ge c Sb−Sa−1≥c
- S 0 = 0 S_0=0 S0=0
- 然后,成功转化为了差分约束问题。由于求的是最小个数,那么就是求最长路径。
其实代码还是比较简单的:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50010, maxm = 3 * maxn, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[maxn], ne[maxm], e[maxm], w[maxm], idx;
int N, M, d[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
void spfa() {
queue<int> que;
fill(d, d + maxn, -INF);
que.push(0), d[0] = 0, vis[0] = true;
while (que.size()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (d[v] < d[u] + w[i]) {
d[v] = d[u] + w[i];
if (!vis[v]) {
que.push(v);
vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &M);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
a++, b++;
add(a - 1, b, c);
N = max(b, N);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
add(i - 1, i, 0);
add(i, i - 1, -1);
}
spfa();
printf("%d\n", d[N]);
return 0;
}
8. 强连通分量
367. 学校网络
- 题意:给一个图 G G G,从中至少挑出多少个点,使得从这些点出发可以遍历图中所有点?需要加几条边,可以把这个图变成一个强连通的图(从任何一个节点出发可以到达所有节点)?
- 可以图通过强连通分量缩点,构成一个 D A G DAG DAG。图中共有 b l o c k block block 个不连通的子图,而强连通分量出度为0的数量是 o u t out out,则
- 然后记入度为 0 0 0 的节点数量为 P P P,出度为 0 0 0 的点的数量为 Q Q Q。第一问答案是 P P P,第二问答案是 m a x ( P , Q ) max(P, Q) max(P,Q). (前后一一相连)
- 必须要缩点,不能只统计入度出度为 0 0 0 的点。因为可能会出现某个强连通分量的每个点出度都不为0但是缩点之后整个连通块出度为0.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 110, maxm = 10010;
int h[maxn], e[maxm], ne[maxm], idx;
int low[maxn], dfn[maxn], scc_cnt, timestamp;
int din[maxn], dout[maxn], id[maxn], sz[maxn], in[maxn], out[maxn];
bool in_stk[maxn];
stack<int> stk;
void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void tarjan(int u) {
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++timestamp;
stk.push(u); in_stk[u] = true;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (!dfn[v]) {
tarjan(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if(in_stk[v]) low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if (dfn[u] == low[u]) {
scc_cnt++;
int v;
do {
v = stk.top(); stk.pop();
in_stk[v] = false;
id[v] = scc_cnt;
sz[scc_cnt]++;
} while (v != u);
}
}
int main() {
int N;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int t;
while (scanf("%d", &t), t) add(i, t);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
}
for (int u = 1; u <= N; u++) {
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
int a = id[u], b = id[v];
if (a != b) {
in[b]++;
out[a]++;
}
}
}
int p = 0, q = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= scc_cnt; i++) {
if (in[i] == 0) p++;
if (out[i] == 0) q++;
}
printf("%d\n", p);
if (scc_cnt == 1) printf("0\n");
else printf("%d\n", max(p, q));
return 0;
}
1175. 最大半连通子图
一个有向图 G = ( V , E ) G = (V,E) G=(V,E) 称为半连通的 (Semi-Connected),如果满足: ∀ u , v ∈ V \forall u,v \in V ∀u,v∈V,满足 u → v u \to v u→v 或 v → u v \to u v→u,即对于图中任意两点 u , v u,v u,v,存在一条 u u u 到 v v v 的有向路径或者从 v v v 到 u u u 的有向路径。
子图定义:子图G’中所有的顶点和边均包含于原图 G G G。即 E ’ ∈ E E’∈E E’∈E,并且 V ’ ∈ V V’∈V V’∈V。
生成子图(Spanning Subgraph)定义:生成子图 G ’ G’ G’ 中顶点个数 V ’ V’ V’ 必须和原图 G G G 中 V V V 的数量相同,而 E ’ ∈ E E’∈E E’∈E 即可。
导出子图 (Induced Subgraph)定义:导出子图 G ’ G’ G’, V ’ ∈ V V’∈V V’∈V,但对于 V ’ V’ V’ 中任一顶点,只要在原图 G G G 中有对应边,那么就要在 E ’ E’ E’ 中。
若 G ′ G' G′ 是 G G G 的导出子图,且 G ′ G' G′ 半连通,则称 G ′ G' G′ 为 G G G 的半连通子图。
若 G ′ G' G′ 是 G G G 所有半连通子图中包含节点数最多的,则称 G ′ G' G′ 是 G G G 的最大半连通子图。
-
题意:给定一个有向图 G G G,请求出 G G G 的最大半连通子图拥有的节点数 K K K,以及不同的最大半连通子图的数目 C C C。由于 C C C 可能比较大,仅要求输出 C C C 对 X X X 的余数。 1 ≤ N ≤ 1 0 5 , 1 ≤ M ≤ 1 0 6 , 1 ≤ X ≤ 1 0 8 . 1 \le N \le 10^5,1 \le M \le 10^6, 1 \le X \le 10^8. 1≤N≤105,1≤M≤106,1≤X≤108.
-
强连通子图一定是半连通子图。那么先跑一遍 T a r j a n Tarjan Tarjan 算法,然后缩点,最长的一条链就是最大半连通子图。
-
一定小心:缩点的时候,对于这道题,是不可以有重边的。因为按照定义半连通子图是否是最大的只与节点数量有关,重边的话,方案数会重复计算。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 2000010;
typedef long long ll;
int h[N], hs[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
void add(int h[], int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
int n, m, X;
int stk[N], low[N], dfn[N], id[N], sz[N];
int top, timestamp, scc_cnt;
bool in_stk[N];
void tarjan(int u)
{
low[u] = dfn[u] = ++timestamp;
stk[++top] = u, in_stk[u] = true;
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int v = e[i];
if(!dfn[v])
{
tarjan(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if(in_stk[v]) low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if(low[u] == dfn[u])
{
++scc_cnt;
int v;
do{
sz[scc_cnt]++;
v = stk[top--];
in_stk[v] = false;
id[v] = scc_cnt;
}while(v != u);
}
}
int din[N], cnt[N], f[N];
int main()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(hs, -1, sizeof hs);
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &X);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(h, a, b);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
}
unordered_set<ll> edge;
for(int u = 1; u <= n; u++)
{
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int v = e[i];
int a = id[u], b = id[v];
ll Hash = (ll)a * (ll)N + b;
if(a != b && !edge.count(Hash))
{
edge.insert(Hash);
add(hs, a, b);
din[b]++;
}
}
}
for(int u = scc_cnt; u; u--)
{
if(!din[u])
{
f[u] = sz[u];
cnt[u] = 1;
}
for(int i = hs[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int v = e[i];
if(f[v] < f[u] + sz[v])
{
f[v] = f[u] + sz[v];
cnt[v] = cnt[u];
}
else if(f[v] == f[u] + sz[v])
{
cnt[v] = (cnt[u] + cnt[v]) % X;
}
}
}
int maxf = 0, sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= scc_cnt; i++)
{
if(f[i] > maxf)
{
maxf = f[i];
sum = cnt[i];
}
else if(f[i] == maxf)
{
sum = (sum + cnt[i]) % X;
}
}
printf("%d\n%d\n", maxf, sum);
return 0;
}
368. 银河
- 这道题原本可以用差分约束+
SPFA去写,有解的条件是不存在正环。但是这道题比较特殊,边权均是非负的。因此,有解的时候,每个强连通分量内部的边权都是0,而且同一个强连通分量的所有节点到零点的距离的是一样的。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 100010, maxm = 600010;
int h[maxn], hs[maxn], e[maxm], ne[maxm], w[maxm], idx;
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], id[maxn], sz[maxn], timestamp, scc_cnt;
int N, M, d[maxn];
bool in_stk[maxn];
void add(int h[], int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
stack<int> stk;
void tarjan(int u) {
low[u] = dfn[u] = ++timestamp;
stk.push(u); in_stk[u] = true;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (!dfn[v]) {
tarjan(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if (in_stk[v]) low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if (low[u] == dfn[u]) {
scc_cnt++;
int v;
do {
v = stk.top(); stk.pop();
in_stk[v] = false;
id[v] = scc_cnt;
sz[scc_cnt]++;
} while (u != v);
}
}
void solve() {
tarjan(0);
bool success = true;
for (int u = 0; u <= N; u++) {
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
int a = id[u], b = id[v];
if (a == b) {
if (w[i] > 0) {
success = false;
break;
}
}
else add(hs, a, b, w[i]);
}
if (!success) break;
}
if (!success) printf("-1\n");
else {
for (int u = scc_cnt; u >= 0; u--) {
for (int i = hs[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
d[v] = max(d[v], d[u] + w[i]);
}
}
/*
注意,这里不用将d[scc_cnt]初始化为1了,因为我们是从0号点开始跑tarjan算法的。
因此,新建立的拓扑图中,是包含0号点的。而且0号点对应的就是新的拓扑图中的第scc_cnt号点。
*/
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= scc_cnt; i++) ans += (ll)d[i] * (ll)sz[i];
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(hs, -1, sizeof hs);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) add(h, 0, i, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, t;
scanf("%d%d%d", &t, &a, &b);
if (t == 1) add(h, b, a, 0), add(h, a, b, 0);
else if (t == 2) add(h, a, b, 1);
else if (t == 3) add(h, b, a, 0);
else if (t == 4) add(h, b, a, 1);
else add(h, a, b, 0);
}
solve();
return 0;
}
9. 欧拉路径和欧拉回路
1124. 骑马修栅栏
- 复原无向图欧拉路径点的编号。
- 这道题还有一个要求,输出字典序最小的路径。
- N不大,存成邻接矩阵就可以,因为字典序最小的话,要涉及到排序的问题,但是链表排序是很麻烦的。
- 图中并没有说是否是回路,因此要先试试从度数为奇数的点开始搜。但是,如果都是偶数的话,就从第一个度数不为0的点开始搜。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 510, maxm = 1100;
int g[maxn][maxn], N = 500, M;
int d[maxn], ans[maxm], cnt;
void dfs(int u) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (g[u][i]) {
g[u][i]--, g[i][u]--;
dfs(i);
}
}
ans[cnt++] = u;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &M);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
g[a][b]++, g[b][a]++;
d[a]++, d[b]++;
}
int start = 0;
while (!d[start]) start++;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (d[i] % 2) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
dfs(start);
for (int i = cnt - 1; i >= 0; i--) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
1185. 单词游戏
有 N N N 个盘子,每个盘子上写着一个仅由小写字母组成的英文单词。你需要给这些盘子安排一个合适的顺序,使得相邻两个盘子中,前一个盘子上单词的末字母等于后一个盘子上单词的首字母。请你编写一个程序,判断是否能达到这一要求。
- 这道题有点坑!我原本以为图不连通的话,一定无法满足入度比出度多1或出度比入度多1的点恰好都有1个。其实不是这样的。比如一个环不与其他图联通,其实这样子就看不出来了。
- 判断图是否连通,可以用dfs, bfs, 并查集,建议用并查集,代码较短。
- 它这个可以形成一个环。题目应该说清楚的。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int din[30], dout[30], N = 26, M;
bool vis[30];
int p[30];
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) p[i] = i;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] == x) return x;
return p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
void unite(int a, int b) {
if (find(a) == find(b)) return;
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
init();
memset(din, 0, sizeof din);
memset(dout, 0, sizeof dout);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
cin >> M;
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cin >> s;
int a = s[0] - 'a', b = s[s.length() - 1] - 'a';
dout[a]++, din[b]++;
vis[a] = vis[b] = true;
unite(a, b);
}
int st = 0, ed = 0;
bool success = true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (din[i] - dout[i] == 1) ed++;
else if (dout[i] - din[i] == 1) st++;
else if (din[i] == dout[i]) continue;
else {
success = false;
break;
}
}
int fa = -1;
if (!(st == 0 && ed == 0) && !(st == 1 && ed == 1)) success = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (vis[i]) {
if (fa == -1) fa = find(i);
else if (fa != find(i)) {
success = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (success) cout << "Ordering is possible.\n";
else cout << "The door cannot be opened.\n";
}
return 0;
}
10. 拓扑排序
456. 车站分级
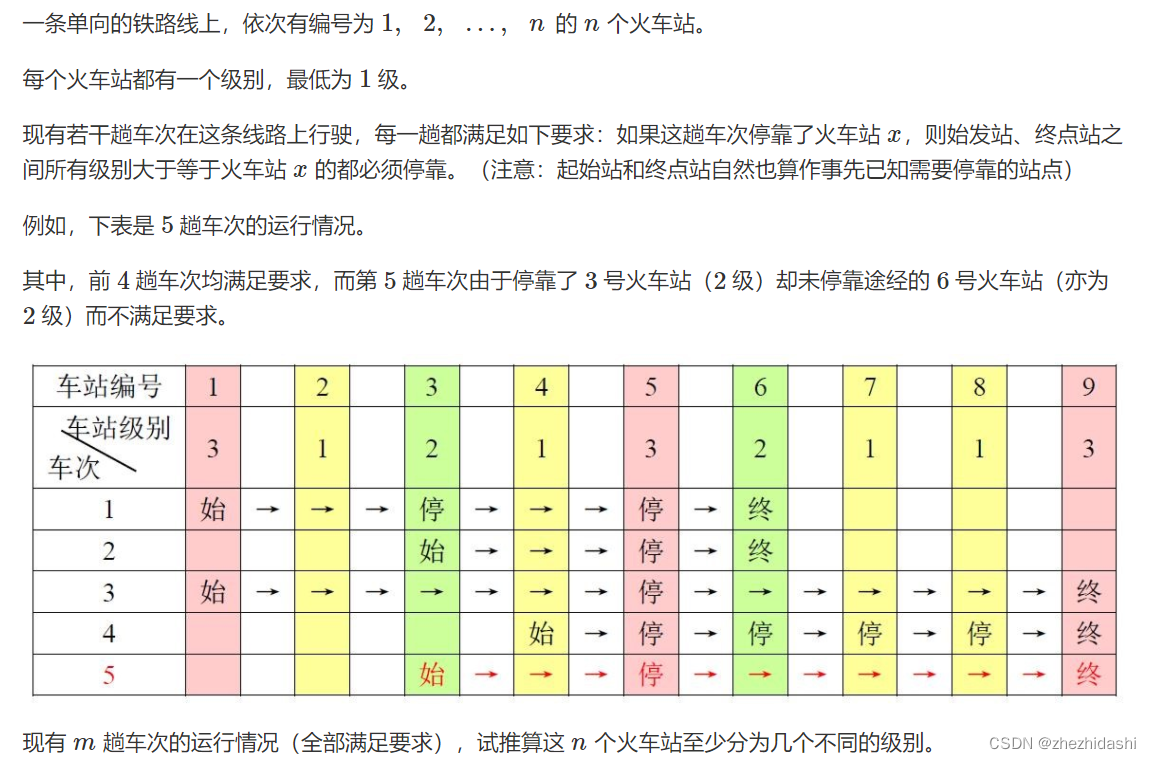
- 这个题其实就是,每趟列车,每一个没有停靠的站向每一个停靠的站连边,即没有停靠的站比停靠的站编号小。这样子在这个拓扑图上面跑一个最长路径即可。不过,这样会有一个性质,就是我们可以把这些点分为两类,一类向另一类两两连边,那么在中间建立一个虚拟节点即可,没有停靠的站全部连向这个虚拟节点,然后虚拟节点连向每一个停靠的站。
- 在图论问题中,如果发现建图会建一个边数达到 n 2 n^2 n2 的稠密图,那么有一个优化,就是在中间建一个虚拟节点,那么边的数量从 n ∗ m n * m n∗m 变成 n + m n + m n+m 个。
- 小心数组不要开小。点数开到
2000
2000
2000,因为
N
+
M
N + M
N+M 最大是
2000
2000
2000,而每次最多建
1000
1000
1000 条边,最多
1000
1000
1000 辆车,因此边数最大是
1000000
1000000
1000000.
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2010, maxm = 1000010;
int h[maxn], e[maxm], ne[maxm], w[maxm], idx;
int N, M, topo[maxn], cnt, din[maxn], d[maxn];
bool st[maxn];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
void toposort() {
queue<int> que;
for (int i = 1; i <= N + M; i++) {
if (!din[i]) que.push(i), topo[++cnt] = i;
}
while (que.size()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
din[v]--;
if(!din[v]) que.push(v), topo[++cnt] = v;
}
}
}
int main() {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
int s, start = N, end = 1;
scanf("%d", &s);
while (s--) {
int stop;
scanf("%d", &stop);
start = min(start, stop);
end = max(end, stop);
st[stop] = true;
}
int ver = N + i;
for (int j = start; j <= end; j++) {
if (st[j]) add(ver, j, 1), din[j]++;
else add(j, ver, 0), din[ver]++;
}
}
toposort();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) d[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= N + M; j++) {
int u = topo[j];
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
d[v] = max(d[v], d[u] + w[i]);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N + M; i++) ans = max(ans, d[i]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
B. Brexit Negotiations
- 就是求一个拓扑序,每一个会议的时间等于会议时长加上拓扑序下标,让会议时间最大值最小化。
- 反向建图,然后反向跑拓扑排序,把用优先队列(小根堆)。然后再把所得拓扑序反过来,就是所求拓扑序。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 400010;
int h[maxn], e[maxn], ne[maxn], w[maxn],idx;
int N, din[maxn];
vector<int> topo;
void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
typedef pair<int, int> P;
void toposort() {
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> que;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (din[i] == 0) que.push(P(w[i], i));
}
while (que.size()) {
auto p = que.top(); que.pop();
int u = p.second, d = p.first;
topo.push_back(u);
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if (--din[v] == 0) que.push(P(w[v], v));
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &N);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int par;
scanf("%d%d", &w[i], &par);
for (int j = 0; j < par; j++) {
int b;
scanf("%d", &b);
add(i, b);
din[b]++;
}
}
toposort();
reverse(topo.begin(), topo.end());
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int v = topo[i];
ans = max(ans, w[v] + i);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}